Содержание
- 2. Include Files The include (or require) statement takes all the text/code/markup that exists in the specified
- 3. Example of include Welcome to my home page! Some text. Some more text.
- 4. PHP include vs. require The require statement is also used to include a file into the
- 5. File and file handleing Web Technology- IITU
- 6. Simple syntax to read file in php echo readfile("webdictionary.txt"); ?>
- 7. File Open/Read/Close $myfile = fopen("webdictionary.txt", "r") or die("Unable to open file!"); echo fread($myfile,filesize("webdictionary.txt")); fclose($myfile); ?> r
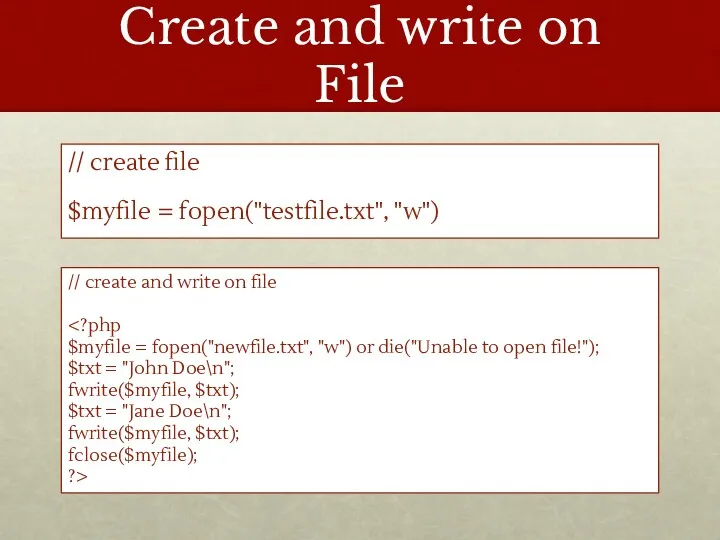
- 8. Create and write on File // create file $myfile = fopen("testfile.txt", "w") // create and write
- 9. Forms and Files Web Technology- IITU
- 10. Create The HTML Form Select image to upload: Web Technology- IITU The type="file" attribute of the
- 11. Create The Upload File PHP Script $target_dir = "uploads/"; $target_file = $target_dir . basename($_FILES["fileToUpload"]["name"]); $uploadOk =
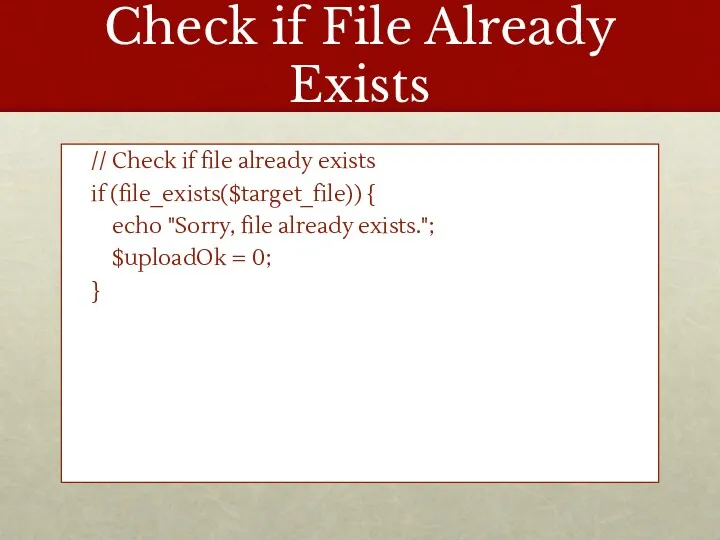
- 12. Check if File Already Exists // Check if file already exists if (file_exists($target_file)) { echo "Sorry,
- 13. Limit File Size // Check file size if ($_FILES["fileToUpload"]["size"] > 500000) { echo "Sorry, your file
- 14. Limit File Type // Allow certain file formats if($imageFileType != "jpg" && $imageFileType != "png" &&
- 15. Complete Upload File PHP Script (part 1) $target_dir = "uploads/"; $target_file = $target_dir . basename($_FILES["fileToUpload"]["name"]); $uploadOk
- 16. Complete Upload File PHP Script (part 2) // Check if file already exists if (file_exists($target_file)) {
- 17. Complete Upload File PHP Script (part 3) // Check if $uploadOk is set to 0 by
- 18. PHP Images from Folder
- 19. Glob () The glob() function returns an array of filenames or directories matching a specified pattern.
- 20. Count () The count() function returns the number of elements in an array. $cars=array("Volvo","BMW","Toyota"); echo count($cars);
- 21. Opendir () & Readdir () Opendir is function to open a directory Readdir is function to
- 22. PHP pathinfo() Function The pathinfo() function returns an array that contains information about a path. The
- 23. in_array () It searches for a value in an array $people = array("Peter", "Joe", "Glenn", "Cleveland");
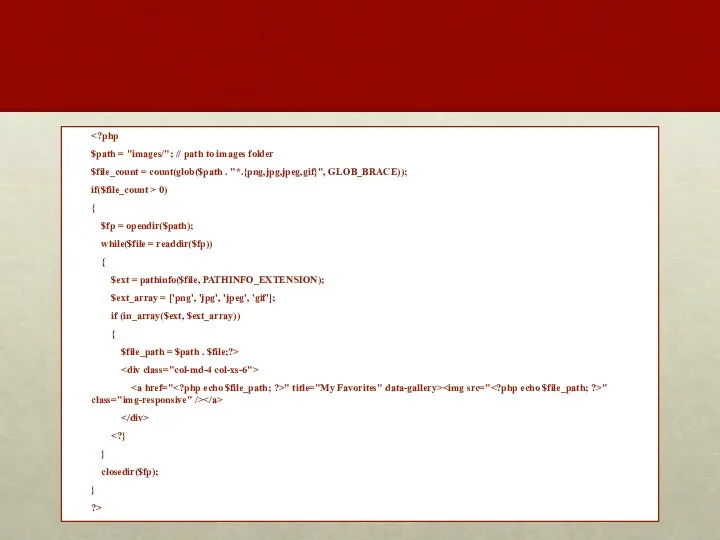
- 24. $path = "images/"; // path to images folder $file_count = count(glob($path . "*.{png,jpg,jpeg,gif}", GLOB_BRACE)); if($file_count >
- 25. PHP Error Handling
- 26. Error Handling When creating scripts and web applications, error handling is an important part. If your
- 27. Example of Error Handling $file=fopen("welcome.txt","r"); ?> Warning: fopen(welcome.txt) [function.fopen]: failed to open stream: No such file
- 28. Exception handling Exception handling is used to change the normal flow of the code execution if
- 29. Exception handling example When an exception is thrown, the code following it will not be executed,
- 31. Скачать презентацию









