Слайд 2
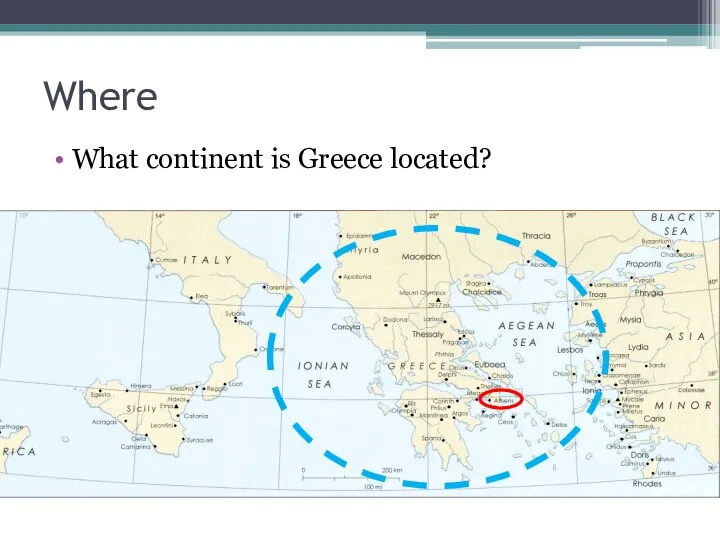
Where
What continent is Greece located?
Слайд 3

City-States
Many settlements were separated from one another….why?
Each city had its own
army, money, and government.
For these reasons these ancient Greek cities became known as city-states
Слайд 4

What types of government were tried in Ancient Greece?
Слайд 5

Government in Athens
Athens tried different types of government
Monarchy:
Oligarchy:
Tyranny:
Democracy:
Слайд 6

Monarchy
At first, Kings were chosen by the people
Kings had many powers
They
made laws and acted as judges
They conducted religious ceremonies
They led the army in wars
Kings had councils of aristocrats to advise them.
At first: no real power
helped in time of war
Over time realized that as a group, they had more power than the king
Слайд 7

Слайд 8

Aristocrats
Group of rich landowners
Ran the economy
served as generals and judges
Advised
the King
Слайд 9

Draco
In 600s BC appointed to create laws.
They were harsh
Loitering was punishable
by death
Today very harsh laws or rules are called draconian
Слайд 10

Solon
590s BC he created laws that gave more rights to common
people
All free men became citizens-
Слайд 11

Слайд 12

Peisistratus (py-sys-truht-uhs)
546BC
Was called a tyrant
Had a strong army and support of
the people
Brought peace and prosperity to the city
Made many improvements to Athens
Слайд 13

The Athenians Celebrating the
Return of Pisistratus
Слайд 14

What is democracy?
What are the two types of democracy?
Слайд 15

Democracy
Greece is the birthplace of democracy
Democracy=rule of the people
Direct and representative
democracy
Слайд 16

Cleisthenes (klys-thuh-neez)
500 BC
The father of democracy
Comes from a powerful family
Did not
want aristocrats to run the government
Established a democracy
Слайд 17

Democracy under Cleisthenes
All citizens had the right to participate in the
assembly
Assembly was held outside so everyone could attend
Every citizen had the right to speak his opinion through speeches and debates
Voting was done by show of hands or by secret ballots
Слайд 18

Слайд 19

For major decisions the assembly needed about 6,000 people to
vote
According to a Greek writer the government sent slaves to the markets to round up more citizens
Select citizens served on a council to decide which laws should be discussed
Слайд 20

Слайд 21

Athenian Democracy
Citizens gained more power
Athenian democracy reached its height under Pericles
(in 460-429 BC)
It was a direct democracy
Слайд 22

