Содержание
- 2. Intro to Databases Database Management System (DBMS) provides…. … efficient, reliable, convenient, and safe multi-user storage
- 3. Intro to Databases Massive Persistent Safe Multi-user Convenient Efficient Reliable
- 4. Intro to Databases Database applications may be programmed via “frameworks” DBMS may run in conjunction with
- 5. Intro to Databases Key concepts Data model Schema versus data Data definition language (DDL) Data manipulation
- 6. Intro to Databases Key people DBMS implementer Database designer Database application developer Database administrator
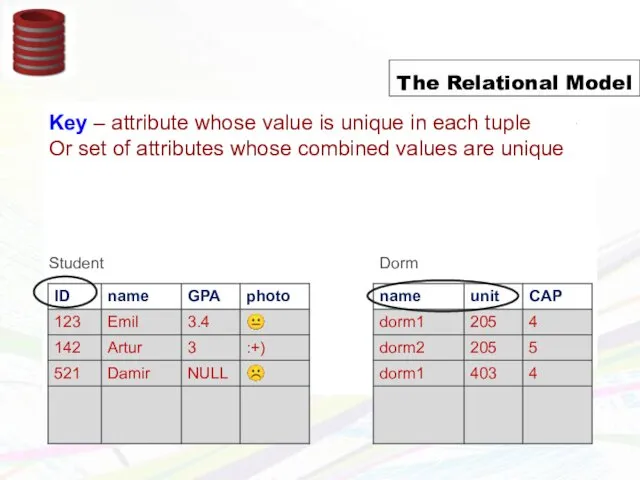
- 7. The Relational Model Used by all major commercial database systems Very simple model Query with high-level
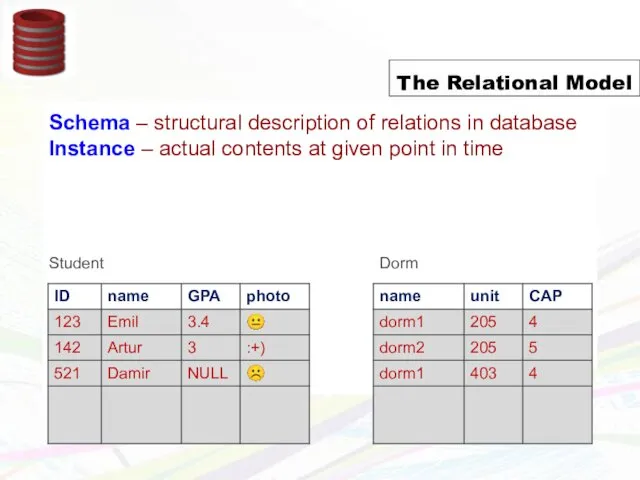
- 8. Schema = structural description of relations in database Instance = actual contents at given point in
- 9. Schema = structural description of relations in database Instance = actual contents at given point in
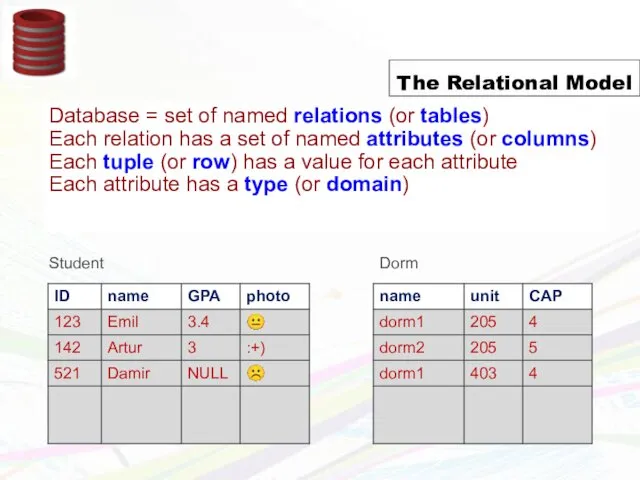
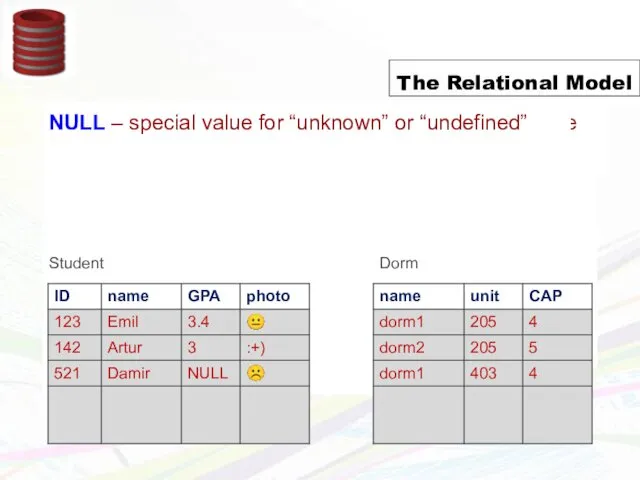
- 10. Schema = structural description of relations in database Instance = actual contents at given point in
- 11. Schema = structural description of relations in database Instance = actual contents at given point in
- 12. Schema = structural description of relations in database Instance = actual contents at given point in
- 13. The Relational Model Creating relations (tables) in SQL Create Table Student(ID, name, GPA, photo) Create Table
- 14. The Relational Model Used by all major commercial database systems Very simple model Query with high-level
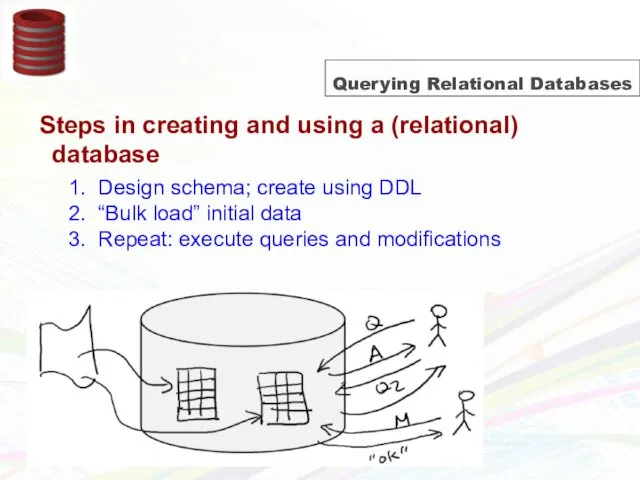
- 15. Querying Relational Databases Steps in creating and using a (relational) database 1. Design schema; create using
- 16. Querying Relational Databases Ad-hoc queries in high-level language All students with GPA > 3.7 applying to
- 17. Querying Relational Databases Queries return relations (“compositional”, “closed”)
- 18. Querying Relational Databases Query Languages Relational Algebra SQL IDs of students with GPA > 3.7 applying
- 19. Assignment 1 Write one page essay in latex [sharelatex.com] that includes the followings: Your name and
- 21. Скачать презентацию











![Assignment 1 Write one page essay in latex [sharelatex.com] that](/_ipx/f_webp&q_80&fit_contain&s_1440x1080/imagesDir/jpg/10450/slide-18.jpg)
 Урок информатики в 6 классе Кодирование растровой графики
Урок информатики в 6 классе Кодирование растровой графики Базовые понятия языка С
Базовые понятия языка С Управление ИТ-инфраструктурой предприятия
