- Главная
- Информатика
- SDLC and Waterfall

Содержание
- 3. SOFTWARE DEVELOPMENT LIFECYCLE (SDLC) is a systematic process for building software that ensures the quality and
- 4. Why SLDS Here, are prime reasons why SDLC is important for developing a software system. It
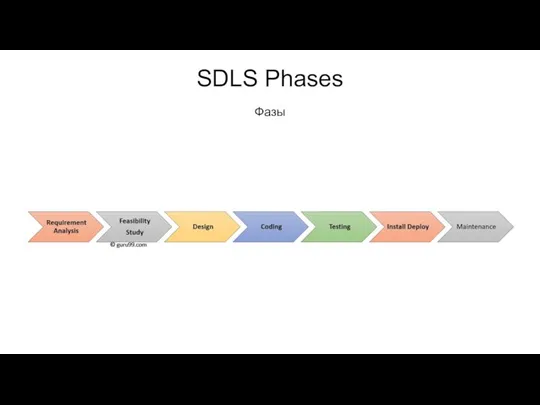
- 5. SDLS Phases Фазы
- 6. SDLS Phases Фазы Phase 1: Requirement collection and analysis: The requirement is the first stage in
- 7. Phase 2: Feasibility study: Once the requirement analysis phase is completed the next step is to
- 8. Phase 3: Design: In this third phase, the system and software design documents are prepared as
- 9. Phase 4: Coding: Once the system design phase is over, the next phase is coding. In
- 10. Phase 5: Testing: Once the software is complete, and it is deployed in the testing environment.
- 11. Phase 6: Installation/Deployment: Once the software testing phase is over and no bugs or errors left
- 12. Phase 7: Maintenance: Once the system is deployed, and customers start using the developed system, following
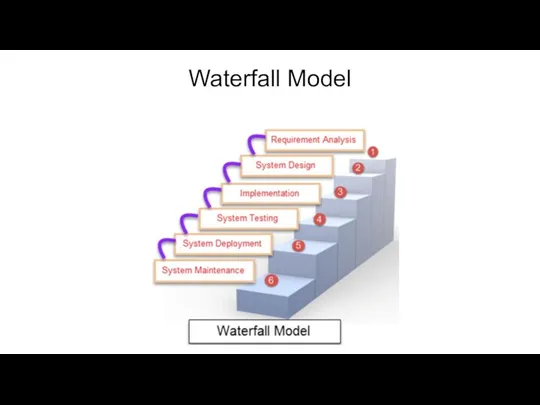
- 13. What is The Waterfall Model? What is The Waterfall Model? WATERFALL MODEL is a sequential model
- 14. Waterfall Model
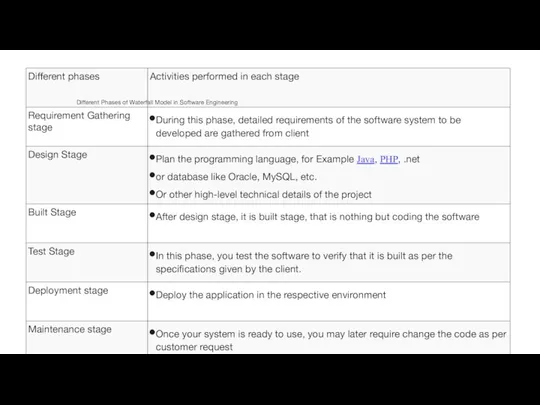
- 15. Different Phases of Waterfall Model in Software Engineering
- 16. When to use SDLC Waterfall Model Waterfall model can be used when Requirements are not changing
- 17. Advantages and Disadvantages of Waterfall-Model
- 18. Verification in Software Testing Verification in Software Testing is a process of checking documents, design, code,
- 19. Waterfall Водопадная модель разработки ПО
- 21. Скачать презентацию
SOFTWARE DEVELOPMENT LIFECYCLE (SDLC)
is a systematic process for building software
SOFTWARE DEVELOPMENT LIFECYCLE (SDLC)
is a systematic process for building software
Why SLDS
Here, are prime reasons why SDLC is important for developing
Why SLDS
Here, are prime reasons why SDLC is important for developing
It offers a basis for project planning, scheduling, and estimating
Provides a framework for a standard set of activities and deliverables
It is a mechanism for project tracking and control
Increases visibility of project planning to all involved stakeholders of the development process
Increased and enhance development speed
Improved client relations
Helps you to decrease project risk and project management plan overhead
SDLS Phases
Фазы
SDLS Phases
Фазы
SDLS Phases
Фазы
Phase 1: Requirement collection and analysis:
The requirement is the
SDLS Phases
Фазы
Phase 1: Requirement collection and analysis:
The requirement is the
This stage gives a clearer picture of the scope of the entire project and the anticipated issues, opportunities, and directives which triggered the project.
