Содержание
- 2. Remarks Links
- 3. This chapter introduces the basic theory, the functionality and location of the supply system components Chapter
- 4. Module 1 estimated time ……. This module introduces the general structure of the fuel supply system
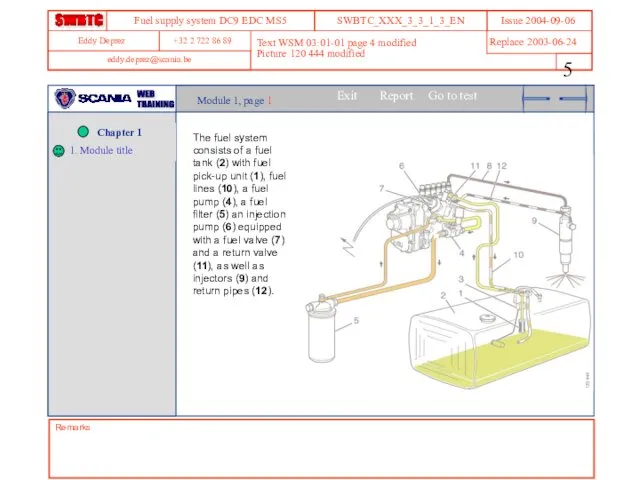
- 5. Remarks Text WSM 03:01-01 page 4 modified Picture 120 444 modified Module 1, page 1 The
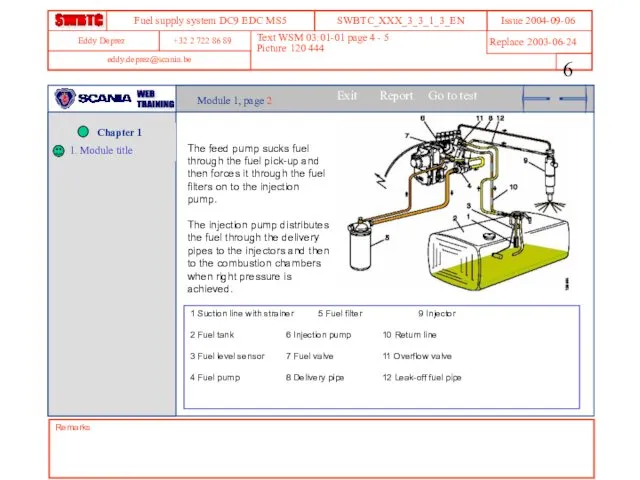
- 6. Remarks Text WSM 03:01-01 page 4 - 5 Picture 120 444 Module 1, page 2 The
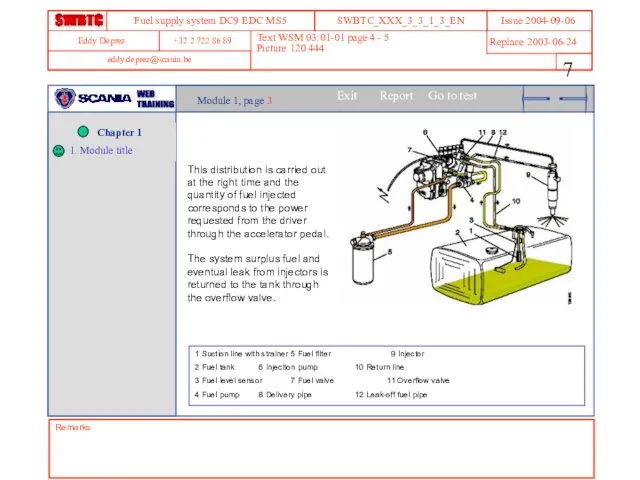
- 7. Remarks Text WSM 03:01-01 page 4 - 5 Picture 120 444 Module 1, page 3 This
- 8. Module 1 Question 1 (45 sec) In the supply circuit, what is the feed pump used
- 9. Module 2 estimated time ……. This module introduces the components of the fuel tank and lines
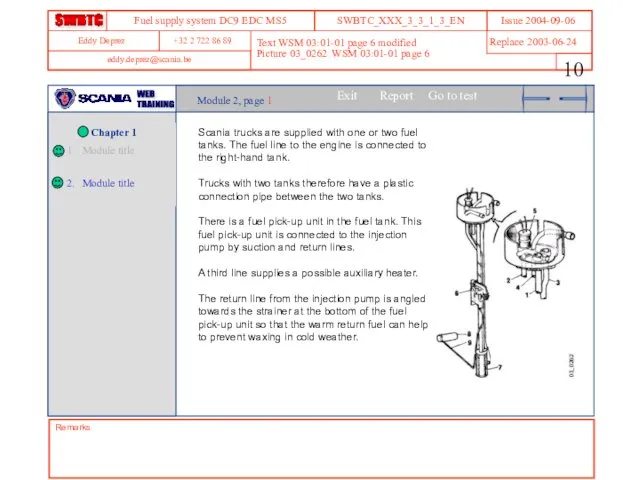
- 10. Remarks Text WSM 03:01-01 page 6 modified Picture 03_0262 WSM 03:01-01 page 6 Module 2, page
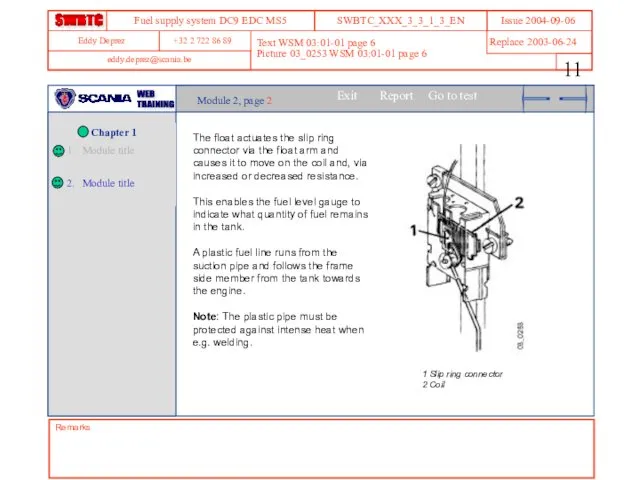
