Содержание
- 2. Lecture 2: roadmap 1.1 what is the Internet? 1.2 protocol layers, service models 1.3 network edge
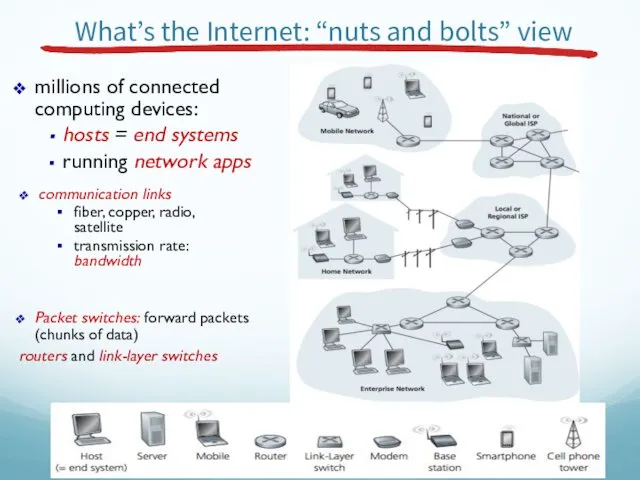
- 3. What’s the Internet: “nuts and bolts” view millions of connected computing devices: hosts = end systems
- 4. Intermediary Network Devices
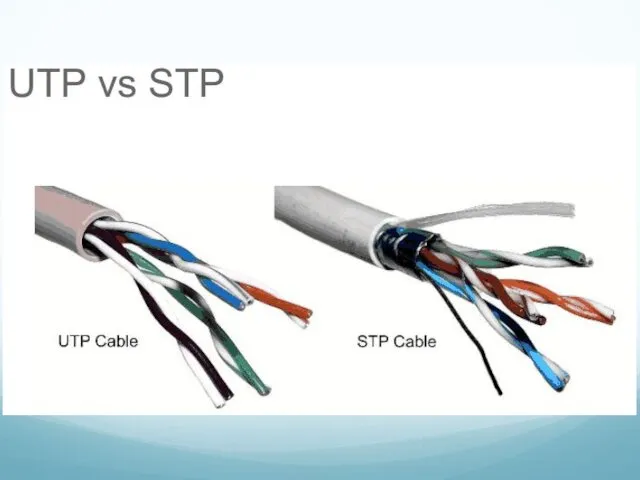
- 5. Network Media
- 6. Physical media bit: propagates between transmitter/receiver pairs physical link: what lies between transmitter & receiver guided
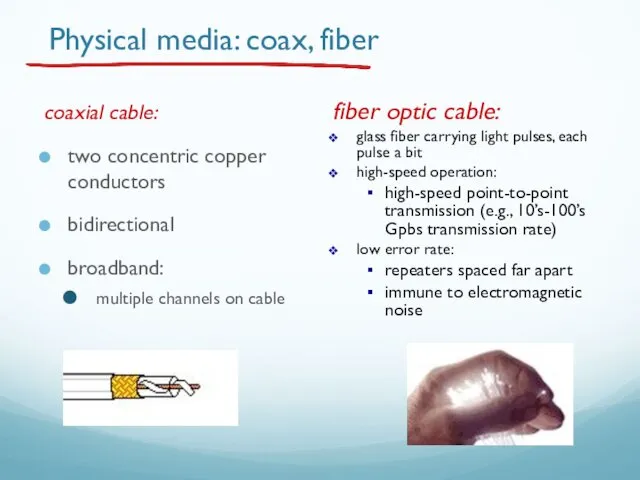
- 10. Physical media: coax, fiber coaxial cable: two concentric copper conductors bidirectional broadband: multiple channels on cable
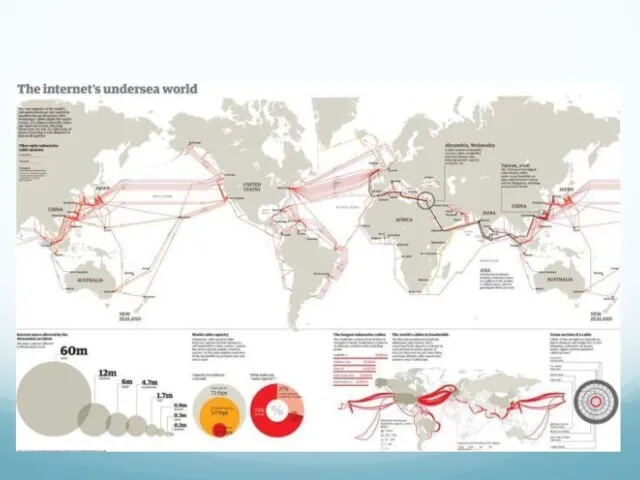
- 11. TAT-14 Cable System Sprint Network Administration System The TAT-14 transatlantic cable system is in full service,
- 19. CS Cable Innovator 1995 Finland (145m*24m), 8500 t fiber optic, 42 day of work (60).
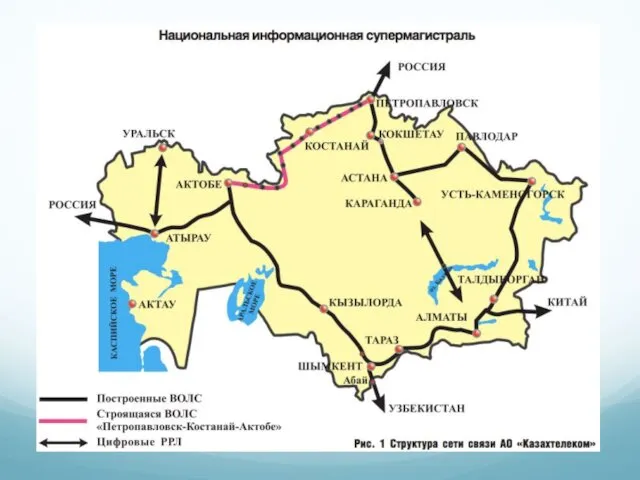
