Содержание
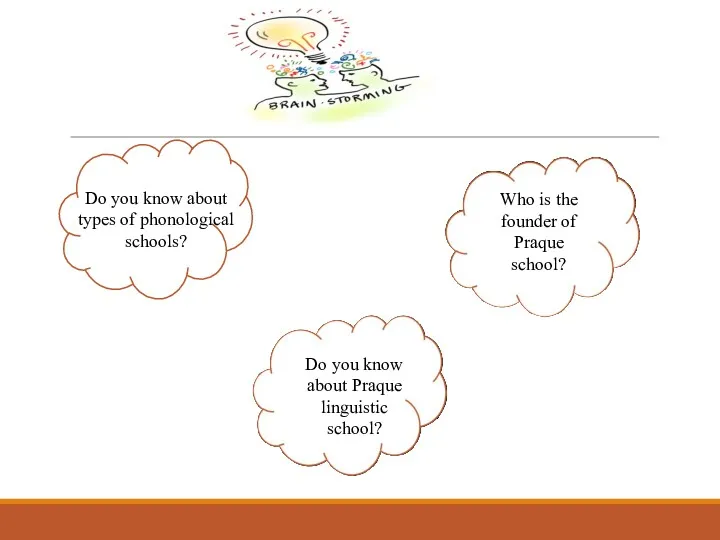
- 2. Do you know about types of phonological schools? Do you know about Praque linguistic school? Who
- 3. Give more information about Praque Phonological School
- 4. Introduction to The Prague School/ (Linguistic Circle of Prague) The Prague School’s Major Contributions: Function in
- 5. 1. Introduction The Prague School (Linguistic Circle of Prague) was established in 1926 by Vilem Mathesius
- 6. Prince Nikolay Sergeyevich Trubetzkoy 1890-1938 Roman Jakobson 1896-1982
- 7. language must be studied as synchronic and as a dynamic system. Language is systemic in that
- 8. 2. The Prague School’s Major Contribution Function in the Prague conception: It was Karl Bühler who
- 9. The cognitive function: It refers to the employment of language in the transmission of factual information.
- 10. The expressive function: It refers to the indication of the mood or attitude of the speaker
- 11. The conative function: It refers to the use for influencing the person one is addressing or
- 12. The Prague School stresses the function of elements within language, their contrast to one another and
- 13. The Theory of Markedness: The notion of markedness was first developed in Prague school phonology but
- 15. Скачать презентацию











 Прикметник та займенник
Прикметник та займенник Презентация SEASONS AND MONTHS
Презентация SEASONS AND MONTHS Дієприкметник як особлива форма дієслова: загальне значення, морфологічні ознаки, синтаксична роль
Дієприкметник як особлива форма дієслова: загальне значення, морфологічні ознаки, синтаксична роль Тестирование как форма учета знаний учащихся при обучении иностранным языкам
Тестирование как форма учета знаний учащихся при обучении иностранным языкам Презентация к уроку 27 во 2 классе
Презентация к уроку 27 во 2 классе Мои первые английские слова
Мои первые английские слова Абайдың атаанасы қандай?
Абайдың атаанасы қандай? Введение в корпусную лингвистику
Введение в корпусную лингвистику планы уроков и презентации Урок немецкого языка в 5 классе (учитель Антипова Надежда Викторовна, Новомихайловская средняя школа). Праздник букваря (Das ABC-Fest) “Miau,miau!”
планы уроков и презентации Урок немецкого языка в 5 классе (учитель Антипова Надежда Викторовна, Новомихайловская средняя школа). Праздник букваря (Das ABC-Fest) “Miau,miau!” Грамматические категории глагола: наклонение и время
Грамматические категории глагола: наклонение и время Еда 食物
Еда 食物 Квантитативная лингвистика
Квантитативная лингвистика RTP/RTCP, RTSP, and RSVP Multimedia protocols for the Internet Jim Chou and Thinh Nguyen
RTP/RTCP, RTSP, and RSVP Multimedia protocols for the Internet Jim Chou and Thinh Nguyen презентация к сценарию Щелкунчик 2 часть Диск Диск
презентация к сценарию Щелкунчик 2 часть Диск Диск Презентация по английскому языку Повторение во 2 классе
Презентация по английскому языку Повторение во 2 классе Службовыя часціны мовы. Злучнік (1)
Службовыя часціны мовы. Злучнік (1) Занятие по китайскому языку. Урок 11
Занятие по китайскому языку. Урок 11 Презентация к уроку по английскому языку по теме: Презентация.Английский язык. English ABC
Презентация к уроку по английскому языку по теме: Презентация.Английский язык. English ABC Let's speak English
Let's speak English Підготовка до ЗНО з української мови
Підготовка до ЗНО з української мови Презентация по теме : Sochi. Olympic Games
Презентация по теме : Sochi. Olympic Games Lições do Português
Lições do Português Future Simple
Future Simple Пунктограми при відокремлених другорядних членах речення
Пунктограми при відокремлених другорядних членах речення Wir stellen Recycling Papier her Диск
Wir stellen Recycling Papier her Диск Computation linguistic
Computation linguistic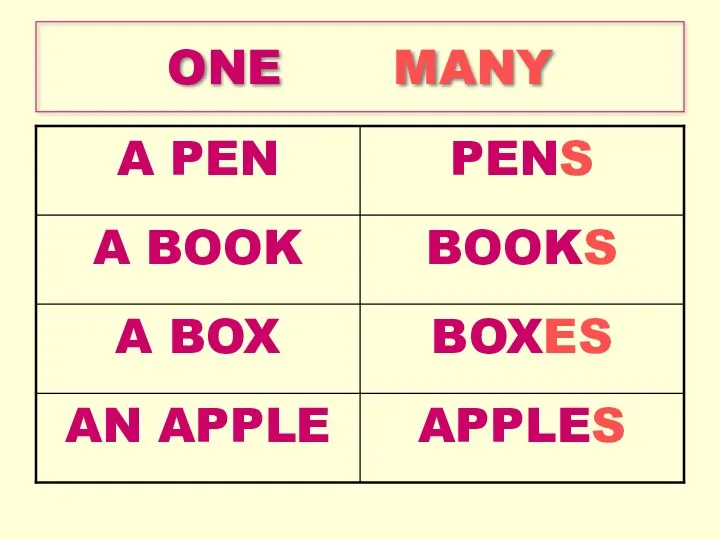 Презентация для учащихся 3 класса One- Many к учебнику Enjoy English
Презентация для учащихся 3 класса One- Many к учебнику Enjoy English Жаңа сөздер
Жаңа сөздер