Содержание
- 2. Plan: 1. The development of the conflict between the North and South of the Sudan problems
- 3. The Republic of Sudan Capital: Khartoum Language: Arabic, English Religion: Islam Population: app. 40 million GDP
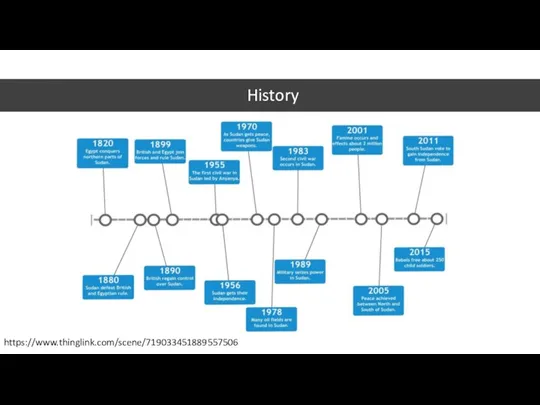
- 4. History https://www.thinglink.com/scene/719033451889557506
- 5. c.a. 2000-1500 BC - Emergence of the Nubian Kingdom of Kush in what is now northern
- 6. Conflict http://app.emaze.com/@AQLQTZIW#4
- 7. Until 1946 British government in a collaboration with Egyptian government administrated South and North Sudan as
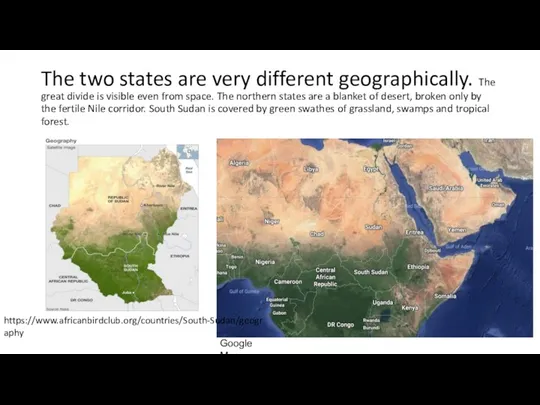
- 8. The two states are very different geographically. The great divide is visible even from space. The
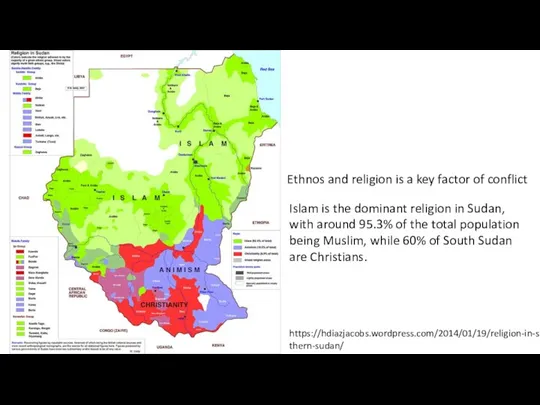
- 9. Ethnos and religion is a key factor of conflict Islam is the dominant religion in Sudan,
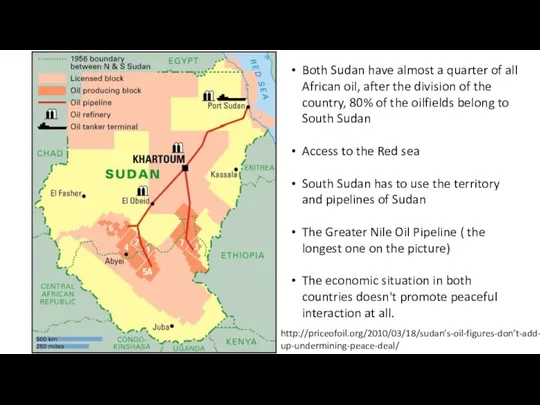
- 10. Both Sudan have almost a quarter of all African oil, after the division of the country,
- 11. Economy and Oil https://www.globalwitness.org/ru/campaigns/south-sudan/
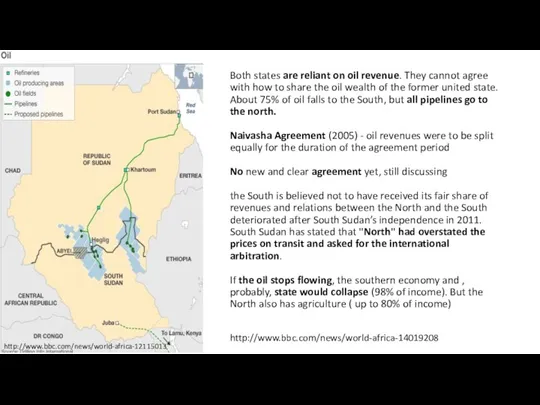
- 12. Both states are reliant on oil revenue. They cannot agree with how to share the oil
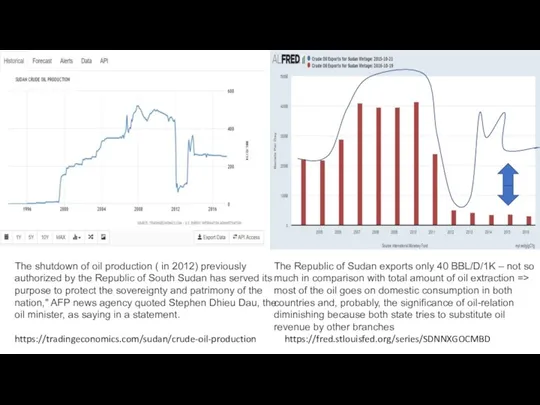
- 13. The shutdown of oil production ( in 2012) previously authorized by the Republic of South Sudan
- 14. The impact of external forces on armed conflict and the peace process http://fijione.tv/fijian-peacekeepers-in-south-sudan-may-be-evacuated-if-tension-escalates/
- 15. The UN has set up a base camp (partly housing IDPs) and deployed troops to maintain
- 16. The Intergovernmental Authority on Development (IGAD consisting of 8 African countries), EU, the US, the UK,
- 17. What is to be done? http://savedarfur.org/the-conflict/darfur/
- 18. Impact of the recent conflict Homeless and displaced people Ethnic tensions between the Dinka and Nuer
- 19. The South Sudan along with being the newest in the world, also became one of the
- 20. References https://www.thinglink.com/scene/719033451889557506 https://www.state.gov/r/pa/ei/bgn/171718.htm https://www.google.co.uk/amp/mobile.reuters.com https://tradingeconomics.com/sudan/crude-oil-production https://fred.stlouisfed.org/series/SDNNXGOCMBD http://www.bbc.com/news/world-africa-14019208 https://www.kerboodle.com/system/images/W1siZiIsIjIwMTQvMTIvMTUvMTUvMjQvMzgvNTc0LzgzMDkyMV9HRl83MjcucGRmIl1d/830921_GF_727.pdf https://stephenjensenpoetry.wordpress.com/page/10/ https://www.reuters.com/article/sudan-southsudan-oil-idUSL6N0AUCNI20130125 