Управление ИТ-инфраструктурой предприятия Лазерный гравер на базе Arduino
Лазерный гравер на базе Arduino Медиапланирование как основа деятельности пресс-службы
Медиапланирование как основа деятельности пресс-службы Программы схемотехнического моделирования
Программы схемотехнического моделирования Дистанционное обучение
Дистанционное обучение Цифровые коммуникации в управлении процессами
Цифровые коммуникации в управлении процессами Ты, я и информатика. Викторина. 7 класс
Ты, я и информатика. Викторина. 7 класс Презентация Подключение к Интернету
Презентация Подключение к Интернету Методи та засоби цифрової обробки інформації
Методи та засоби цифрової обробки інформації Вероятностный подход к определению количества информации
Вероятностный подход к определению количества информации Информационные системы и базы данных
Информационные системы и базы данных Компьютерная графика
Компьютерная графика Основные характеристики ЭВМ
Основные характеристики ЭВМ Информатика в условиях реализации ФГОС в основной школе
Информатика в условиях реализации ФГОС в основной школе Computer Security Revision
Computer Security Revision Прикладные информационные технологии: информационные технологии в образовании, технологии автоматизированного проектирования
Прикладные информационные технологии: информационные технологии в образовании, технологии автоматизированного проектирования Создание виртуального пространства для обучения в 3D на базе среды разработки компьютерных игр Unity
Создание виртуального пространства для обучения в 3D на базе среды разработки компьютерных игр Unity Операционные системы реального времени.Ч 2. Лекция 17
Операционные системы реального времени.Ч 2. Лекция 17 Экономическая информатика и информационные технологии
Экономическая информатика и информационные технологии Японский институт международных отношений
Японский институт международных отношений Сетевое взаимодействие библиотекарей Игринского района
Сетевое взаимодействие библиотекарей Игринского района Диаграмма композитной структуры. Диаграмма пакетов. Диаграмма объектов
Диаграмма композитной структуры. Диаграмма пакетов. Диаграмма объектов Інженерія вимог до програмного забезпечення. (Лекція 2.1)
Інженерія вимог до програмного забезпечення. (Лекція 2.1) Умные города на примере Цюриха и Ганьчжоу
Умные города на примере Цюриха и Ганьчжоу Introduction to serialization
Introduction to serialization Автоматизация технологических процессов камнеобрабатывающего и ювелирного производств (главы 4-6)
Автоматизация технологических процессов камнеобрабатывающего и ювелирного производств (главы 4-6)