Слайд 2

Слайд 3
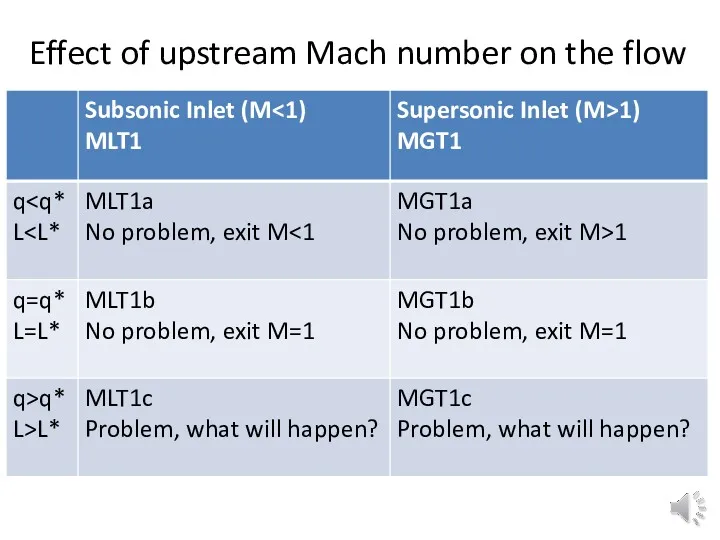
Effect of upstream Mach number on the flow
Слайд 4
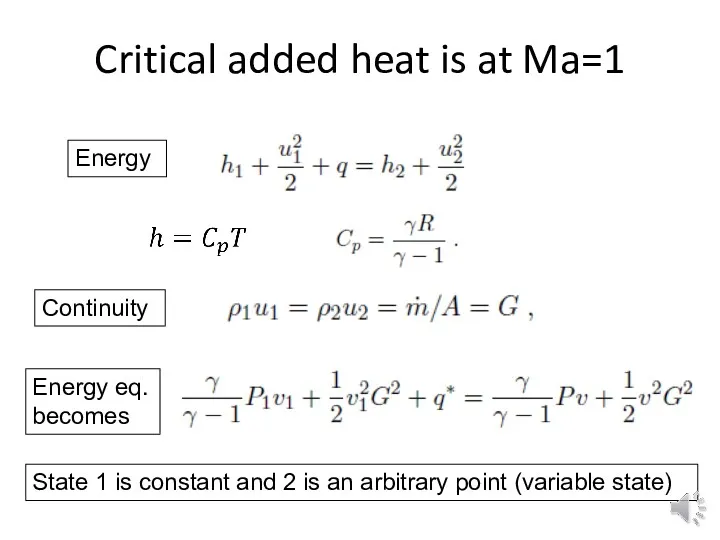
Critical added heat is at Ma=1
Energy
Energy eq. becomes
Continuity
State 1 is constant
and 2 is an arbitrary point (variable state)
Слайд 5

At the point of tangency of H-curve and Rayleigh line the
Mach number ALWAYS equals one
Слайд 6
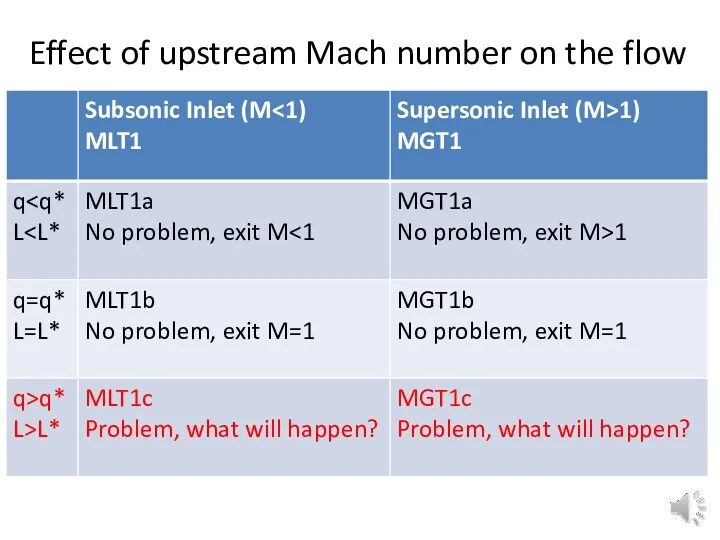
Effect of upstream Mach number on the flow
Слайд 7
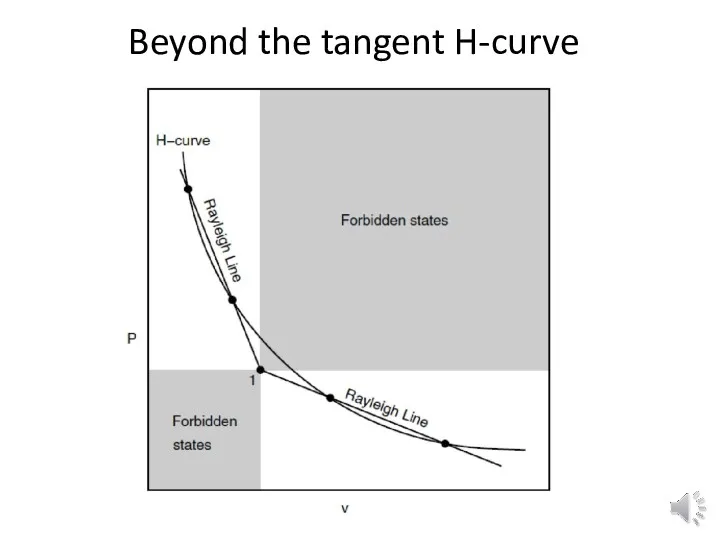
Beyond the tangent H-curve
Слайд 8
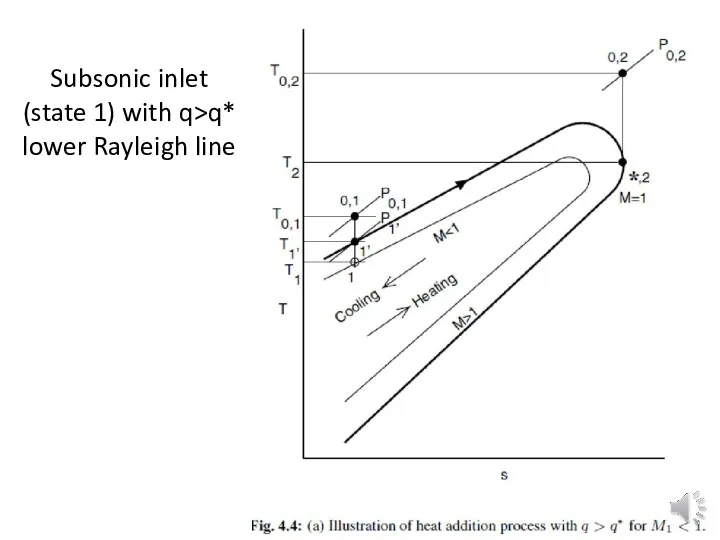
Subsonic inlet (state 1) with q>q*
lower Rayleigh line
Слайд 9
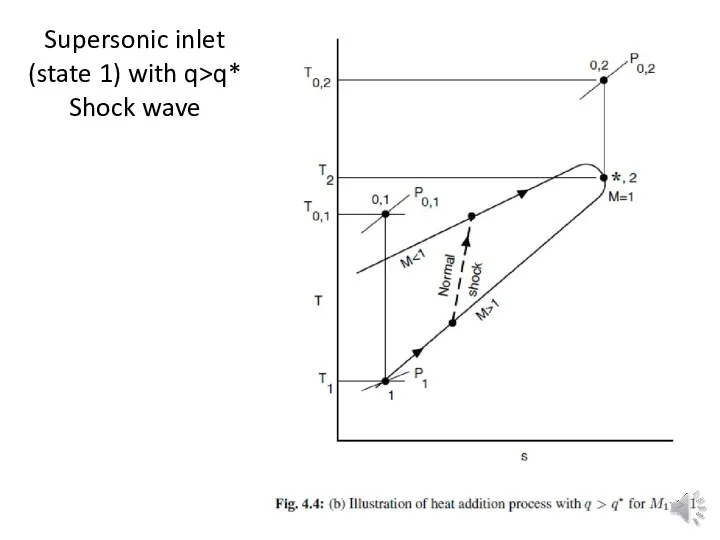
Supersonic inlet (state 1) with q>q*
Shock wave
Слайд 10

