Содержание
- 2. Outline Quick reminder of the Stack structure. The Unbounded Lock-Free Stack. The Elimination Backoff Stack.
- 3. Concurrent Stack The Stack class is a collection of items (of type T) that provides the
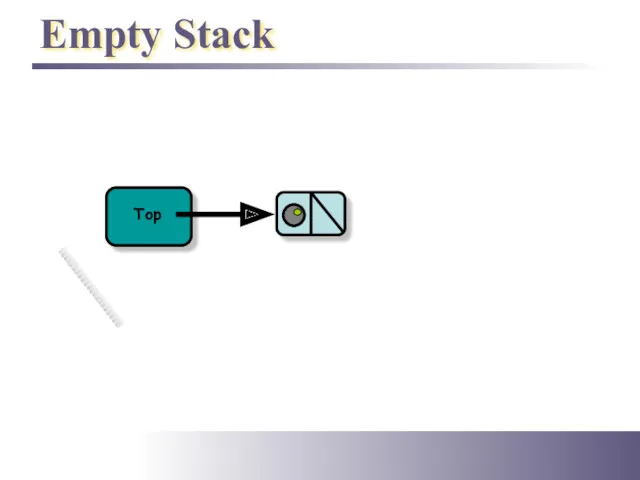
- 4. Empty Stack Top
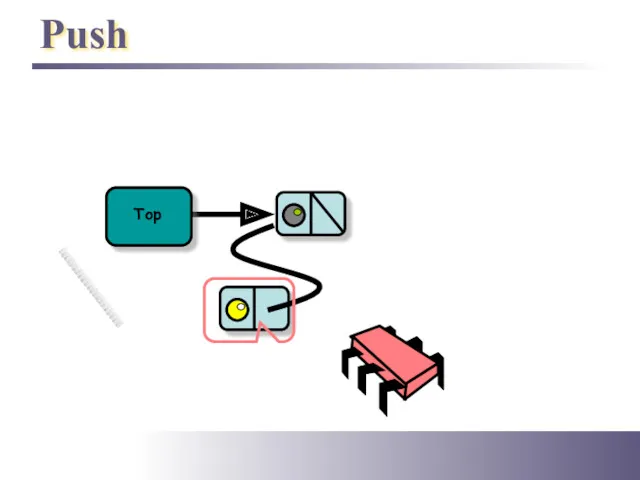
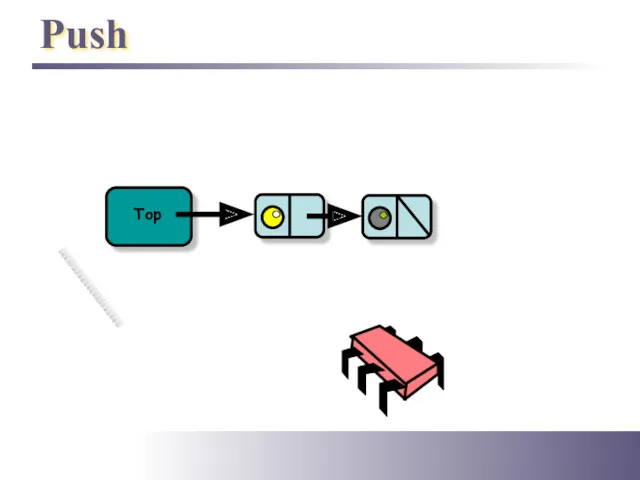
- 5. Push Top
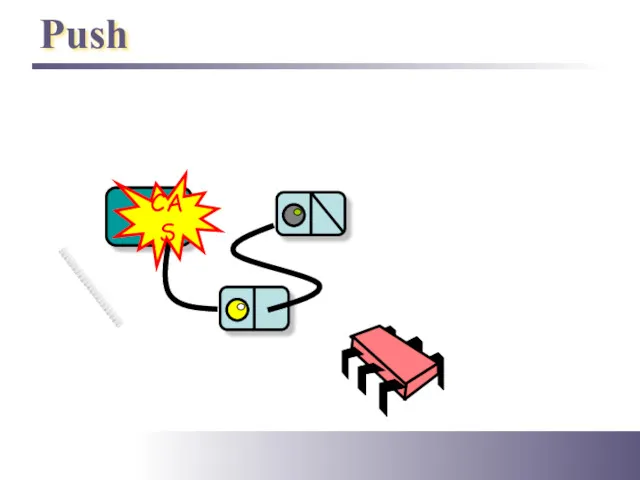
- 6. Push Top CAS
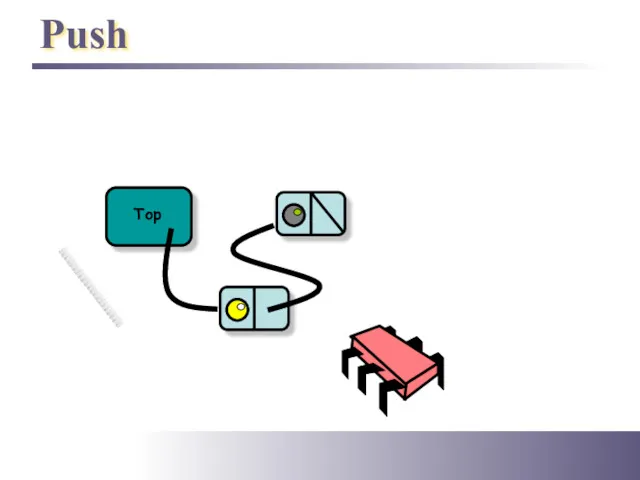
