Содержание
- 2. Content Introduction to Computer Networks Types of Networks Network Topologies Networking Hardwares References
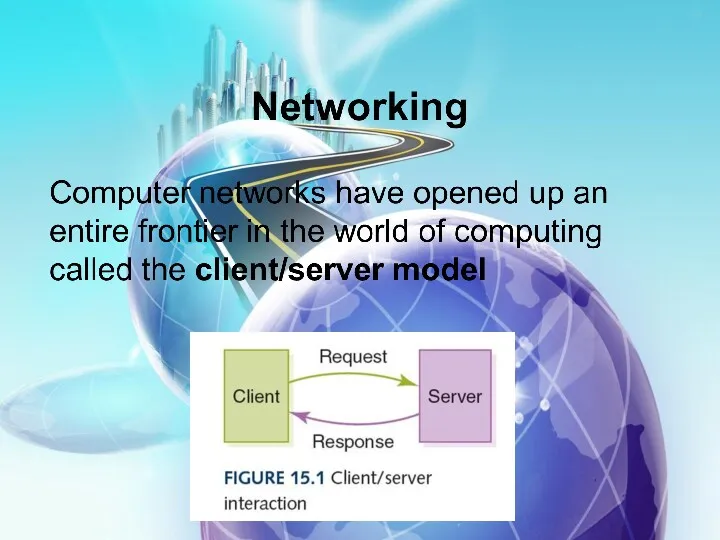
- 3. A network consists of two or more computers that are linked in order to share resources
- 4. 1. At least two computers that have something to share. 2. A cable or wireless pathway,
- 6. File Sharing: Networks offer a quick and easy way to share files directly. Resource Sharing: All
- 7. What is a Topology? • Network topologies describe the ways in which the elements of a
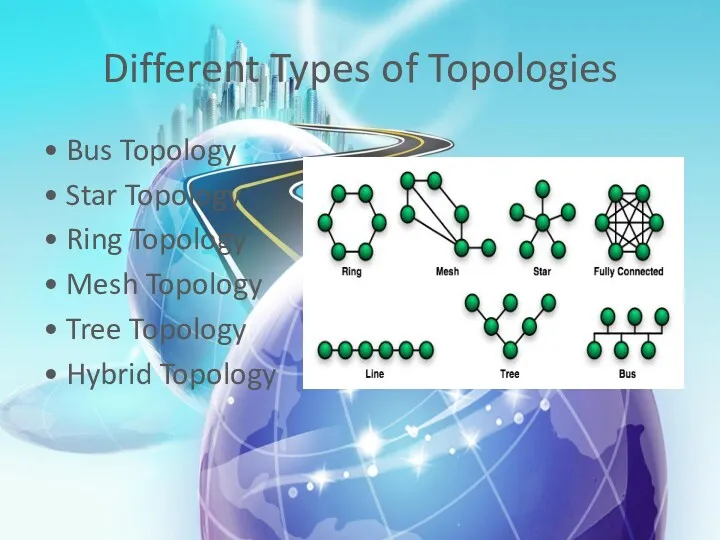
- 8. Different Types of Topologies • Bus Topology • Star Topology • Ring Topology • Mesh Topology
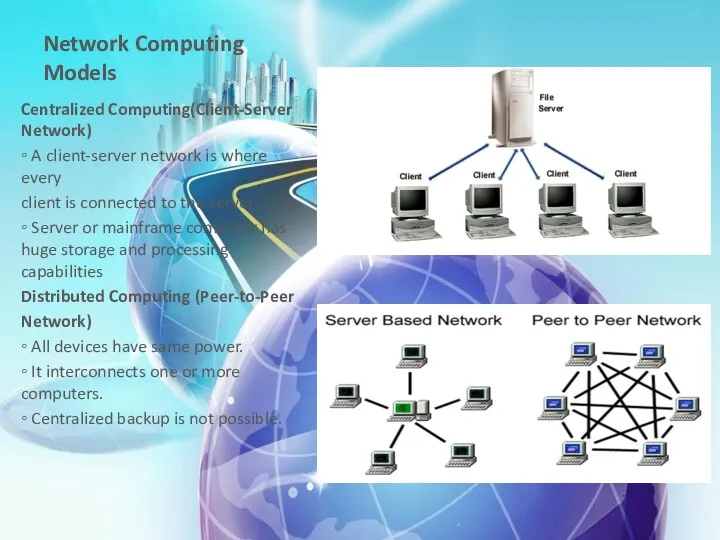
- 9. Network Computing Models Centralized Computing(Client-Server Network) ◦ A client-server network is where every client is connected
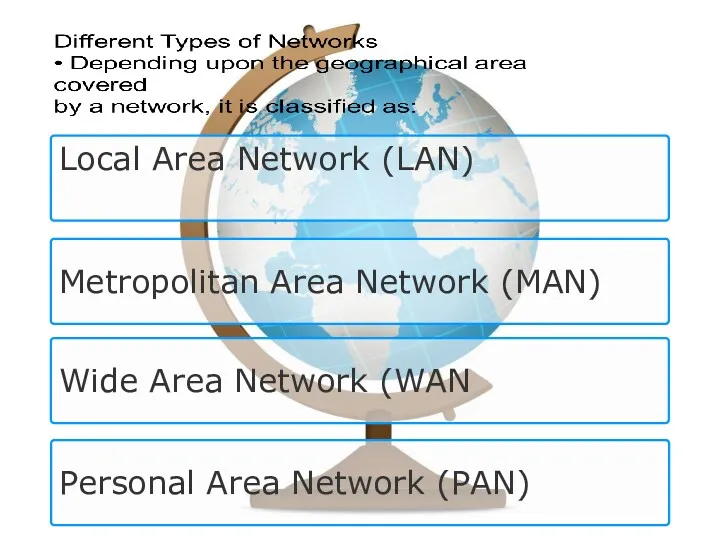
- 10. Local Area Network (LAN) Metropolitan Area Network (MAN) Wide Area Network (WAN Personal Area Network (PAN)
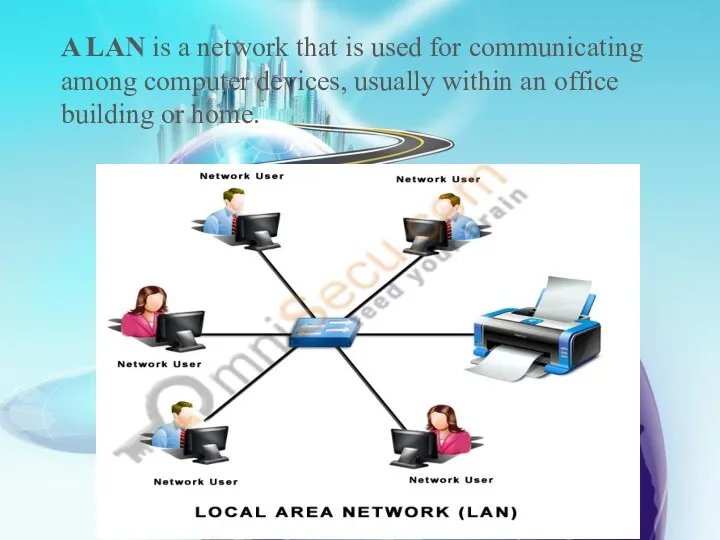
- 11. A LAN is a network that is used for communicating among computer devices, usually within an
