Содержание
- 2. POCKET COMPUTERS LAPTOP COMPUTERS DESKTOP COMPUTER
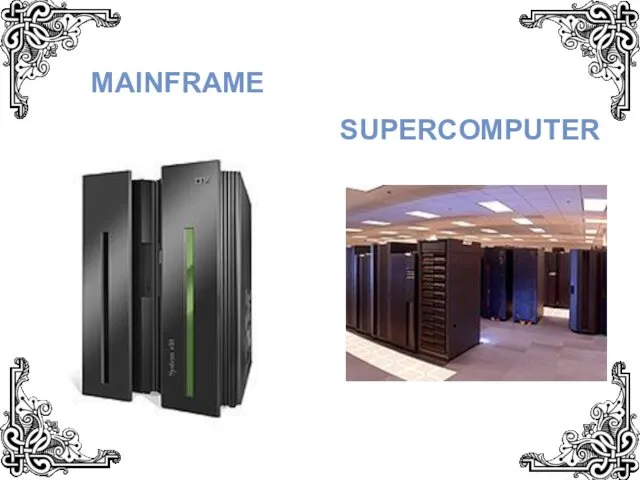
- 3. SUPERCOMPUTER MAINFRAME
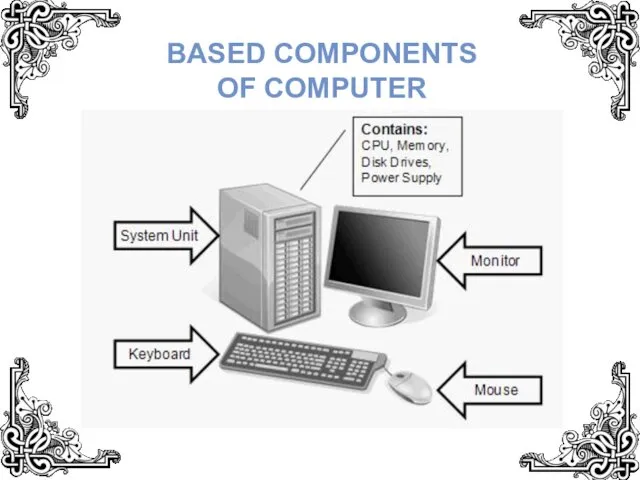
- 4. BASED COMPONENTS OF COMPUTER
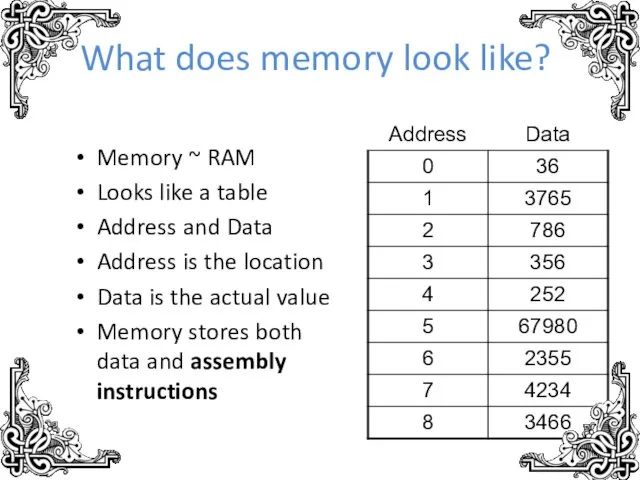
- 6. What does memory look like? Memory ~ RAM Looks like a table Address and Data Address
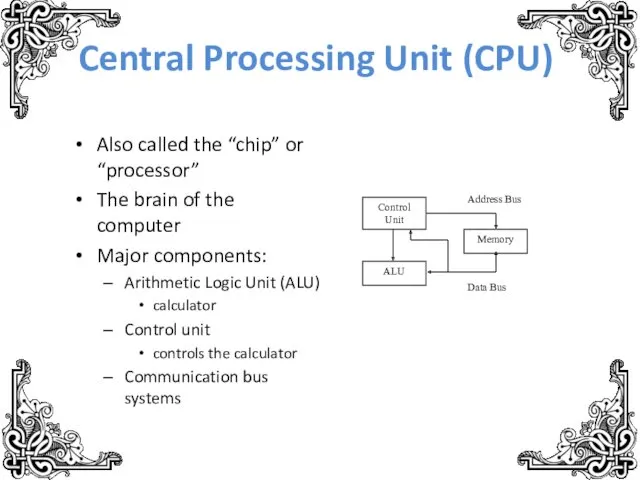
- 7. Central Processing Unit (CPU) Also called the “chip” or “processor” The brain of the computer Major
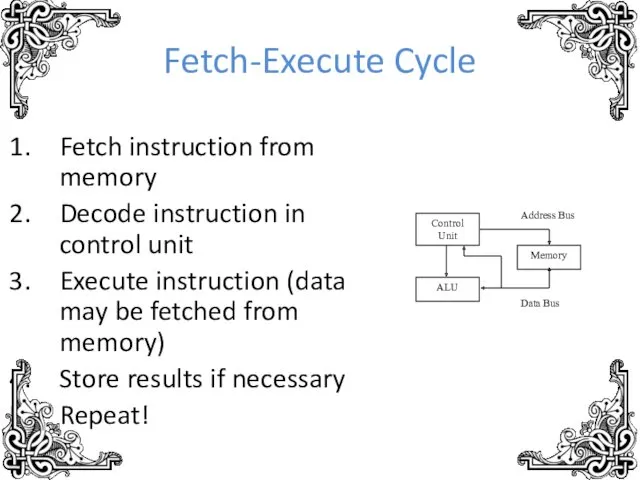
- 8. Fetch-Execute Cycle Fetch instruction from memory Decode instruction in control unit Execute instruction (data may be
- 9. Registers Temporary storage containers used inside the CPU Extremely fast Fixed size, usually multiples of 8-bits
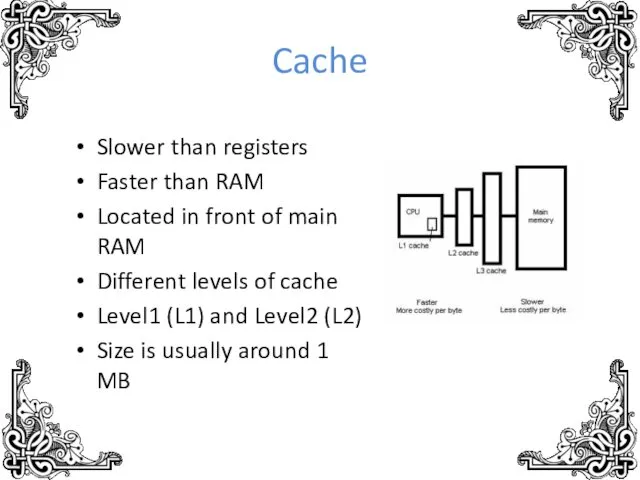
- 10. Cache Slower than registers Faster than RAM Located in front of main RAM Different levels of
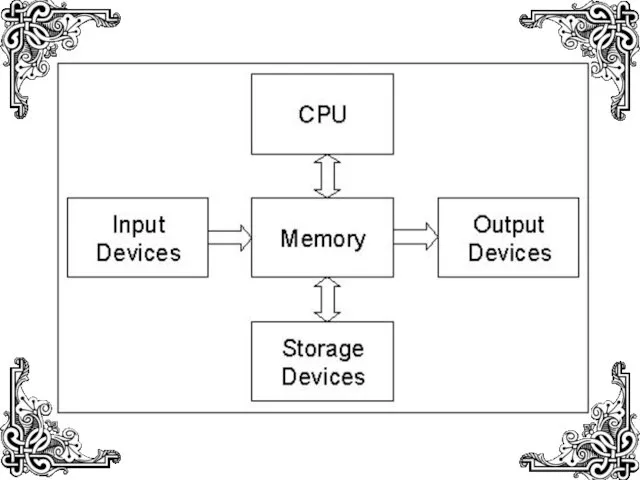
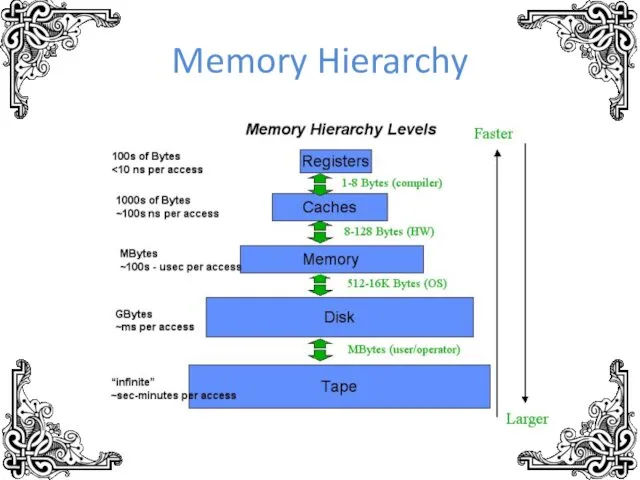
- 11. Memory Hierarchy