- 11. Text WSM 03:01-01 page 6 Picture 03_0253 WSM 03:01-01 page 6 Remarks Module 2, page 2
- 12. Module 2 Question 1 (40 sec) A vehicle fitted with two tanks is equipped with: An
- 13. Module 2 Question 2 (40 sec) The return pipe coming from the injection pump is angled
- 14. Module 3 estimated time ……. This module introduces the fuel valve, as well as its location
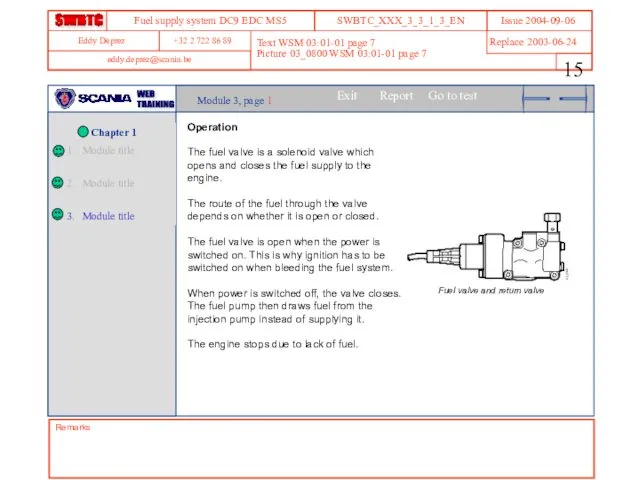
- 15. Text WSM 03:01-01 page 7 Picture 03_0800 WSM 03:01-01 page 7 Remarks Module 3, page 1
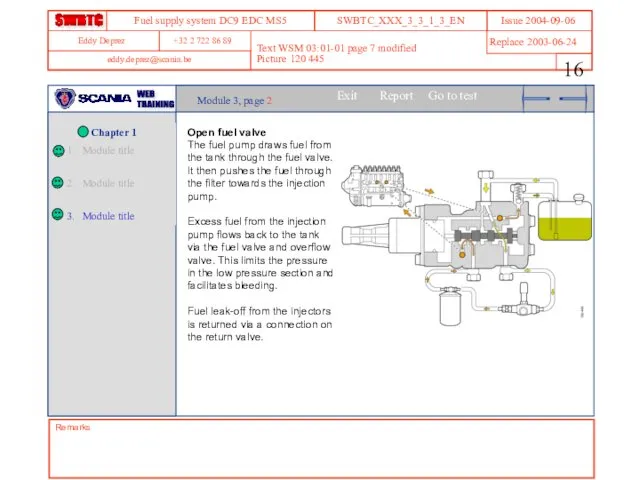
- 16. Remarks Text WSM 03:01-01 page 7 modified Picture 120 445 Module 3, page 2 Open fuel
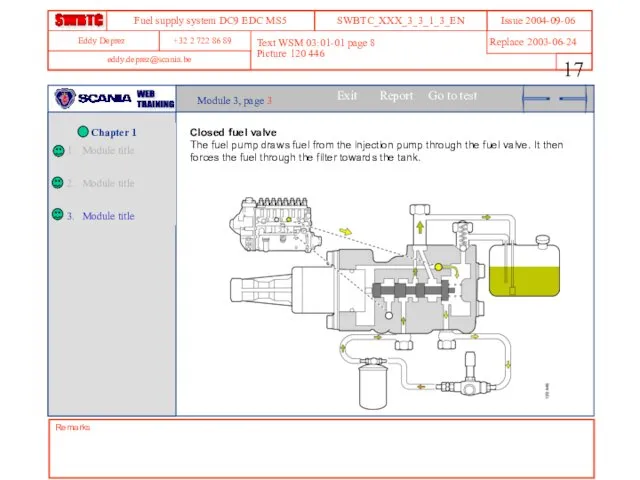
- 17. Remarks Text WSM 03:01-01 page 8 Picture 120 446 Module 3, page 3 Closed fuel valve
- 18. Module 3 Question 1 (40 sec) In the supply circuit, what is the overflow valve used
- 19. Module 3 Question 2 (40 sec) During the bleeding of the fuel system, it is necessary:
- 20. Module 4 estimated time ……. This module introduces the fuel pump, as well as its location