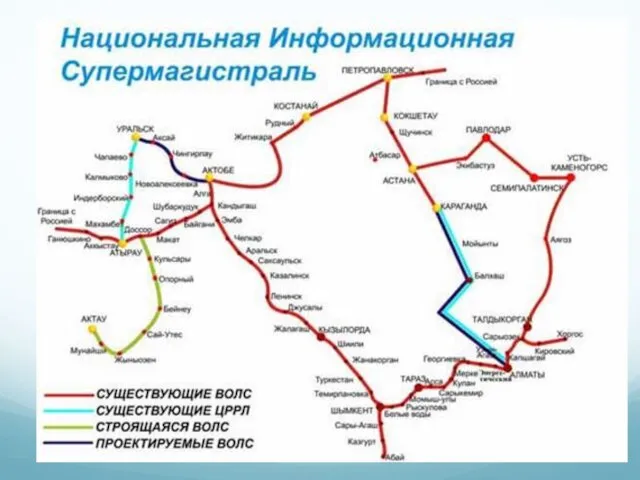
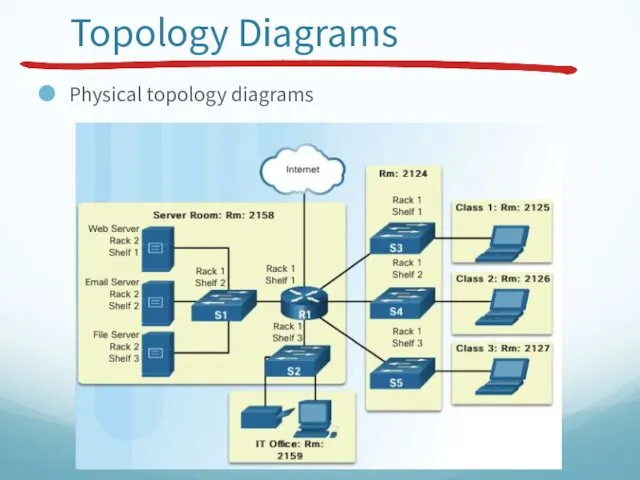
- 24. Topology Diagrams Physical topology diagrams
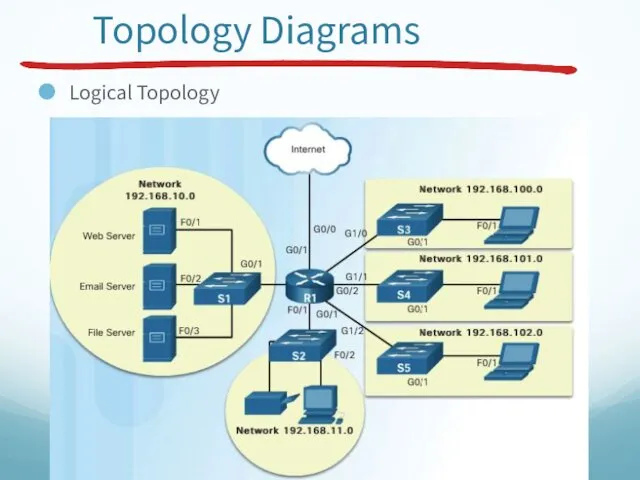
- 25. Topology Diagrams Logical Topology
- 26. Internet: “network of networks” Interconnected ISPs protocols control sending, receiving of msgs e.g., TCP, IP, HTTP,
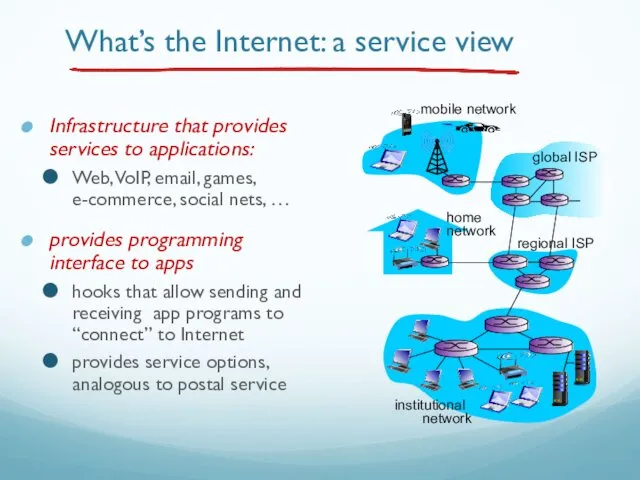
- 27. What’s the Internet: a service view Infrastructure that provides services to applications: Web, VoIP, email, games,
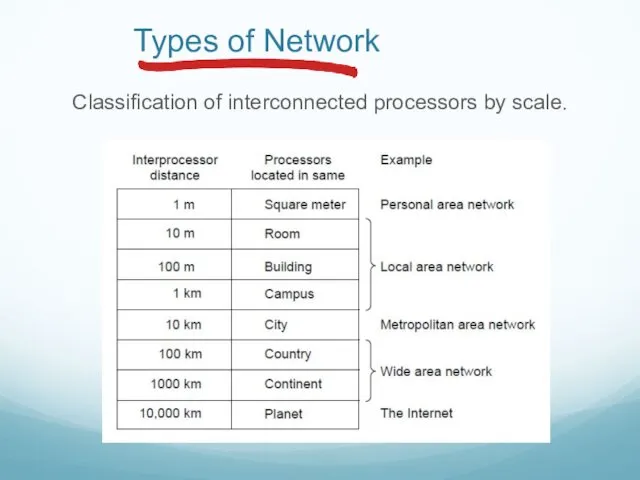
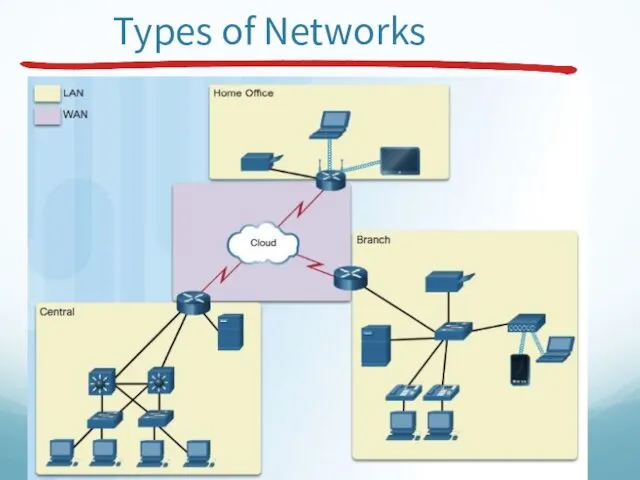
- 28. Types of Network Classification of interconnected processors by scale.
- 29. Types of Networks
- 30. Personal Area Network Bluetooth PAN configuration
- 31. Local Area Networks Wireless and wired LANs. (a) 802.11. (b) Switched Ethernet.
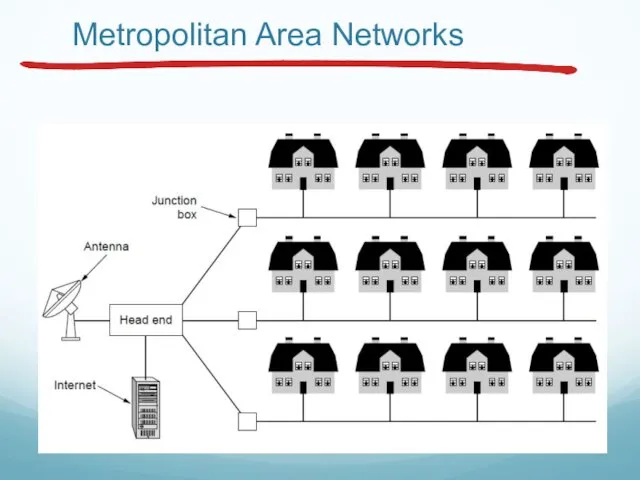
- 32. Metropolitan Area Networks
- 33. Wide Area Networks WAN using an ISP network.
