Содержание
- 2. "Computer" was originally a job title: it was used to describe those human beings (usually women
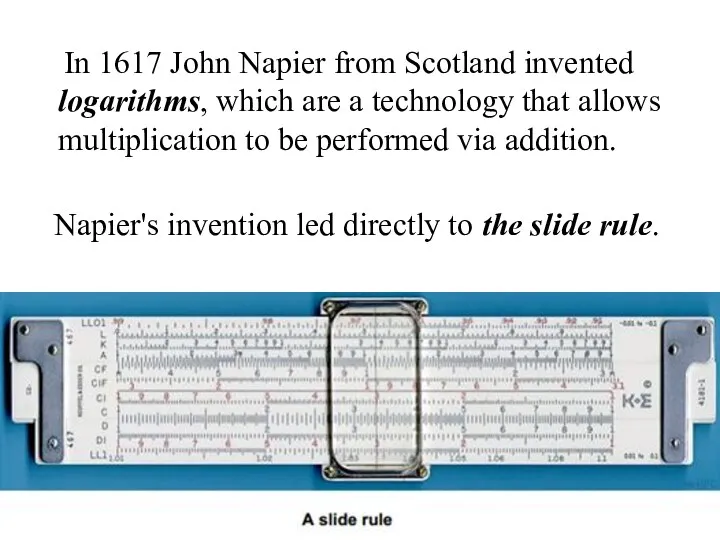
- 4. In 1617 John Napier from Scotland invented logarithms, which are a technology that allows multiplication to
- 5. The Pascaline Blaise Pascal invented it in 1642 , at age 19, to help his father
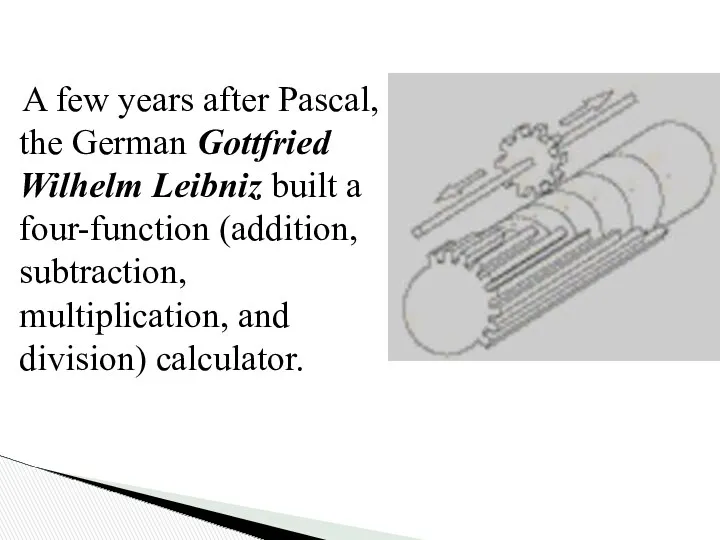
- 6. A few years after Pascal, the German Gottfried Wilhelm Leibniz built a four-function (addition, subtraction, multiplication,
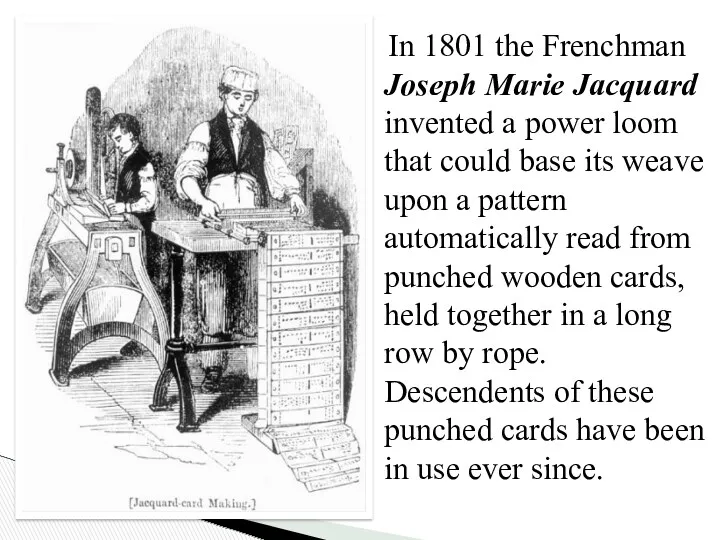
- 7. In 1801 the Frenchman Joseph Marie Jacquard invented a power loom that could base its weave
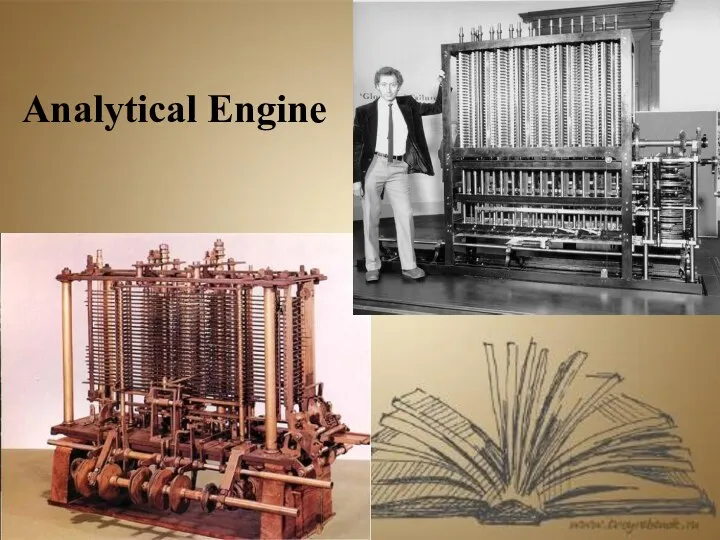
- 9. Charles Babbage, the English mathematician of the 19th century, was the first who conceived the idea
- 10. Analytical Engine
- 11. In 1834 Charles Babbage and Lady Lovelace, Lord Byron's daughter, worked out the first coded program.