http://venturesafrica.com/why-south-sudan-is-now-a-dangerous-place-for-aid-workers/ https://www.africanbirdclub.org/countries/South-Sudan/geography https://www.globalwitness.org/ru/campaigns/south-sudan/ http://priceofoil.org/2010/03/18/sudan’s-oil-figures-don’t-add-up-undermining-peace-deal/ https://hdiazjacobs.wordpress.com/2014/01/19/religion-in-southern-sudan/ http://fijione.tv/fijian-peacekeepers-in-south-sudan-may-be-evacuated-if-tension-escalates/
- 22. Скачать презентацию













 Співпраця України з міжнародними організаціями
Співпраця України з міжнародними організаціями Саяси қақтығыс
Саяси қақтығыс Turkey-EU relations after Özal
Turkey-EU relations after Özal Нации и межнациональные отношения
Нации и межнациональные отношения Politics. Introduction
Politics. Introduction Международные организации
Международные организации Национальные интересы России в современном мире
Национальные интересы России в современном мире Методы урегулирования политического конфликта
Методы урегулирования политического конфликта Политические партии и движения
Политические партии и движения Геополитические эпохи России
Геополитические эпохи России Mikhail Gorbachev - russian politic
Mikhail Gorbachev - russian politic Основные политические идеологии
Основные политические идеологии Soft Power Мягкая сила
Soft Power Мягкая сила Либералы, консерваторы, социалисты
Либералы, консерваторы, социалисты Международные конфликты
Международные конфликты Природа и механизмы политической власти
Природа и механизмы политической власти Либерализм и либералы. Идеи либерализма
Либерализм и либералы. Идеи либерализма Политика как общественное явление и научная теория
Политика как общественное явление и научная теория Политические партии и партийные системы
Политические партии и партийные системы Геополитические интересы РФ
Геополитические интересы РФ Саяси картаның қалыптасу кезеңдері
Саяси картаның қалыптасу кезеңдері Проблема мультикультурализма : сравнительный анализ стран СНГ и ЕС
Проблема мультикультурализма : сравнительный анализ стран СНГ и ЕС Мировые политические процессы в эпоху позднего модерна
Мировые политические процессы в эпоху позднего модерна Распад Югославии и позиция России
Распад Югославии и позиция России Этноцентризм
Этноцентризм Қоғамның саяси жүйесі
Қоғамның саяси жүйесі Політичний конфлікт як предмет дослідження геоконфліктології
Політичний конфлікт як предмет дослідження геоконфліктології FactChek. Отличие факта от фейка. Элементы материалов FactChek
FactChek. Отличие факта от фейка. Элементы материалов FactChek