Содержание
- 2. self introduction name : Gaofeng (chinese) clark(English) age: 38 years old occupation:college instructor education background: double
- 3. rules and suggestions 1.your attendece is very important whether you will pass or fail 2. this
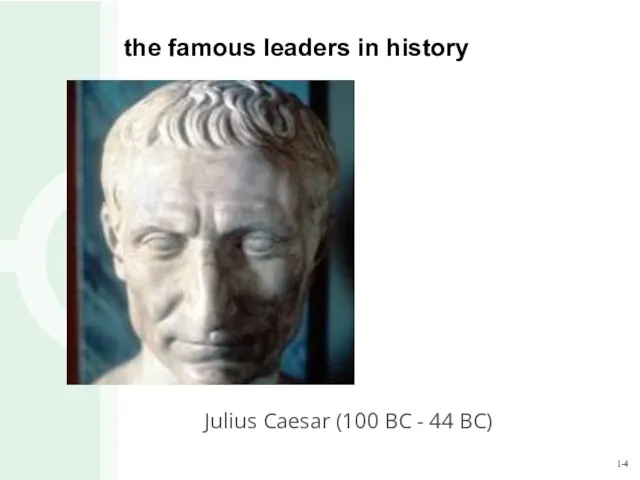
- 4. the famous leaders in history Julius Caesar (100 BC - 44 BC)
- 5. Genghis Khan (c. 1162 - 1227)
- 6. George Washington (1732 - 1799)
- 7. Napoleon Bonaparte (1769 - 1821)
- 8. Mahatma Gandhi (1869 - 1948)
- 9. Vladimir Lenin (1870 - 1924)
- 10. Mao Zedong (1893 - 1976)
- 11. What is Leadership? Leadership is a complex phenomenon involving the leader, the followers, and the situation.
- 12. different perspectives that people study leadership due to its complesxity The process by which an agent
- 13. What is Leadership? (continued) The process of influencing an organized group toward accomplishing its goals. Actions
- 14. the definition of leadership Leadership is the process of influencing an organized group toward achieving its
- 15. Leadership science or art ? what is science and art Some managers may be effective leaders
- 16. Leadership is Both Rational and Emotional Leadership includes actions and influences based on reason and logic
- 17. Leadership is Both Rational and Emotional (continued) Aroused feelings can be used either positively or negatively,
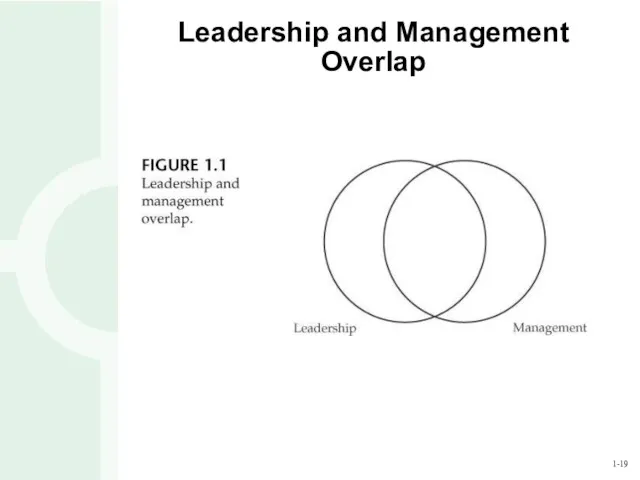
- 18. Leadership and Management Managers: administer maintain control have a short-term view ask how and when imitate
- 19. Leadership and Management Overlap
- 20. Leadership Myths Myth: Good Leadership is All Common Sense Most leadership literature only confirms common sense
- 21. Leadership Myths Myth: Leaders are Born, not Made Many factors and formative experiences influence behavior and
- 22. Leadership Myths Myth: The Only School You Learn Leadership from the School Formal study and experiential
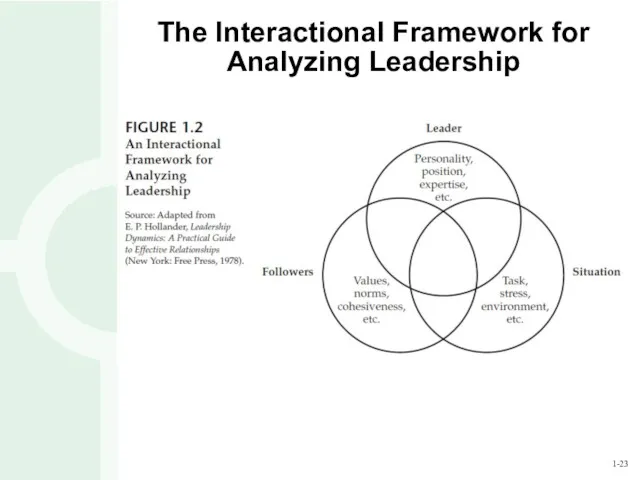
- 23. The Interactional Framework for Analyzing Leadership
- 24. The Interactional Framework for Analyzing Leadership The interactional framework depicts leadership as a function of three
- 25. The Leader Individual aspects of the leadership equation: Unique personal history Interests Character traits Motivation Effective
- 26. The Leader (continued) How leadership status is reached is important. Leaders appointed by superiors may have
- 27. The Followers Both practitioners and scholars stress the relatedness of leadership and followership. Aspects of followers
- 28. The Followers (continued) The leader-follower relationship has undergone dynamic change for many reasons: Increased pressure to
