Содержание
- 2. The Market Forces of Supply and Demand
- 3. Supply and demand are the two words that economists use most often. Supply and demand are
- 4. A market is a group of buyers and sellers of a particular good or service. The
- 5. MARKETS AND COMPETITION Buyers determine demand. Sellers determine supply
- 6. Competitive Markets A competitive market is a market in which there are many buyers and sellers
- 7. Perfect Competition Products are the same Numerous buyers and sellers so that each has no influence
- 8. Oligopoly Few sellers Not always aggressive competition Monopolistic Competition Many sellers Slightly differentiated products Each seller
- 9. DEMAND Quantity demanded is the amount of a good that buyers are willing and able to
- 10. The Demand Curve: The Relationship between Price and Quantity Demanded Demand Schedule The demand schedule is
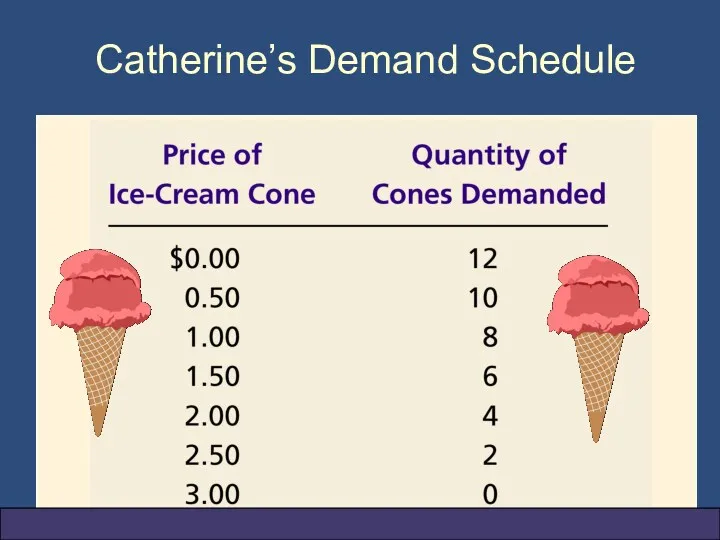
- 11. Catherine’s Demand Schedule
- 12. The Demand Curve: The Relationship between Price and Quantity Demanded Demand Curve The demand curve is
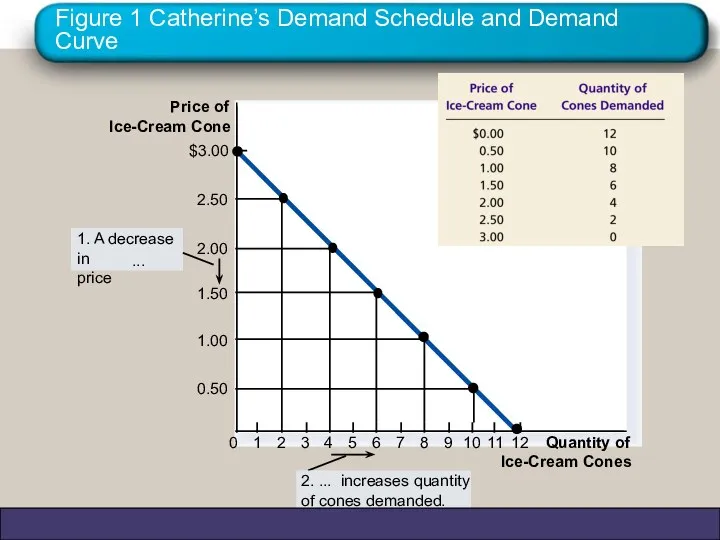
- 13. Figure 1 Catherine’s Demand Schedule and Demand Curve Copyright © 2004 South-Western Price of Ice-Cream Cone
- 14. Market Demand versus Individual Demand Market demand refers to the sum of all individual demands for
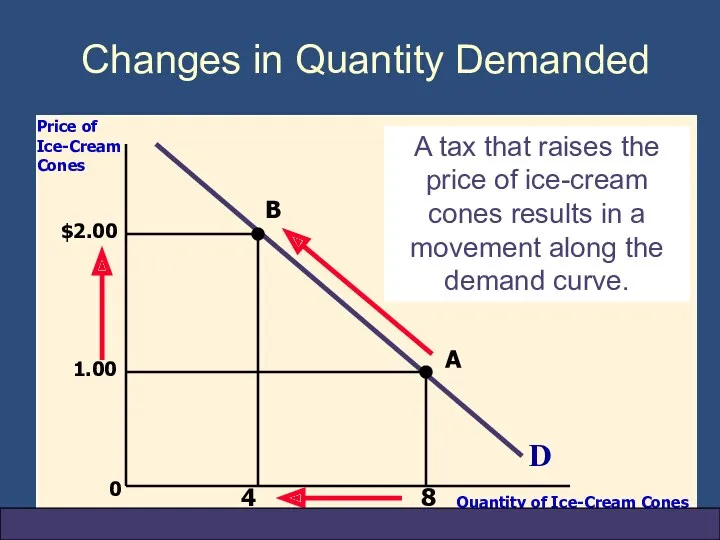
- 15. Shifts in the Demand Curve Change in Quantity Demanded Movement along the demand curve. Caused by
- 16. 0 D Price of Ice-Cream Cones Quantity of Ice-Cream Cones A tax that raises the price
- 17. Shifts in the Demand Curve Consumer income Prices of related goods Tastes Expectations Number of buyers
- 18. Shifts in the Demand Curve Change in Demand A shift in the demand curve, either to
- 19. Shifts in the Demand Curve Consumer Income As income increases the demand for a normal good
- 20. Shifts in the Demand Curve Prices of Related Goods When a fall in the price of
- 21. SUPPLY Quantity supplied is the amount of a good that sellers are willing and able to
- 22. The Supply Curve: The Relationship between Price and Quantity Supplied Supply Schedule The supply schedule is
- 23. The Supply Curve: The Relationship between Price and Quantity Supplied Supply Curve The supply curve is
- 24. Market Supply versus Individual Supply Market supply refers to the sum of all individual supplies for
- 25. Shifts in the Supply Curve Input prices Technology Expectations Number of sellers
- 26. Shifts in the Supply Curve Change in Quantity Supplied Movement along the supply curve. Caused by
- 27. Shifts in the Supply Curve Change in Supply A shift in the supply curve, either to
- 28. SUPPLY AND DEMAND TOGETHER Equilibrium refers to a situation in which the price has reached the
- 29. SUPPLY AND DEMAND TOGETHER Equilibrium Price The price that balances quantity supplied and quantity demanded. On
- 30. Equilibrium Surplus When price > equilibrium price, then quantity supplied > quantity demanded. There is excess
- 31. Equilibrium Shortage When price the quantity supplied. There is excess demand or a shortage. Suppliers will