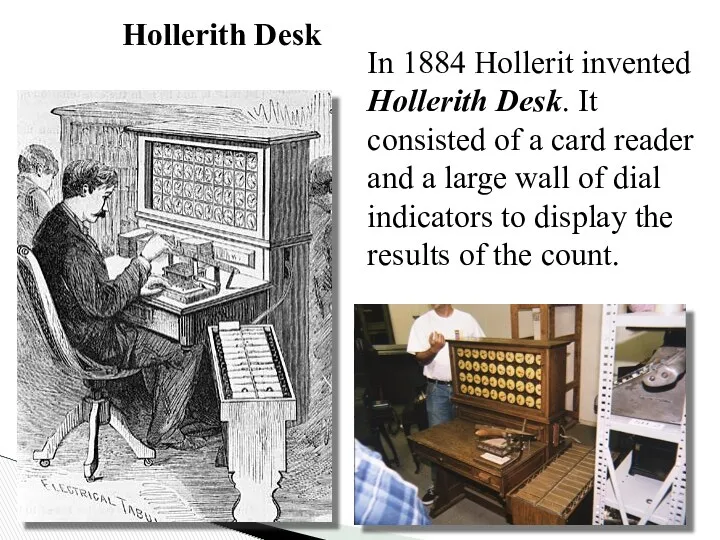
- 12. In 1884 Hollerit invented Hollerith Desk. It consisted of a card reader and a large wall
- 13. The Hollerith census machine was the first machine to ever be featured on a magazine cover.
- 14. Hollerith built a company, the Tabulating Machine Company which eventually became International Business Machines, known today
- 15. In 1937 Dr. H. Aiken of Harvard University began to work at the first completely automatic
- 16. The first electronic computer, the Electronic Numerical Integrator and Calculator (ENIAC) was constructed in 1946 at
- 17. In 1945 John von Neuman worked out the concept of the stored program.
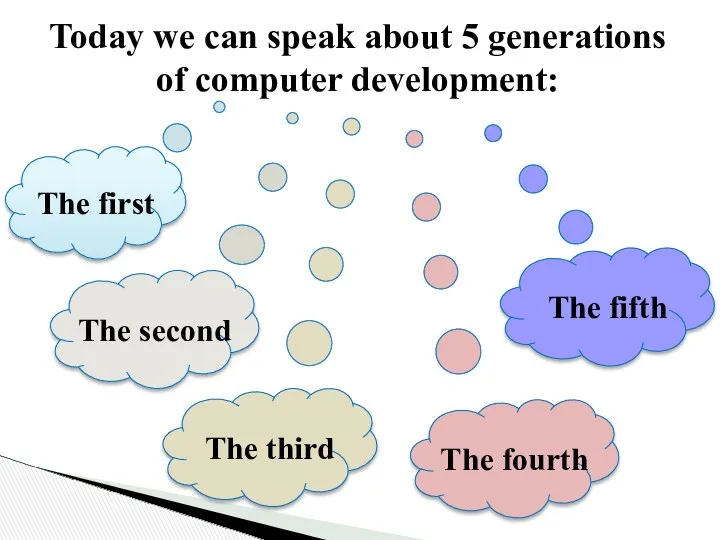
- 18. Today we can speak about 5 generations of computer development: The first The second The third
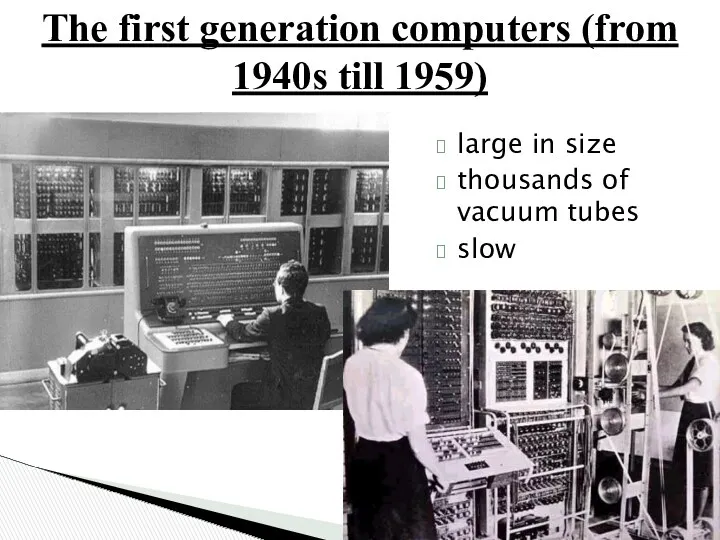
- 19. The first generation computers (from 1940s till 1959) large in size thousands of vacuum tubes slow
- 20. The second generation (began in 1959) use of transistors smaller, more powerful, and more reliable programming
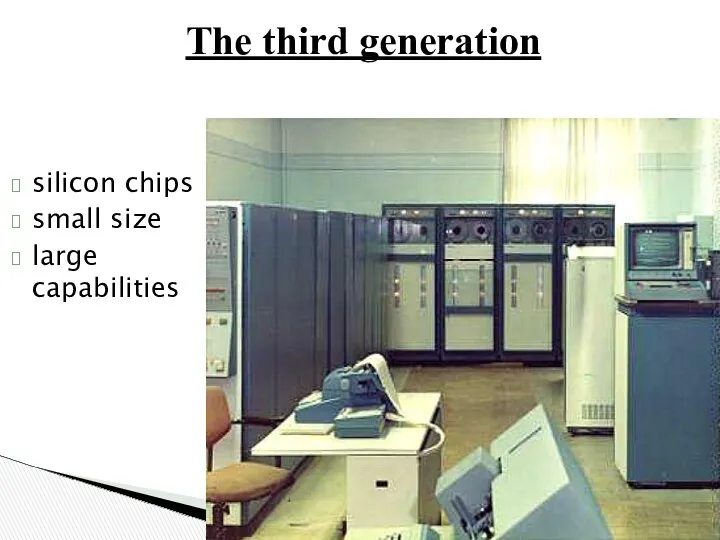
- 21. The third generation silicon chips small size large capabilities
- 22. The fourth generation All computers of the present time, from the microcomputer to the supercomputer
- 25. The fifth generation computer differ in size, speed, and storage capacity artificial intelligence
- 26. natural languages large-scale integration technologies
- 28. Скачать презентацию

















 Интеллектуальная игра к 23 февраля А ну-ка, мальчики!
Интеллектуальная игра к 23 февраля А ну-ка, мальчики! Человек и животные в космосе
Человек и животные в космосе Внутренняя политика Екатерины II
Внутренняя политика Екатерины II Прогулки по Спб. Грифоны.Хмель 4В
Прогулки по Спб. Грифоны.Хмель 4В Основные даты XIX века. Карточки
Основные даты XIX века. Карточки Внешняя политика Павла 1
