Содержание
- 2. INTRODUCTION Language is the ability to express one’s thoughts by means of a set of signs,
- 3. Speech Speech is major component of a language Oldest means of communication Levels of speech: 1.
- 4. Perfect TTS Synthesizer Human beings The reading process involves: Seeing, Thinking, Saying, Hearing These are most
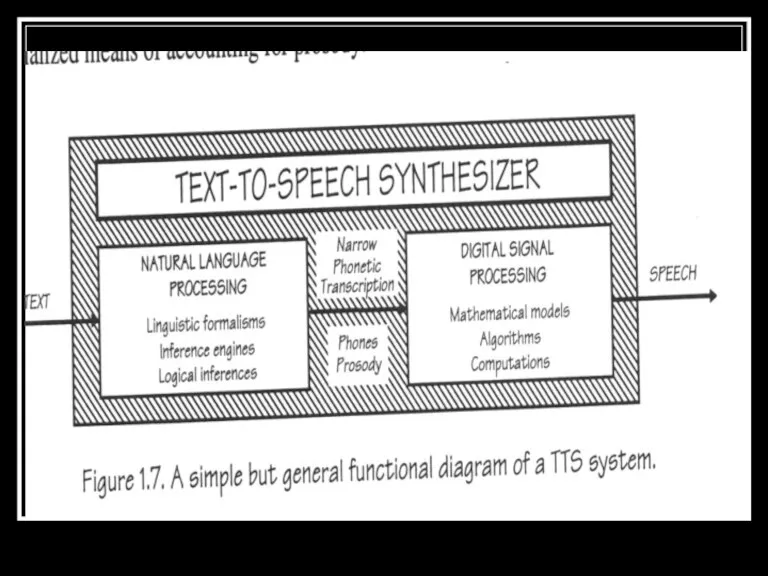
- 5. TTS Synthesizer System A text to speech synthesizer is a computer based system that should be
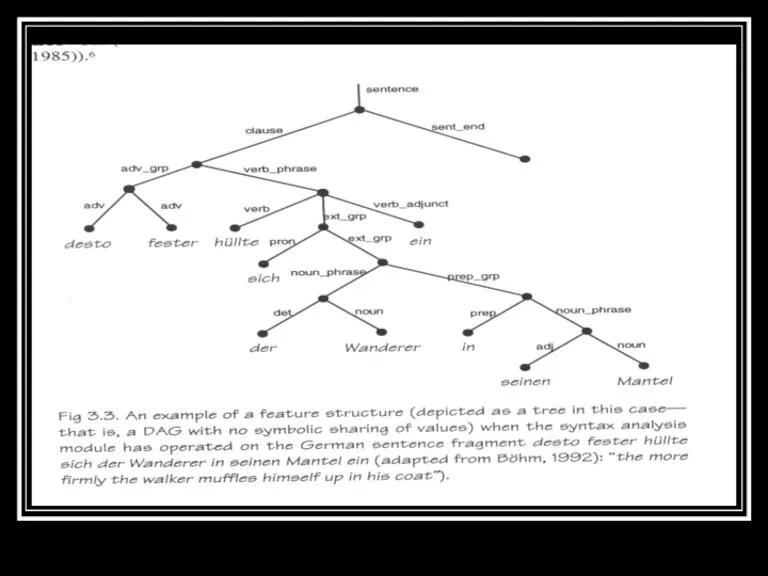
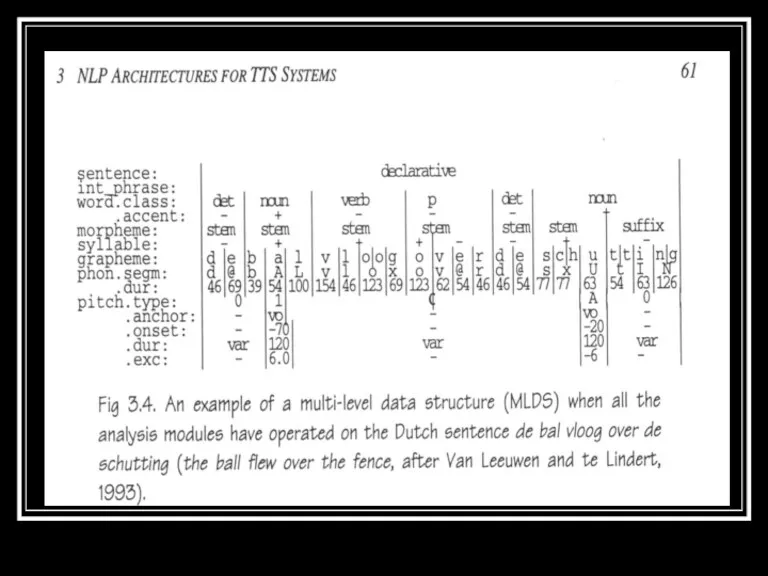