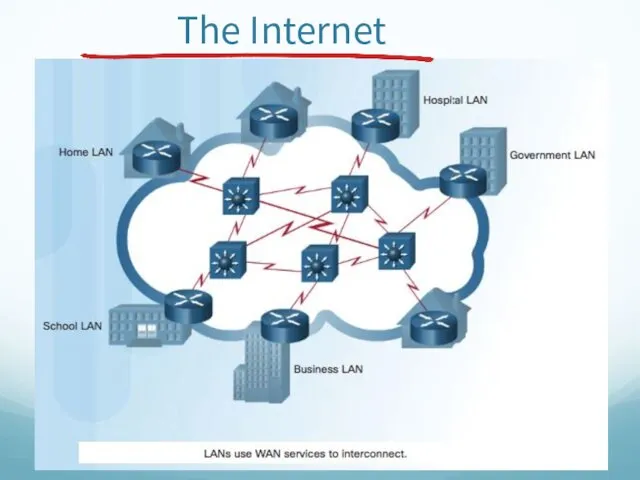
- 34. The Internet
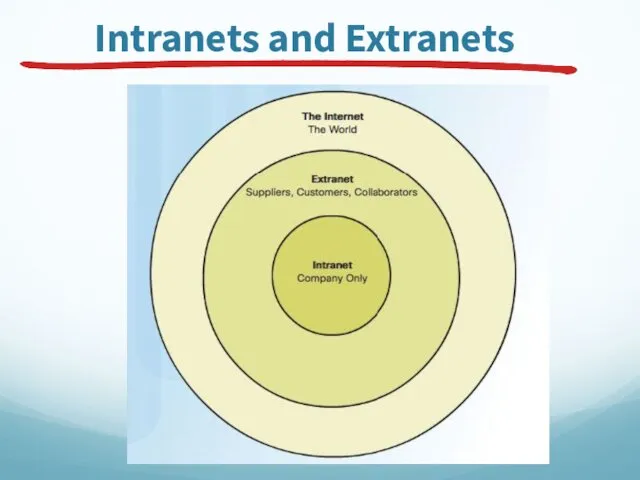
- 35. Intranets and Extranets
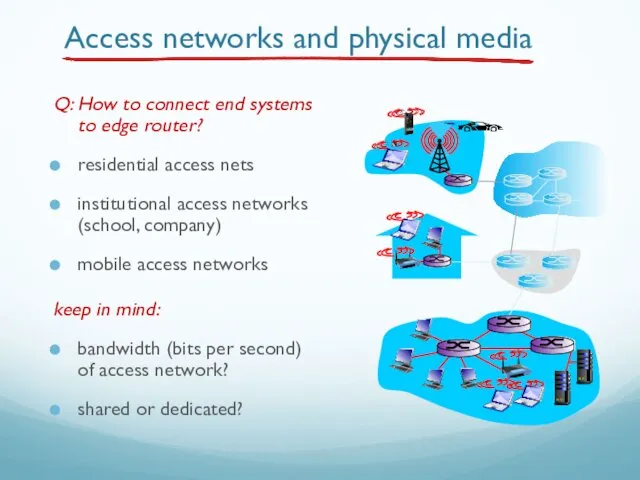
- 36. Access networks and physical media Q: How to connect end systems to edge router? residential access
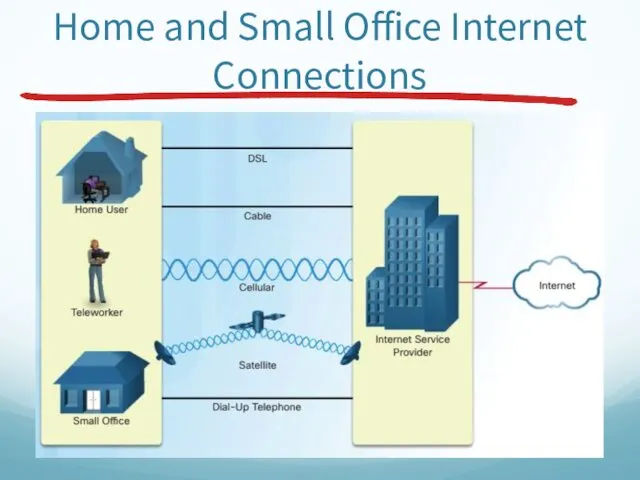
- 37. Home and Small Office Internet Connections
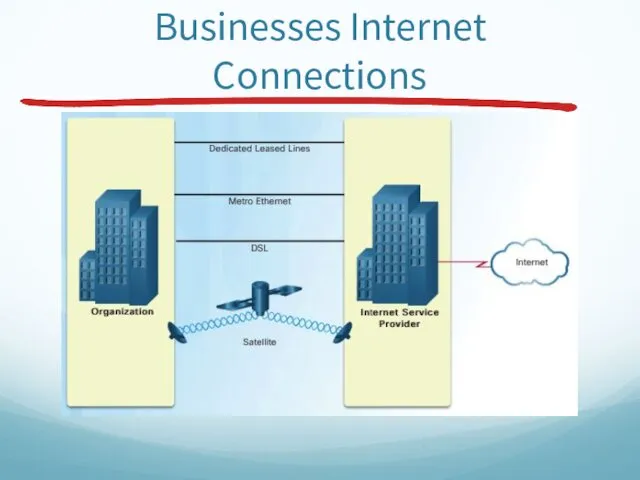
- 38. Businesses Internet Connections
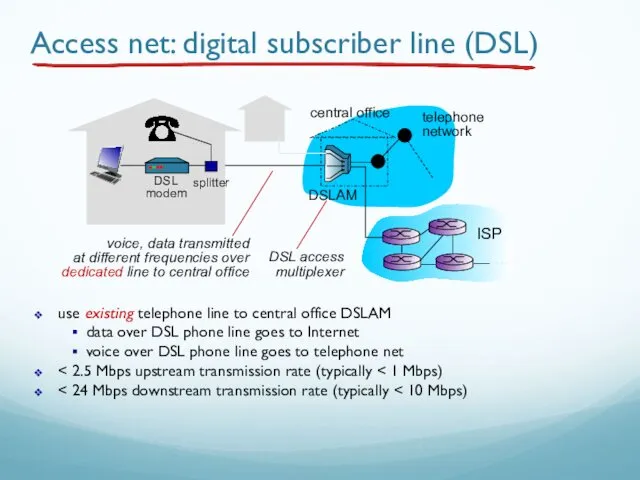
- 39. Access net: digital subscriber line (DSL) central office telephone network DSLAM use existing telephone line to
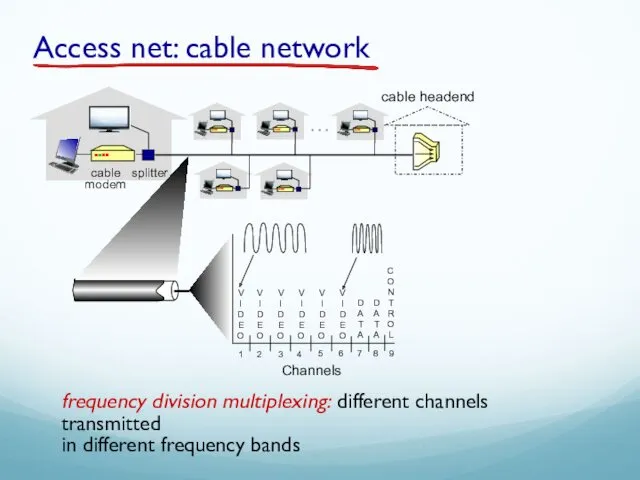
- 40. Access net: cable network cable modem splitter … cable headend frequency division multiplexing: different channels transmitted
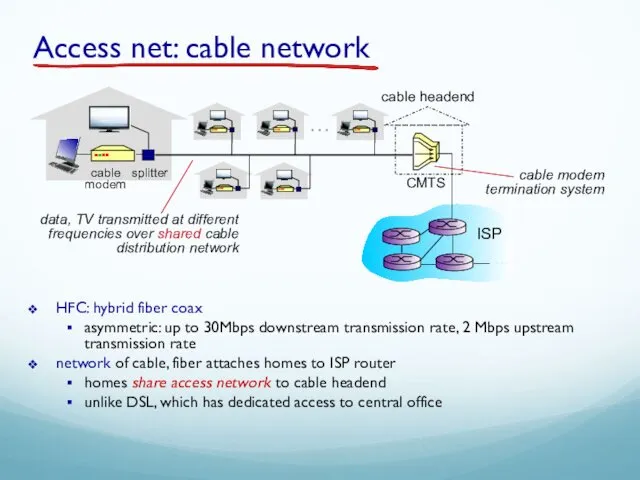
- 41. cable modem splitter … cable headend CMTS HFC: hybrid fiber coax asymmetric: up to 30Mbps downstream
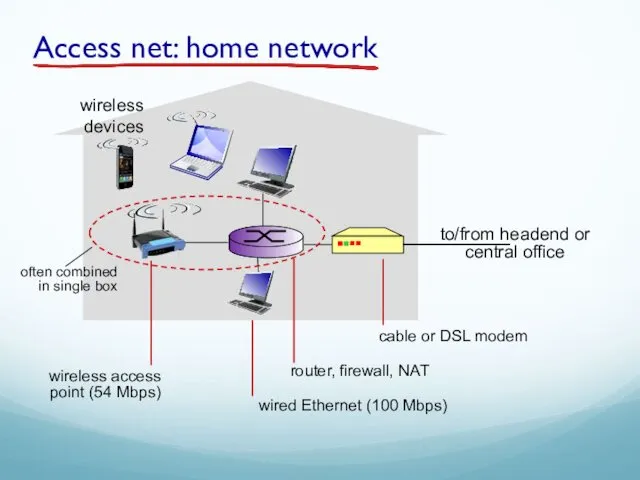
- 42. Access net: home network to/from headend or central office wireless devices
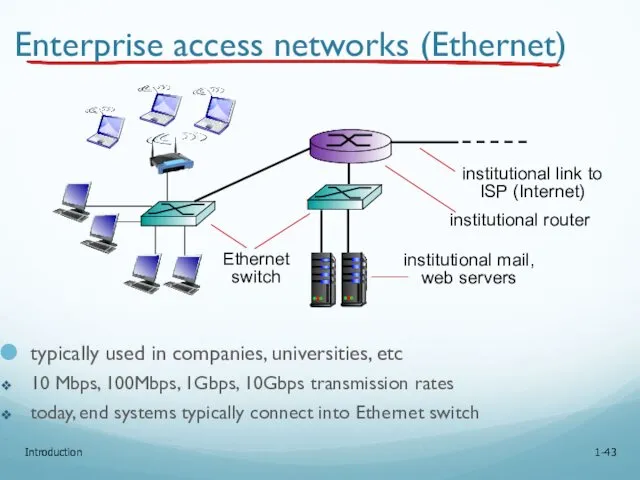
- 43. Introduction 1- Enterprise access networks (Ethernet) typically used in companies, universities, etc 10 Mbps, 100Mbps, 1Gbps,
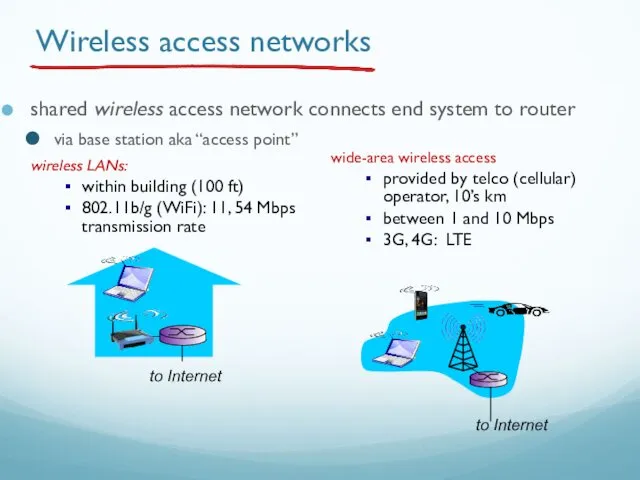