- 29. The Situation Leadership often makes sense only in the context of how the leader and followers
- 30. There is No Simple Recipe for Effective Leadership Leadership must always be assessed in the context
- 31. There is No Simple Recipe for Effective Leadership (continued) The right behavior in one situation is
- 32. Summary Leadership is the process of influencing an organized group toward achieving its goals. Considerable overlap
- 33. homework it was six men of Indostan / To learning much inclined, Who went to see
- 34. it was six men of Indostan / To learning much inclined, Who went to see the
- 35. The Third approached the animal, / And happening to take The squirming trunk within his hands,
- 37. Скачать презентацию































 К 70-летию Курской битвы.
К 70-летию Курской битвы. Древняя Греция III–II тыс. до н.э
Древняя Греция III–II тыс. до н.э Абсолютизм в Испании
Абсолютизм в Испании Правители СССР (4)
Правители СССР (4) Классный час Героями славна земля наша
Классный час Героями славна земля наша History of photography
History of photography Власть и церковь. Церковный раскол
Власть и церковь. Церковный раскол Славянское язычество
Славянское язычество Висло-Одерская операция
Висло-Одерская операция Расцвет русской скульптуры
Расцвет русской скульптуры Русская культура во второй половине XIX века
Русская культура во второй половине XIX века Презентация Политические лидеры СССР, РФ
Презентация Политические лидеры СССР, РФ Восточные славяне в VI – IX вв
Восточные славяне в VI – IX вв Защитники Отечества
Защитники Отечества Герои Великой Отечественной войны села Липовец
Герои Великой Отечественной войны села Липовец Памятники архитектуры. Исторические события
Памятники архитектуры. Исторические события Сухой закон в СССР
Сухой закон в СССР Вводное занятие - 5 класс
Вводное занятие - 5 класс Сценарий исторического вечера Война 12-го года
Сценарий исторического вечера Война 12-го года Наши отцы и деды - защитники Родины
Наши отцы и деды - защитники Родины Искусство Древнего Египта
Искусство Древнего Египта Эпоха эллинизма. От Александра до Цезаря и не только
Эпоха эллинизма. От Александра до Цезаря и не только Эпоха возрождения и гуманизма
Эпоха возрождения и гуманизма Презентация к лекции Незавершенная российская модернизация в контексте всемирной истории (конец Х1Х - начало ХХвека) Диск
Презентация к лекции Незавершенная российская модернизация в контексте всемирной истории (конец Х1Х - начало ХХвека) Диск Эпоха Брежнева в СССР (1964-1982)
Эпоха Брежнева в СССР (1964-1982) Изобретение телефона
Изобретение телефона Система специального образования в Швеции
Система специального образования в Швеции День Славянской письменности
День Славянской письменности