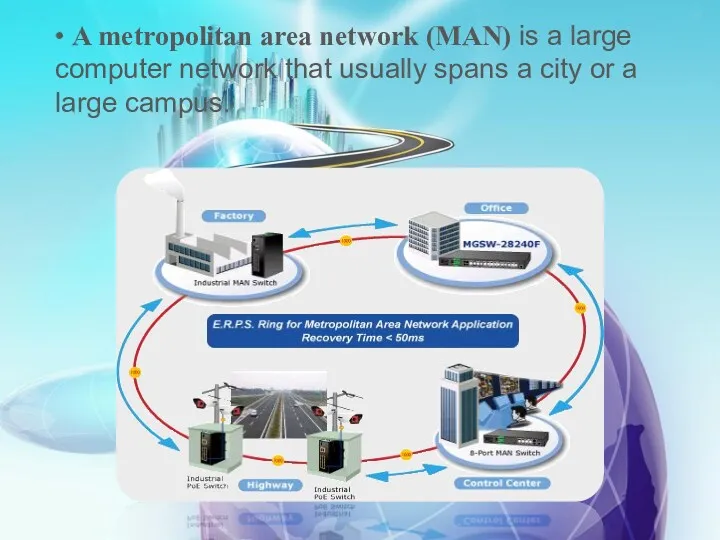
- 12. • A metropolitan area network (MAN) is a large computer network that usually spans a city
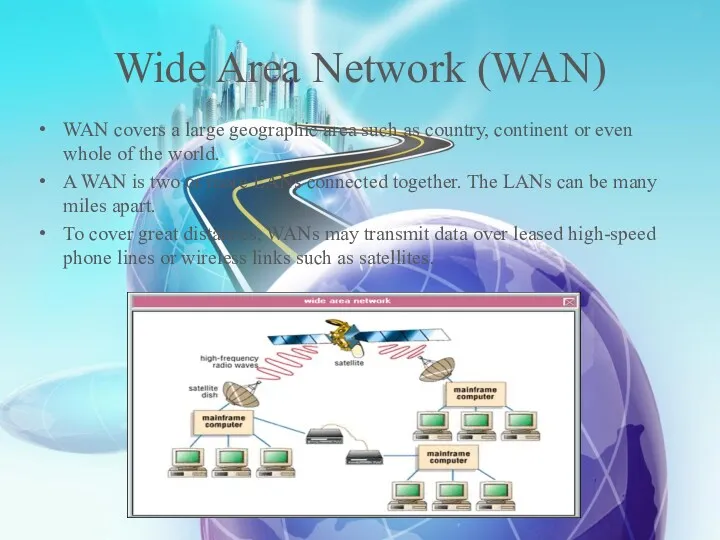
- 13. Wide Area Network (WAN) WAN covers a large geographic area such as country, continent or even
- 14. Personal Area Network (PAN) • A personal area network (PAN) is a computer network used for
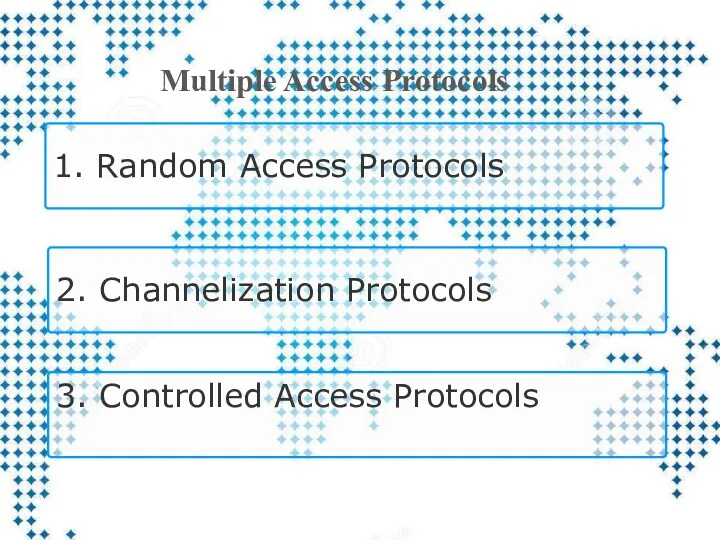
- 15. 1. Random Access Protocols 2. Channelization Protocols 3. Controlled Access Protocols Multiple Access Protocols
- 16. Data Link Layer in Internet We know that Internet consists of individual systems that are connected
- 17. Differences Between SLIP & PPP SLIP SLIP stands for Serial Line Internet Protocol. SLIP does not
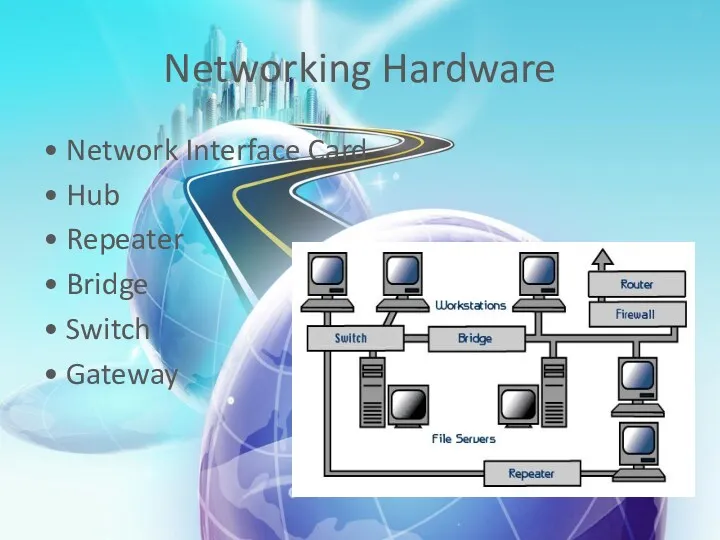
- 18. What is Networking Hardware? Networking hardware includes all computers, peripherals, interface cards and other equipment needed
- 19. Networking Hardware • Network Interface Card • Hub • Repeater • Bridge • Switch • Gateway
- 21. Скачать презентацию









 Разработка и стандартизация программных средств и информационных технологий
Разработка и стандартизация программных средств и информационных технологий Деректердің иерархиялық моделі
