Содержание
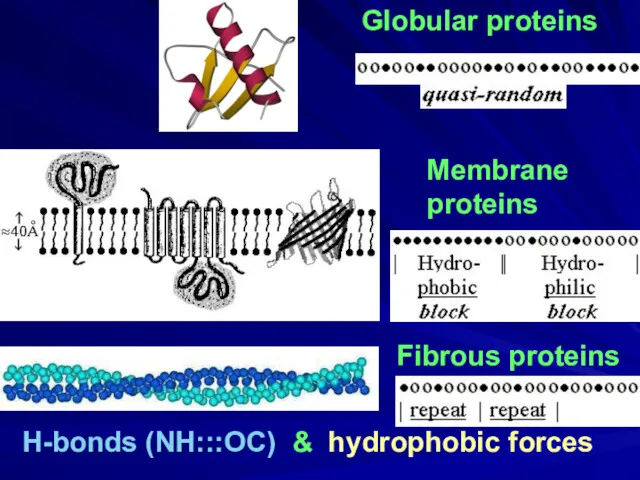
- 2. Globular proteins Fibrous proteins H-bonds (NH:::OC) & hydrophobic forces Membrane proteins
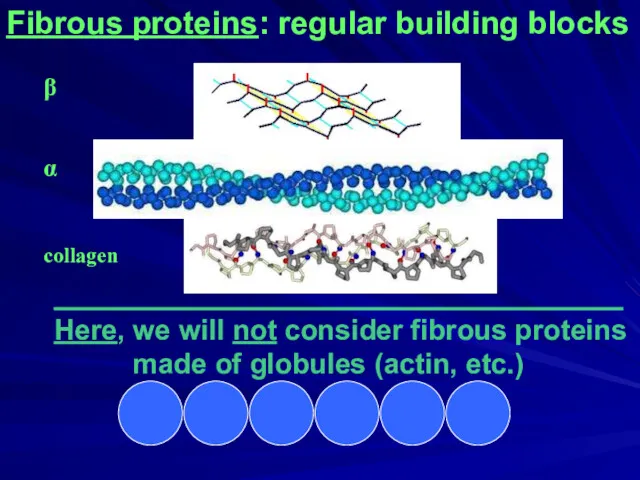
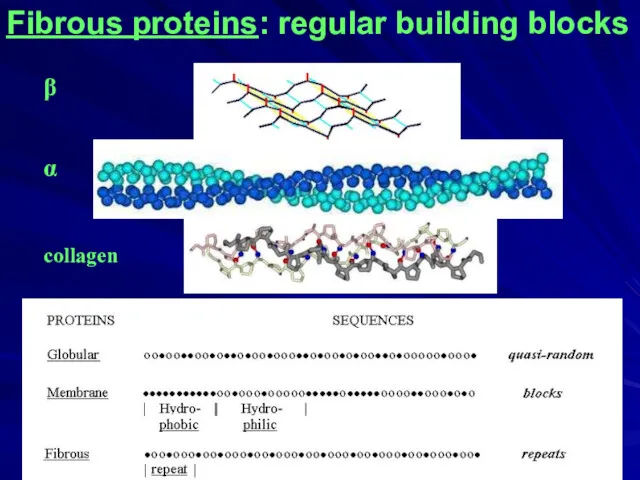
- 3. Fibrous proteins: regular building blocks ____________________________________ Here, we will not consider fibrous proteins made of globules
- 4. Fibrous proteins: regular building blocks β α collagen
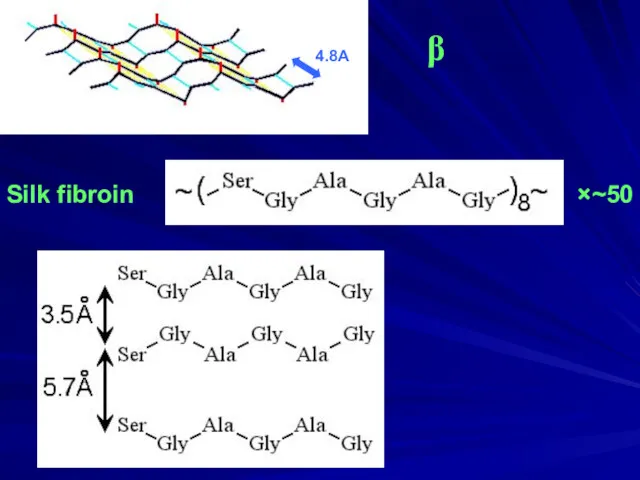