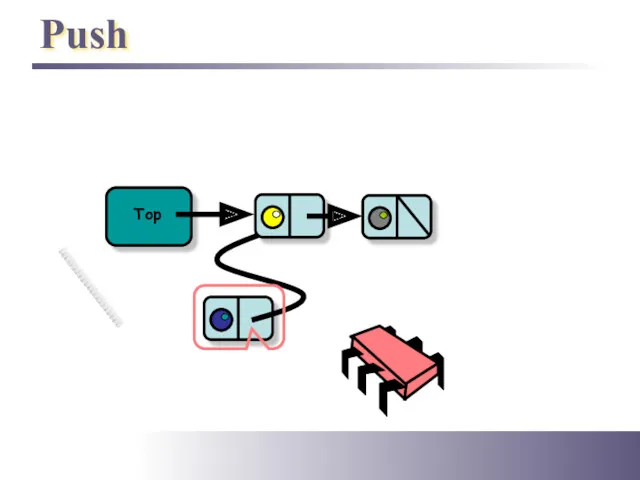
- 7. Push Top
- 8. Push Top
- 9. Push Top
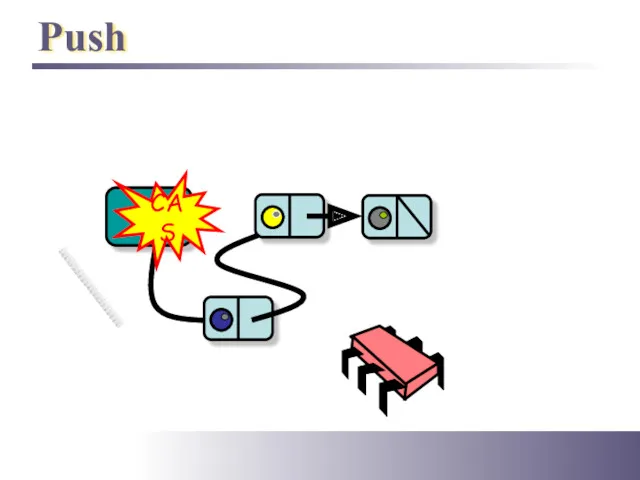
- 10. Push Top CAS
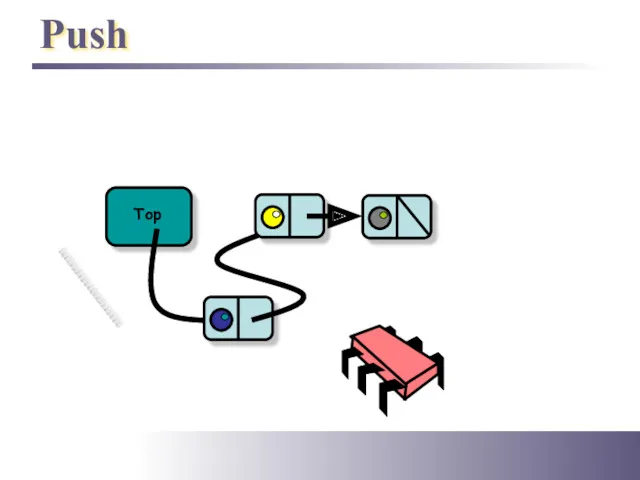
- 11. Push Top
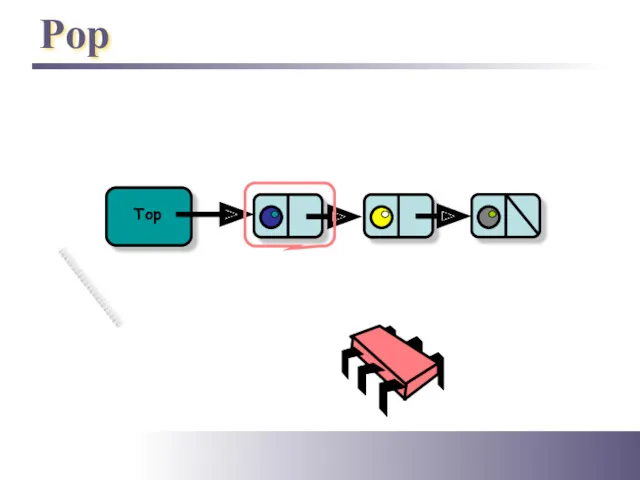
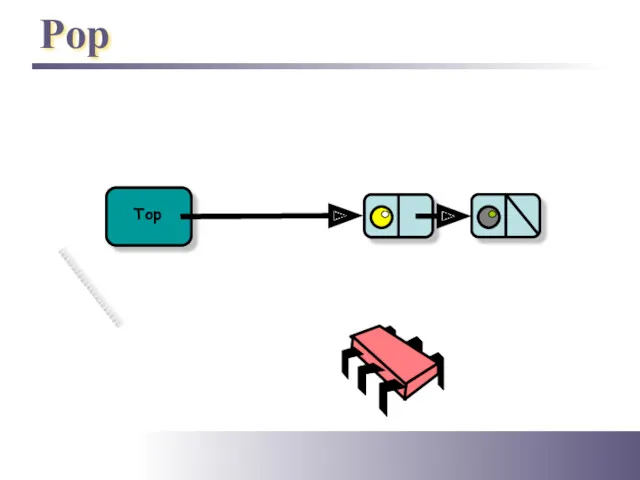
- 12. Pop Top
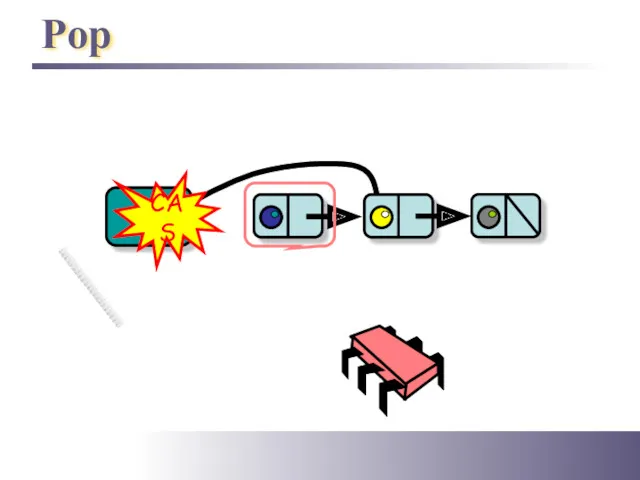
- 13. Pop Top CAS
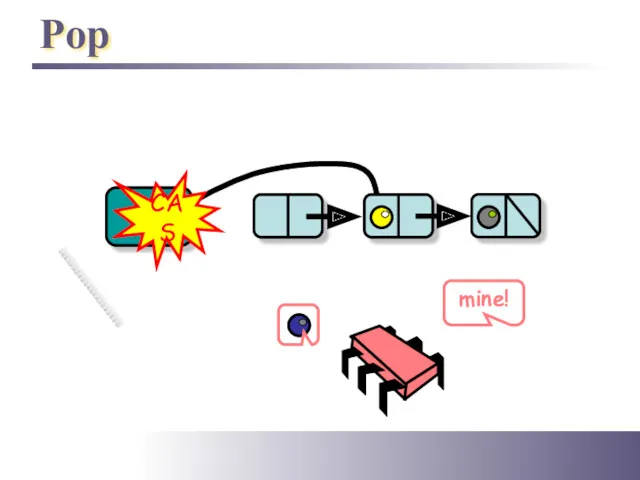
- 14. Pop Top CAS mine!
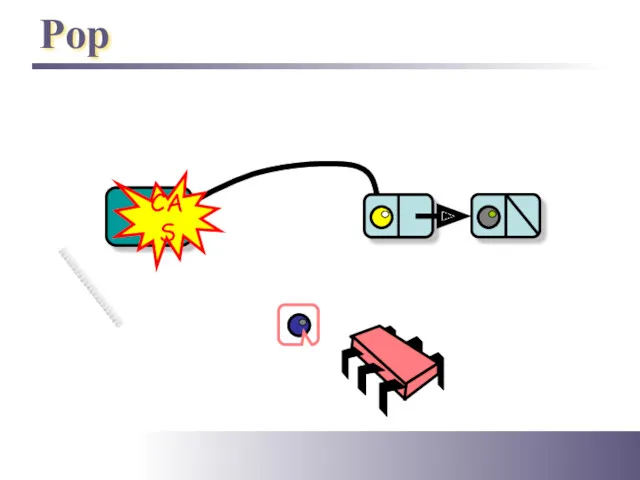
- 15. Pop Top CAS
