Слайд 2

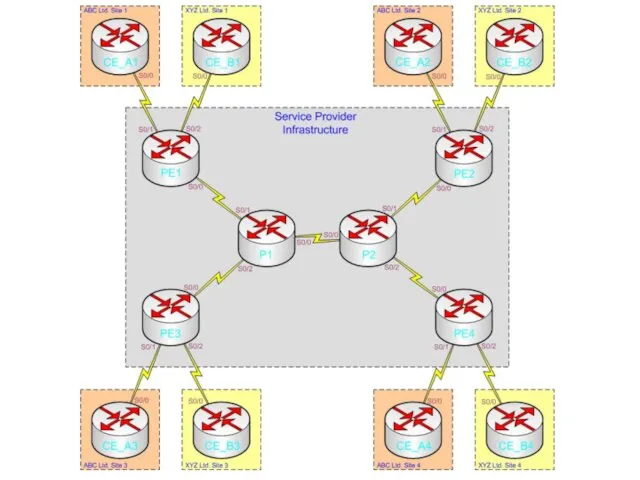
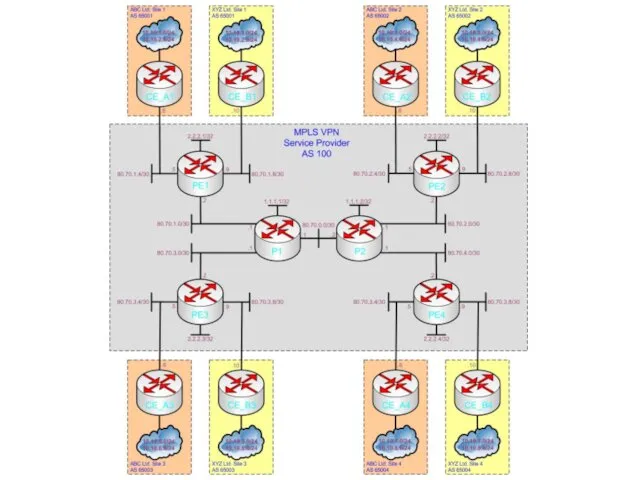
The Topology
The next two slides display both the physical and logical
topology of our simple example network
Please study the diagrams carefully before moving on
Слайд 3
Слайд 4
Слайд 5

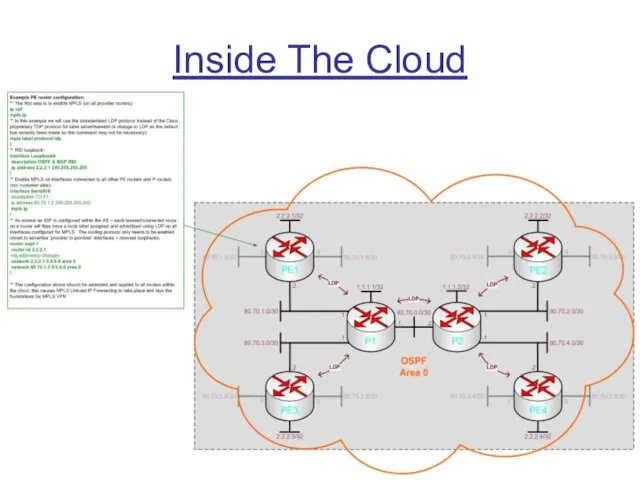
Laying The Foundations
Terms that are often heard in close proximity to
“MPLS VPN” are “VRFs” and “Multiprotocol BGP”. However, before we begin to look at protocols/features such as these we need to get basic MPLS Unicast IP Forwarding functioning correctly:
Step 1 - Enable an IGP on each router within the cloud and verify routing tables are populated correctly
BGP (& OSPF) RID reachability is key here
Step 2 - Enable MPLS on all ‘provider router to provider router’ interfaces
An available label will then be chosen by each router and advertised on all interfaces configured for MPLS using TDP (old default) or LDP (new default & what we’ll use) for each prefix learned via the IGP
OSPF will be configured as the IGP in this example
Remember. LDP ‘floods’ in all directions so routers will consult the routing table to make a decision on which label path to use for a given prefix (important when loops exist)
Слайд 6
Слайд 7

