Ukraine under the rule of Russian and Austro-Hungarian monarchy (xviii - beginning of xx century) презентация
Содержание
- 2. The Russian victory in the Battle of Poltava in 1709 freed Tsar Peter I from any
- 3. In 1775 the Zaporozhian Sich was destroyed. By 1782 all the traditional Cossack regiments of the
- 4. Ukrainian people participated together with Russians in the Patriotic War 1812 against the French invaders of
- 5. West Ukrainian territories was under the rule of Austro-Hungarian monarchy. During the 1st half of the
- 6. The Revolution of 1848-1849 in the Habsburg monarchy played a decisive role in the process of
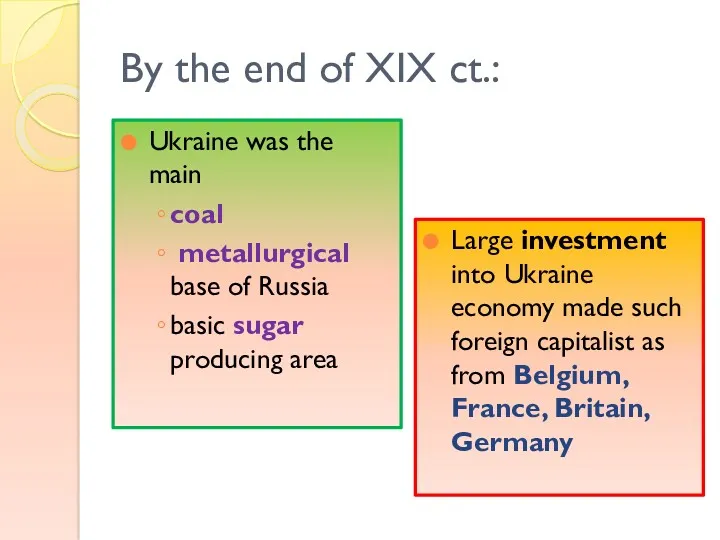
- 7. By the end of XIX ct.: Ukraine was the main coal metallurgical base of Russia basic
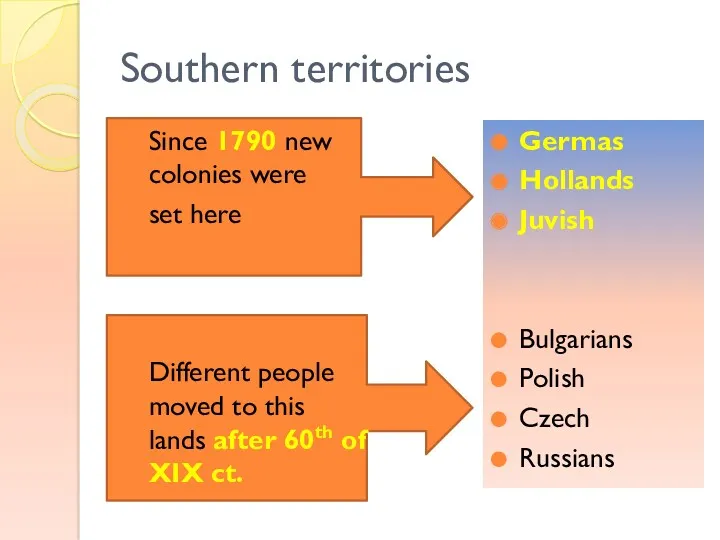
- 8. Southern territories Since 1790 new colonies were set here Different people moved to this lands after
- 9. First Russian Revolution 1905 - 1907 Reasons: Necessity of reformation industry and agricultural complex Results: Reforming
- 10. Beginning of XX ct. – arising of different problems between European states World War I (Great
- 11. Background of the war: Antagonisms between great states Economical imperialism Militarism
- 12. February revolution 1917 results Abdication of Tsar Nicolas II results The collapse of Russian Empire results
- 13. October Revolution 1917 Bolsheviks took the power The end of Monarchy Changes in all spheres of
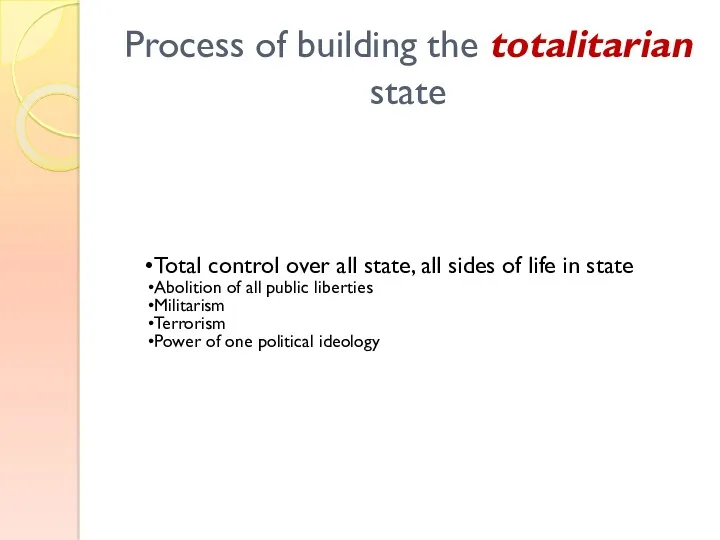
- 14. Process of building the totalitarian state Total control over all state, all sides of life in
- 15. As Bolsheviks came to power a new period of Ukrainian history began. On 17 March 1917
- 16. Central Rada (Tsentralna Rada). At first, an all-Ukrainian center that united political, community, cultural, and professional
- 17. Universals of the Central Rada First Universal (23 June 1917) the CR proclaimed Ukraine's autonomy ‘from
- 18. Second Universal (16 July 1917) reflected the results of the negotiations between the General Secretariat and
- 19. Third Universal 20 November 1917 it proclaimed the creation of the Ukrainian National Republic within a
- 20. Fourth Universal 22 January 1918 was issued after the Ukrainian-Soviet War, 1917–21 began it proclaimed the
