Содержание
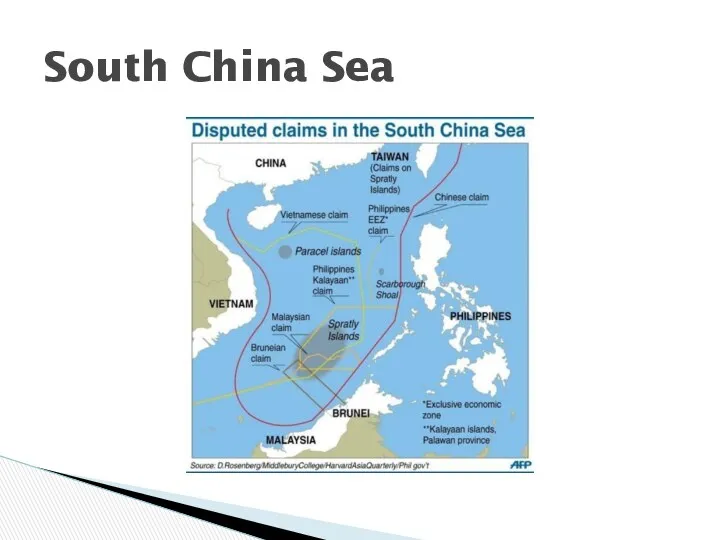
- 2. South China Sea
- 3. Natural resources – oil and gas. “Industrial revolution of Asia” Fisheries – particularly important between China
- 4. South China Sea extremely busy trade route – 5 trillion in trade passes through annually. U.S
- 5. Building military bases – questions over purpose. Potential for aircraft deployment, missiles and missile defences. China
- 6. ADIZ – “East China Sea air Defence Identification Zone” – China trying to restrict aircraft travel
- 7. Government has successfully used state-controlled media and subtle propaganda- themes and tones in media and news
- 8. US strengthening ties with ASEAN, and security cooperation with countries in the region like Vietnam. Other
- 9. Who are the stakeholders involved – this doesn’t just mean states, but the individual stakeholders within
- 10. What is the domestic situation within those states – how will the motion affect it? How
- 12. Скачать презентацию







 Дмитрий Анатольевич Медведев
Дмитрий Анатольевич Медведев Политическая элита
Политическая элита Геронтократия
Геронтократия Государство, нация и гендер
Государство, нация и гендер Россия в международных отношениях. Место России в современном мире
Россия в международных отношениях. Место России в современном мире Политические институты. Государство, как политический институт. (Лекция 2)
Политические институты. Государство, как политический институт. (Лекция 2) Евромайдан. Революция от начала и до конца
Евромайдан. Революция от начала и до конца Розкол в українській православній церкві та шляхи його подолання
Розкол в українській православній церкві та шляхи його подолання Национальная политика Российской Федерации
Национальная политика Российской Федерации Сравнительная политика: институты и процессы
Сравнительная политика: институты и процессы The political system of Great Britain
The political system of Great Britain Личность и политика. Власть
Личность и политика. Власть Политика. Часть1. Подготовка к ЕГЭ по обществознанию
Политика. Часть1. Подготовка к ЕГЭ по обществознанию Формы, виды и направления международного таможенного сотрудничества
Формы, виды и направления международного таможенного сотрудничества Либералы, консерваторы, социалисты: какими должно быть общество и государство
Либералы, консерваторы, социалисты: какими должно быть общество и государство Цели, средства, инструменты и направления антикоррупционной политики государства
Цели, средства, инструменты и направления антикоррупционной политики государства Политическая власть
Политическая власть Зе! Молодіжка. Хмельниччина
Зе! Молодіжка. Хмельниччина Горячие точки в мире
Горячие точки в мире Модель соціальної політики в Україні
Модель соціальної політики в Україні Политические режимы
Политические режимы Политическое устройство мира
Политическое устройство мира Government in Canada
Government in Canada Тоталитаризм: история и современность
Тоталитаризм: история и современность Politics
Politics Формирование антитеррористического поведения
Формирование антитеррористического поведения Геополитика. Теория и практика
Геополитика. Теория и практика Моделі політичних систем
Моделі політичних систем