Содержание
- 2. CONTENT Theory Instrumentation Fourier transform IR spectrometers(FTIR) Measurement techniques Mid-infrared (MIR) Near-infrared (NIR)
- 3. THEORY measurement of IR radiation absorbed by or reflected from a sample absorption of IR radiation
- 4. VIBRATIONAL TRANSITIONS Fundamental (normal): change of vibrational quantum number ∆v = 1 high probability → high
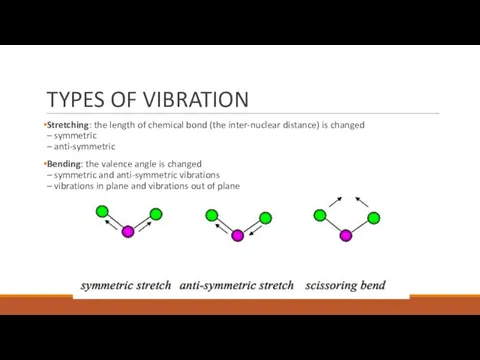
- 5. TYPES OF VIBRATION Stretching: the length of chemical bond (the inter-nuclear distance) is changed – symmetric
- 6. WHICH SUBSTANCES GIVE A SIGNAL IN IR SPECTRUM? YES Molecules that contain polar bonds Molecules composed
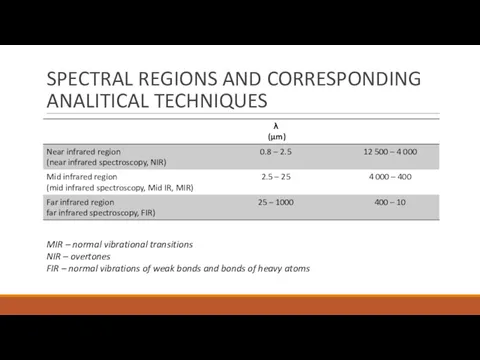
- 7. SPECTRAL REGIONS AND CORRESPONDING ANALITICAL TECHNIQUES MIR – normal vibrational transitions NIR – overtones FIR –
- 8. INSTRUMENTATION FOR IR SPECTROSCOPY MAIN COMPONENTS OF AN INSTRUMENT radiation source measuring (and reference) cell wavelength
- 9. SOURCES OF IR RADIATION For NIR: tungsten lamp For MIR: – Globar = electrically heated (1100
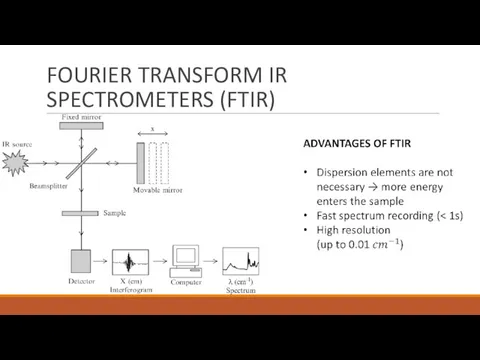
- 10. FOURIER TRANSFORM IR SPECTROMETERS (FTIR)
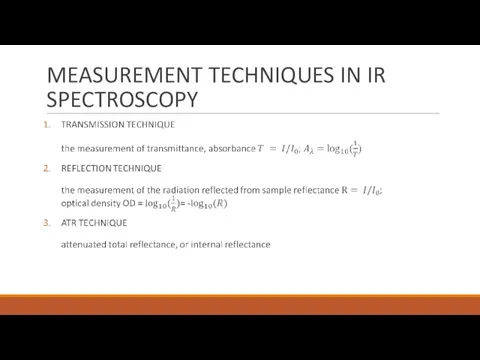
- 11. MEASUREMENT TECHNIQUES IN IR SPECTROSCOPY
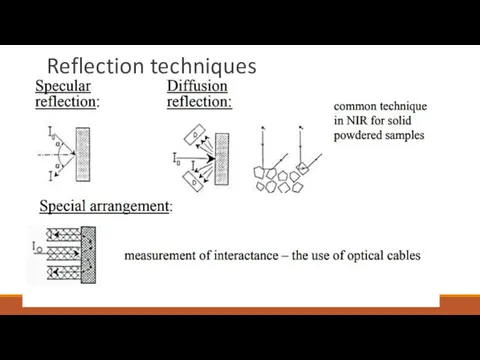
- 12. Reflection techniques
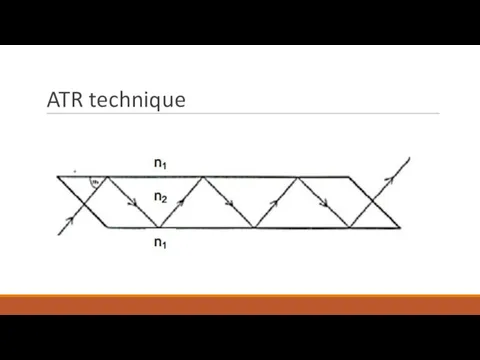
- 13. ATR technique
- 14. ADVANTAGES OF ATR Simple preparation of sample before measurement Non-transparent samples can be analyzed REQUIREMENTS FOR
- 15. MID-INFRARED SPECROSCOPY (Mid IR)
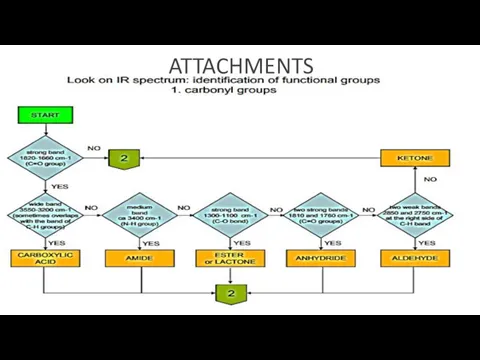
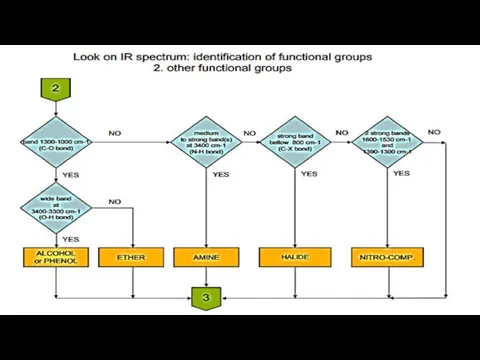
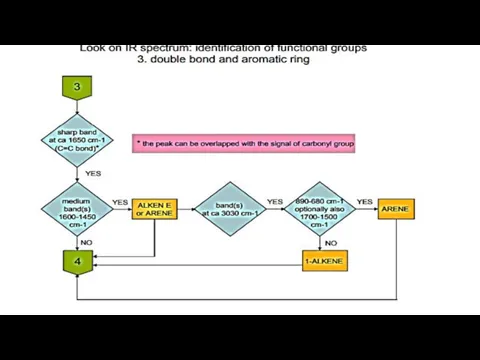
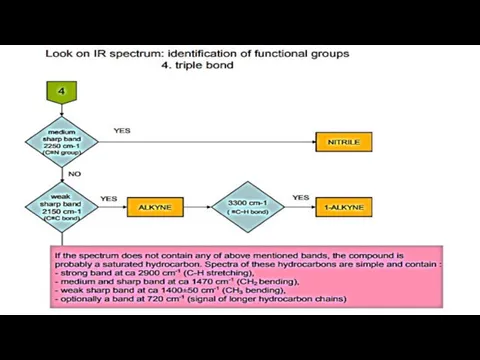
- 16. Steps of identification process 1. Searching for functional groups on the basis of characteristic vibrations (using
- 17. NEAR INFRARED SPECTROSCOPY (NIR)
- 18. Making determinations of … in food analysis WATER FAT PROTEINS CARBOHYDRATES SUGARS ALCOHOLS
- 19. ATTACHMENTS
- 25. Скачать презентацию












 Магнитные материалы
Магнитные материалы Иондық күшті анықтау
Иондық күшті анықтау Формула Максвелла для относительных скоростей
Формула Максвелла для относительных скоростей Ультразвук. Свойства ультразвука и области его применения
Ультразвук. Свойства ультразвука и области его применения Твердая фаза и поровое пространство почв. Реология. Основа, модельные представления
