The International Nuclear and Radiological Event Scale (INES) was introduced
in 1990 by the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) in order to enable prompt communication of safety-significant information in case of nuclear accidents.
The scale is intended to be logarithmic, similar to the moment magnitude scale that is used to describe the comparative magnitude of earthquakes. Each increasing level represents an accident approximately ten times more severe than the previous level. Compared to earthquakes, where the event intensity can be quantitatively evaluated, the level of severity of a man-made disaster, such as a nuclear accident, is more subject to interpretation. Because of the difficulty of interpreting, the INES level of an incident is assigned well after the incident occurs. Therefore, the scale has a very limited ability to assist in disaster-aid deployment.
As INES ratings are not assigned by a central body, high-profile nuclear incidents are sometimes assigned INES ratings by the operator, by the formal body of the country, but also by scientific institutes, international authorities or other experts which may lead to confusion as to the actual severity.
International Nuclear Event Scale
A number of criteria and indicators are defined to assure coherent reporting of nuclear events by different official authorities. There are seven nonzero levels on the INES scale: three incident-levels and four accident-levels. There is also a level 0.










 Методы и средства измерения частоты, временных интервалов и фазового сдвига
Методы и средства измерения частоты, временных интервалов и фазового сдвига Простые механизмы
Простые механизмы Самостоятельная робота на уроках физики
Самостоятельная робота на уроках физики Imitation of low voltage DC arc
Imitation of low voltage DC arc Оборудование для заземления нейтрали в сетях 6-35 кВ
Оборудование для заземления нейтрали в сетях 6-35 кВ Вес тела. Единицы силы. Связь между силой тяжести и массой тела. Физика. 7 класс
Вес тела. Единицы силы. Связь между силой тяжести и массой тела. Физика. 7 класс Портфолио учителя физики Бушмакиной Е. С.
Портфолио учителя физики Бушмакиной Е. С. Разработка урока по теме Изучение колебаний математического маятника
Разработка урока по теме Изучение колебаний математического маятника Устройство и принцип работы воздухораспределителя 483
Устройство и принцип работы воздухораспределителя 483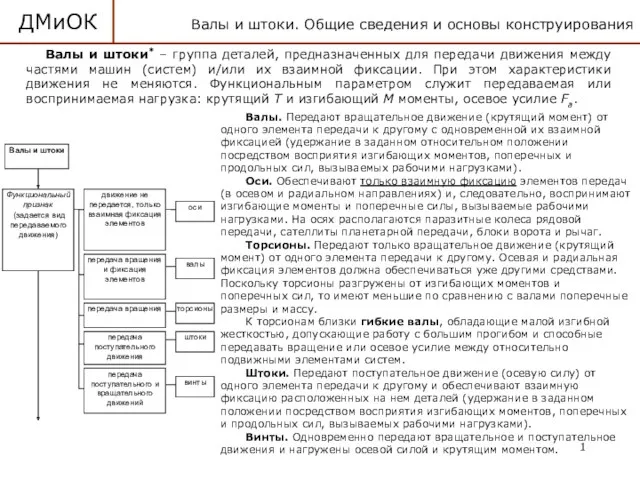 Детали машин и основы конструирования. Валы и штоки. (Лекция 11)
Детали машин и основы конструирования. Валы и штоки. (Лекция 11) Плотность вещества
Плотность вещества Тепловое излучение. Глава 5
Тепловое излучение. Глава 5 Реактивное движение
Реактивное движение Корабельные гироскопические системы. (Тема 2)
Корабельные гироскопические системы. (Тема 2) Температура
Температура Умови плавання тіл
Умови плавання тіл Углекислотные лазеры высокого и низкого давления
Углекислотные лазеры высокого и низкого давления Лекція №5. Закон збереження імпульсу
Лекція №5. Закон збереження імпульсу Взаємодія тіл. Імпульс. Закон збереження імпульсу
Взаємодія тіл. Імпульс. Закон збереження імпульсу Магнитное поле. Действие магнитного поля на движущийся электрический заряд
Магнитное поле. Действие магнитного поля на движущийся электрический заряд Современные приборы измерения температуры
Современные приборы измерения температуры Измерение активного сопротивления обмоток постоянному току
Измерение активного сопротивления обмоток постоянному току Законы отражения
Законы отражения Newton’s Laws of Motion
Newton’s Laws of Motion Технологический процесс проведения опрессовки форсунок судового двигателя
Технологический процесс проведения опрессовки форсунок судового двигателя Гамма-излучение
Гамма-излучение Спектрально-люминесцентные свойства кристаллов стабилизированного диоксида циркония, активированных ионами
Спектрально-люминесцентные свойства кристаллов стабилизированного диоксида циркония, активированных ионами Оптическое явление атмосферы гало
Оптическое явление атмосферы гало