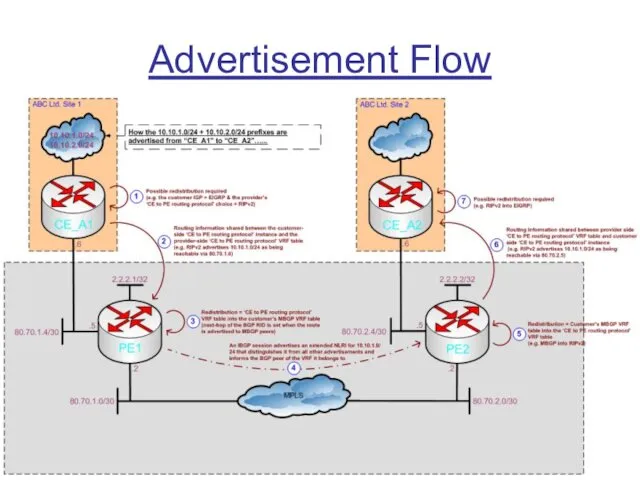
Overlaying MPLS VPNs
Now that the ‘cloud’ has basic MPLS IP Unicast
Forwarding enabled we can create Virtual Routing and Forwarding (VRF) tables and make use of Multiprotocol BGP (MP-BGP/MBGP) to advertise prefixes held within the VRFs
In addition to the standard MPLS label used for Unicast IP Forwarding (now the “outer label” and used to reach a BGP next-hop), an “inner label” will now be added to packets to inform other PE routers of the correct egress VRF tables to place packets in upon receiving them (ready for standard forwarding)
This is how a ‘VPN’ is created – by separating routing information per-customer at the edge of the cloud and ignoring IP headers for forwarding within the cloud
Слайд 8

Customer to Provider
As MPLS is a layer 3 technology a method
of communicating routing information between the customer (with possible overlapping prefixes with other customers) and the provider (VRF tables used to separate customers) is required
Methods of CE to PE route advertisement include:
Static routing
RIPv2
EIGRP
OSPF
BGP
Слайд 9
Слайд 10
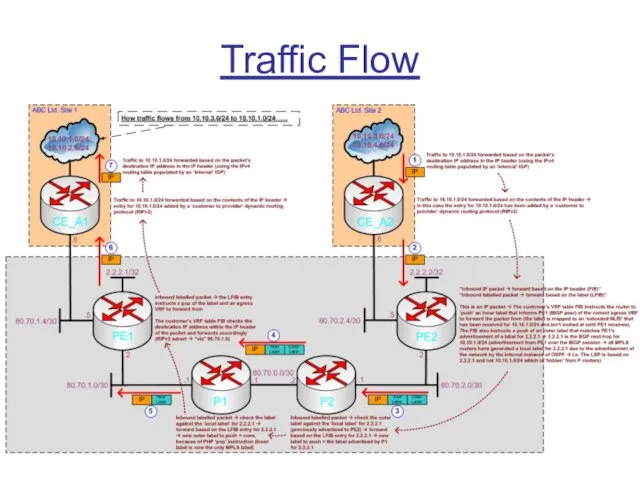
Слайд 11
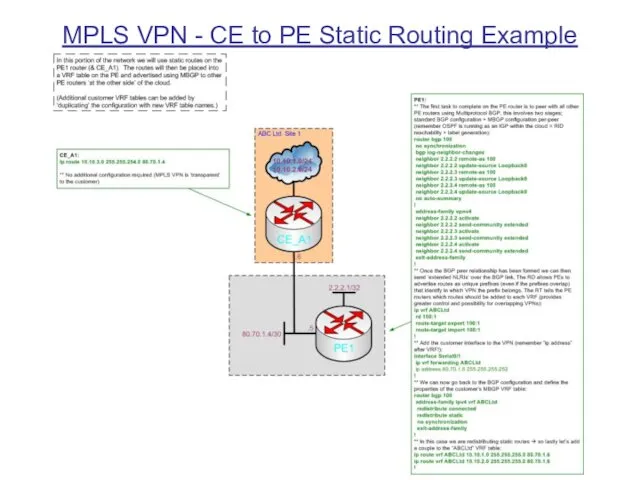
MPLS VPN - CE to PE Static Routing Example
Слайд 12
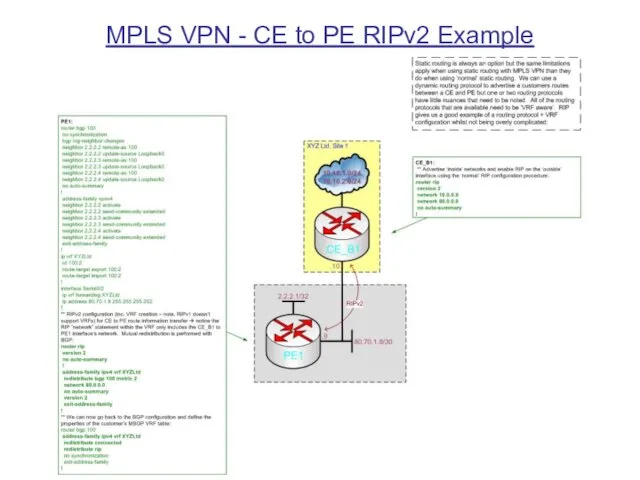
MPLS VPN - CE to PE RIPv2 Example
Слайд 13
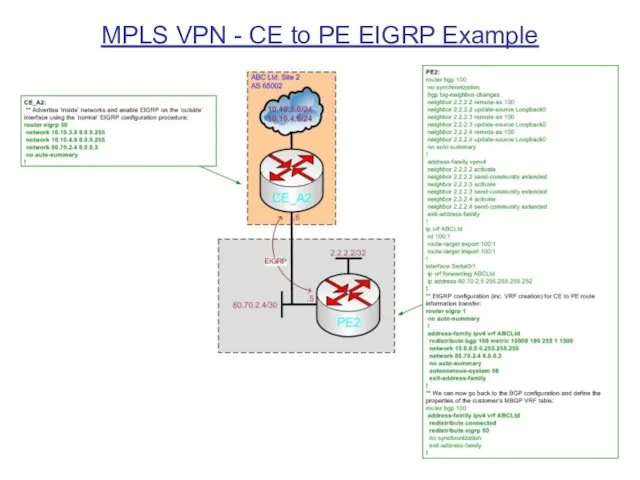
MPLS VPN - CE to PE EIGRP Example
Слайд 14
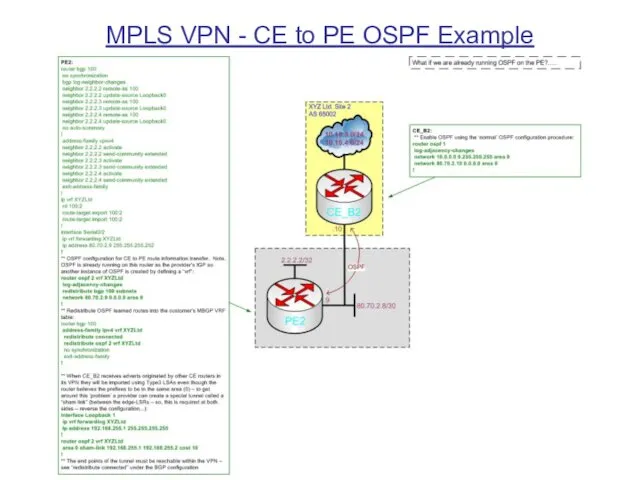
MPLS VPN - CE to PE OSPF Example













