Содержание
- 2. COMMUNITIES AND URBANIZATION
- 4. Contents Urbanization Causes of Urban Growth Perspectives on Urbanization Problems of Urban Areas
- 5. URBANIZATION Transformation of a society from a rural to an urban one. Urban population - Persons
- 6. Megacities - Cities with 10 million residents or more.
- 7. Metropolitan Area A metropolitan area is a densely populated core area together with adjacent communities. .The
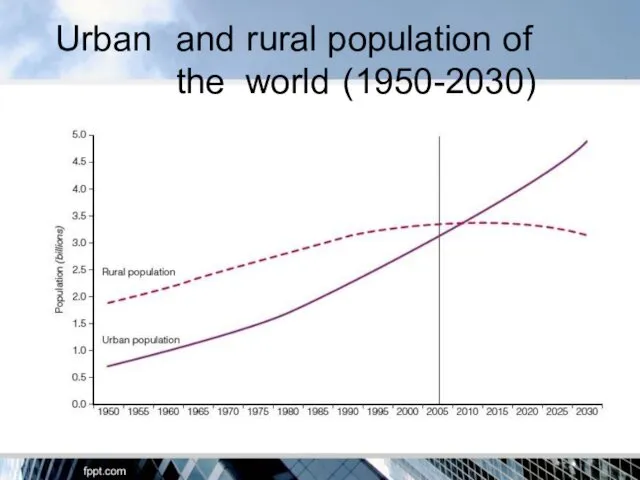
- 9. Urban and rural population of the world (1950-2030)
- 10. Causes of Urban Growth ϖBetter food supply ϖGood medical care ϖEducation ϖJobs ϖEntertainment ϖSpecialization of professions
- 11. Functionalist View Focuses on how changes in one aspect of the social system affect other aspects
- 12. Functionalist View The development of urban areas is functional for societal development. Urbanization is also dysfunctional,
- 13. Human Ecology Human ecology is an area of study that is concerned with the interrelationships between
- 14. Urban Ecology An area of study that focuses on the interrelationships between people and their environment
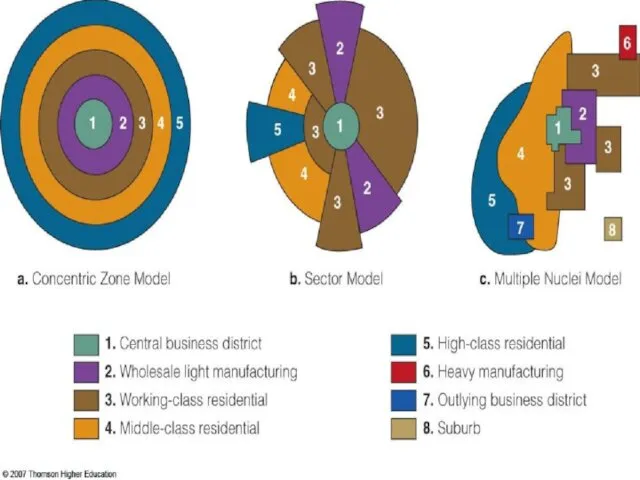
- 15. Functionalist View There are different theories: Concentric-zone theory Demographic transition theory Multiple-nuclei theory
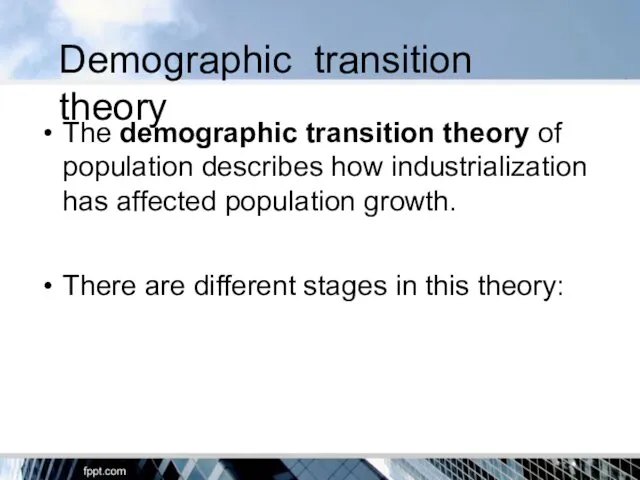
- 16. Demographic transition theory The demographic transition theory of population describes how industrialization has affected population growth.