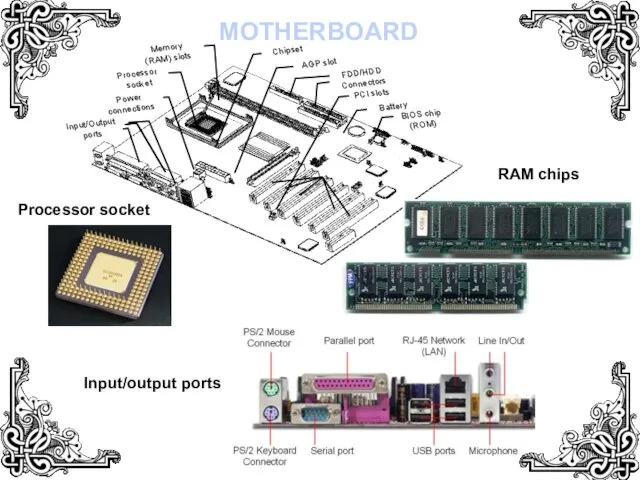
- 13. MOTHERBOARD Processor socket RAM chips Input/output ports
- 14. EXTERNAL MEMORY
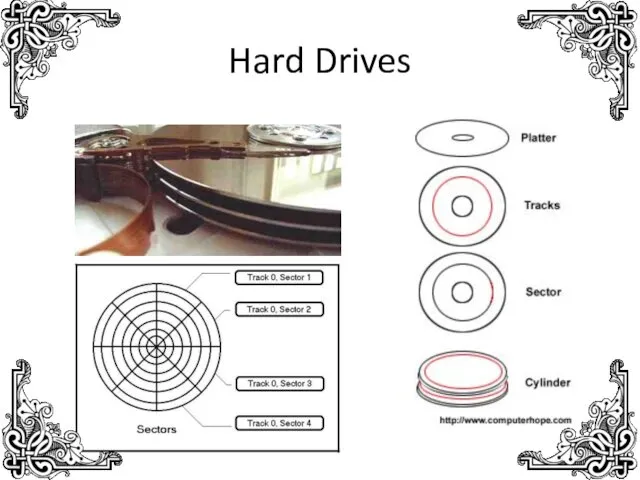
- 15. Hard Drives
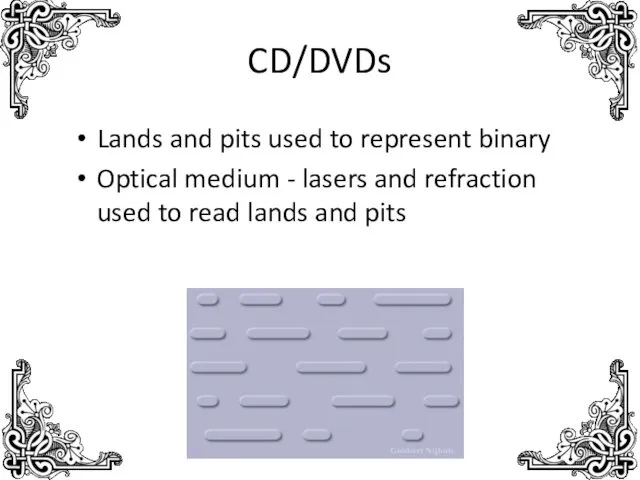
- 16. CD/DVDs Lands and pits used to represent binary Optical medium - lasers and refraction used to
- 17. INPUT
- 18. Output Devices
- 20. Скачать презентацию






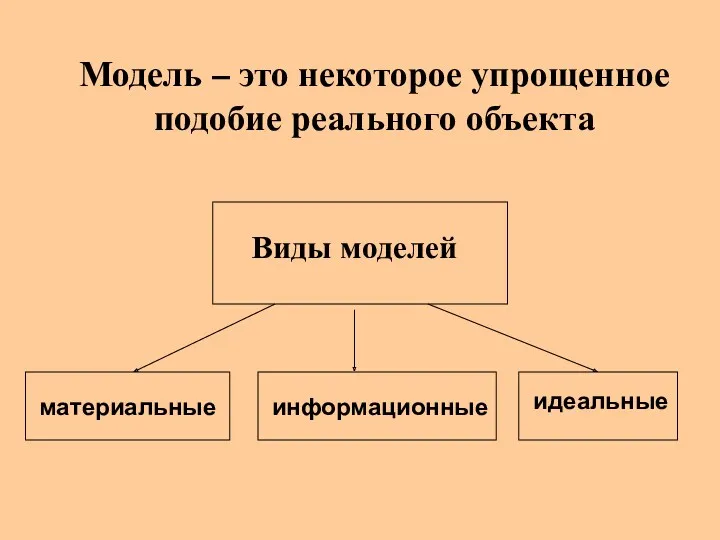 Модель – это некоторое упрощенное подобие реального объекта
Модель – это некоторое упрощенное подобие реального объекта Работа с файлами в Python
Работа с файлами в Python Web-сайт – гиперструктура данных технология использования и разработки
Web-сайт – гиперструктура данных технология использования и разработки Безопасность в Интернете
Безопасность в Интернете Структура УП и ее формат
Структура УП и ее формат Программа, как модель предметной области
Программа, как модель предметной области Государственная информационная система жилищно-коммунального хозяйства