 Локальные и глобальные компьютерные сети. Коммуникационные технологии
Локальные и глобальные компьютерные сети. Коммуникационные технологии Алгоритмы и исполнители. Основы алгоритмизации
Алгоритмы и исполнители. Основы алгоритмизации Табличные информационные модели. Моделирование и формализация (9 класс)
Табличные информационные модели. Моделирование и формализация (9 класс) Цензура в США: СМИ и Интернет
Цензура в США: СМИ и Интернет Урок в рамках модуля Время. Люди. События
Урок в рамках модуля Время. Люди. События Конструктор игр
Конструктор игр Программирование на языке Python
Программирование на языке Python Творческий проект Дизайн школьного кабинета
Творческий проект Дизайн школьного кабинета Разработка корпоративного веб-сайта
Разработка корпоративного веб-сайта Вебинар. Трансформация. Дизайн женщины
Вебинар. Трансформация. Дизайн женщины Основы безопасности информационных технологий. Средства защиты от нарушений
Основы безопасности информационных технологий. Средства защиты от нарушений Сообщество adidas runners и RunClubKirov в Strava
Сообщество adidas runners и RunClubKirov в Strava Технология подготовки текстовых документов
Технология подготовки текстовых документов Secrets Which you never noticed in Night Shift at Freddy’s
Secrets Which you never noticed in Night Shift at Freddy’s Логическая организация баз данных. Лекция 2
Логическая организация баз данных. Лекция 2 Визуализация информации в текстовых документах
Визуализация информации в текстовых документах Моделирование на UML. Первая ступень Тест
Моделирование на UML. Первая ступень Тест Компьютер в жизни ребенка
Компьютер в жизни ребенка Каналы передачи информации
Каналы передачи информации Растровая модель пространственных данных. Лекция 2
Растровая модель пространственных данных. Лекция 2 Электронные энциклопедии и справочники
Электронные энциклопедии и справочники Информационно-технологический профиль
Информационно-технологический профиль Информационно-коммуникационные технологии в учебном процессе
Информационно-коммуникационные технологии в учебном процессе Основні режими Microsoft PowerPoint
Основні режими Microsoft PowerPoint Тестирование ПО. Методики тестирования. Лекция 5
Тестирование ПО. Методики тестирования. Лекция 5 Графикалық режім
Графикалық режім Роботы
Роботы Операционная система Linux
Операционная система Linux