9TH Day:
RN: 50 --> NO ACCIDENT.
10TH Day:
RN: 51 --> NO
ACCIDENT.
11TH Day:
RN: 09 --> ACCIDENT.
RN: 31 --> Number of accidents = 4 accidents
?1st Accident:
RN: 12 --> Amount of money paid= 50 L.E
?2nd Accident:
RN: 94 --> Amount of money paid= 200 L.E
?3rd Accident:
RN: 96 --> Amount of money paid= 200 L.E
?4th Accident:
RN: 97 --> Amount of money paid= 200 L.E
Then the total paid in this day = 50 + 200 + 200 + 200 = 650 L.E
12th Day:
RN: 77 --> NO ACCIDENT
Based on the above simulation :- The minimum money the owner must have to cover the penalties occurred per day (The maximum paid money in all days) = 650 L.E
Solution 5: The owner of car renting company
Use the following R.N:
44 99 15 97 21 47 80 28 87 13 33 42 84 27 64
59 33 84 00 10 50 51 09 31 12 94 96 97 77
















 Встроенные функции и их использование
Встроенные функции и их использование Все о лого-мирах
Все о лого-мирах Somos Una Piña by Slidesgo. Шаблон
Somos Una Piña by Slidesgo. Шаблон Презентация-тест по теме Действия с информацией
Презентация-тест по теме Действия с информацией информационные процессы
информационные процессы Microsoft Office Word, Excel, Access, PowerPoint, Internet Explorer
Microsoft Office Word, Excel, Access, PowerPoint, Internet Explorer Особливості використання класів
Особливості використання класів Основы инстаграм
Основы инстаграм Концепція необмеженого паралелізму. Лекція №7
Концепція необмеженого паралелізму. Лекція №7 Multimedia technologies
Multimedia technologies Основы WEB технологий
Основы WEB технологий Устройство персонального компьютера
Устройство персонального компьютера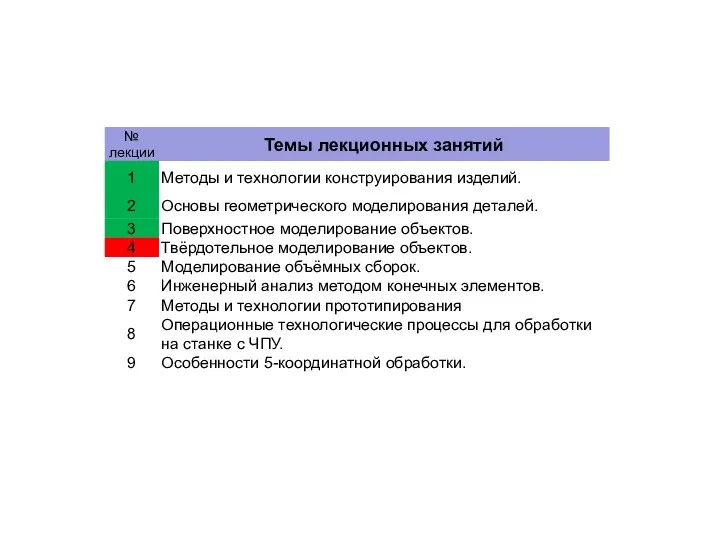 Методы и технологии конструирования изделий. Твёрдотельное моделирование объектов. (Лекция 4)
Методы и технологии конструирования изделий. Твёрдотельное моделирование объектов. (Лекция 4) Полиморфизм
Полиморфизм Строковые функции в Visual Basic
Строковые функции в Visual Basic 1С управление торговлей как средство автоматизации торгово-расчетных операций
1С управление торговлей как средство автоматизации торгово-расчетных операций Компьютер – универсальная машина для работы с информацией
Компьютер – универсальная машина для работы с информацией Cmpe 466 computer graphics. A survey of graphics applications. (Chapter 1)
Cmpe 466 computer graphics. A survey of graphics applications. (Chapter 1) Виды информационно-поисковых тезаурусов
Виды информационно-поисковых тезаурусов Библиотеки и фреймворки
Библиотеки и фреймворки Визуальное программирование
Визуальное программирование Основы компьютерного черчения в системе КОМПАС
Основы компьютерного черчения в системе КОМПАС Методы визуализации
Методы визуализации Ғаламтор- өміріміздің ажырамас бөлігі
Ғаламтор- өміріміздің ажырамас бөлігі Создание форм и отчетов с помощью мастера и конструктора
Создание форм и отчетов с помощью мастера и конструктора How did we make the biggest game on Defold in 1 year
How did we make the biggest game on Defold in 1 year Ticton - esports info at the speed of thought
Ticton - esports info at the speed of thought Классификация моделей
Классификация моделей