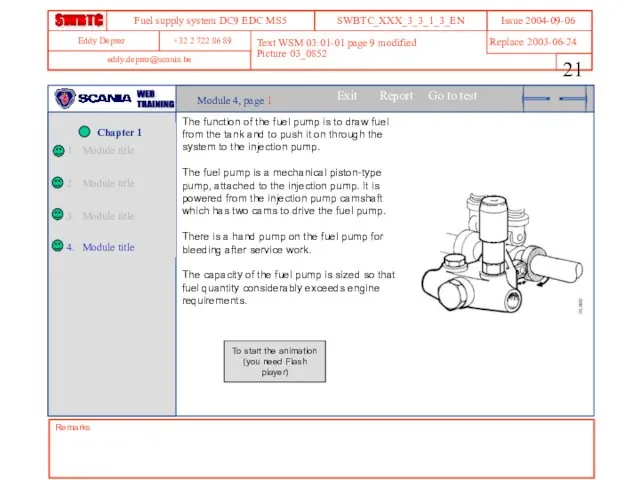
- 21. Remarks Text WSM 03:01-01 page 9 modified Picture 03_0852 Module 4, page 1 The function of
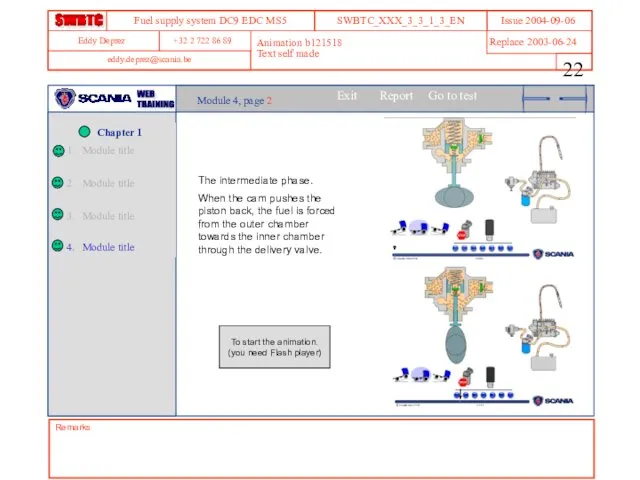
- 22. Remarks Animation b121518 Text self made Module 4, page 2 The intermediate phase. When the cam
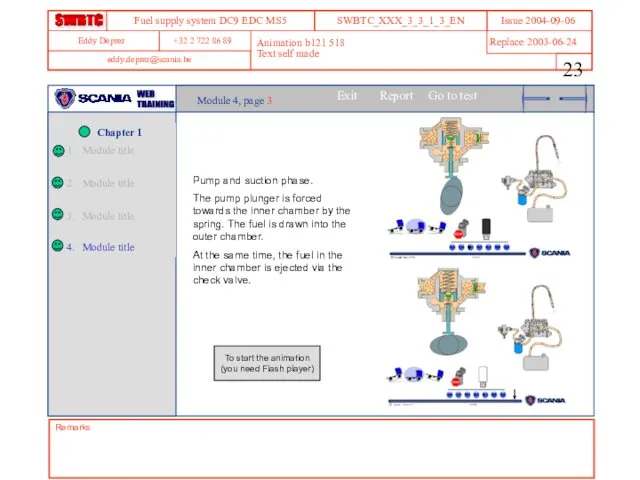
- 23. Remarks Animation b121 518 Text self made Module 4, page 3 Pump and suction phase. The
- 24. Module 4 Question 1 (40 sec) The fuel pump is equipped with a hand pump. This
- 25. Module 5 estimated time ……. This module introduces the fuel filter, as well as its location
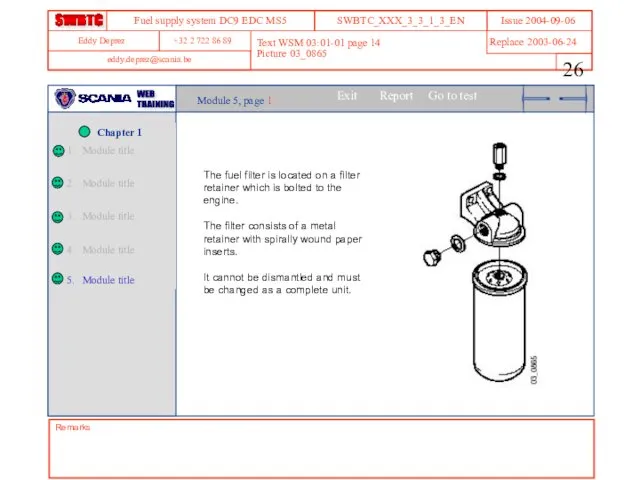
- 26. Remarks Text WSM 03:01-01 page 14 Picture 03_0865 Module 5, page 1 The fuel filter is
- 27. Module 5 Question 1 (30 sec) Is it possible to replace just the paper cartridge of
- 28. In this chapter you learned: The general structure of the fuel supply system as well as
- 29. This chapter introduces the injection pump and the injectors Chapter 2 estimated time ……. Links Remarks
