Слайд 2

Political Culture
Political Culture - widely shared beliefs, values and norms concerning
relationships of citizens to government and to one another
Слайд 3

Political Culture
Important Elements of American Political Culture
liberty - preoccupation with rights
equality
- equal vote, equal opportunity, equality under the law, but not equal wealth
democracy - politicians accountable to the people
civic duty - serve community
individual responsibility – barring some disability, individuals responsible for own actions and well being
Слайд 4

Political Socialization
Political Socialization is the complex process by which people acquire
their political values.
Agents of Early Socialization include two fundamental principles that characterize early learning
Primacy principle—what is learned first is learned best
Structuring principle—what is learned first structures later learning. Agents that structure early socialization are the family, school and community and peers.
Слайд 5

Agents of Socialization
The most important agents of early socialization are:
1. The family:
For example, children often adopt the party identification of their parents
2. Primary and secondary schools:
a) Primary schools introduce authority figures outside the family and teach the importance of national slogans
b) Secondary schools often teach civic responsibility
Слайд 6

Political Socialization
Continuing Socialization includes newspaper and television news for the older
American’s source of political news, while younger Americans are more likely to rely on radio, magazines or the Internet.
The socialization process continues in later life through other agents, most notably through:
1. College
2. Coworkers, club members, friends, neighbors, and spouses
3. Political leaders ,mass media
4. Election campaigns ,voting
5. The maturation process (government actions, such as taxing and regulation)
Слайд 7

Political Socialization
3. The community and peers (religious organizations, youth groups, civic activities):
a) A homogeneous community exerts strong pressure to conform.
b) Peer groups may offer protection against community pressures, allowing individuals to develop political attitudes that may be substantially different from their parents and other community authority figures.
Слайд 8

Social Groups and Political Values
No two people are influenced by precisely
the same socialization agents or in precisely the same way. People with similar backgrounds, however, do tend to develop similar political opinions
Слайд 9

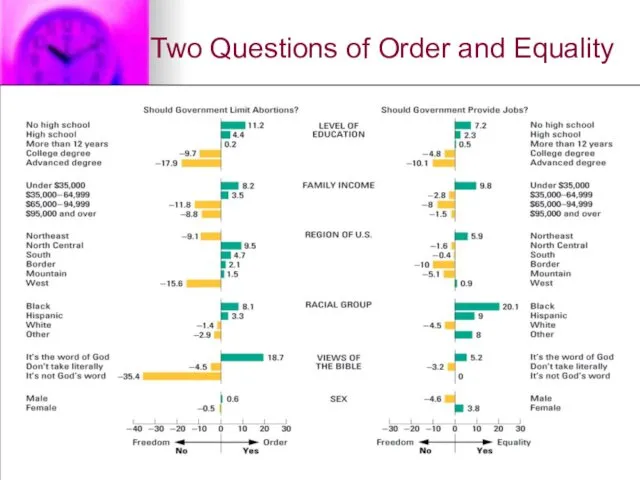
Social Groups and Political Values
Examples used to demonstrate this included abortion
and guaranteed employment.
Perspectives applied to these issues included education, income, region, race and ethnicity, religion and gender.
Слайд 10

Current Trends
1. People with high education choose freedom over both order
and equality more often than those with low education.
2. People with high income are more opposed to government policies of income redistribution than are those with low income.
3. Regional differences
4. Old ethnicity (European nation of origin) 5. Race and ethnicity have emerged as a more critical variable
6. Religiosity has replaced religion as a strong predictor of political values
7. The gender factor has come to indicate the greater willingness of women to support social programs.
Слайд 11
Two Questions of Order and Equality
Слайд 12

From Values to Ideology
Liberals are associated with change and Conservatives with
tradition.
Liberals support intervention to promote economic equality while Conservatives favor less government intervention and more individual freedom in economic activities.
Слайд 13

The Quality of Ideological Thinking
in Public Opinion
Liberals are people who
believe that government should promote equality, even if some freedom is lost in the process, but who oppose surrendering freedom to government-imposed order.
Слайд 14

The Quality of Ideological Thinking
in Public Opinion
Conservatives are people who
place a higher value on freedom than on equality when the two conflict. Will restrict freedom when threatened with the loss of order.
Слайд 15