- 5. Silk fibroin ×~50 β 4.8A
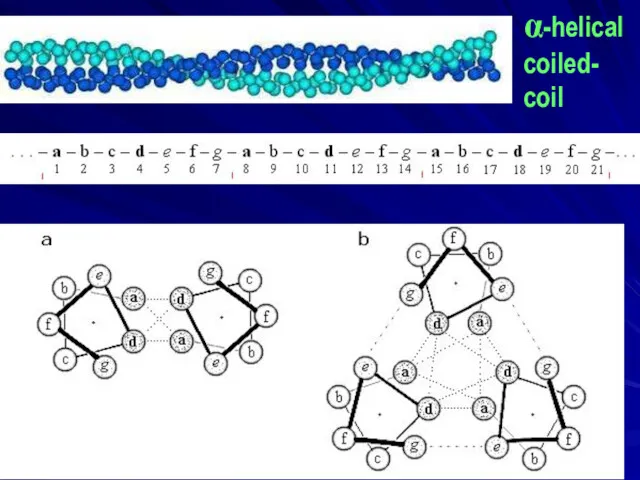
- 6. α-helical coiled- coil
- 7. Francis Harry Compton Crick (1916 – 2004) Nobel Prize 1962 for DNA structure, 1953 Coiled coil
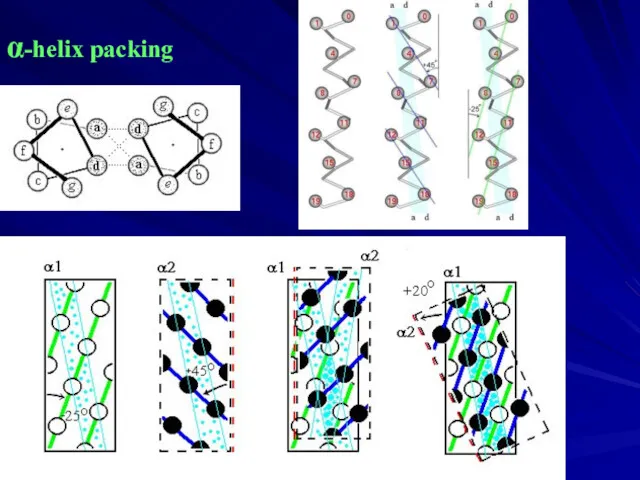
- 8. α-helix packing
- 9. collagen triple helix: 3 chains ≈ [Gly-X-Pro]≈500
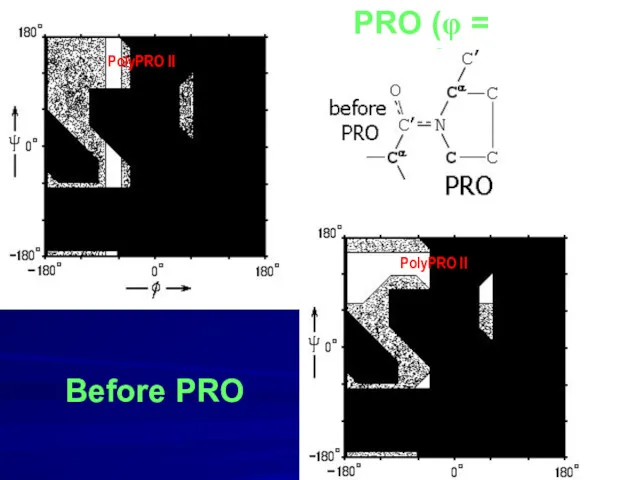
- 10. PRO (φ = -70o) Before PRO PolyPRO II PolyPRO II
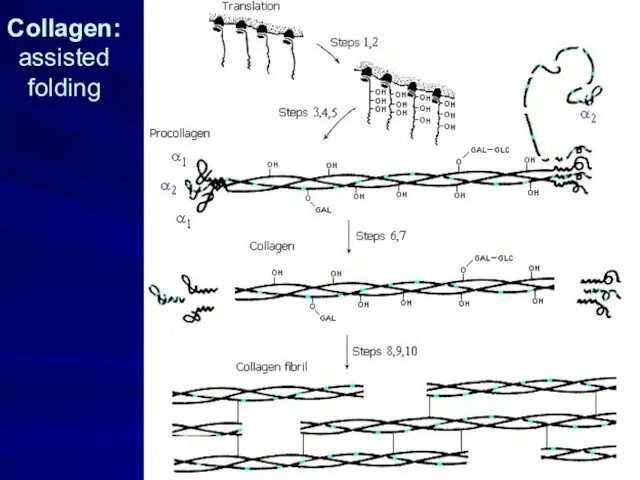