Государственная информационная система жилищно-коммунального хозяйства Робота із бінарними файлами
Робота із бінарними файлами Сети связи и ПД. Основные понятия
Сети связи и ПД. Основные понятия Что такое алгоритм. Последовательность действий
Что такое алгоритм. Последовательность действий Школьный кошелек. Оплата питания в школе без проблем
Школьный кошелек. Оплата питания в школе без проблем Программирование на Java. Объектная модель Java. (Лекция 3.1)
Программирование на Java. Объектная модель Java. (Лекция 3.1) Типы алгоритмов
Типы алгоритмов Сетикет. Правила поведения в сети интернета
Сетикет. Правила поведения в сети интернета Операционные системы. Взаимодействие между процессами. (Лекция 9)
Операционные системы. Взаимодействие между процессами. (Лекция 9) Просмотр слайдов
Просмотр слайдов Безопасная связь и мобильные рабочие места Samsung
Безопасная связь и мобильные рабочие места Samsung Создание школьных сайтов
Создание школьных сайтов Интеллектуальная игра для обучающихся 8-10 лет
Интеллектуальная игра для обучающихся 8-10 лет Функции. Модульный стиль программирования
Функции. Модульный стиль программирования Разработка и использование стиля. Форматирование символов, абзацев и заголовков Word 2007
Разработка и использование стиля. Форматирование символов, абзацев и заголовков Word 2007 Корпоративные информационные системы (КИС)
Корпоративные информационные системы (КИС) Системы интеллектуального анализа данных
Системы интеллектуального анализа данных Jizzax viloyat xalq ta’limi xodimlarini qayta tayyorlash va ularning malakasini oshirish hududiy markazi tomonidan tayyorlangan
Jizzax viloyat xalq ta’limi xodimlarini qayta tayyorlash va ularning malakasini oshirish hududiy markazi tomonidan tayyorlangan Программирование на Python. Создание telegram-бота
Программирование на Python. Создание telegram-бота The Python Programming Language
The Python Programming Language Линейные структуры данных. Лекция 2
Линейные структуры данных. Лекция 2 Электронный учебник по информатике
Электронный учебник по информатике