Requirements Gathering stage need teams to get detailed and precise requirements. This helps companies to finalize the necessary timeline to finish the work of that system.
Phase 2: Feasibility study:
Once the requirement analysis phase is completed the
Phase 2: Feasibility study:
Once the requirement analysis phase is completed the
There are mainly five types of feasibilities checks:
Economic: Can we complete the project within the budget or not?
Legal: Can we handle this project as cyber law and other regulatory framework/compliances.
Operation feasibility: Can we create operations which is expected by the client?
Technical: Need to check whether the current computer system can support the software
Schedule: Decide that the project can be completed within the given schedule or not
Phase 3: Design:
In this third phase, the system and software design
Phase 3: Design:
In this third phase, the system and software design
This design phase serves as input for the next phase of the model.
There are two kinds of design documents developed in this phase:
High-Level Design (HLD)
Brief description and name of each module
An outline about the functionality of every module
Interface relationship and dependencies between modules
Database tables identified along with their key elements
Complete architecture diagrams along with technology details
Low-Level Design(LLD)
Functional logic of the modules
Database tables, which include type and size
Complete detail of the interface
Addresses all types of dependency issues
Listing of error messages
Complete input and outputs for every module
Phase 4: Coding:
Once the system design phase is over, the next
Phase 4: Coding:
Once the system design phase is over, the next
In this phase, Developer needs to follow certain predefined coding guidelines. They also need to use programming tools like compiler, interpreters, debugger to generate and implement the code.
Phase 5: Testing:
Once the software is complete, and it is deployed
Phase 5: Testing:
Once the software is complete, and it is deployed
During this phase, QA and testing team may find some bugs/defects which they communicate to developers. The development team fixes the bug and send back to QA for a re-test. This process continues until the software is bug-free, stable, and working according to the business needs of that system.
Phase 6: Installation/Deployment:
Once the software testing phase is over and no
Phase 6: Installation/Deployment:
Once the software testing phase is over and no
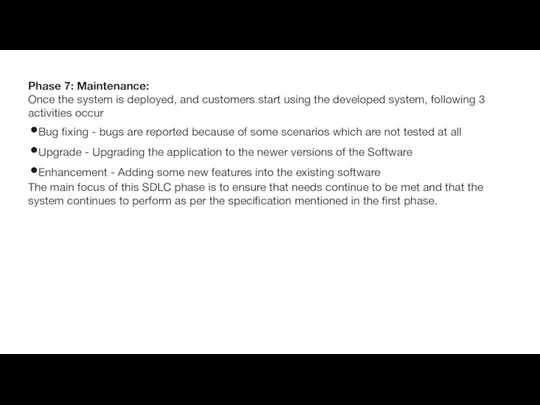
Phase 7: Maintenance:
Once the system is deployed, and customers start using
Phase 7: Maintenance:
Once the system is deployed, and customers start using
Bug fixing - bugs are reported because of some scenarios which are not tested at all
Upgrade - Upgrading the application to the newer versions of the Software
Enhancement - Adding some new features into the existing software
The main focus of this SDLC phase is to ensure that needs continue to be met and that the system continues to perform as per the specification mentioned in the first phase.
What is The Waterfall Model?
What is The Waterfall Model?
WATERFALL MODEL is
What is The Waterfall Model?
What is The Waterfall Model?