- 32. Equilibrium Law of supply and demand The claim that the price of any good adjusts to
- 34. Скачать презентацию



























 Takeovers & mergers
Takeovers & mergers Economic system
Economic system Факторы трудовой миграции
Факторы трудовой миграции Государственная программа развития агропромышленного комплекса Республики Казахстан на 2017-2021 годы
Государственная программа развития агропромышленного комплекса Республики Казахстан на 2017-2021 годы Ford Motor Company
Ford Motor Company Практическое занятие с презентацией расчёт НДФЛ
Практическое занятие с презентацией расчёт НДФЛ Организация стран - экспортеров нефти (ОПЕК)
Организация стран - экспортеров нефти (ОПЕК) Совокупный спрос и совокупное предложение
Совокупный спрос и совокупное предложение Экономические взгляды Ибн-Хальдуна
Экономические взгляды Ибн-Хальдуна Макроэкономикалық статистикалық көрсеткіштерге талдау
Макроэкономикалық статистикалық көрсеткіштерге талдау Статистика основных и оборотных фондов предприятий
Статистика основных и оборотных фондов предприятий Министерство экономического развития Российской Федерации. Функционально-структурный анализ
Министерство экономического развития Российской Федерации. Функционально-структурный анализ Оценка в бизнес-среде уровня коррупции и избыточного административного давления в деятельности государственных органов
Оценка в бизнес-среде уровня коррупции и избыточного административного давления в деятельности государственных органов Экономическая сфера жизни общества
Экономическая сфера жизни общества Использование машин и оборудования
Использование машин и оборудования Инфляция: сущность, виды и методы борьбы
Инфляция: сущность, виды и методы борьбы Конфлікт корпоративних інтересів та запобігання рейдерству і корпоративному шантажу
Конфлікт корпоративних інтересів та запобігання рейдерству і корпоративному шантажу Венчурный капитал, как источник инновационных инвестиций
Венчурный капитал, как источник инновационных инвестиций Інноваційно-технологічний ресурс глобального економічного розвитку
Інноваційно-технологічний ресурс глобального економічного розвитку Глобальный цифровой рынок и место России на нём
Глобальный цифровой рынок и место России на нём Бізнес-планування, характеристика бізнес-плану
Бізнес-планування, характеристика бізнес-плану Роль государства в экономике
Роль государства в экономике Частные и общественные блага. Внешние эффекты. Функции государства в экономике
Частные и общественные блага. Внешние эффекты. Функции государства в экономике Совершенствование системы государственного регулирования фармацевтической промышленности России
Совершенствование системы государственного регулирования фармацевтической промышленности России Экономика для школьников. Схемы, таблицы, графики.
Экономика для школьников. Схемы, таблицы, графики. World Tourism Market. Introduction to the market and international tourism
World Tourism Market. Introduction to the market and international tourism Measuring a nation’s income
Measuring a nation’s income Основы грузоведения и технологии грузопереработки
Основы грузоведения и технологии грузопереработки