- 16. Pop Top
- 17. The LockfreeStack class The lock-free stack is a linked list, where the top field points to
- 18. public class LockFreeStack { private AtomicReference top = new AtomicReference(null); static final int MIN_DELAY = …;
- 19. public boolean tryPop() throws EmptyException { Node oldTop = top.get(); if (oldTop == null) { throw
- 20. Lock-free Stack Good No locking Bad huge contention at top No parallelism
- 21. Elimination-Backoff Stack Ways to solve it : exponential backoff (reduces contention but does not solve the
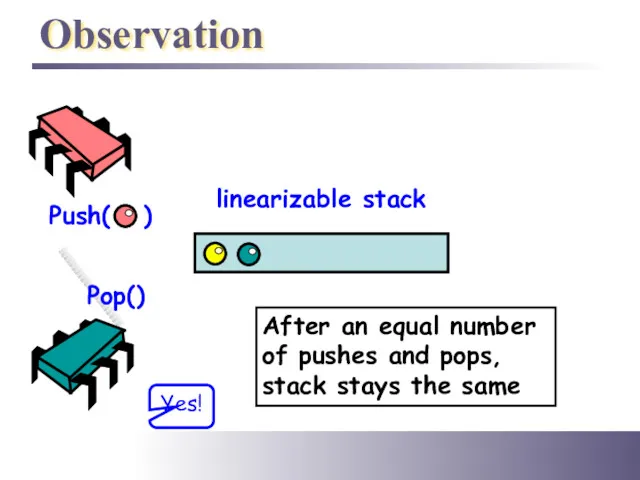
- 22. Observation Push( ) Pop() linearizable stack After an equal number of pushes and pops, stack stays
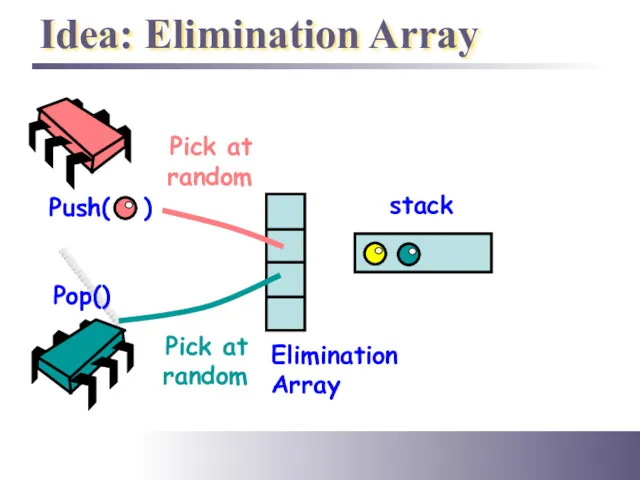
- 23. Idea: Elimination Array Push( ) Pop() stack Pick at random Pick at random Elimination Array
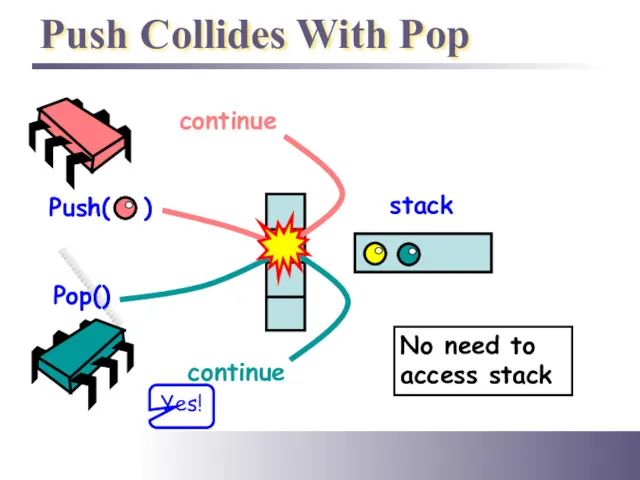
- 24. Push Collides With Pop Push( ) Pop() stack continue No need to access stack Yes!
