Содержание
- 2. CA Standards
- 3. Modern Atomic Theory All matter is composed of atoms Atoms cannot be subdivided, created, or destroyed
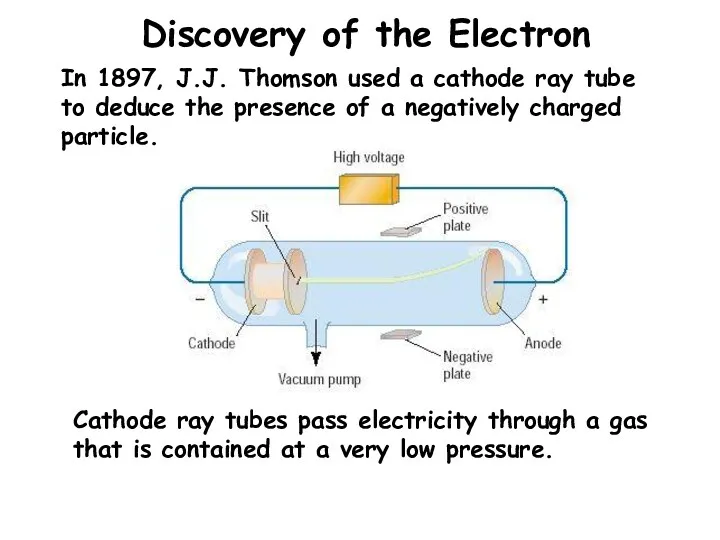
- 4. Discovery of the Electron In 1897, J.J. Thomson used a cathode ray tube to deduce the
- 5. Conclusions from the Study of the Electron Cathode rays have identical properties regardless of the element
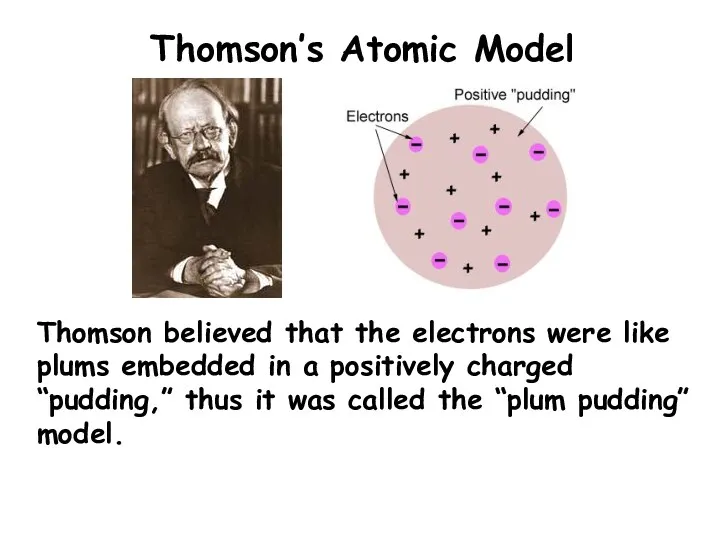
- 6. Thomson’s Atomic Model Thomson believed that the electrons were like plums embedded in a positively charged
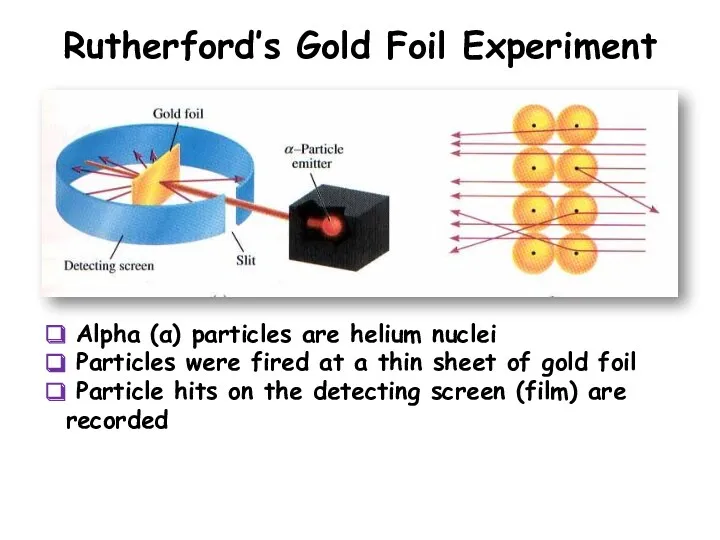
- 7. Rutherford’s Gold Foil Experiment Alpha (α) particles are helium nuclei Particles were fired at a thin
- 8. Rutherford’s Findings The nucleus is small The nucleus is dense The nucleus is positively charged Most
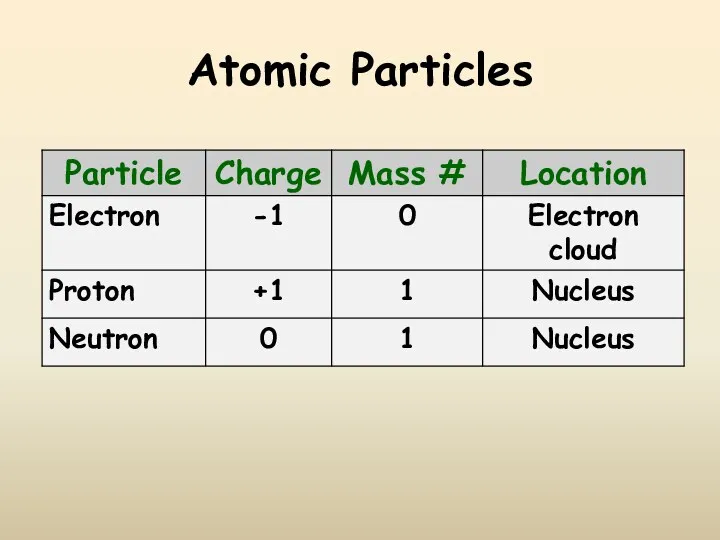
- 9. Atomic Particles
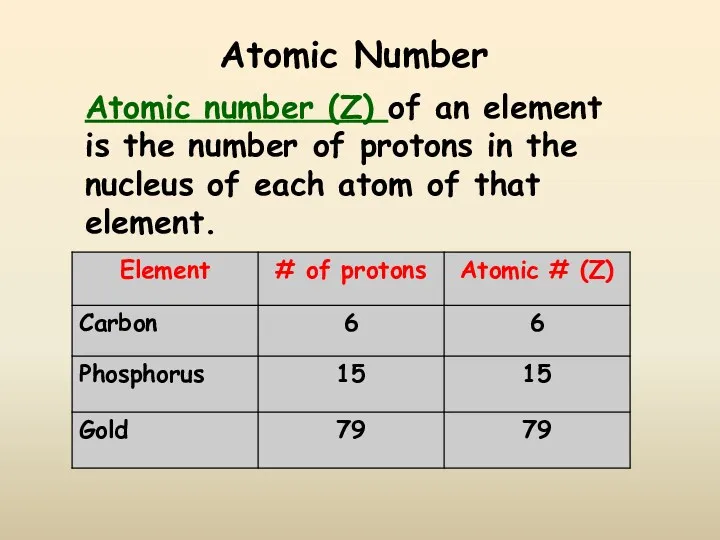
- 10. Atomic Number Atomic number (Z) of an element is the number of protons in the nucleus