- 11. Collagen: assisted folding
- 12. Kuru: a mysterious disease, later demonstrated to be infectious prion disease. Daniel Carleton Gajdusek (1923 –2008)
- 13. β ______ NMR
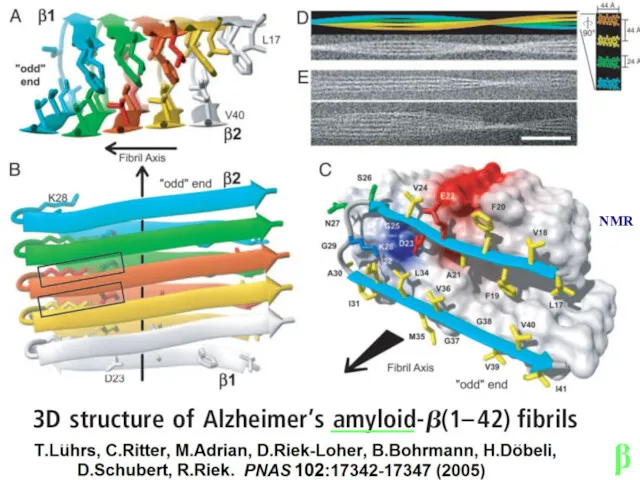
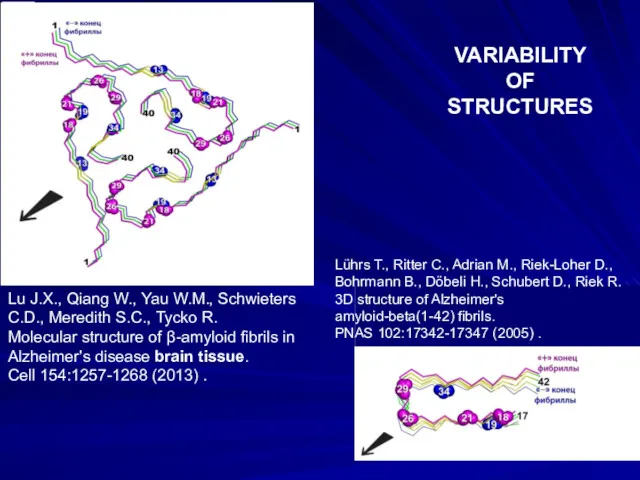
- 14. Lu J.X., Qiang W., Yau W.M., Schwieters C.D., Meredith S.C., Tycko R. Molecular structure of β-amyloid
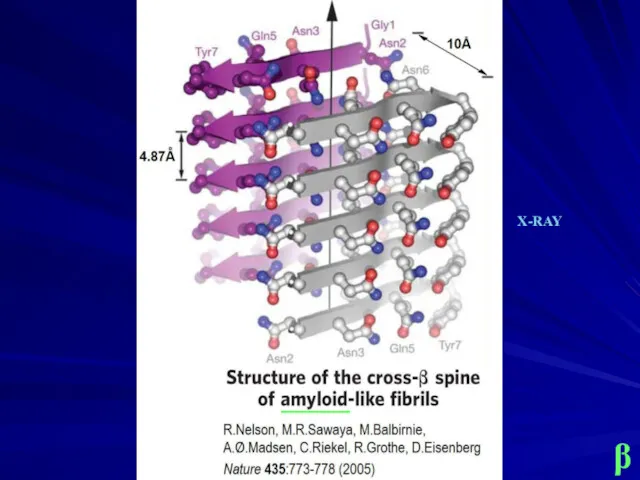
- 15. β _____ X-RAY
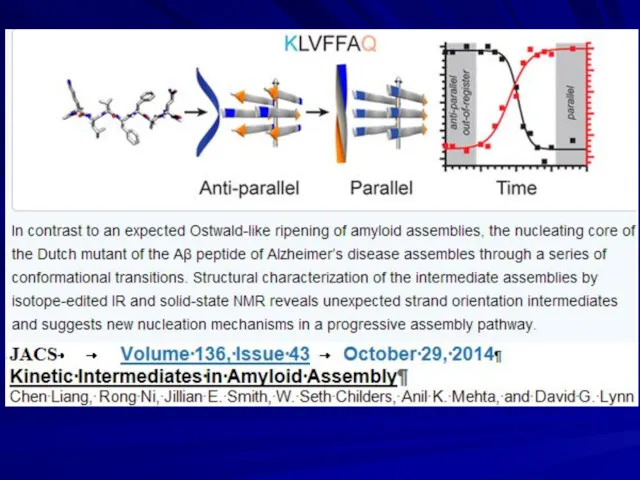