Who was Pericles?
What was democracy like when he was the ruler?
Слайд 23

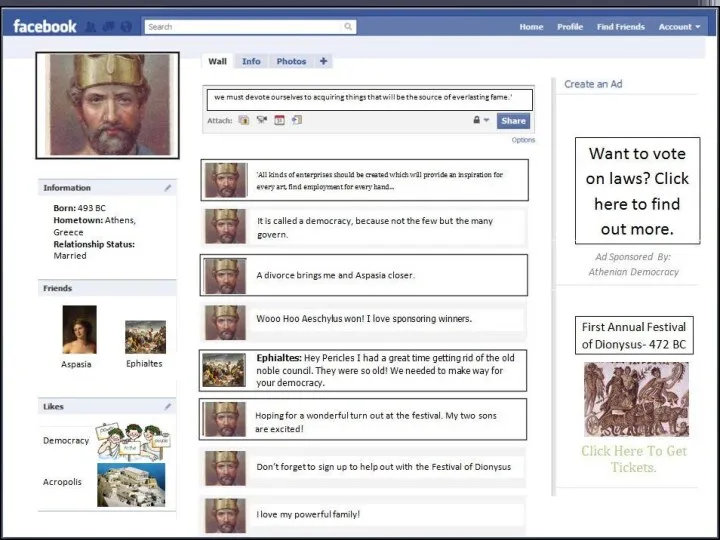
Pericles
Encouraged Athenians to take pride in their city
Encouraged people to participate
in government by paying those who served in public offices or on juries
Encouraged the spread of democracy
Слайд 24
Слайд 25

End of democracy in Athens
Athens was conquered by the Macedonians and
fell under their influence- democracy changed, less power was given to the people
A new king took over (320s BC) and ended democracy
Слайд 26

What kind of democracy did Athens have?
What kind of government
does the
United States of America have?
Слайд 27

How is our government different from the government of Ancient
Athens?
Слайд 28
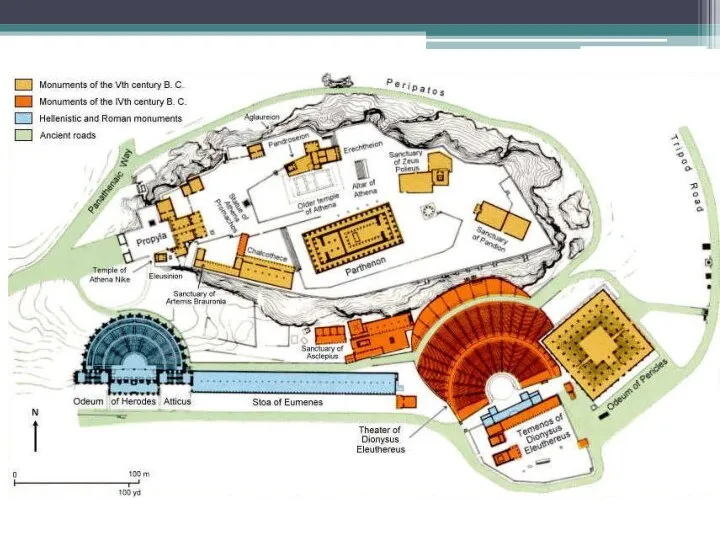
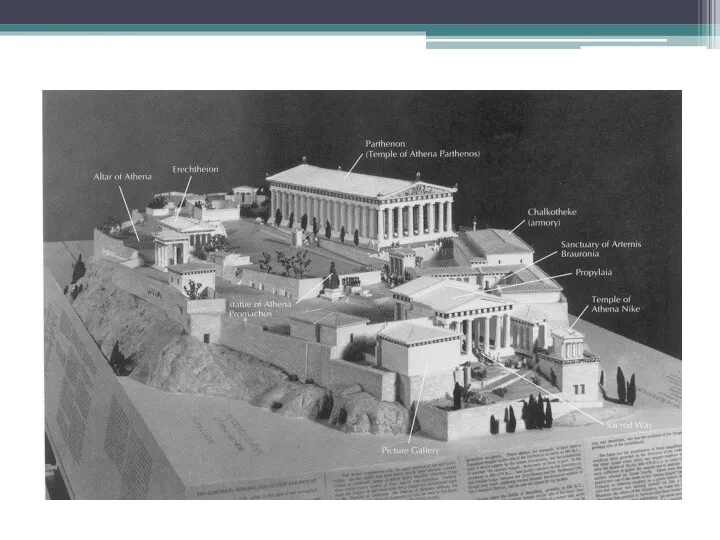
Acropolis
http://www.history.com/topics/classical-greece/videos#deconstructing-history-the-acropolis
Слайд 29

