Слайд 2

Lasers in science
1. What actually is laser?
2. The first working
prototype of a laser.
3. The Spectroscopy.
4. Space mission.
5. Conclusion.
Слайд 3

1. What actually is laser?
Laser - a device that converts various
types of energy (light, electric, thermal, chemical, etc.) into the energy of coherent monochromatic light radiation. L.A.S.E.R means Light Amplification by Stimulated Emission of Radiation.
Слайд 4

2. The first working prototype of a laser.
Theodere Maiman builds the
firs working prototype of laser at Hughes Research Laboratories in Malibu, California. This laser uses synthetic ruby as the active medium and emits a deep green beam of coherent light.
Слайд 5
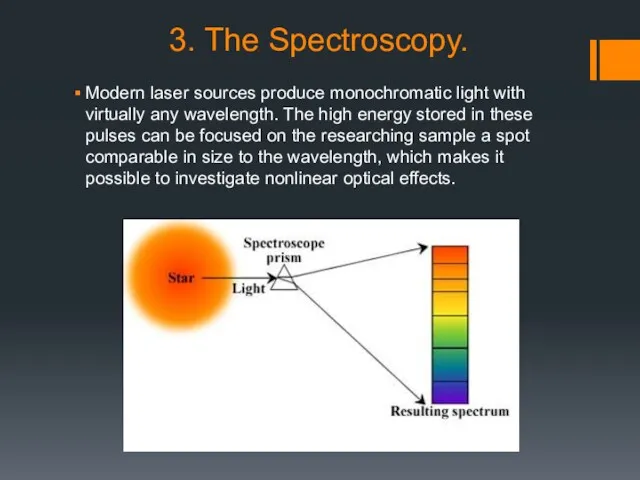
3. The Spectroscopy.
Modern laser sources produce monochromatic light with virtually any
wavelength. The high energy stored in these pulses can be focused on the researching sample a spot comparable in size to the wavelength, which makes it possible to investigate nonlinear optical effects.
Слайд 6

4. Space mission.
During the flight to the moon, several special angular
reflectors were delivered by vehicles. With the help of a telescope, a specially focused laser beam. It became possible to calculate the distance to the moon, know only light speed and travel time of laser beam .





 Структурные уровни организации материи. Лекция 6 (1ч)
Структурные уровни организации материи. Лекция 6 (1ч) Водород. Физические свойства
Водород. Физические свойства Урок физики в 8 классе Электризация тел
Урок физики в 8 классе Электризация тел Ядролық гамма-резонанс
Ядролық гамма-резонанс Тепловые двигатели. Устройство и принцип действия
Тепловые двигатели. Устройство и принцип действия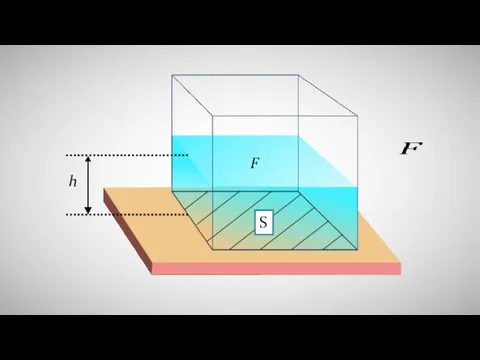 Расчёт давления жидкости на дно и стенки сосуда
Расчёт давления жидкости на дно и стенки сосуда Зависимость скорости испарения от рода жидкости
Зависимость скорости испарения от рода жидкости Основы технической диагностики. Диагностическая модель объекта контроля
Основы технической диагностики. Диагностическая модель объекта контроля Система питания дизельного двигателя
Система питания дизельного двигателя Посвящение в юные физики
Посвящение в юные физики Урок-соревнование Восхождение на пик механики
Урок-соревнование Восхождение на пик механики Источники электрического тока_презентация
Источники электрического тока_презентация Эволюция открытых систем
Эволюция открытых систем Детали машин
Детали машин ФРЕКС. Науковий образ світу. Мікросвіт
ФРЕКС. Науковий образ світу. Мікросвіт Ионные двигатели
Ионные двигатели Тербелістердің жалпы сипаттамалары
Тербелістердің жалпы сипаттамалары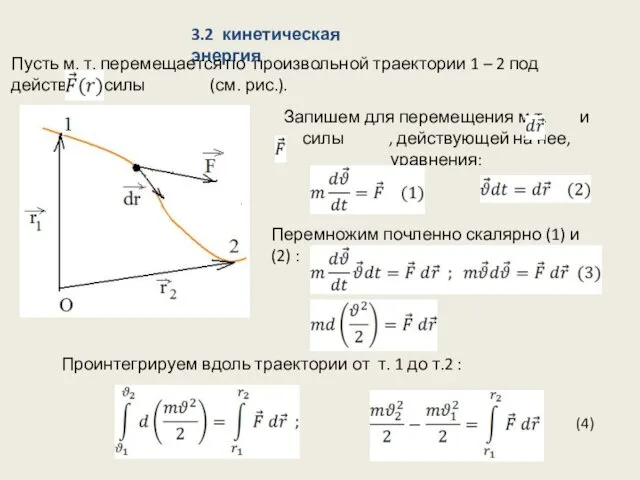 Кинетическая энергия
Кинетическая энергия Люмінесценція оксидних і халькогенідних стекол та їх кристалічних аналогів. (Лекція 7)
Люмінесценція оксидних і халькогенідних стекол та їх кристалічних аналогів. (Лекція 7) Молекулярная физика и термодинамика
Молекулярная физика и термодинамика Циклы. Теплотехника
Циклы. Теплотехника Влажность воздуха на различных широтах Земли
Влажность воздуха на различных широтах Земли Тепловые двигатели
Тепловые двигатели Основи молекулярно - кінетичної теорії газів (лекція 6)
Основи молекулярно - кінетичної теорії газів (лекція 6) Резание металла слесарной ножовкой (6 класс)
Резание металла слесарной ножовкой (6 класс) Домалау мойынтіректері
Домалау мойынтіректері Динамика, обобщение темы
Динамика, обобщение темы Лампа ДРВ, ДРЛ, ДРИ и ДНаТ
Лампа ДРВ, ДРЛ, ДРИ и ДНаТ