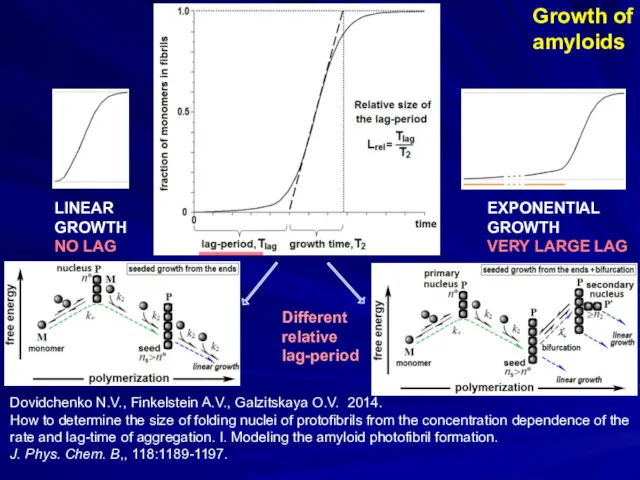
- 17. Growth of amyloids Dovidchenko N.V., Finkelstein A.V., Galzitskaya O.V. 2014. How to determine the size of
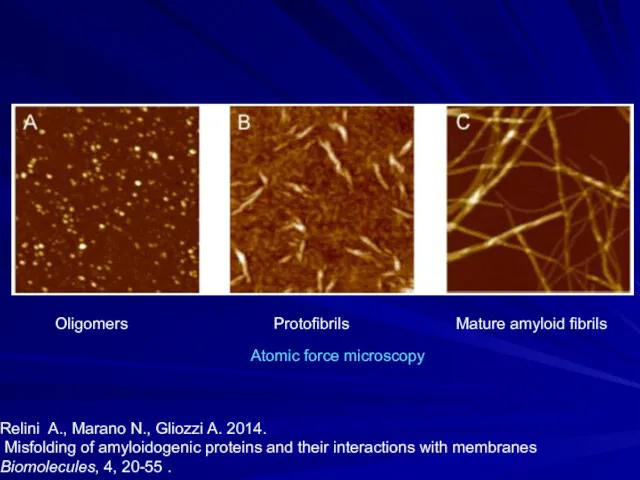
- 18. Oligomers Protofibrils Mature amyloid fibrils Relini A., Marano N., Gliozzi A. 2014. Misfolding of amyloidogenic proteins
- 19. Elastin: Matrix protein. Short repeats. Poor secondary structure. Chains are linked by chemically modified Lys residues.