- 44. Wireless access networks shared wireless access network connects end system to router via base station aka
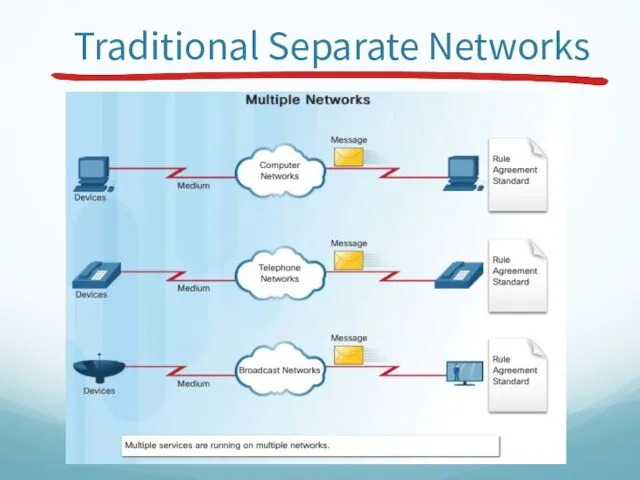
- 45. Traditional Separate Networks
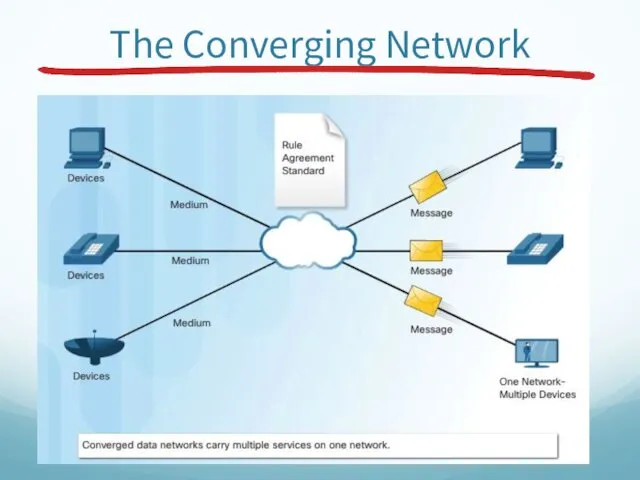
- 46. The Converging Network
- 47. Network Architecture
- 48. Fault Tolerance
- 49. Scalability
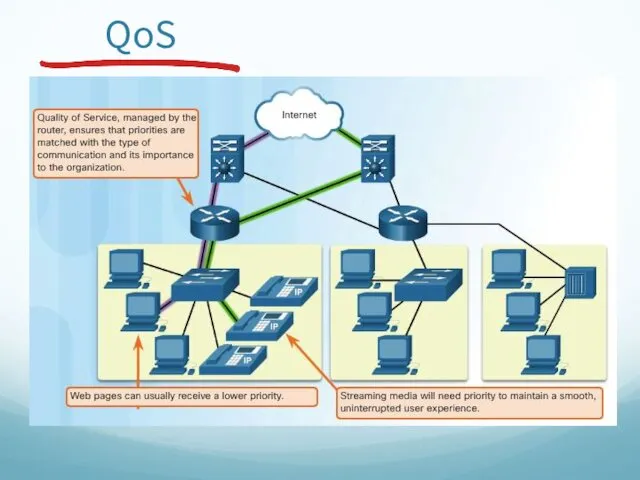
- 50. QoS
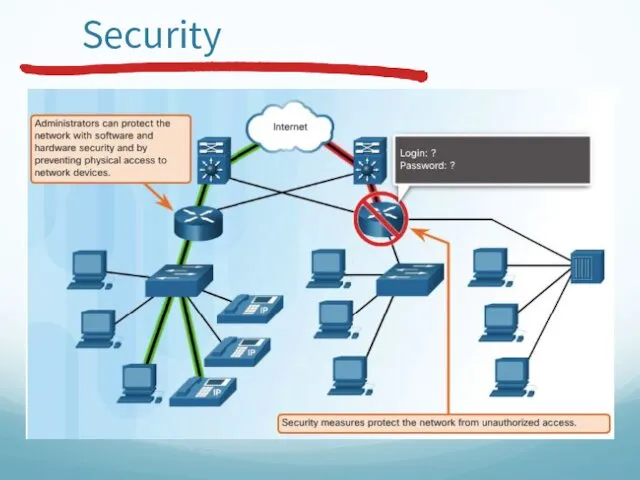
- 51. Security
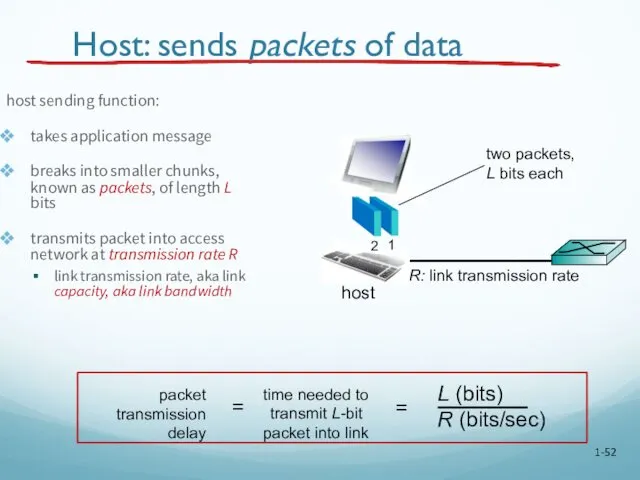
- 52. 1- Host: sends packets of data host sending function: takes application message breaks into smaller chunks,
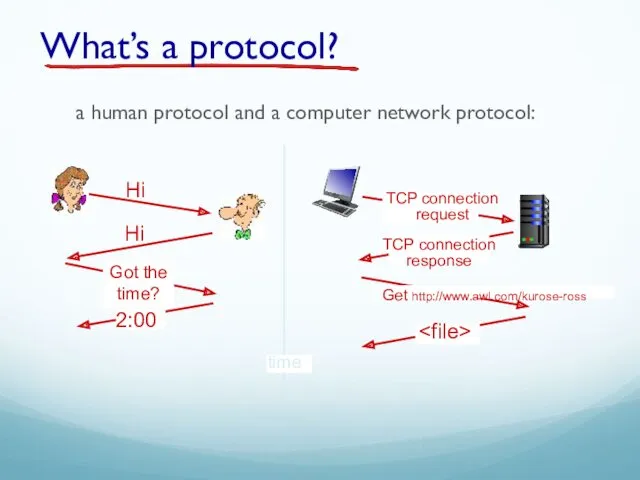
- 53. a human protocol and a computer network protocol: Hi Hi TCP connection response TCP connection request
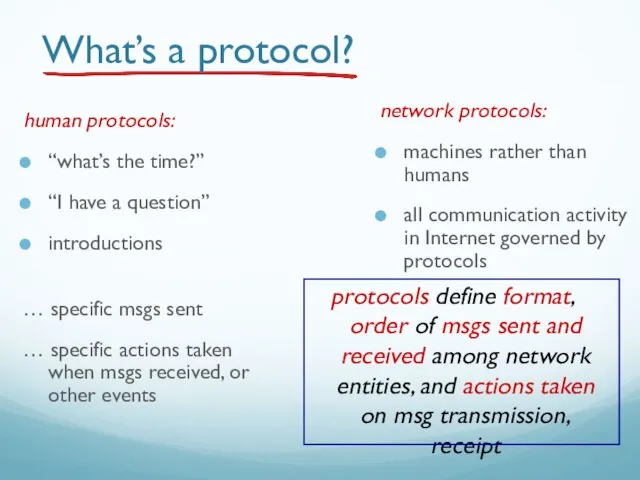
- 54. What’s a protocol? human protocols: “what’s the time?” “I have a question” introductions … specific msgs
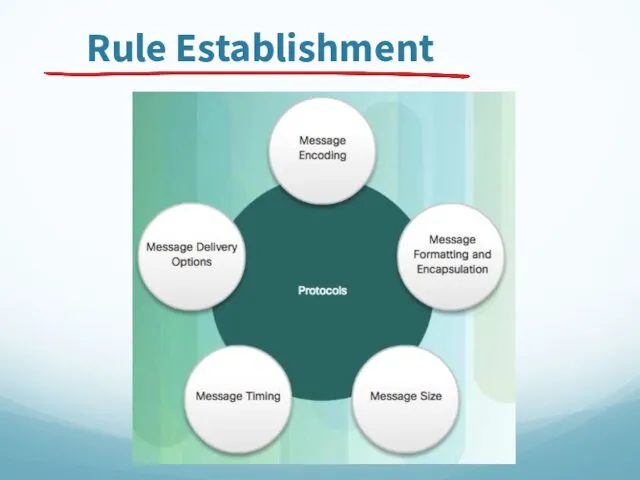
- 55. Rule Establishment
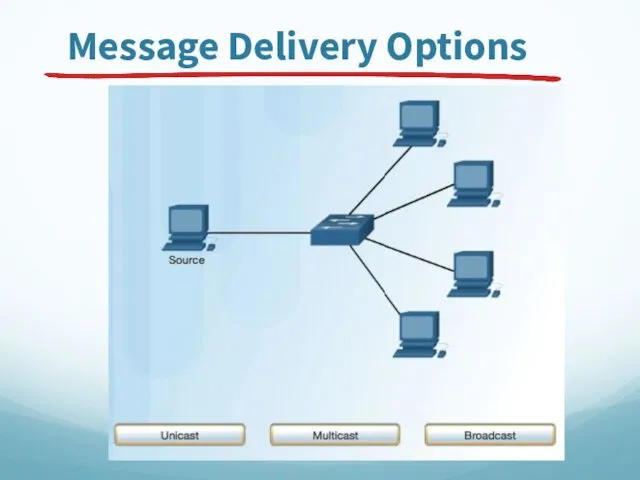
- 56. Message Delivery Options
- 57. Layering of airline functionality layers: each layer implements a service via its own internal-layer actions relying
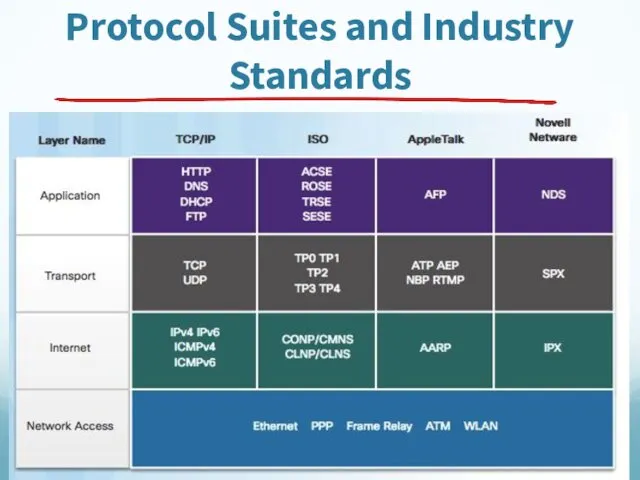
- 58. Protocol Suites and Industry Standards
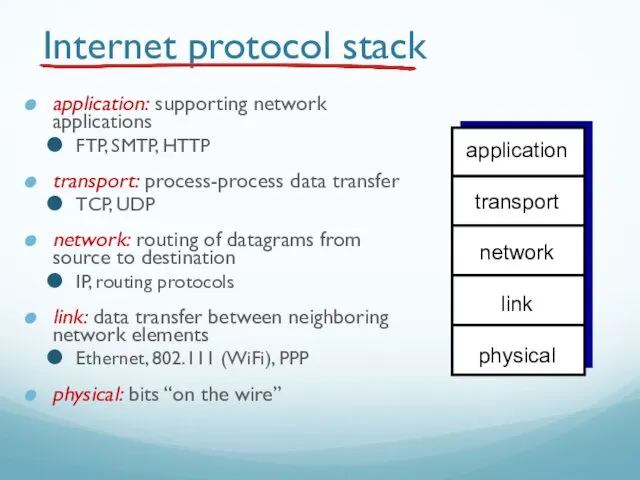