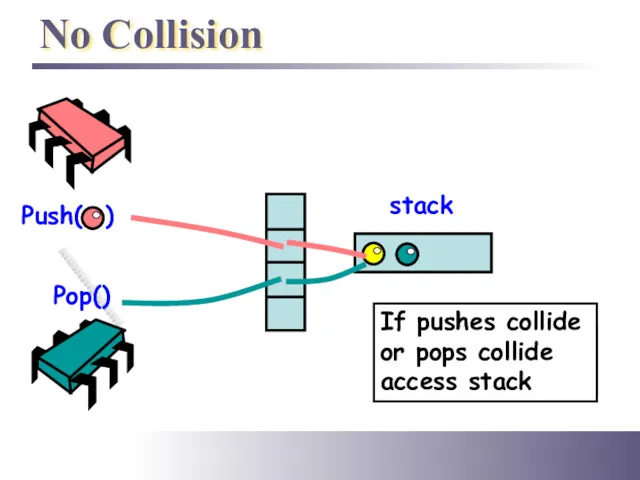
- 25. No Collision Push( ) Pop() stack If no collision, access stack If pushes collide or pops
- 26. Elimination-Backoff Stack A union of the LockFreeStack class with the elimination array Access Lock-free stack, If
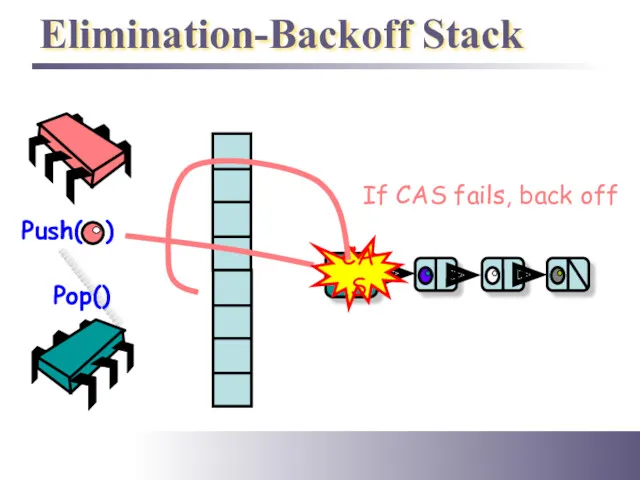
- 27. Elimination-Backoff Stack Push( ) Pop() CAS If CAS fails, back off
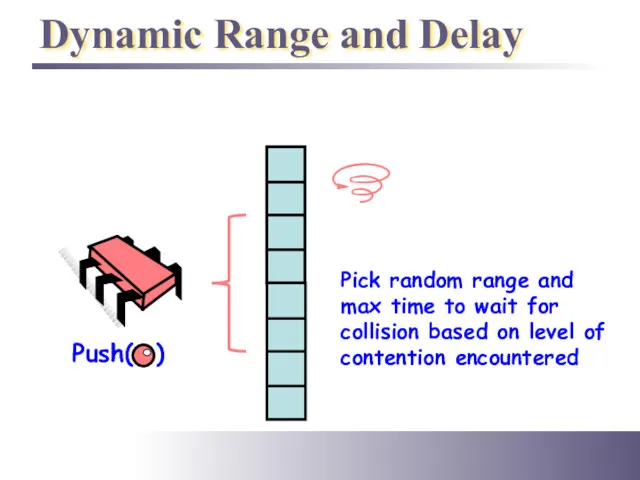
- 28. Dynamic Range and Delay Push( ) Pick random range and max time to wait for collision
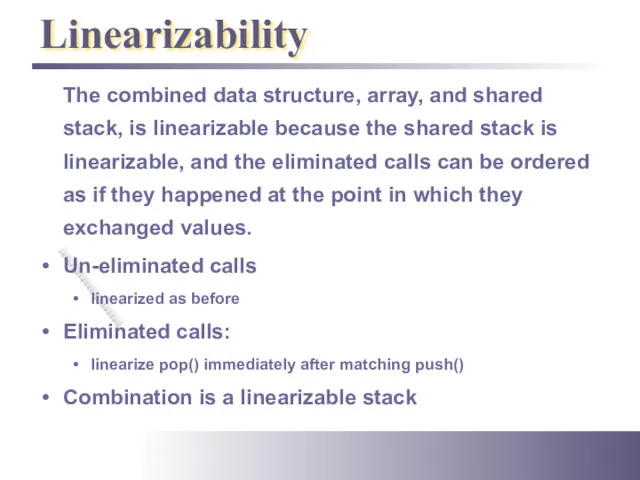
- 29. Linearizability The combined data structure, array, and shared stack, is linearizable because the shared stack is
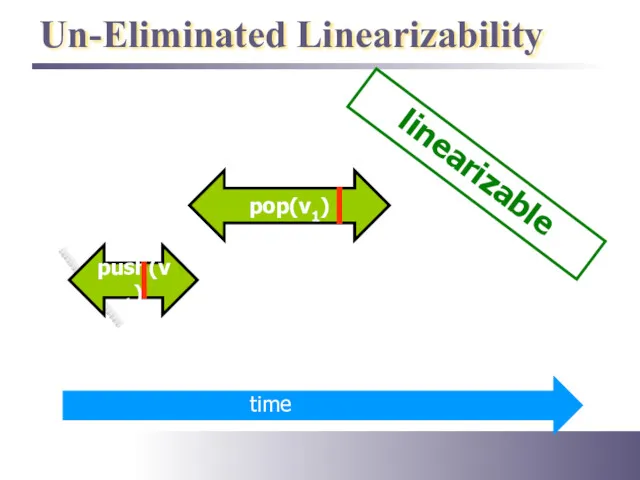
- 30. Un-Eliminated Linearizability push(v1) linearizable pop(v1)
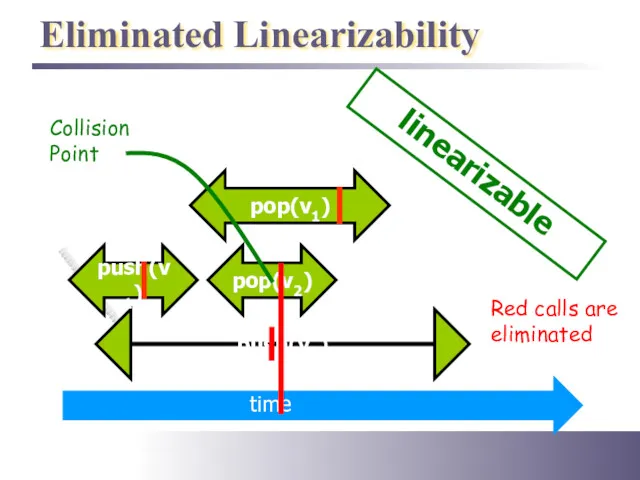
- 31. Eliminated Linearizability pop(v2) push(v1) push(v2) linearizable pop(v2) pop(v1) Red calls are eliminated
