Содержание
- 2. Contents Operating System & Features Definition & Naming of Linux History of Linux Components of Linux
- 3. Operating System An operating system is a software that communicates with the hardware and allows other
- 4. Definition & Naming of Linux Operating System The Linux open source operating system, or Linux OS,
- 5. History of Linux Operating System UNIX: 1969 Thompson & Ritchie AT&T Bell Labs. Commercial Vendors: Sun,
- 6. Components of Linux System a) Kernel − Kernel is the core part of Linux. It is
- 7. Basic Features of Linux Portable − Portability means software can works on different types of hardware
- 8. Architecture of Linux Operating System
- 9. The architecture of Linux contains some layers : Hardware layer − Hardware consists of all peripheral
- 10. About Kernel It interacts with the actual hardware in machine language. It is the monarch who
- 11. User-Interface of Linux The user interface is either a command line interface (CLI), a graphical user
- 12. CLI view of Linux
- 13. Desktop View of Linux
- 14. Inside view of Linux
- 15. Distribution of Linux Corel Linux Debian GNU/Linux OpenLinux (Caldera) Red Hat Ubuntu TurboLinux
- 16. Hardware requirements to installing Linux CPU Main memory Optical Drive Graphic card Hard Drive Sound
- 17. Software application for Linux OpenOffice: word processing, spreadsheets, drawing Adobe Acrobat Reader Konqueror: The KDE File
- 18. Editors of Linux There are some editors in Linux Vi/Vm editor Gedit editor Nano editor GNU
- 19. Now Comparison of Linux with Other Operating System
- 20. Linux v/s Windows Linux is freely available or online downloads, for windows companies have pay for
- 21. Linux v/s IOS Hardware Requirement: IOS has restrictive hardware requirement, while Linux does not. Customizability: IOS
- 22. Commands of Linux There are some commands in Linux which give direct accessories to the
- 23. Why we use Linux? Costless Stable Reliable Extremely powerful Highly Secure
- 24. Merits and Demerits of Linux It can be easily accessible to the old computers .
- 25. Use of Linux in various fields It is used also used in the department of Defence,
- 26. Commercial use of Linux Operating System Adoption of Linux in production environments, rather than being used
- 28. Скачать презентацию

























 20230921_izmerenie_informatsii
20230921_izmerenie_informatsii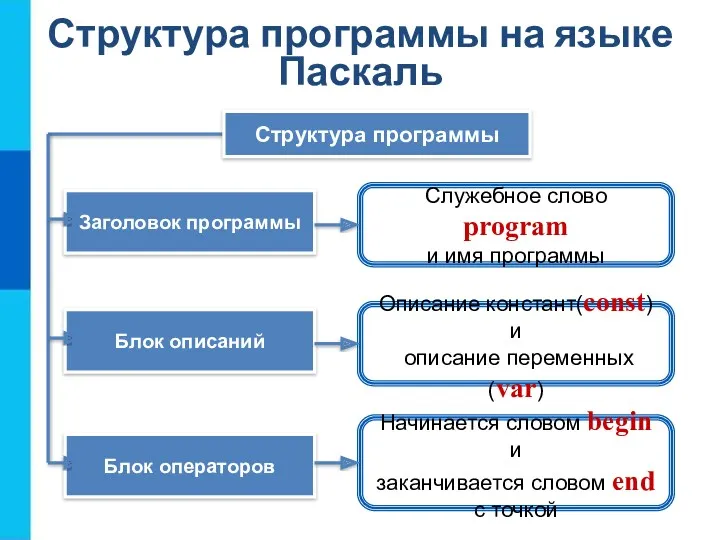 Операторы ввода и вывода данных
Операторы ввода и вывода данных Веб-страницы и веб-сайты (самый крупный) до (самый мелкий).Некоторые тэги имеют атрибуты, которые являются именами свойств и принимают определенные значения.ALIGN =“ center” – тип выравнивания заголовкаС помощью тега FONT можно зад
Веб-страницы и веб-сайты (самый крупный) до (самый мелкий).Некоторые тэги имеют атрибуты, которые являются именами свойств и принимают определенные значения.ALIGN =“ center” – тип выравнивания заголовкаС помощью тега FONT можно зад Размещение запросов в Service Central
Размещение запросов в Service Central Концепция прикладного решения 1С:ERP
Концепция прикладного решения 1С:ERP Понятие алгоритма, его свойства, способы описания и виды
Понятие алгоритма, его свойства, способы описания и виды Программирование передачи информации между компьютерами по сети. Клиент-серверные приложения
Программирование передачи информации между компьютерами по сети. Клиент-серверные приложения How to Activate AutoDesk any product for free
How to Activate AutoDesk any product for free Информация и знания. Восприятие информации человеком
Информация и знания. Восприятие информации человеком Электронное приложение к учебнику информатики Юным умникам и умницам Холодовой, 1 класс Пояснительная записка
Электронное приложение к учебнику информатики Юным умникам и умницам Холодовой, 1 класс Пояснительная записка Планировщик. Планирование. Алгоритмы планирования в операционной системе
Планировщик. Планирование. Алгоритмы планирования в операционной системе Электронные ресурсы ЦГАСО. Электронные ресурсы в помощь изучения семейной истории
Электронные ресурсы ЦГАСО. Электронные ресурсы в помощь изучения семейной истории Активизация мыслительной деятельности воспитанников на уроках физики с использованием ИКТ
Активизация мыслительной деятельности воспитанников на уроках физики с использованием ИКТ The systems development life cycle
The systems development life cycle Модель процесса управления
Модель процесса управления Сектор удаленного обслуживания центральной городской библиотеки
Сектор удаленного обслуживания центральной городской библиотеки Презентация к уроку Ссылки в электронных таблицах.
Презентация к уроку Ссылки в электронных таблицах. Понятие информационная безопасность. Понятие информационная безопасность
Понятие информационная безопасность. Понятие информационная безопасность Парадигмы программирования. Концепции ООП
Парадигмы программирования. Концепции ООП Логические функции
Логические функции Разработка настольной игры
Разработка настольной игры Пресс-служба в органах власти
Пресс-служба в органах власти Графический дизайнер
Графический дизайнер Человек и информация
Человек и информация Бесплатный вебинар. Начинаем учить испанский
Бесплатный вебинар. Начинаем учить испанский Разработка и проектирование интернет магазина в розничной торговле
Разработка и проектирование интернет магазина в розничной торговле Компьютеры будущего (9 класс)
Компьютеры будущего (9 класс) Кодирование звуковой информации
Кодирование звуковой информации