Внешняя политика Павла 1 Германский оккупационный режим на территории Беларуси в годы ВОВ
Германский оккупационный режим на территории Беларуси в годы ВОВ Царство Древнего Египта
Царство Древнего Египта Культура и искусство в эпоху классицизма в России
Культура и искусство в эпоху классицизма в России Изобразительное искусство Украины XIX ст
Изобразительное искусство Украины XIX ст Окончание Великой Отечественной войны. Берлинская операция
Окончание Великой Отечественной войны. Берлинская операция Международные отношения в 1930-е гг. История. 10 класс
Международные отношения в 1930-е гг. История. 10 класс Опричнина Ивана Грозного
Опричнина Ивана Грозного Герои России — гордость Оренбургской области
Герои России — гордость Оренбургской области СССР после И.В. Сталина
СССР после И.В. Сталина Українська держава
Українська держава Музеи Ульяновска
Музеи Ульяновска Экономика России в первой четверти XVIII века
Экономика России в первой четверти XVIII века Исторические здания моего города
Исторические здания моего города Битва под Москвой
Битва под Москвой Беларусь в первой половине XIX века: общественно-политическое положение и социально- экономическое развитие
Беларусь в первой половине XIX века: общественно-политическое положение и социально- экономическое развитие Франция: Третья республика
Франция: Третья республика Россия в годы правления Александра III Миротворца (1881 – 1894 гг.)
Россия в годы правления Александра III Миротворца (1881 – 1894 гг.) Восстановление народного хозяйства в СССР после ВОВ
Восстановление народного хозяйства в СССР после ВОВ Сталинградская битва (17 июля 1942 - 2 февраля 1943). Фронтовые фотографии
Сталинградская битва (17 июля 1942 - 2 февраля 1943). Фронтовые фотографии Дмитрий Пожарский
Дмитрий Пожарский Установление_Советской_власти_в_Кыргызстане_презент
Установление_Советской_власти_в_Кыргызстане_презент Новое время
Новое время