Содержание
- 2. Plan 1. Cohesive and not-cohesive text. 2. Grammatical cohesion. 3. Lexical cohesion.
- 3. Halliday/Hasan (1976): “Where the interpretation of any time in the discourse requires making reference to some
- 4. The difference between cohesive and not-cohesive text (1) To reach the movie theater you will need
- 7. Reference occurs when one item in text points to another element for its interpretation.
- 8. Examples of exophoric, anaphoric & cataphoric reference: (in a fitting room) Daughter: Mom, what do you
- 9. Personal reference I, you, she, they (subject pronouns), him, her, us (object pronoun), my, your (possessive
- 10. Examples of personal, demonstrative & comparative reference: I never met him before. My friends said that
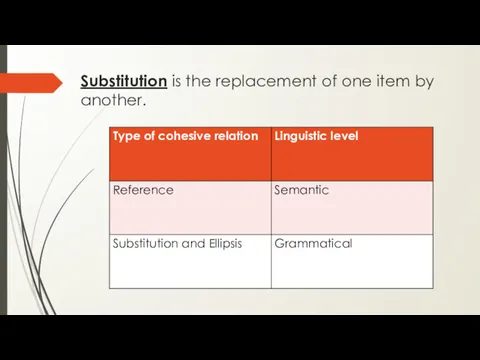
- 11. Substitution is the replacement of one item by another.
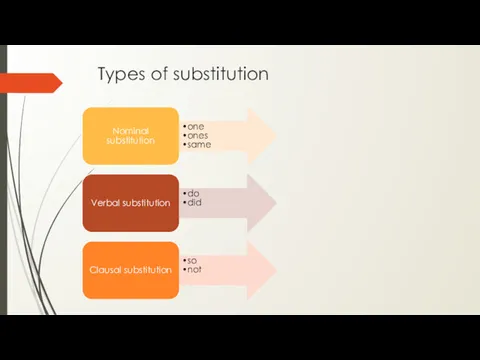
- 12. Types of substitution Nominal substitution one ones same Verbal substitution do did Clausal substitution so not
- 13. Examples of substitution: When I was a kid, I had a kitten but then it lost.
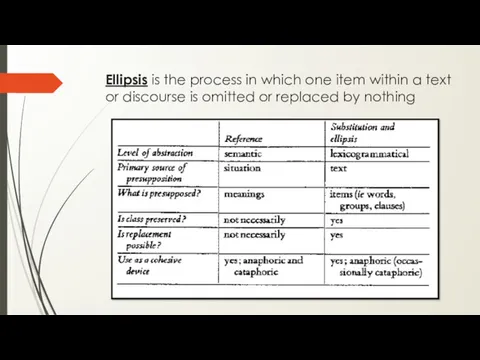
- 14. Ellipsis is the process in which one item within a text or discourse is omitted or
- 15. Find reference, substitution and ellipsis: a. This is a fine hall you have here. I’m proud
- 16. Types of ellipsis nominal (1) They do not like it, yet (they) said nothing. How did
- 17. Conjunction refers to a specification of the way in which what is to follow is systematically
- 18. Example of сonjunctions: Doing work with passion will bear great result. Similarly, doing work professionally will
- 19. Another classification of conjunctions: Simple adverbs for, and, but, or, yet, so accordingly, subsequently, actually therefore,
- 20. Lexical Cohesion reiteration collocation
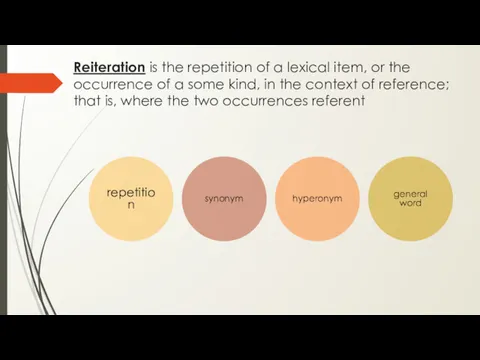
- 21. Reiteration is the repetition of a lexical item, or the occurrence of a some kind, in
- 22. Example of reiteration:
- 23. Identify types of reiteration: I saw a boy in the garden. The boy (_______)was climbing a
- 24. Collocation is the use of “a word that is in some way associated with another word
- 25. Example of collocation: Sing a song of sixpence, a pocket full of rye, Four-and-twenty blackbirds baked
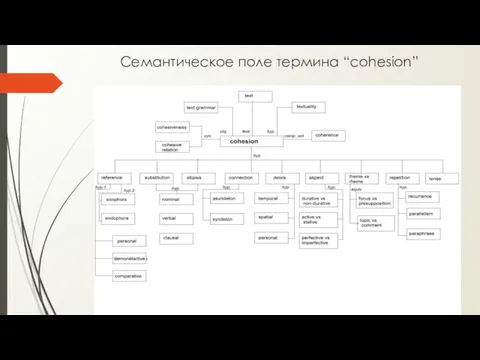
- 26. Cемантическое поле термина “cohesion”
- 27. Conclusion Lexical cohesion is more basic than grammatical cohesion; However, without grammatical cohesion, even coherent discourse
- 29. Скачать презентацию





















 Презентация по английскому языку Slang
Презентация по английскому языку Slang 초급 1A(1-1) 초급1B(1-2) 말하기 연습 01
초급 1A(1-1) 초급1B(1-2) 말하기 연습 01 Лексичні засоби стилістики (лекція 2)
Лексичні засоби стилістики (лекція 2) Японский клуб НСО МГИМО