- 30. Module 1 estimated time ... This module introduces the injection pump Links Remarks Links
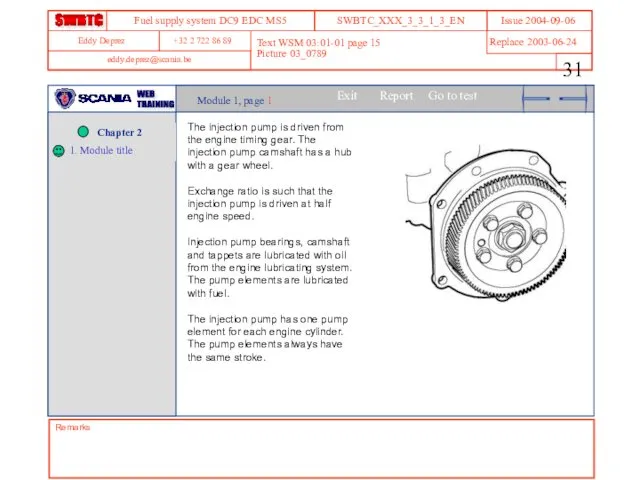
- 31. Text WSM 03:01-01 page 15 Picture 03_0789 Remarks Module 1, page 1 The injection pump is
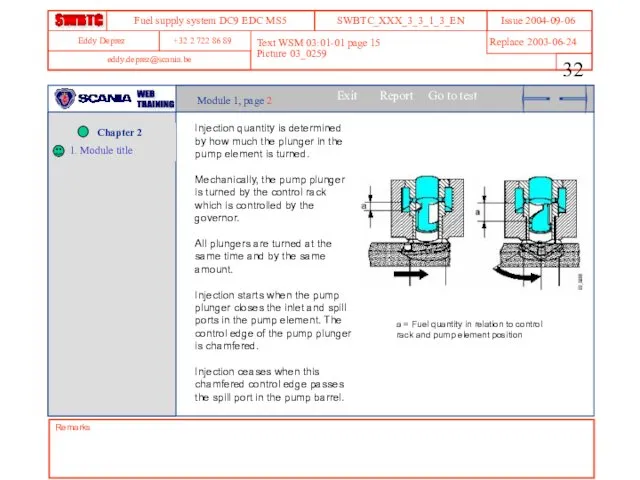
- 32. Remarks Text WSM 03:01-01 page 15 Picture 03_0259 Module 1, page 2 Injection quantity is determined
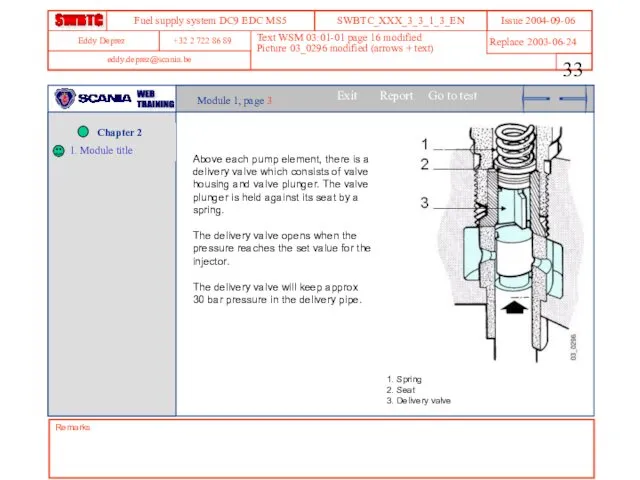
- 33. Remarks Text WSM 03:01-01 page 16 modified Picture 03_0296 modified (arrows + text) Module 1, page
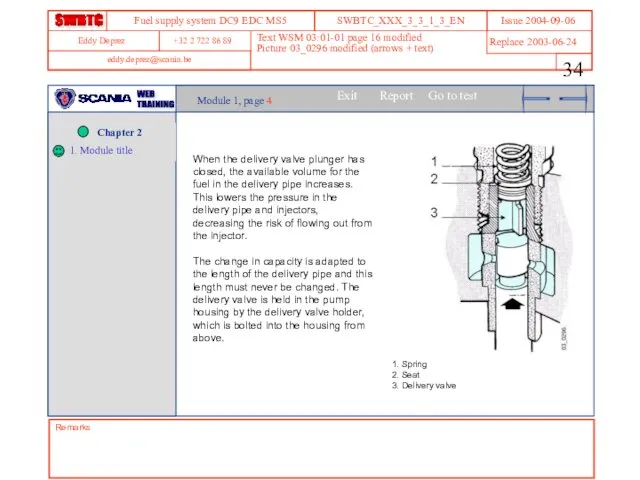
- 34. Remarks Text WSM 03:01-01 page 16 modified Picture 03_0296 modified (arrows + text) Module 1, page
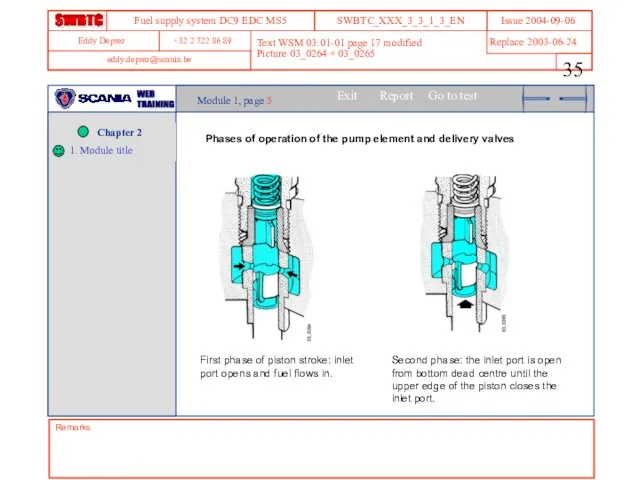
- 35. Remarks Text WSM 03:01-01 page 17 modified Picture 03_0264 + 03_0265 Module 1, page 5 Phases
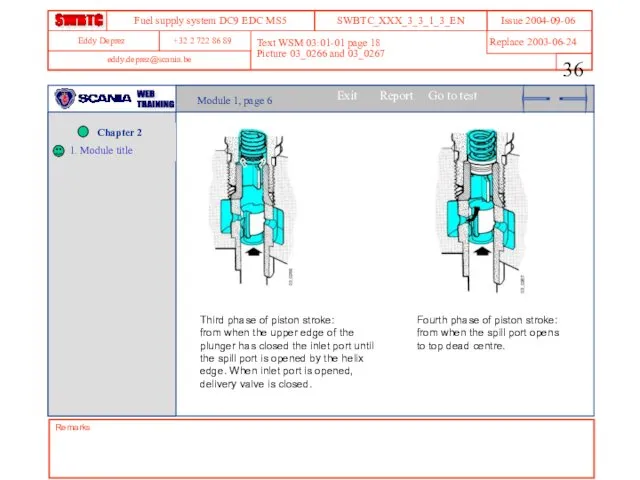
- 36. Remarks Text WSM 03:01-01 page 18 Picture 03_0266 and 03_0267 Module 1, page 6 Third phase
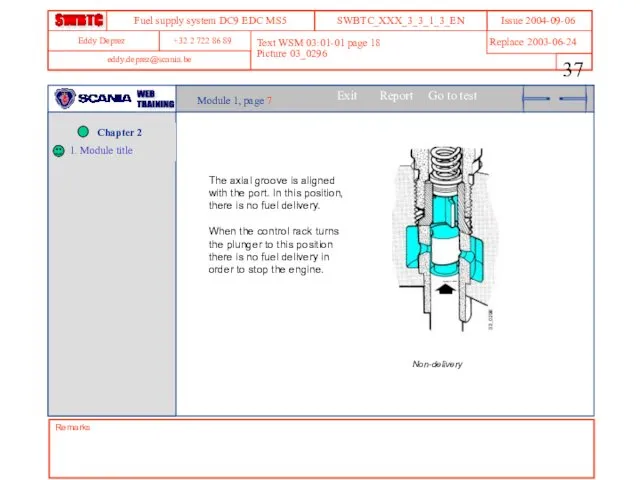