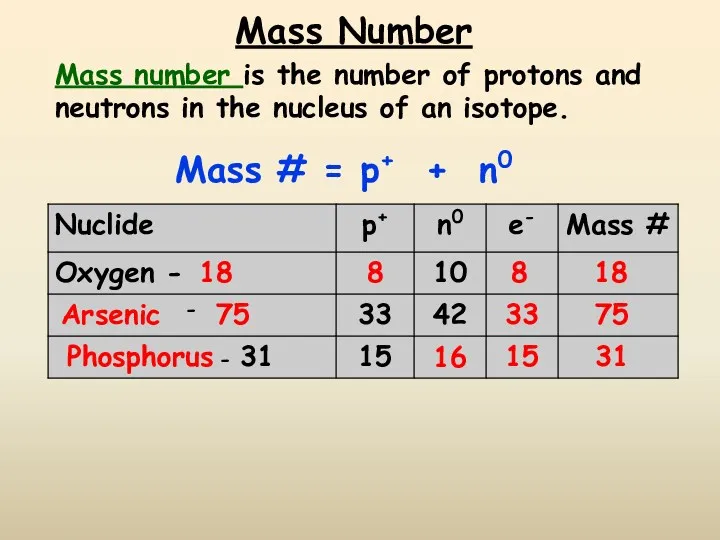
- 11. Mass Number Mass number is the number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus of an
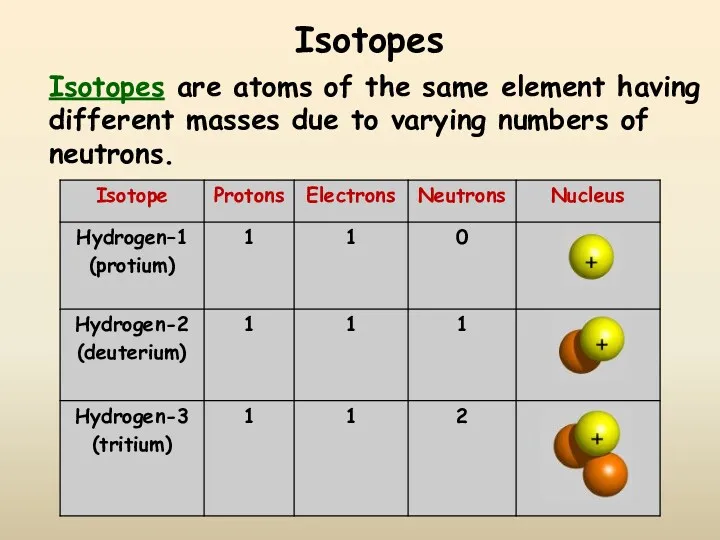
- 12. Isotopes Isotopes are atoms of the same element having different masses due to varying numbers of
- 14. Скачать презентацию




 X6000平台电子电气系统介绍. Внедрение электронной и электрической системы платформы X6000
X6000平台电子电气系统介绍. Внедрение электронной и электрической системы платформы X6000 UTC (PTB) as the basis for legal time in Germany: realization and dissemination
UTC (PTB) as the basis for legal time in Germany: realization and dissemination Методы испытаний ГТД и СУ. Лекция 1,2
Методы испытаний ГТД и СУ. Лекция 1,2 Презентация Силы в природе
Презентация Силы в природе Техническое обслуживание двигателя автомобиля MAN Lions City A78
Техническое обслуживание двигателя автомобиля MAN Lions City A78 Производство и применение технических жидкостей и специальных продуктов масляного производства