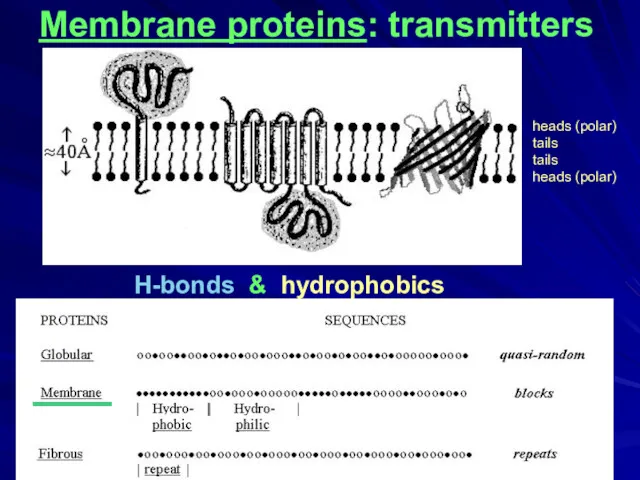
- 20. H-bonds & hydrophobics Membrane proteins: transmitters ____ heads (polar) tails tails heads (polar)
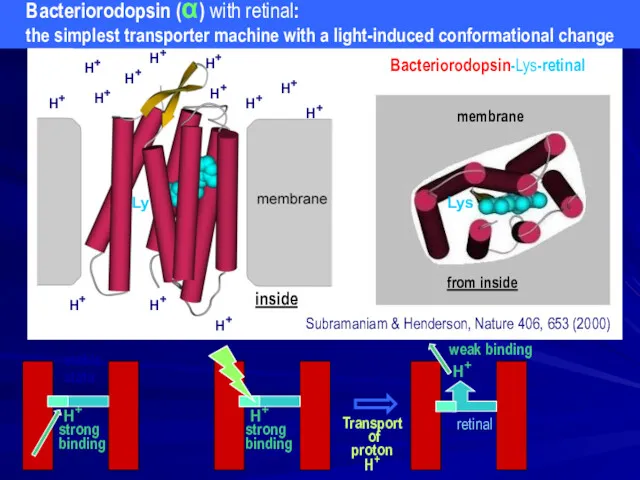
- 21. H+ strong binding H+ inside H+ H+ H+ H+ H+ H+ H+ H+ H+ H+ H+
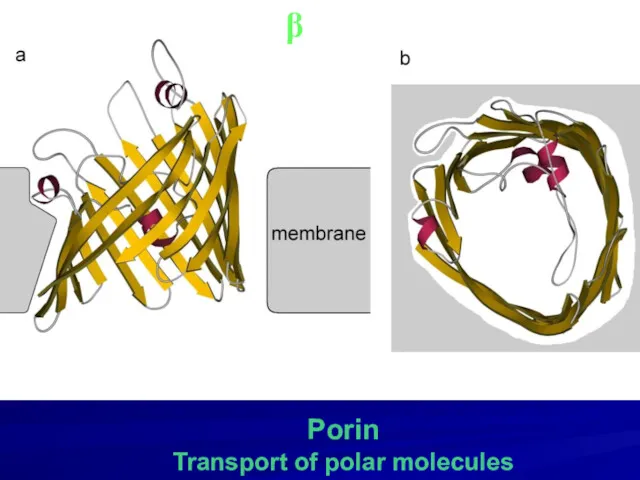
- 22. Porin Transport of polar molecules β
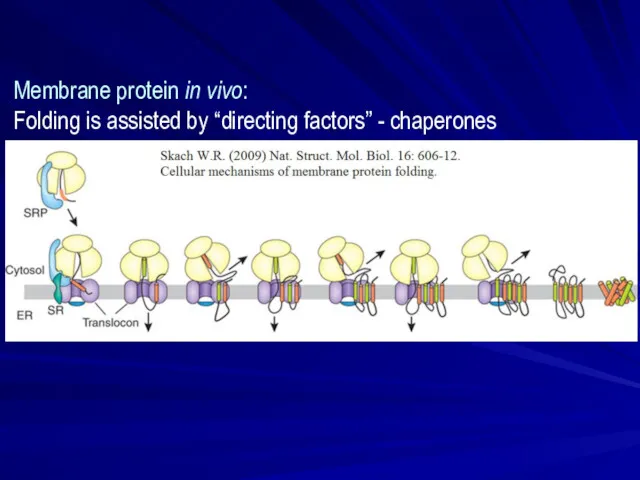
- 23. Membrane protein in vivo: Folding is assisted by “directing factors” - chaperones
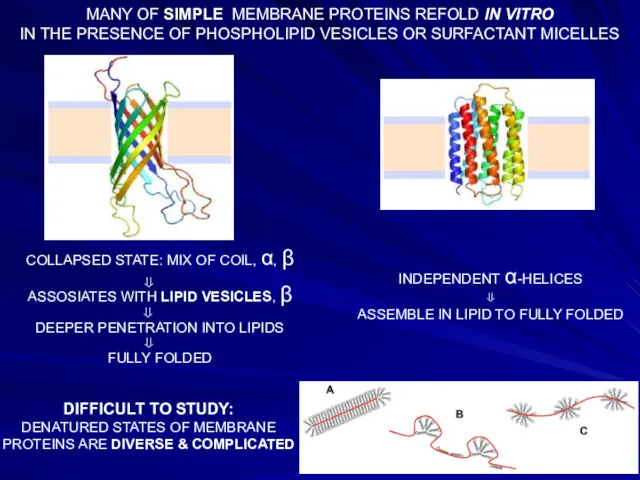