![Limit File Size // Check file size if ($_FILES["fileToUpload"]["size"] >](/_ipx/f_webp&q_80&fit_contain&s_1440x1080/imagesDir/jpg/249414/slide-12.jpg)












![Example of Error Handling $file=fopen("welcome.txt","r"); ?> Warning: fopen(welcome.txt) [function.fopen]: failed](/_ipx/f_webp&q_80&fit_contain&s_1440x1080/imagesDir/jpg/249414/slide-26.jpg)


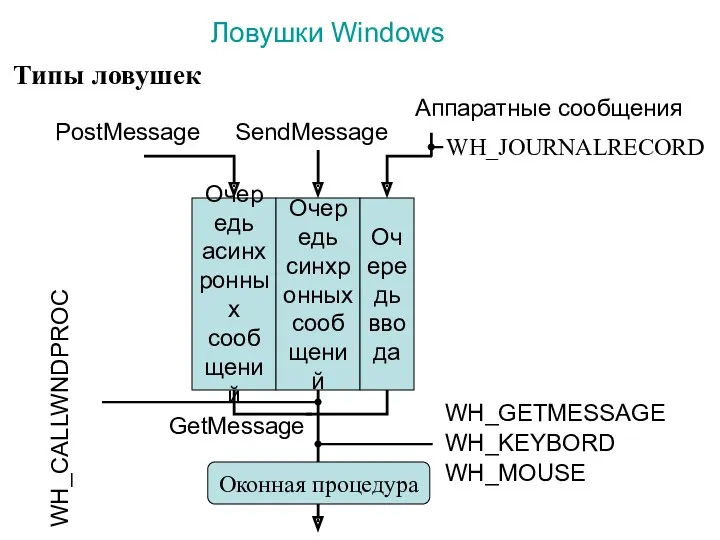 Ловушки Windows. Типы ловушек. (Лекция 14)
Ловушки Windows. Типы ловушек. (Лекция 14) Программирование на Java. Collections Framework - фреймверк коллекций объектов. (Лекция 7.1)
Программирование на Java. Collections Framework - фреймверк коллекций объектов. (Лекция 7.1) Наше время! Ноябрь-декабрь, 2019. Выпуск № 2
Наше время! Ноябрь-декабрь, 2019. Выпуск № 2 Робототехніка на основі Arduino
Робототехніка на основі Arduino Динамические модели в среде OO Impress
Динамические модели в среде OO Impress Информация. Виды и свойства
Информация. Виды и свойства Использование MS Office для автоматизации профессиональной деятельности. Microsoft Word. Microsoft Office XP. ч.2
Использование MS Office для автоматизации профессиональной деятельности. Microsoft Word. Microsoft Office XP. ч.2 Usability testing
Usability testing Универсальная энциклопедия в сети Интернет. Википедия
Универсальная энциклопедия в сети Интернет. Википедия Лекция 7. Collections [.NET Framework]
Лекция 7. Collections [.NET Framework] Хакеризм. Понятие хакера
Хакеризм. Понятие хакера Порядок регистрации на Портале
Порядок регистрации на Портале контейнеры STL
контейнеры STL Счастливый случай. Игра по информатике
Счастливый случай. Игра по информатике Представление символьной информации и десятичных чисел в ЭВМ
Представление символьной информации и десятичных чисел в ЭВМ Linux ОЖ CD және DVD көшіру
Linux ОЖ CD және DVD көшіру Применение дистанционных технологий при обучении детей с ОВЗ
Применение дистанционных технологий при обучении детей с ОВЗ Тестирование программного обеспечения. Цели и задачи тестирования
Тестирование программного обеспечения. Цели и задачи тестирования Основы теории компьютерной безопасности
Основы теории компьютерной безопасности Зачем человек приходит в этот мир?
Зачем человек приходит в этот мир? Этапы решения задач на компьютере. Языки программирования
Этапы решения задач на компьютере. Языки программирования Цепочечные команды. Обработка строк
Цепочечные команды. Обработка строк Электронная проходная. Электронная столовая
Электронная проходная. Электронная столовая Путешествие по стране Интернетии
Путешествие по стране Интернетии Моделирование информационных потоков. Диаграмма потоков данных (data fow diagram, DFD)
Моделирование информационных потоков. Диаграмма потоков данных (data fow diagram, DFD) Портфолио
Портфолио Основные принципы построения операционных систем
Основные принципы построения операционных систем Хабар 24. Главный информационный
Хабар 24. Главный информационный