- 37. Remarks Text WSM 03:01-01 page 18 Picture 03_0296 Module 1, page 7 The axial groove is
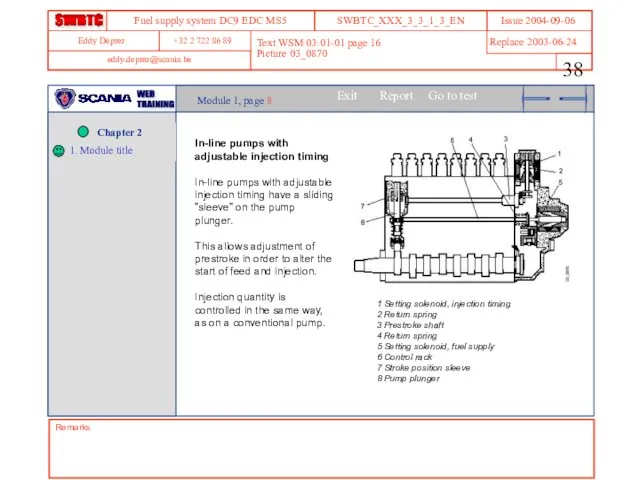
- 38. Remarks Text WSM 03:01-01 page 16 Picture 03_0870 Module 1, page 8 In-line pumps with adjustable
- 39. Module 1 Question 1 (40 sec) The injection pump runs at a speed: Equivalent to double
- 40. Module 1 Question 2 (40 sec) The rotation of a pump element piston influences: The time
- 41. Module 1 Question 3 (40 sec) After injection, when the pressure valve is closed again, pressure
- 42. Module 2 estimated time ……. This module introduces the injector and the delivery pipe Remarks Links
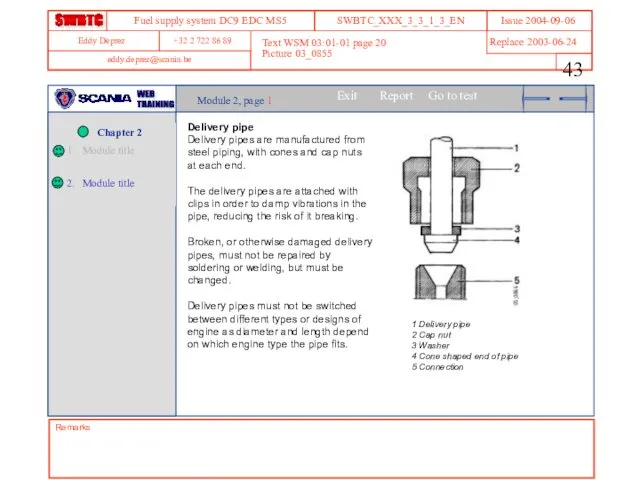
- 43. Remarks Text WSM 03:01-01 page 20 Picture 03_0855 Module 2, page 1 Delivery pipe Delivery pipes
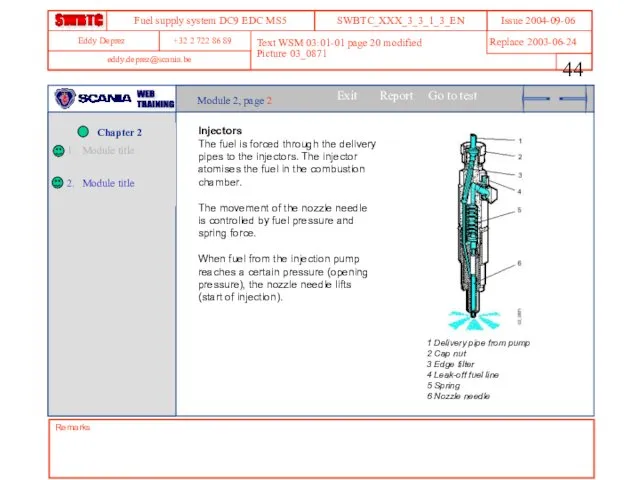
- 44. Remarks Text WSM 03:01-01 page 20 modified Picture 03_0871 Module 2, page 2 Injectors The fuel
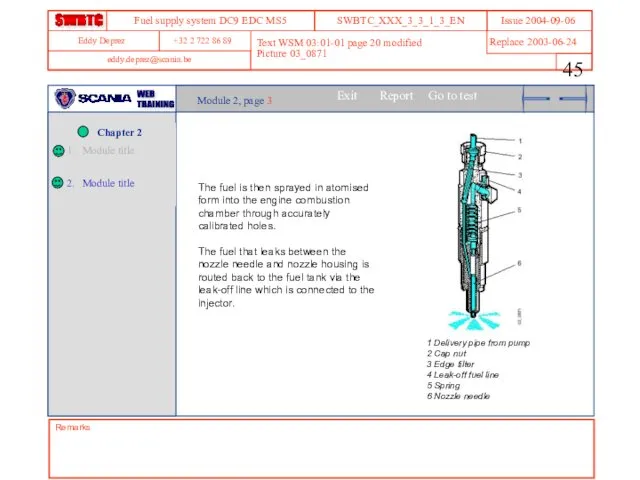
- 45. Remarks Text WSM 03:01-01 page 20 modified Picture 03_0871 Module 2, page 3 The fuel is