- 17. Stage 1: Preindustrial Societies - little population growth, high birth rates offset by high death rates.
- 18. Stage 3: Advanced Industrialization and Urbanization - very little population growth occurs, birth rates and death
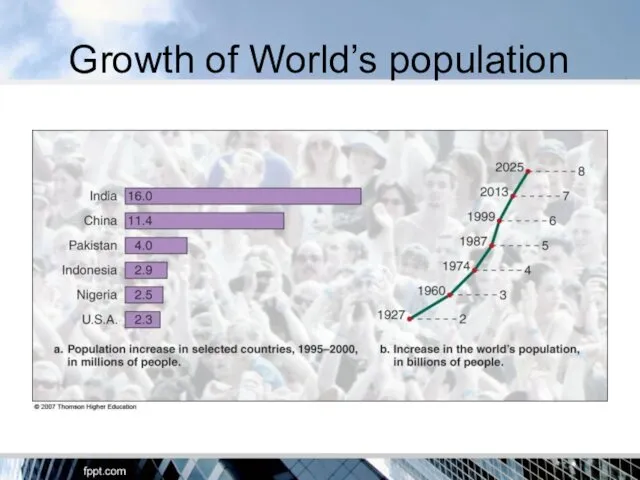
- 19. Growth of World’s population
- 20. Concentric Zone Theory Ernest Rurgess Theory of urban growth Growth in terms of a series of
- 21. Multiple Nuclei Theory Chauncy D.Harris and Edward Ullman in 1945 A theory of urban growth. Growth
- 23. Symbolic View Simmel’s view of city life The intensity of city life causes people to become
- 24. Conflict View Emphasizes the role of power, wealth and profit motive in development of urban areas.
- 25. Conflict View The capitalist class chooses locations for skyscrapers and housing projects, limiting individual choices by
- 26. New Urban Sociology An approach to urbanization that considers the interplay of local, national, and worldwide
- 27. World System Analysis Wallerstein was a person who gave this view. He argued that global economic
- 28. Current Urban Problems For Developing world 1-uncontrollable growth 2-trraffic noise pollution dirty water increase in unemployment
- 30. Скачать презентацию























 Географическая карта. Масштаб. 6 класс
Географическая карта. Масштаб. 6 класс Северная Америка и её особенности
Северная Америка и её особенности Рекреационно-оздоровительный поход Кольцо по Нарочанскому краю
Рекреационно-оздоровительный поход Кольцо по Нарочанскому краю Человек и мир камня
Человек и мир камня Изучение нивелира и работа с ним
Изучение нивелира и работа с ним КВН для 5-6 классов
КВН для 5-6 классов Shymkent
Shymkent Компас. Азимут
Компас. Азимут Основные зоны вулканизма на земле. Вулканы, гейзеры, горячие источники
Основные зоны вулканизма на земле. Вулканы, гейзеры, горячие источники Инженерно-геологические исследования для строительства
Инженерно-геологические исследования для строительства Природно-хозяйственные зоны России
Природно-хозяйственные зоны России Биосфера Земли. Обобщающий урок
Биосфера Земли. Обобщающий урок Химическая промышленность России
Химическая промышленность России Canada
Canada Инженерно-геодезические изыскания для строительства
Инженерно-геодезические изыскания для строительства Республика Крым
Республика Крым Мы – союз народов России
Мы – союз народов России Червоні фералітні грунти сезонно-вологих лісів і високотравних саван
Червоні фералітні грунти сезонно-вологих лісів і високотравних саван Ласкаво просимо до Німеччини
Ласкаво просимо до Німеччини Влажность воздуха. Способы определения влажности воздуха
Влажность воздуха. Способы определения влажности воздуха Презентация по географии Контроль по теме Северная Америка
Презентация по географии Контроль по теме Северная Америка Мастер-класс Гимн географии
Мастер-класс Гимн географии Испарение и конденсация. Насыщенный пар. Влажность воздуха
Испарение и конденсация. Насыщенный пар. Влажность воздуха Брендинг территорий
Брендинг территорий Australia. Or down under
Australia. Or down under Астана-аймақтар: көші-қон ағымдарының географиялық ерекшеліктері
Астана-аймақтар: көші-қон ағымдарының географиялық ерекшеліктері Африка
Африка Республика Северная Осетия-Алания
Республика Северная Осетия-Алания