WATERFALL MODEL is
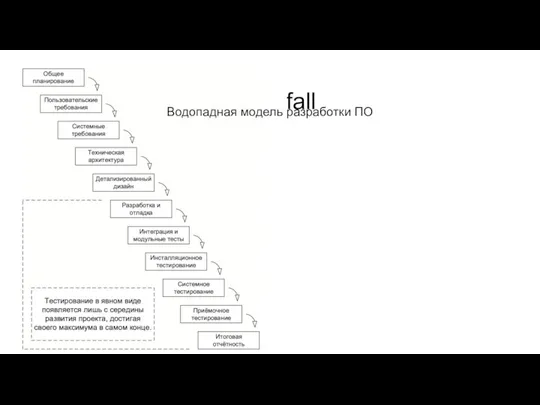
Waterfall Model
Waterfall Model
Different Phases of Waterfall Model in Software Engineering
Different Phases of Waterfall Model in Software Engineering
When to use SDLC Waterfall Model
Waterfall model can be used when
Requirements
When to use SDLC Waterfall Model
Waterfall model can be used when
Requirements
Application is not complicated and big
Project is short
Requirement is clear
Environment is stable
Technology and tools used are not dynamic and is stable
Resources are available and trained
Advantages and Disadvantages of Waterfall-Model
Advantages and Disadvantages of Waterfall-Model
Verification in Software Testing
Verification in Software Testing is a process of
Verification in Software Testing
Verification in Software Testing is a process of
Validation in Software Testing
Validation in Software Testing is a dynamic mechanism of testing and validating if the software product actually meets the exact needs of the customer or not. The process helps to ensure that the software fulfills the desired use in an appropriate environment. The validation process involves activities like unit testing, integration testing, system testing and user acceptance testing.
KEY DIFFERENCE
Verification process includes checking of documents, design, code and program whereas Validation process includes testing and validation of the actual product.
Verification does not involve code execution while Validation involves code execution.
Verification uses methods like reviews, walkthroughs, inspections and desk-checking whereas Validation uses methods like black box testing, white box testing and non-functional testing.
Verification checks whether the software confirms a specification whereas Validation checks whether the software meets the requirements and expectations.
Verification finds the bugs early in the development cycle whereas Validation finds the bugs that verification can not catch.
Verification process targets on software architecture, design, database, etc. while Validation process targets the actual software product.
Verification is done by the QA team while Validation is done by the involvement of testing team with QA team.
Verification process comes before validation whereas Validation process comes after verification.
Waterfall
Водопадная модель разработки ПО
Waterfall
Водопадная модель разработки ПО













 Тірілген графика. Айнымалылармен жұмыс
Тірілген графика. Айнымалылармен жұмыс Длина цепочки
Длина цепочки Роль СМИ в политической жизни
Роль СМИ в политической жизни Списки и строки
Списки и строки Модели объектов и их назначение
Модели объектов и их назначение Операторы PHP
Операторы PHP Sheriff. DDoS detection system
Sheriff. DDoS detection system Школа подготовки технических администраторов. (Занятие 16)
Школа подготовки технических администраторов. (Занятие 16) Современные информационные технологии. Методы информационных технологий
Современные информационные технологии. Методы информационных технологий Нормализация отношений
Нормализация отношений Классификация ЭВМ и их основные характеристики
Классификация ЭВМ и их основные характеристики Лекция 4. Жизненный цикл дефекта
Лекция 4. Жизненный цикл дефекта Computer Science
Computer Science Процессы программного обеспечения
Процессы программного обеспечения SQLite менеджер. Создание БД и таблиц. DDL и DML запросы
SQLite менеджер. Создание БД и таблиц. DDL и DML запросы Chapter 4 Computation
Chapter 4 Computation Открытое образование. Свободный доступ к информационным ресурсам мира
Открытое образование. Свободный доступ к информационным ресурсам мира Разработка защиты базы данных университетского колледжа информационных технологий от несанкционированного доступа
Разработка защиты базы данных университетского колледжа информационных технологий от несанкционированного доступа Сравнительный анализ программных продуктов по электронной отчетности
Сравнительный анализ программных продуктов по электронной отчетности ИС скачивания фильмов по сети
ИС скачивания фильмов по сети Количество информации
Количество информации Системы счисления
Системы счисления Основы алгоритмизации и программирования. Указатели
Основы алгоритмизации и программирования. Указатели кл. Создание текстовых документов на компьютере
кл. Создание текстовых документов на компьютере Abstract Factory. Creational design pattern
Abstract Factory. Creational design pattern Рекомендательные библиографические пособия : виды, структура, составление
Рекомендательные библиографические пособия : виды, структура, составление Открытый урок по теме: Графика в MS Word 2003
Открытый урок по теме: Графика в MS Word 2003 Сущность и значение комплектования государственных архивов. Технотронные документы
Сущность и значение комплектования государственных архивов. Технотронные документы