Производство и применение технических жидкостей и специальных продуктов масляного производства Исследование минералов под микроскопом
Исследование минералов под микроскопом Раздаточная коробка КамАЗ
Раздаточная коробка КамАЗ Развитие взглядов на природу света. Волновые и квантовые свойства света
Развитие взглядов на природу света. Волновые и квантовые свойства света Фотоаппарат. Виды линз
Фотоаппарат. Виды линз Команда Пятый Элемент. Почему для полетов в космосе всегда используются ракеты
Команда Пятый Элемент. Почему для полетов в космосе всегда используются ракеты Карбюраторный двигатель
Карбюраторный двигатель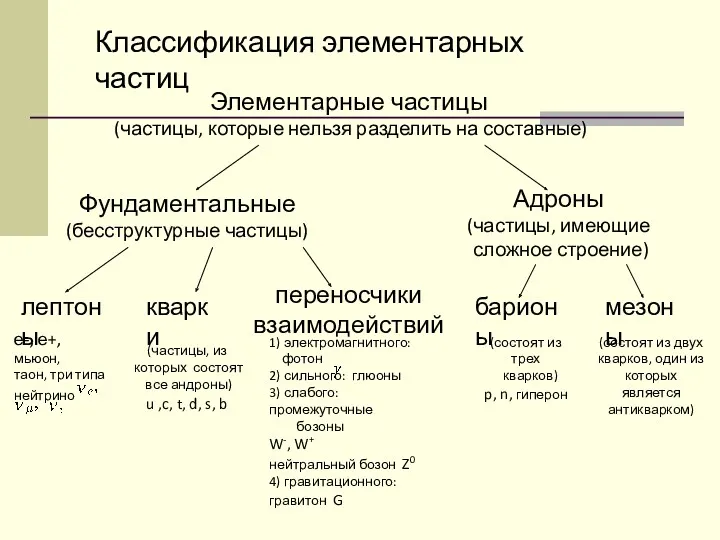 конспект урока по теме Мир элементарных частиц
конспект урока по теме Мир элементарных частиц Источники света (презентация)
Источники света (презентация) Фотоны. Внешний фотоэффект
Фотоны. Внешний фотоэффект Взаимодействие ускоренных электронов с веществом (часть 3)
Взаимодействие ускоренных электронов с веществом (часть 3) Произвольная плоская система сил