The Quality of Ideological Thinking
in Public Opinion
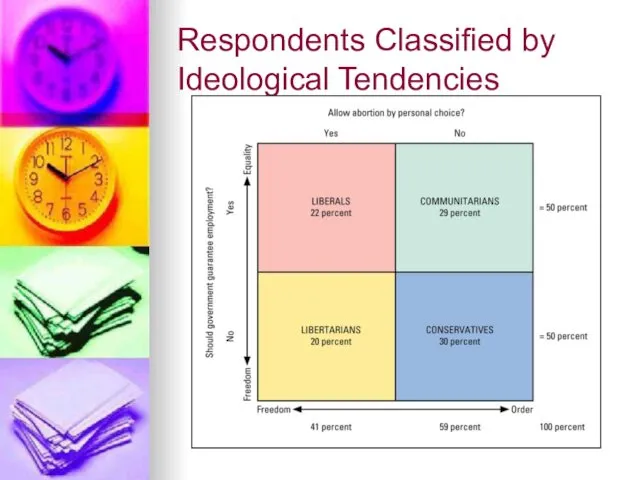
Ideological Types in the
United States also include:
Libertarians: People who favor freedom over both equality and order
Communitarians: People who favor equality and order over freedom
Слайд 16
Respondents Classified by Ideological Tendencies
Слайд 17

The Process of Forming Political Opinions
Political knowledge is not randomly distributed
within our society. People with equivalent knowledge of public affairs and levels of conceptualization are equally likely to call themselves liberals or conservatives.
Слайд 18

The Process of Forming Political Opinions
The self-interest principle—the implication that people
choose what benefits them personally—plays an obvious role in how people form opinions on government policies.
Слайд 19

The Process of Forming Political Opinions
An opinion schema constitutes a network
of organized knowledge and beliefs that guide a person’s processing of information regarding a particular subject.


















 Эволюция формирования национальной идеи и национальной государственности на современном этапе
Эволюция формирования национальной идеи и национальной государственности на современном этапе Международные организации
Международные организации Политические партии
Политические партии Политика и власть
Политика и власть Политическая сфера ЕГЭ. Основные вопросы
Политическая сфера ЕГЭ. Основные вопросы Государство, как главный институт политической системы
Государство, как главный институт политической системы Структура, задачи и основные направления деятельности организации договора о коллективной безопасности
Структура, задачи и основные направления деятельности организации договора о коллективной безопасности Қазақстан ядролық қарусыз әлемді қолдайды
Қазақстан ядролық қарусыз әлемді қолдайды От общих теоретических оснований к сравнению результатов функционирования институтов: концепт Governance
От общих теоретических оснований к сравнению результатов функционирования институтов: концепт Governance Политическая власть
Политическая власть Политико-правовая доктрина Н. М. Коркунова
Политико-правовая доктрина Н. М. Коркунова Политические партии и движения
Политические партии и движения Политическая система
Политическая система Геополитические взаимоотношения России и Китая
Геополитические взаимоотношения России и Китая Локальные войны или открытые международные конфликты
Локальные войны или открытые международные конфликты Политические элиты в фокусе отечественных исследований
Политические элиты в фокусе отечественных исследований Политическая культура Российской Федерации
Политическая культура Российской Федерации Международные политические отношения
Международные политические отношения Nelson Mandela & South African Apartheid
Nelson Mandela & South African Apartheid Политическое поведение. Политическое сознание. Политическая культура
Политическое поведение. Политическое сознание. Политическая культура Деятельность субъектов политического процесса
Деятельность субъектов политического процесса Политология. Левые и правые в политике. Схема всех возможных политических курсов
Политология. Левые и правые в политике. Схема всех возможных политических курсов Идеология и ее роль в жизнедеятельности современного общества
Идеология и ее роль в жизнедеятельности современного общества Политический плюрализм
Политический плюрализм Организация Объединенных Наций. Создание ООН. Место и роль ООН в современном мире
Организация Объединенных Наций. Создание ООН. Место и роль ООН в современном мире Беларусь і праблемы міжнароднай бяспекі ў 2000-х гг. Пагрозы
Беларусь і праблемы міжнароднай бяспекі ў 2000-х гг. Пагрозы The split of Sudan. The role of the oil extraction and transit
The split of Sudan. The role of the oil extraction and transit Қазақстан Республикасының қоғамдық-саяси дамуы
Қазақстан Республикасының қоғамдық-саяси дамуы