Твердая фаза и поровое пространство почв. Реология. Основа, модельные представления Механические колебания и волны
Механические колебания и волны Фундаментальные отношения между пикселами
Фундаментальные отношения между пикселами Решение задач на гидравлические машины
Решение задач на гидравлические машины Определение скорости света
Определение скорости света Сила тяжести, вес тела
Сила тяжести, вес тела Тепловые машины и их КПД (презентация 8 класс)
Тепловые машины и их КПД (презентация 8 класс) презентация к уроку на тему: Основные положения МКТ
презентация к уроку на тему: Основные положения МКТ Изменение энергии нейтронов при рассеянии. Замедляющая способность вещества
Изменение энергии нейтронов при рассеянии. Замедляющая способность вещества Интегрированный урок физики и информатики
Интегрированный урок физики и информатики Применение законов сохранения импульса и энергии
Применение законов сохранения импульса и энергии Режимы работы промышленных электрических сетей
Режимы работы промышленных электрических сетей Нормирование точности деталей вал и стакан цилиндрического двухступенчатого редуктора
Нормирование точности деталей вал и стакан цилиндрического двухступенчатого редуктора Ветрогенератор - альтернативный источник энергии: разработка и исследование
Ветрогенератор - альтернативный источник энергии: разработка и исследование Плавание тел
Плавание тел Цепные передачи
Цепные передачи Резание металла слесарной ножовкой (6 класс)
Резание металла слесарной ножовкой (6 класс) Презентация по теме Второй закон Ньютона
Презентация по теме Второй закон Ньютона Электромагнитные волны. Электромагнитные колебания. Понятие об электромагнитном поле
Электромагнитные волны. Электромагнитные колебания. Понятие об электромагнитном поле Электростатика. Тема 2. Теорема Остроградского-Гаусса
Электростатика. Тема 2. Теорема Остроградского-Гаусса Сила трения скольжения
Сила трения скольжения Физика атомного ядра
Физика атомного ядра Тепломассообмен. Теплопроводность при стационарном тепловом режиме (часть 1)
Тепломассообмен. Теплопроводность при стационарном тепловом режиме (часть 1) Свободное движение твердого тела. (Лекция 5, Кафедра теоретической механики)
Свободное движение твердого тела. (Лекция 5, Кафедра теоретической механики)