Японский клуб НСО МГИМО Звук [дж], позначення його буквосполученням дж. Відпрацювання злитої вимови звука [дж]. Урок №187. 1 клас
Звук [дж], позначення його буквосполученням дж. Відпрацювання злитої вимови звука [дж]. Урок №187. 1 клас Учитель Морозова О.Н. Презентация My Pet
Учитель Морозова О.Н. Презентация My Pet Обобщение опыта работы
Обобщение опыта работы Написання великої букви Ї. Письмо складів, слів і речень з вивченими буквами. Урок №81
Написання великої букви Ї. Письмо складів, слів і речень з вивченими буквами. Урок №81 Презентация-игра футбол к уроку Венди и ее семья во 2 классе по УМК Happy English В. П. Кузовлев
Презентация-игра футбол к уроку Венди и ее семья во 2 классе по УМК Happy English В. П. Кузовлев Дієслово: загальне значення, морфологічні ознаки, синтаксична роль
Дієслово: загальне значення, морфологічні ознаки, синтаксична роль Деревья. Названия деревьев на русском и греческом языках
Деревья. Названия деревьев на русском и греческом языках Обобщение опыта КСО и современные информационные технологии как средство развития навыков устной речи
Обобщение опыта КСО и современные информационные технологии как средство развития навыков устной речи Стратегии подготовки к письменному экзамену: аудирование
Стратегии подготовки к письменному экзамену: аудирование Жаңартылған білім беру аясында бастауыш сыныптарда лексиканы үйрету
Жаңартылған білім беру аясында бастауыш сыныптарда лексиканы үйрету Құрмалас сөйлемнің қалыптасу тарихы, дамуы. Құрмалас сөйлемнің түрлері
Құрмалас сөйлемнің қалыптасу тарихы, дамуы. Құрмалас сөйлемнің түрлері Презентация по теме Мой родной город Диск
Презентация по теме Мой родной город Диск Esperanto. Грамматика
Esperanto. Грамматика Прагматические аспекты перевода. (Лекция 7)
Прагматические аспекты перевода. (Лекция 7) презентация- тренажер
презентация- тренажер Презентация по английскому языку Holidays in New Zealand
Презентация по английскому языку Holidays in New Zealand 5 лучших онлайн-переводчиков. 5 лучших онлайн-словарей
5 лучших онлайн-переводчиков. 5 лучших онлайн-словарей Информационный прект Образование в Великобритании и России
Информационный прект Образование в Великобритании и России Суффикс множественного числа
Суффикс множественного числа Конспект урока немецкого языка 5 класс
Конспект урока немецкого языка 5 класс Корейский. 길 찾기
Корейский. 길 찾기 Мультимедийная презентация Система построения уроков иностранного языка на базе ИКТ
Мультимедийная презентация Система построения уроков иностранного языка на базе ИКТ Обобщение изученного материала в начальной школе Рождество в Англии
Обобщение изученного материала в начальной школе Рождество в Англии Фонетические процессы в речевом потоке
Фонетические процессы в речевом потоке