Слайд 30
Слайд 31

Слайд 32
Слайд 33
































 День народного единства
День народного единства Гайдамацький рух
Гайдамацький рух Отдел комплектования и обработки документов Былого незабвенные страницы. Обзор новинок, посвященных теме ВОВ
Отдел комплектования и обработки документов Былого незабвенные страницы. Обзор новинок, посвященных теме ВОВ Архитектура XVIII века
Архитектура XVIII века Союз Советских Социалистических Республик (СССР) в 1920-е годы
Союз Советских Социалистических Республик (СССР) в 1920-е годы Волжские казаки-кавалеристы герои Великой Отечественной войны
Волжские казаки-кавалеристы герои Великой Отечественной войны История Крыма – Таврии
История Крыма – Таврии Становление абсолютной монархии и ее правовое оформление. Государственно-правовые реформы первой четверти XVIII века
Становление абсолютной монархии и ее правовое оформление. Государственно-правовые реформы первой четверти XVIII века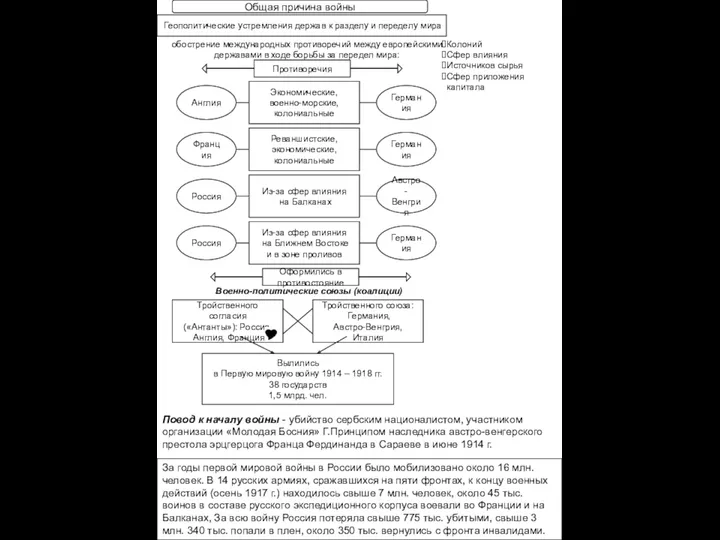 Первая Мировая война. Общая причина войны
Первая Мировая война. Общая причина войны Изобразительное искусство Древней Руси. Мир русской иконы
Изобразительное искусство Древней Руси. Мир русской иконы Они защищали Родину
Они защищали Родину презентация на тему: Дворцовые перевороты
презентация на тему: Дворцовые перевороты Италия мен Германиядағы фашизм
Италия мен Германиядағы фашизм День Защитника Отечества
День Защитника Отечества Україна у період загострення кризи радянської системи. Культурне і духовне життя суспільства
Україна у період загострення кризи радянської системи. Культурне і духовне життя суспільства Город Муром
Город Муром Всеукраїнські турніри юних істориків та правознавців
Всеукраїнські турніри юних істориків та правознавців Сельское хозяйство и положение крестьян в первой половине XIX века
Сельское хозяйство и положение крестьян в первой половине XIX века Річ Посполита. Всесвітня історія. 8 клас
Річ Посполита. Всесвітня історія. 8 клас Юные герои Первой Мировой войны
Юные герои Первой Мировой войны Завоевание Римом Италии.
Завоевание Римом Италии. Презентация Проекты в гуманитарном образовании - работа Ю.А. Кожина (ГБОУ гимназия № 1562 г. Москвы)
Презентация Проекты в гуманитарном образовании - работа Ю.А. Кожина (ГБОУ гимназия № 1562 г. Москвы) Презентация Великобритания. Конец викторианской эпохи 8 класс
Презентация Великобритания. Конец викторианской эпохи 8 класс Земляк-защитник. Визитная карточка
Земляк-защитник. Визитная карточка №4.От якобинской диктатуры к 18 брюмера Наполеона Бонапарта
№4.От якобинской диктатуры к 18 брюмера Наполеона Бонапарта В гаванях афинского порта Пирей
В гаванях афинского порта Пирей Новомученики и исповедники земли Астраханской
Новомученики и исповедники земли Астраханской Культура домонгольской Руси (IX- начала XIII веков)
Культура домонгольской Руси (IX- начала XIII веков)