Произвольная плоская система сил Работа и мощность
Работа и мощность Линза. Построение изображений, даваемых линзой
Линза. Построение изображений, даваемых линзой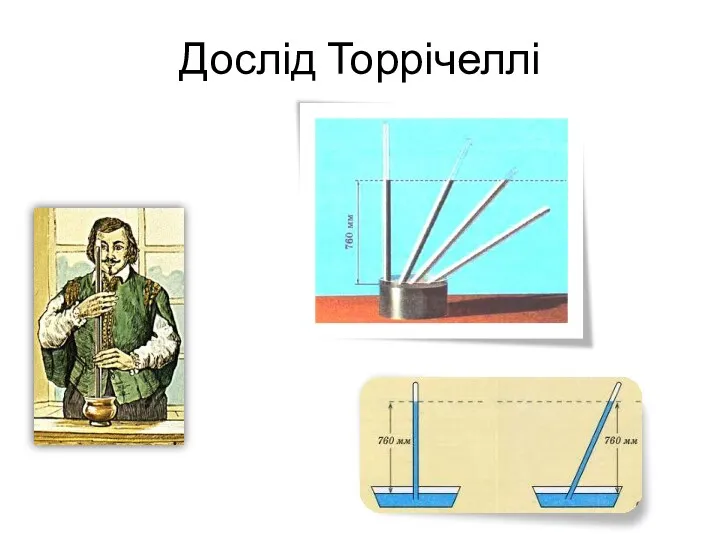 Дослід Торрічеллі
Дослід Торрічеллі Инструментальные методы анализа
Инструментальные методы анализа Основные законы постоянного тока
Основные законы постоянного тока Система охлаждения с заданными значениями
Система охлаждения с заданными значениями Ученые Ленинграда в отечественной и мировой науке и технике. Посвящается 70-летию снятия блокады.
Ученые Ленинграда в отечественной и мировой науке и технике. Посвящается 70-летию снятия блокады. Зубчатая передача
Зубчатая передача Обпилювачі. Аерозольні генератори. Лабораторна робота
Обпилювачі. Аерозольні генератори. Лабораторна робота Коммерческий транспорт Groupe PSA - Opel Vivaro
Коммерческий транспорт Groupe PSA - Opel Vivaro Глава 5. Пьезоэлектрический эффект и электрострикция
Глава 5. Пьезоэлектрический эффект и электрострикция