- 24. MANY OF SIMPLE MEMBRANE PROTEINS REFOLD IN VITRO IN THE PRESENCE OF PHOSPHOLIPID VESICLES OR SURFACTANT
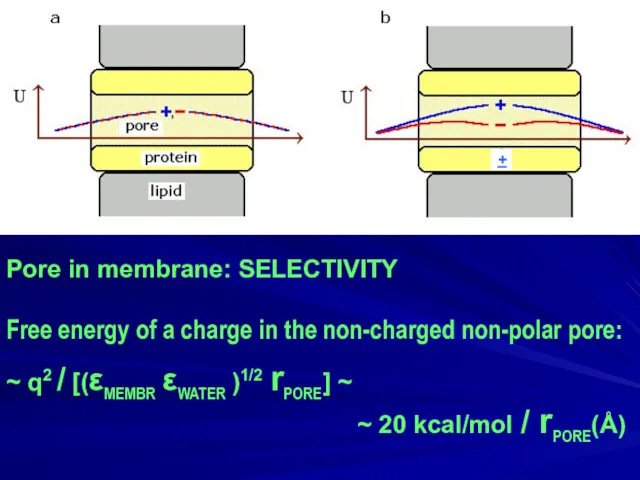
- 25. Pore in membrane: SELECTIVITY Free energy of a charge in the non-charged non-polar pore: ~ q2
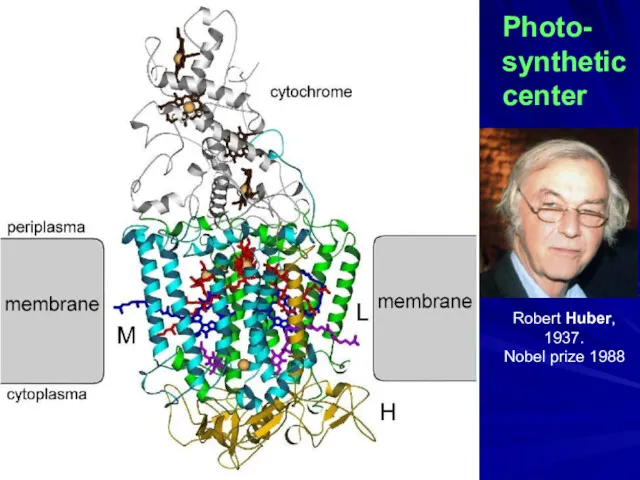
- 26. Photo- synthetic center Robert Huber, 1937. Nobel prize 1988
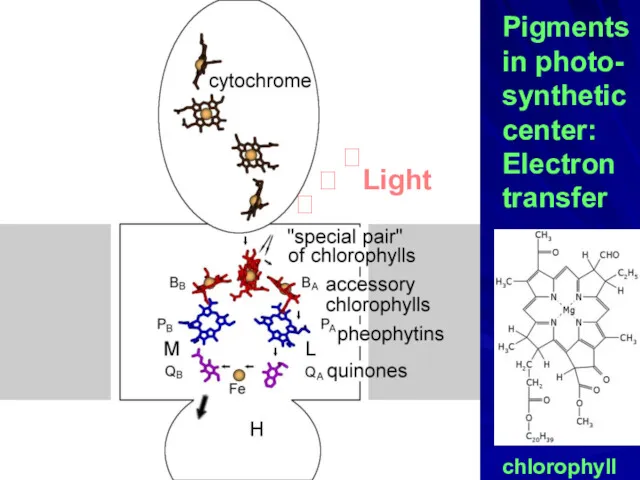
- 27. Pigments in photo- synthetic center: Electron transfer chlorophyll ? ? Light ?