Деректердің иерархиялық моделі Презентация к уроку Съёмные носители информации
Презентация к уроку Съёмные носители информации Использование геоинформационных систем при обновлении крупномасштабных топографических карт
Использование геоинформационных систем при обновлении крупномасштабных топографических карт Защита информации
Защита информации Контур. ERP Фокус для SAP - RU 3
Контур. ERP Фокус для SAP - RU 3 Прерывания в защищённом режиме
Прерывания в защищённом режиме Логические элементы компьютера
Логические элементы компьютера Веб-сайт туристского предприятия как инструмент продвижения гостиничных услуг
Веб-сайт туристского предприятия как инструмент продвижения гостиничных услуг Система делает возможным приобрести билеты на многие мероприятия на сайте
Система делает возможным приобрести билеты на многие мероприятия на сайте Создание, изменение и удаление таблиц
Создание, изменение и удаление таблиц Страничный механизм трансляции. (Тема 14)
Страничный механизм трансляции. (Тема 14) Обобщенные методы и классы. Лекция 35
Обобщенные методы и классы. Лекция 35 Графика. Графический режим
Графика. Графический режим Проектування мобільних застосунків. Ресурси (Лекція №5)
Проектування мобільних застосунків. Ресурси (Лекція №5) Створення комп'ютерних презентацій (10 клас)
Створення комп'ютерних презентацій (10 клас) Использование технологий ТРИЗ для повышения мотивации обучения при изучении отдельных разделов информатики
Использование технологий ТРИЗ для повышения мотивации обучения при изучении отдельных разделов информатики Тема: Интернет. Всемирная паутина.
Тема: Интернет. Всемирная паутина. Комп’ютерні віруси
Комп’ютерні віруси Веб-сайт Интернет-магазин оружия
Веб-сайт Интернет-магазин оружия Компьютерная графика. Обработка графической информации
Компьютерная графика. Обработка графической информации Верификация приложений
Верификация приложений Робик. Команды для Робика (3 кл.)
Робик. Команды для Робика (3 кл.) Обработка информации
Обработка информации Компьютерная графика. Векторная и растровая графика
Компьютерная графика. Векторная и растровая графика Новости (НЕ)больших городов. Что такое журналистика?
Новости (НЕ)больших городов. Что такое журналистика? История Windows OC
История Windows OC Презентация по информатике
Презентация по информатике