- 59. Internet protocol stack application: supporting network applications FTP, SMTP, HTTP transport: process-process data transfer TCP, UDP
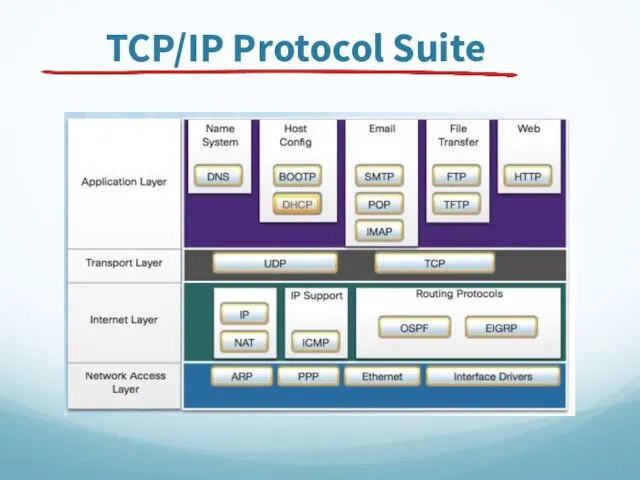
- 60. TCP/IP Protocol Suite
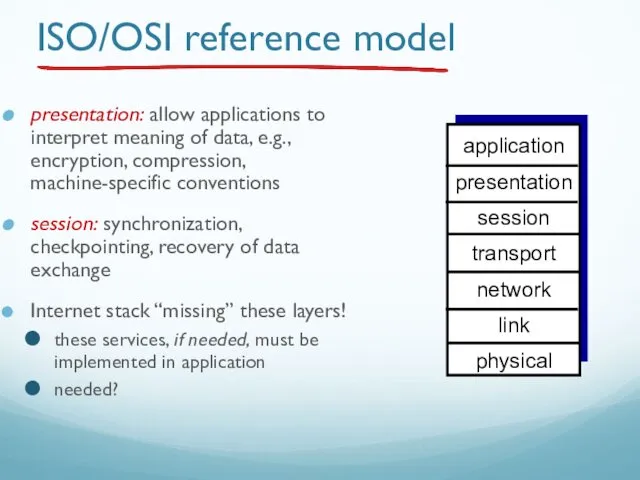
- 61. ISO/OSI reference model presentation: allow applications to interpret meaning of data, e.g., encryption, compression, machine-specific conventions
- 62. Why is the Network Layer often called “Layer 3”?
- 63. Distinguishing Points
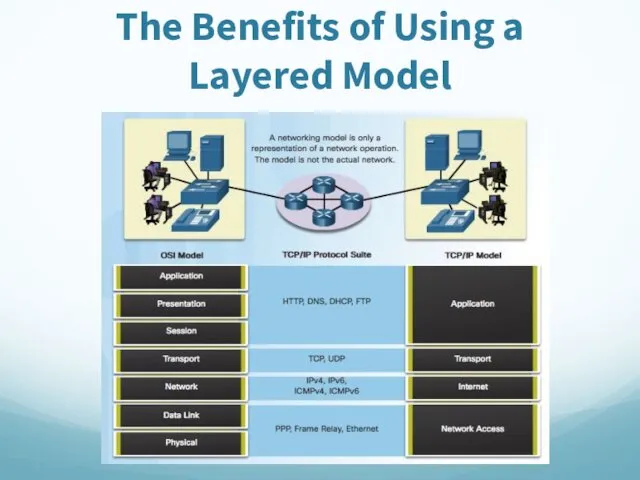
- 65. The Benefits of Using a Layered Model
- 66. Encapsulation source application transport network link physical segment datagram destination application transport network link physical router
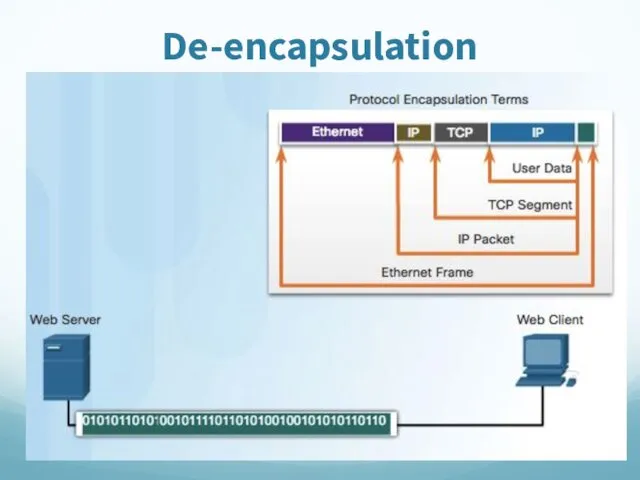
- 67. De-encapsulation
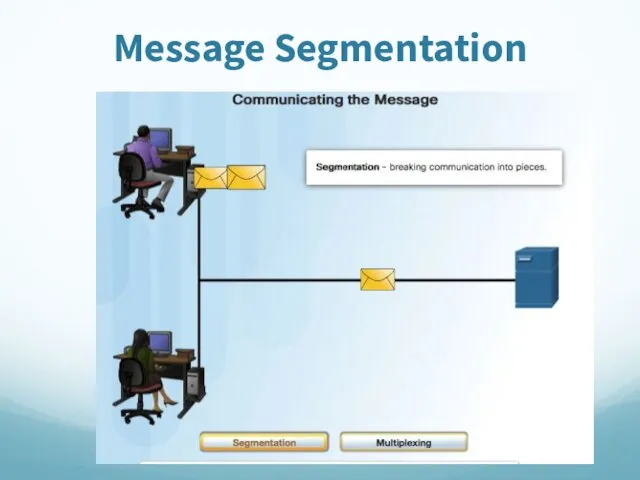
- 68. Message Segmentation
- 69. Message Segmentation
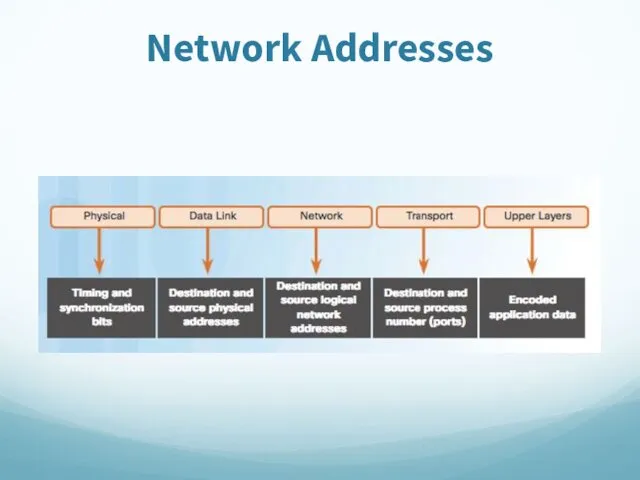
- 70. Network Addresses
- 74. Open Standards
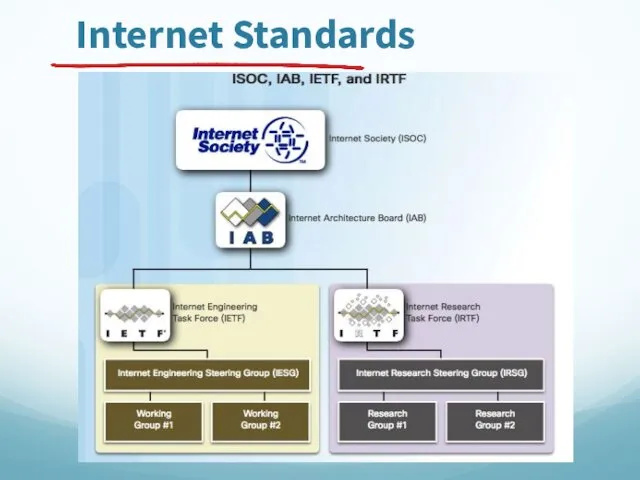
- 75. Internet Standards
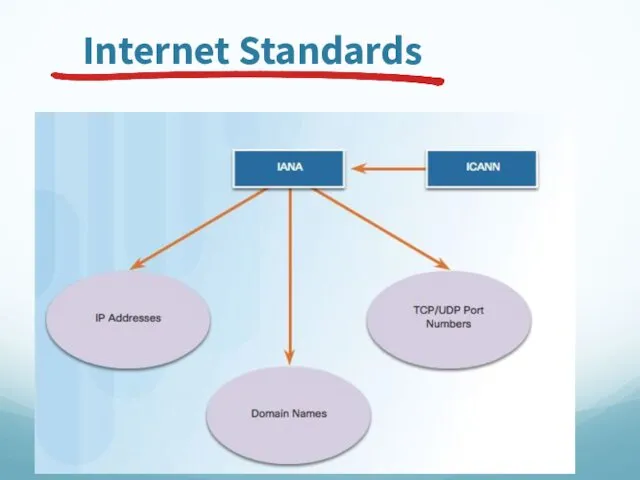
- 76. Internet Standards
- 77. Electronics and Communications Standard Organizations
- 78. Internet structure: network of networks End systems connect to Internet via access ISPs (Internet Service Providers)
