Other Energy Considerations
Solar Power – uses the sun energy to
either boil water or directly converts
solar energy to electrical energy
Ocean Thermal Energy Conversion – uses temperature differences
between different depths of ocean water to drive a heat engine. Working
fluid is ammonia which is gas at room temperature.
-Biomass Energy: Municipal Solid Waste – burning wastes to drive heat
engines
Geothermal Energy – based on naturally occurring heat in the Earth in the
Earth due to radioactive decay
Tidal Energy – uses the gravitational pull of the moon on our oceans to
drive turbines



 Выбор оборудования для участка подготовки, кузовного ремонта и покраски легковых автомобилей
Выбор оборудования для участка подготовки, кузовного ремонта и покраски легковых автомобилей Жылу алмасу үдерістері
Жылу алмасу үдерістері Элементы атомной физики. (Лекция 14)
Элементы атомной физики. (Лекция 14) Что изучает физика? Слово физика
Что изучает физика? Слово физика Хроматографічні методи
Хроматографічні методи Техническое обслуживание и ремонт автомобильных кранов
Техническое обслуживание и ремонт автомобильных кранов Проводники и диэлектрики в электростатическом поле 10 класс
Проводники и диэлектрики в электростатическом поле 10 класс Теоретические и правовые основы метрологического обеспечения
Теоретические и правовые основы метрологического обеспечения Зонная теория твёрдых тел
Зонная теория твёрдых тел Электрический ток в металлах
Электрический ток в металлах Катушки индуктивности
Катушки индуктивности Конусні дробарки
Конусні дробарки Электростатика
Электростатика Метод проектов на уроках физики
Метод проектов на уроках физики Неоднородное одномерное уравнение теплопроводности
Неоднородное одномерное уравнение теплопроводности Ақаулар. Кристалл торларының ақаулары
Ақаулар. Кристалл торларының ақаулары Презентация к уроку Термоядерные реакции
Презентация к уроку Термоядерные реакции Исследовательская работа Электричество в повседневной жизни
Исследовательская работа Электричество в повседневной жизни Презентация к уроку в 10 классе по теме Сила упругости и сила трения
Презентация к уроку в 10 классе по теме Сила упругости и сила трения Создание вакуума в выпарных аппаратах. Принцип работы барометрического конденсатора
Создание вакуума в выпарных аппаратах. Принцип работы барометрического конденсатора Действия электрического тока
Действия электрического тока Сполучені посудини. Манометри
Сполучені посудини. Манометри Юнг тәжірибесі
Юнг тәжірибесі Міцність при змінних навантаженнях. (Лекція 2)
Міцність при змінних навантаженнях. (Лекція 2) Урок физики в 8 классе Электризация тел
Урок физики в 8 классе Электризация тел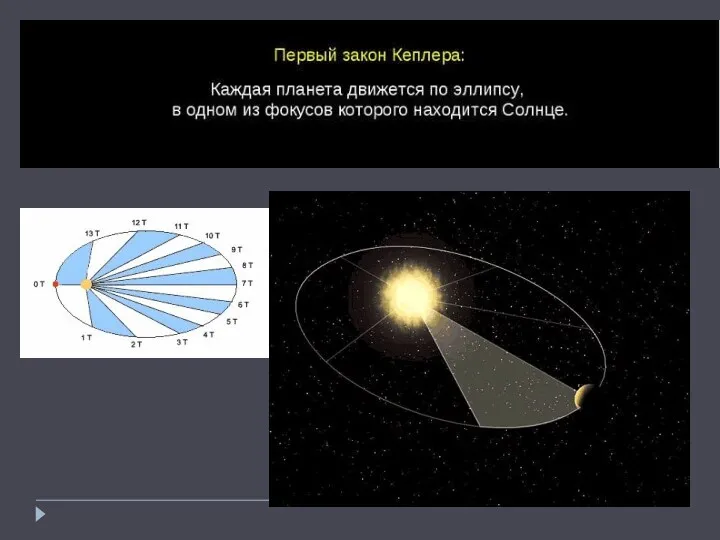 Первый закон Кеплера
Первый закон Кеплера Физическая викторина 7-8 классы.
Физическая викторина 7-8 классы. Контроль качества сварных соединений
Контроль качества сварных соединений