- 22. Скачать презентацию
















 Великая степь в истории мировой цивилизации
Великая степь в истории мировой цивилизации История автобусов марки ЗИС
История автобусов марки ЗИС Использование технологии Дебаты на уроках истории
Использование технологии Дебаты на уроках истории Минең өлкән олатайым Бөйөк Ватан һуғышында
Минең өлкән олатайым Бөйөк Ватан һуғышында Непридуманные истории Великой Отечественной войны (1941-1945)
Непридуманные истории Великой Отечественной войны (1941-1945) Культура Древнего Междуречья (Месопотамии)
Культура Древнего Междуречья (Месопотамии) Китай. Своя игра
Китай. Своя игра Культура России в XVIII в
Культура России в XVIII в Эпоха великих реформ в России, в 1860-1870 годы
Эпоха великих реформ в России, в 1860-1870 годы 9 декабря - День Героев Отечества России
9 декабря - День Героев Отечества России Моя Москва.
Моя Москва. День Героев Отечества
День Героев Отечества Сословия в XVII веке: низы общества
Сословия в XVII веке: низы общества Мартин Лютер
Мартин Лютер Group Abu Nidal. Organisation
Group Abu Nidal. Organisation Тема 10. Россия в Новейшее время (XX-XXI). Лекция 14. Мир и Россия на качелях революций и мировых войн в первой половине XX века
Тема 10. Россия в Новейшее время (XX-XXI). Лекция 14. Мир и Россия на качелях революций и мировых войн в первой половине XX века Русская культура XVI века. (10 класс)
Русская культура XVI века. (10 класс) В Риме при императоре Нероне 54-68 гг
В Риме при императоре Нероне 54-68 гг Н.В. Гоголь. Историческая основа повести Тарас Бульба
Н.В. Гоголь. Историческая основа повести Тарас Бульба Мировой экономический кризис
Мировой экономический кризис Октавіан Август
Октавіан Август The language of the British isles
The language of the British isles Великая Отечественная война в воспоминаниях ветеранов
Великая Отечественная война в воспоминаниях ветеранов Российское общество в XVI веке. Служилые и тяглые
Российское общество в XVI веке. Служилые и тяглые Золотой век русской истории: эпоха Екатерины Великой
Золотой век русской истории: эпоха Екатерины Великой Советско-канадские отношения в 1924-1927 годах
Советско-канадские отношения в 1924-1927 годах День славянской письменности и культуры
День славянской письменности и культуры США в XIX-XX веках
США в XIX-XX веках