- 46. Module 2 Question 1 (40 sec) The opening pressure of the injector depends on: The pressure
- 48. Скачать презентацию

 Methods and technical means for using the energy of waves
Methods and technical means for using the energy of waves Презентация Механическое движение
Презентация Механическое движение Экспериментальные методы исследования частиц
Экспериментальные методы исследования частиц Неисправности кривошипно-шатунного механизма и газораспределительного механизма
Неисправности кривошипно-шатунного механизма и газораспределительного механизма Свойства звука: отражение, эхо
Свойства звука: отражение, эхо Лазеры ультракоротких импульсов. Фемтосекундные лазеры
Лазеры ультракоротких импульсов. Фемтосекундные лазеры Введение в Физику
Введение в Физику Разработка урока по физике(с элементами робототехники) на тему наблюдение и исследование явления инерции
Разработка урока по физике(с элементами робототехники) на тему наблюдение и исследование явления инерции Эквивалентная схема диэлектрика и диэлектрическая дисперсия
Эквивалентная схема диэлектрика и диэлектрическая дисперсия Электрооборудование автомобилей. Схемы автомобильного бортового электрооборудования
Электрооборудование автомобилей. Схемы автомобильного бортового электрооборудования Архимедова сила
Архимедова сила Разработка урока по физике в 8 классе на тему: Последовательное и параллельное соединение проводников
Разработка урока по физике в 8 классе на тему: Последовательное и параллельное соединение проводников Явление электромагнитной индукции
Явление электромагнитной индукции Активізація пізнавальної діяльності учнів на уроках фізики шляхом використання проблемних ситуацій
Активізація пізнавальної діяльності учнів на уроках фізики шляхом використання проблемних ситуацій Амортизаторы. Назначение амортизаторов
Амортизаторы. Назначение амортизаторов Линзы. Урок 62. Изображения, даваемые линзой
Линзы. Урок 62. Изображения, даваемые линзой Электрический ток в газах
Электрический ток в газах Основные термины и понятия в области диагностирования
Основные термины и понятия в области диагностирования конспект урока физики в 7 классе Давление. Способы уменьшения и увеличения давления
конспект урока физики в 7 классе Давление. Способы уменьшения и увеличения давления Магниттік күштік микроскопия
Магниттік күштік микроскопия Влияние электромагнитного поля на окружающую среду и человека. 8 класс
Влияние электромагнитного поля на окружающую среду и человека. 8 класс Prezentatsia_k_preddiplomnoy_praktiki_Butin_I_A
Prezentatsia_k_preddiplomnoy_praktiki_Butin_I_A Взаимодействие электронов с веществом. Опыты по рассеянию электронов в газе. АФ1.7
Взаимодействие электронов с веществом. Опыты по рассеянию электронов в газе. АФ1.7 Первый закон Ньютона
Первый закон Ньютона Увлекательная физика
Увлекательная физика Испарение. Насыщенный и ненасыщенный пар
Испарение. Насыщенный и ненасыщенный пар Ядерная энергия, атомная энергия
Ядерная энергия, атомная энергия Радиоактивность как свидетельство сложного строения атомов
Радиоактивность как свидетельство сложного строения атомов