- 32. Backoff Has Dual Effect Elimination introduces parallelism Backoff onto array cuts contention on lock-free stack Elimination
- 33. public class EliminationArray { private static final int duration = ...; private static final int timeUnit
- 34. public class Exchanger { AtomicStampedReference slot = new AtomicStampedReference (null, 0); A Lock-Free Exchanger
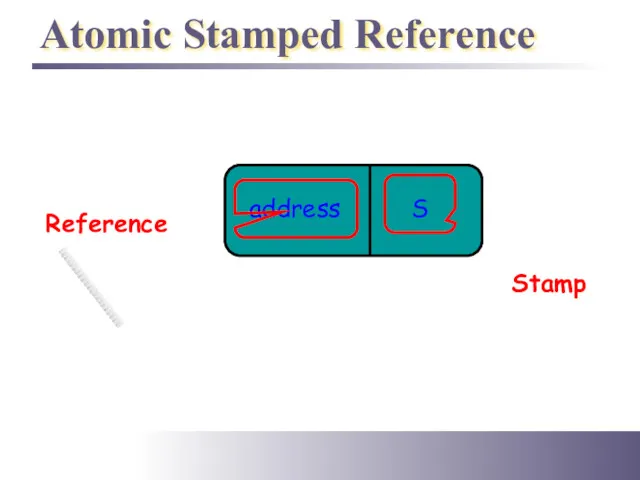
- 35. Atomic Stamped Reference address S Stamp Reference
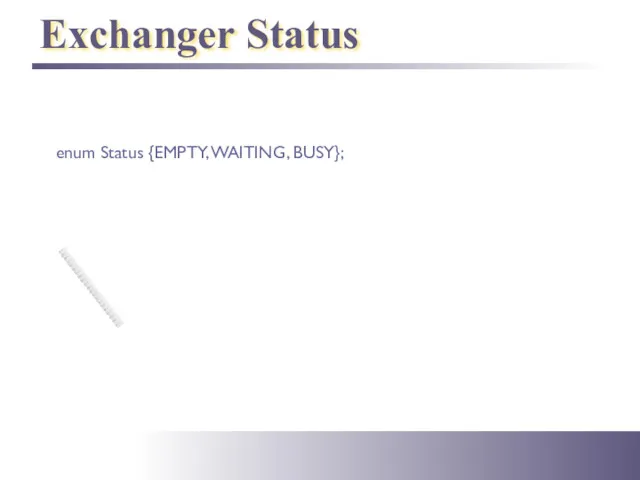
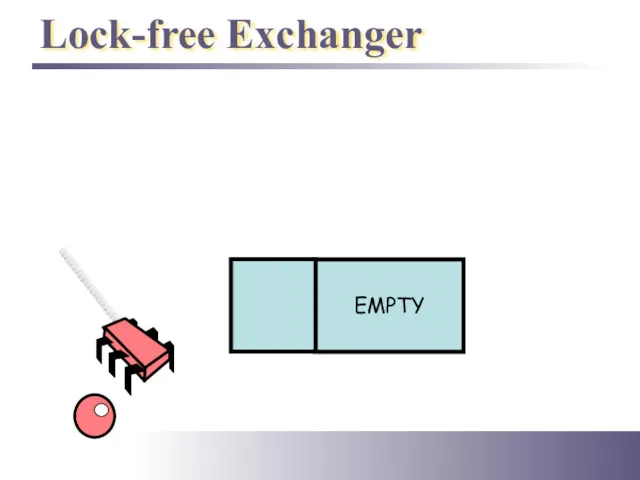
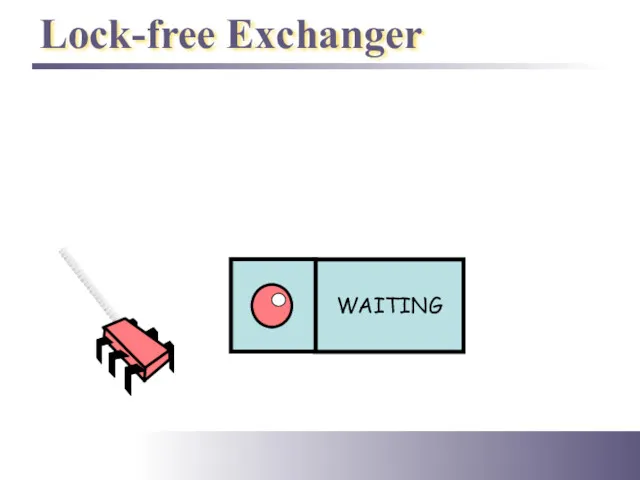
- 36. Exchanger Status enum Status {EMPTY, WAITING, BUSY};
- 37. Lock-free Exchanger
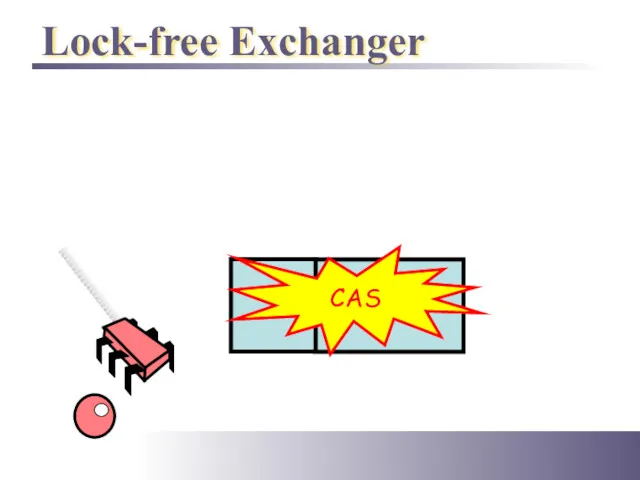
- 38. Lock-free Exchanger CAS
- 39. Lock-free Exchanger
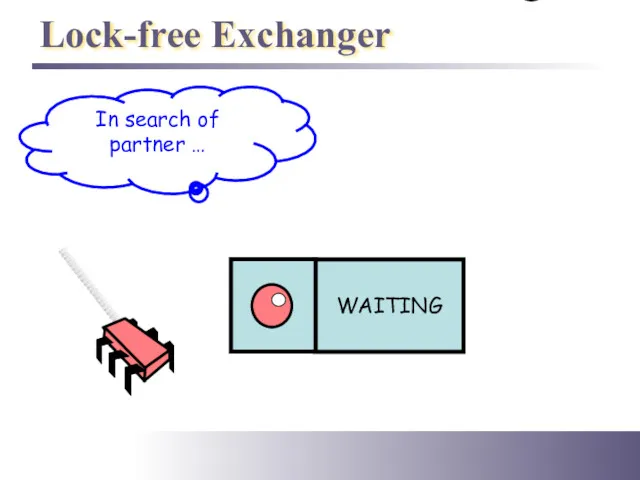
- 40. Lock-free Exchanger In search of partner …