- 29. Скачать презентацию

![collagen triple helix: 3 chains ≈ [Gly-X-Pro]≈500](/_ipx/f_webp&q_80&fit_contain&s_1440x1080/imagesDir/jpg/141138/slide-8.jpg)


 Үйкеліс күші
Үйкеліс күші Дозиметрия ионизирующих излучений. Лекция 1
Дозиметрия ионизирующих излучений. Лекция 1 Mechanical System
Mechanical System Методы наблюдения и регистрации элементарных частиц
Методы наблюдения и регистрации элементарных частиц Технология ультразвукового контроля узлов и агрегатов электропоезда
Технология ультразвукового контроля узлов и агрегатов электропоезда X6000平台电子电气系统介绍. Внедрение электронной и электрической системы платформы X6000
X6000平台电子电气系统介绍. Внедрение электронной и электрической системы платформы X6000 Коробка передач (4AT,JATCO). Составные части
Коробка передач (4AT,JATCO). Составные части Рентгеновские лучи. Свойства, дифракция, устройство, применение рентгеновских лучей
Рентгеновские лучи. Свойства, дифракция, устройство, применение рентгеновских лучей Лекции 3-4 курса Ф -3 2020 — копия
Лекции 3-4 курса Ф -3 2020 — копия Термодинамические циклы холодильных машин
Термодинамические циклы холодильных машин Состав молекулы. Современные представления о строении атома
Состав молекулы. Современные представления о строении атома Электромагнитные переходные процессы в электроэнергетических системах
Электромагнитные переходные процессы в электроэнергетических системах презентация урока Выталкивающая сила
презентация урока Выталкивающая сила Отчет о лабораторной работе №14 Изучение явления электромагнитной индукции
Отчет о лабораторной работе №14 Изучение явления электромагнитной индукции Магнитное поле
Магнитное поле Решение задач. Магнитное поле и проводник с током
Решение задач. Магнитное поле и проводник с током Построение изображений в тонких линзах
Построение изображений в тонких линзах Взаимное притяжение и отталкивание молекул
Взаимное притяжение и отталкивание молекул Электрические явления
Электрические явления Демонстрационные задания. Физика. 8 класс
Демонстрационные задания. Физика. 8 класс Прямолинейное равноускоренное движение. Ускорение
Прямолинейное равноускоренное движение. Ускорение Буксовый узел грузового вагона. Техническая ревизия буксового узла колесный пары РУ1-Ш
Буксовый узел грузового вагона. Техническая ревизия буксового узла колесный пары РУ1-Ш Расчет электрических нагрузок жилых и общественных зданий. (Лекция 4)
Расчет электрических нагрузок жилых и общественных зданий. (Лекция 4) ТО системи пуску двигунів автомобілів. ТО акумуляторних батарей. ТО генераторів та реле-регуляторів
ТО системи пуску двигунів автомобілів. ТО акумуляторних батарей. ТО генераторів та реле-регуляторів Окружающий мир как иерархическая система
Окружающий мир как иерархическая система Тепловое излучение
Тепловое излучение Газовые законы
Газовые законы Призначення, технічна характеристика, загальна будова системи живлення двигуна УТД-20С1 паливом
Призначення, технічна характеристика, загальна будова системи живлення двигуна УТД-20С1 паливом