Chapter 4: Lecture Problems
In Rayleigh flow, prove that the point of
tangency of H-curve and Rayleigh line represents a sonic flow.
Stagnation pressure proof.
Слайд 11











 Измерение давления в покоящейся жидкости
Измерение давления в покоящейся жидкости Physics basics (Unit 1)
Physics basics (Unit 1) Презентация. Гости из космоса
Презентация. Гости из космоса Властивості радіохвиль. Розподіл спектру радіохвиль. Особливості розповсюдження радіохвиль (Лекція 2.1)
Властивості радіохвиль. Розподіл спектру радіохвиль. Особливості розповсюдження радіохвиль (Лекція 2.1) Машины и оборудование для свайных работ. Лекция 6
Машины и оборудование для свайных работ. Лекция 6 Электромагнитные переходные процессы в электроэнергетических системах
Электромагнитные переходные процессы в электроэнергетических системах Открытое мероприятие Добро пожаловать в космос
Открытое мероприятие Добро пожаловать в космос Применение сообщающихся сосудов
Применение сообщающихся сосудов Презентация по теме Решение задач по кинематике с помощью квадратных уравнений.
Презентация по теме Решение задач по кинематике с помощью квадратных уравнений. Айнымалы ток тізбегіндегі актив кедергі. (Лекция 14)
Айнымалы ток тізбегіндегі актив кедергі. (Лекция 14) Своя игра. Строения атома. (11 класс)
Своя игра. Строения атома. (11 класс) Три состояния вещества
Три состояния вещества Индукция магнитного поля. Магнитный поток
Индукция магнитного поля. Магнитный поток Газовые законы
Газовые законы Автокөліктерді жөндеу технологиясы
Автокөліктерді жөндеу технологиясы Зеленый дом
Зеленый дом Энтропия в техносфере
Энтропия в техносфере Раздел 3. Оценка технического состояния, ТО и Р автомобилей. Урок №72. Тема ТО рулевого управления
Раздел 3. Оценка технического состояния, ТО и Р автомобилей. Урок №72. Тема ТО рулевого управления Ядерные реакции. Радиоактивность
Ядерные реакции. Радиоактивность Пучковые технологии. Вакуум: физические свойства, получение, измерение
Пучковые технологии. Вакуум: физические свойства, получение, измерение Тепловой расчет сферического носка ЛА. Вариант 34
Тепловой расчет сферического носка ЛА. Вариант 34 Исследование процесса вытяжки деталей ч.1
Исследование процесса вытяжки деталей ч.1 Магнитное поле
Магнитное поле Работа и мощность электрического тока
Работа и мощность электрического тока Своя игра по физике
Своя игра по физике Техническое обслуживание и ремонт сцепления автомобиля ВАЗ 2107
Техническое обслуживание и ремонт сцепления автомобиля ВАЗ 2107 Робототехника. Робот-дворник
Робототехника. Робот-дворник Коррозионные процессы
Коррозионные процессы