- 41. Lock-free Exchanger Slot Still waiting … Try to exchange item and set state to BUSY CAS
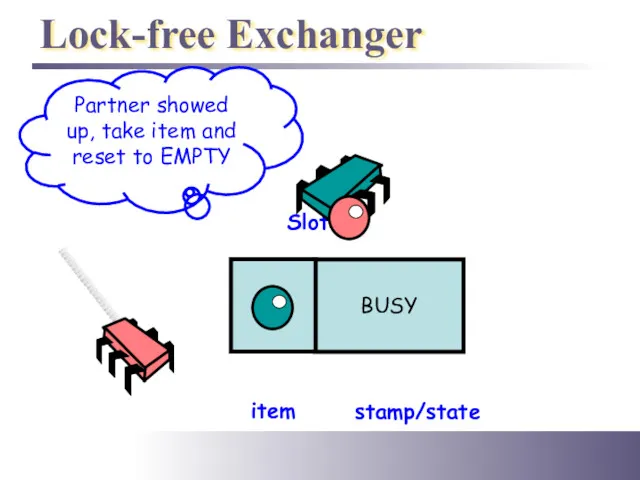
- 42. Lock-free Exchanger Slot Partner showed up, take item and reset to EMPTY item stamp/state
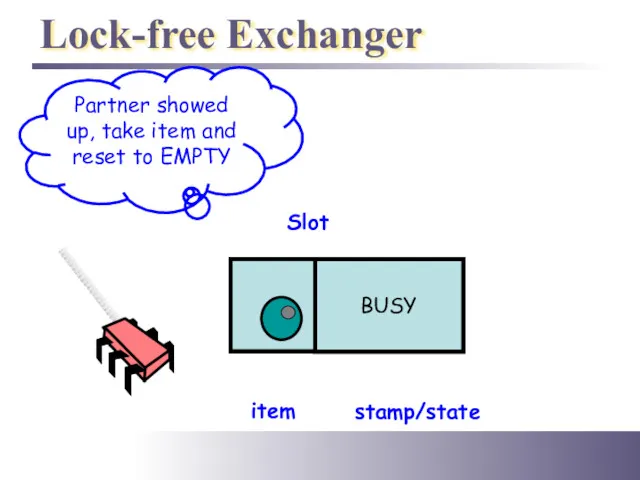
- 43. Lock-free Exchanger Slot item stamp/state Partner showed up, take item and reset to EMPTY
- 44. The Exchanger Slot Exchanger is lock-free Because the only way an exchange can fail is if
- 45. public class EliminationArray { … public T visit(T value, int Range) throws TimeoutException { int slot
- 46. public void push(T value) { ... while (true) { if (tryPush(node)) { return; } else try
- 47. public T pop() { ... while (true) { if (tryPop()) { return returnNode.value; } else try
- 48. Summary Quick reminder of the Stack structure. The Unbounded Lock-Free Stack. The Elimination Backoff Stack.