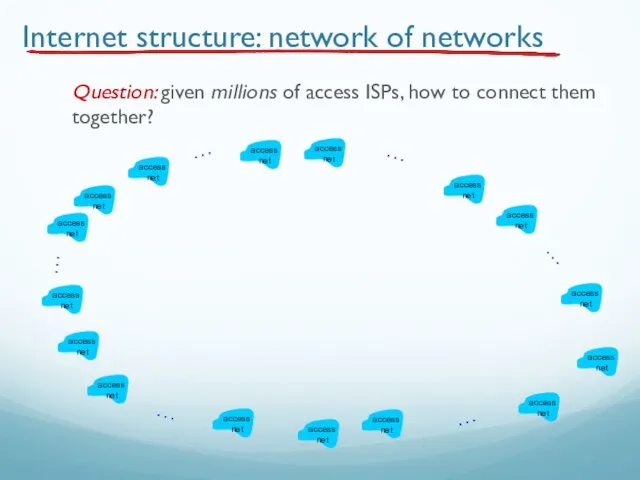
- 79. Internet structure: network of networks Question: given millions of access ISPs, how to connect them together?
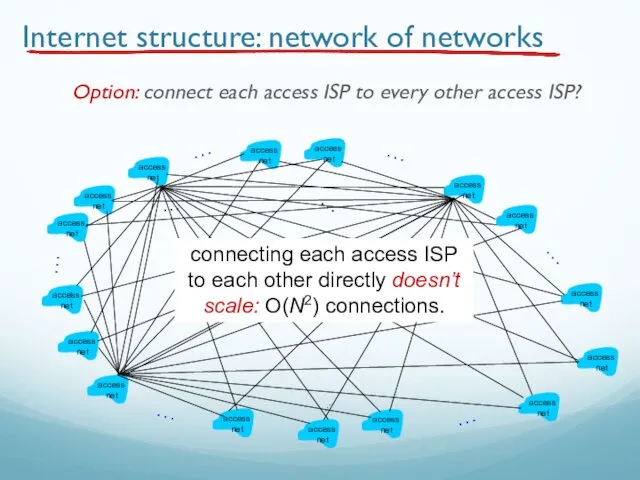
- 80. Internet structure: network of networks Option: connect each access ISP to every other access ISP? connecting
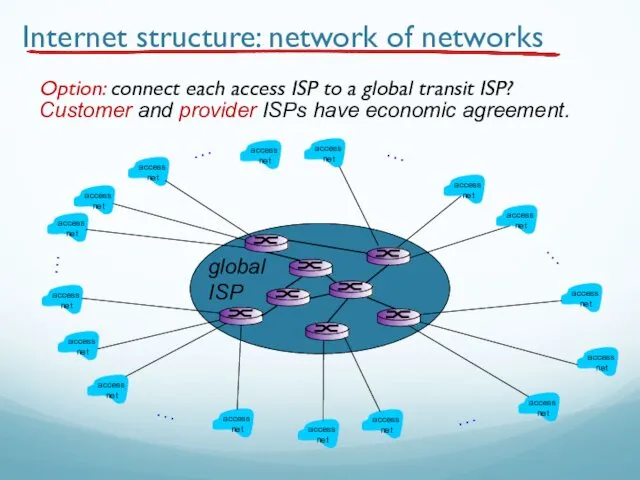
- 81. Internet structure: network of networks Option: connect each access ISP to a global transit ISP? Customer
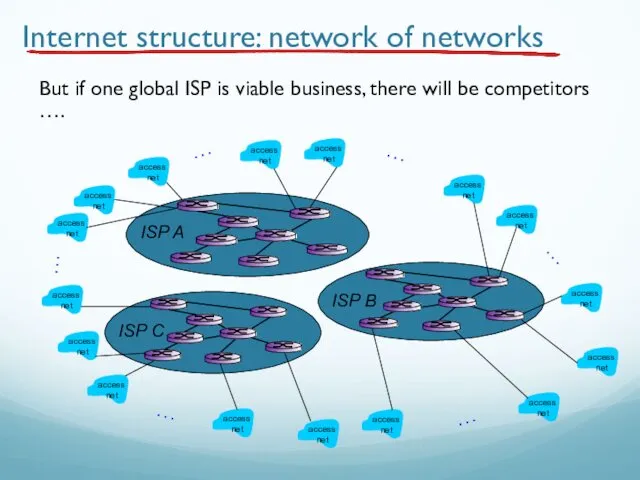
- 82. Internet structure: network of networks But if one global ISP is viable business, there will be
- 83. Internet structure: network of networks But if one global ISP is viable business, there will be
- 84. Internet structure: network of networks … and regional networks may arise to connect access nets to
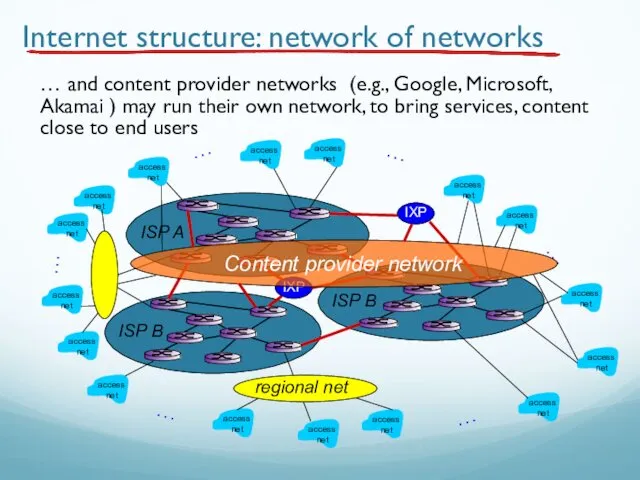
- 85. Internet structure: network of networks … and content provider networks (e.g., Google, Microsoft, Akamai ) may
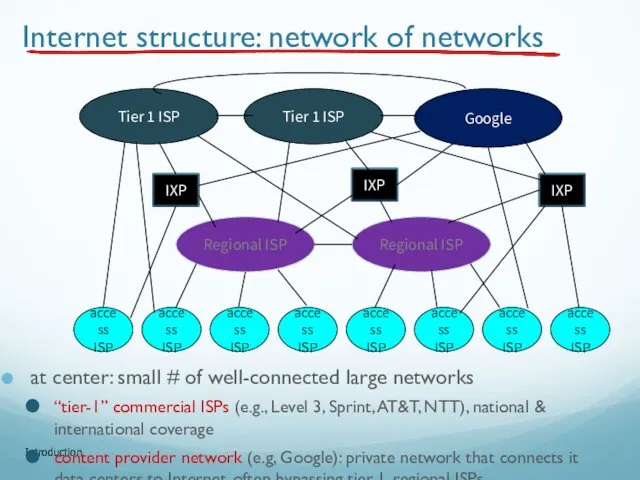
- 86. Introduction Internet structure: network of networks at center: small # of well-connected large networks “tier-1” commercial
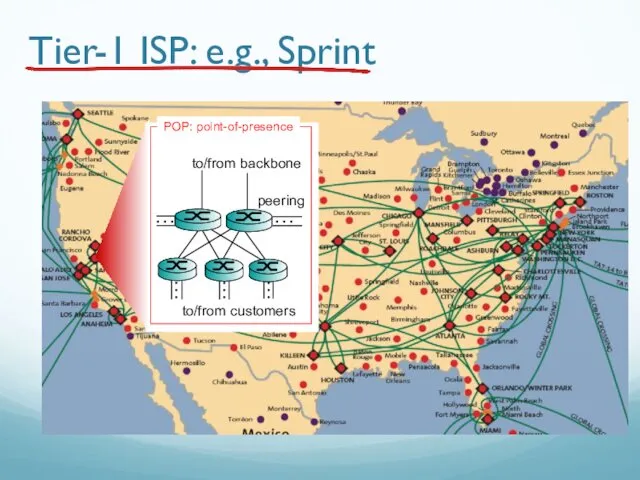
- 87. Tier-1 ISP: e.g., Sprint