- 50. Скачать презентацию
















 Целевая аудитория
Целевая аудитория Конвергентная журналистика
Конвергентная журналистика История языков программирования
История языков программирования Типы алгоритмов. Линейные алгоритмы
Типы алгоритмов. Линейные алгоритмы Презентация Профессии, по которым необходимы знания по программе Microsoft Access
Презентация Профессии, по которым необходимы знания по программе Microsoft Access Журналистика. Первые шаги в создании сюжетов
Журналистика. Первые шаги в создании сюжетов Практична робота №4 Анімація тексту
Практична робота №4 Анімація тексту Основы работы с пакетом имитационного моделирования Arena
Основы работы с пакетом имитационного моделирования Arena Введение в проектную деятельность. Лекция 1. Введение. Цифровые порты ввода-вывода
Введение в проектную деятельность. Лекция 1. Введение. Цифровые порты ввода-вывода Сабақтың тақырыбы: Ақпаратты сығу. Ақпаратты қорғау. Вирусқа қарсы программалар
Сабақтың тақырыбы: Ақпаратты сығу. Ақпаратты қорғау. Вирусқа қарсы программалар Проблемы изучения информационных технологий в общеобразовательной и профессиональной школе
Проблемы изучения информационных технологий в общеобразовательной и профессиональной школе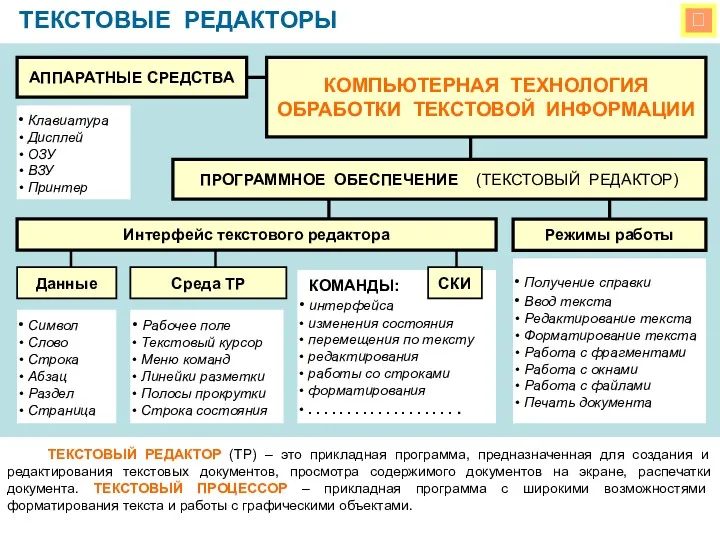 Компьютерная технология обработки текстовой информации
Компьютерная технология обработки текстовой информации Конспект урока информатики на тему Исследование физической модели
Конспект урока информатики на тему Исследование физической модели Платформы HeadHunter
Платформы HeadHunter Конспект урока по теме Информация и знания.
Конспект урока по теме Информация и знания. Java. Inheritance
Java. Inheritance Роль графического дизайнера в мультипликации
Роль графического дизайнера в мультипликации Интернет-портал администрации Масальского сельсовета, Алтайского края
Интернет-портал администрации Масальского сельсовета, Алтайского края Захист інформації в банківських та комерційних системах
Захист інформації в банківських та комерційних системах Компьютерные вирусы, признаки заражения
Компьютерные вирусы, признаки заражения Test automation
Test automation Битва за килобиты
Битва за килобиты Основы интернет-технологий. PL/SQL. (Лекция 10)
Основы интернет-технологий. PL/SQL. (Лекция 10) Особенности электронной почты
Особенности электронной почты Презентация к первому уроку по теме Системы счисления
Презентация к первому уроку по теме Системы счисления Устройство персонального компьютера
Устройство персонального компьютера Компьютерные вирусы и защита от них
Компьютерные вирусы и защита от них Списки (окончание). Графы. Лекция 9, 10
Списки (окончание). Графы. Лекция 9, 10