- 88. Readings Kurose, James F. Computer networking : a top-down approach / James F. Kurose, Keith W.
- 90. Скачать презентацию




































 Инструкция по Зарплатному проекту в ИБ ПСБ Бизнес
Инструкция по Зарплатному проекту в ИБ ПСБ Бизнес Профессия “Разработчик игр”
Профессия “Разработчик игр” Информационная система специалиста по охране труда. Версия 6.0
Информационная система специалиста по охране труда. Версия 6.0 Линейные алгоритмы. Структура программы на языке Паскаль
Линейные алгоритмы. Структура программы на языке Паскаль Organizational communication. Netiquette
Organizational communication. Netiquette Списки с целыми числами
Списки с целыми числами Числа в памяти компьютера
Числа в памяти компьютера KEY test file
KEY test file Кто играл в PACMAN? Какие правила игры?
Кто играл в PACMAN? Какие правила игры? Контроль качества стратиграфического разреза и структурного каркаса
Контроль качества стратиграфического разреза и структурного каркаса Что такое Deepfake?
Что такое Deepfake? ARBot. Приложение дополнительной реальности
ARBot. Приложение дополнительной реальности Информационные ресурсы и технологии
Информационные ресурсы и технологии Цифровая социализация детей и подростков в современном обществе
Цифровая социализация детей и подростков в современном обществе ООО Интеллект-Авто – Интеллектуальная Система Управления Автотранспортом
ООО Интеллект-Авто – Интеллектуальная Система Управления Автотранспортом Технология перевернутого обучения с применением СДО Moodle 3.0
Технология перевернутого обучения с применением СДО Moodle 3.0 Общение в Интернете в реальном времени
Общение в Интернете в реальном времени Управление транспортерами в Logo! Soft Comfort
Управление транспортерами в Logo! Soft Comfort Деловая графика
Деловая графика Информационные технологии в деятельности правоохранительных органов
Информационные технологии в деятельности правоохранительных органов Использование логических функций Microsoft Excel
Использование логических функций Microsoft Excel Магистрально-модульный принцип построения компьютера
Магистрально-модульный принцип построения компьютера Визуальное программирование для начинающих (Scratch)
Визуальное программирование для начинающих (Scratch) Фирменные цвета
Фирменные цвета Алгоритмы и структуры данных. Лекция 1. Основные понятия
Алгоритмы и структуры данных. Лекция 1. Основные понятия Історія створення Інтернету
Історія створення Інтернету Египетская система счислений
Египетская система счислений 1C:ERP 2 Enterprise Resource Management
1C:ERP 2 Enterprise Resource Management