- 6. Feature and Multilevel Data Structures Plays an important role in contemporary TTS systems for Natural Language
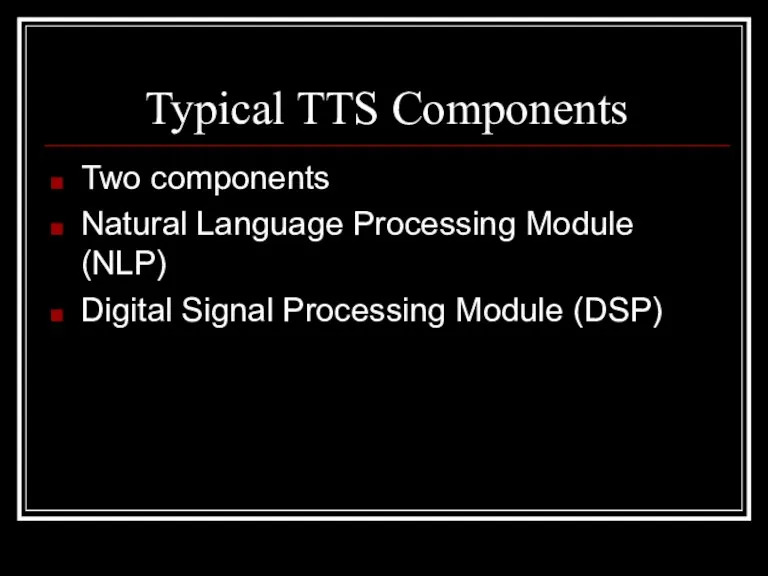
- 9. Typical TTS Components Two components Natural Language Processing Module (NLP) Digital Signal Processing Module (DSP)
- 11. NLP and DSP Modules The NLP module is capable of producing a phonetic transcription of the
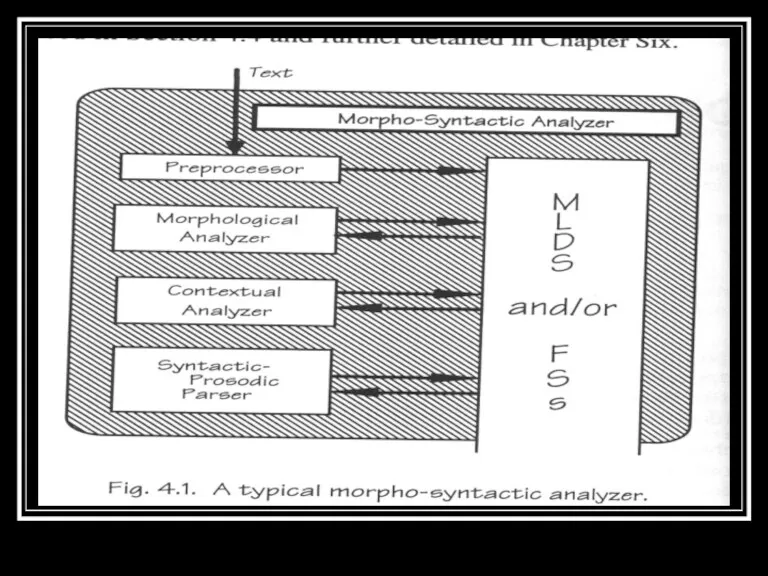
- 12. NLP Module of typical TTS system Text Analyzer (Morpho Syntactic Analysis) Pre-processor Morphological Analyzer Contextual Analyzer
- 15. Preprocessor Takes in texts as strings of ASCII characters Transforms text into Broad Segmentation Units (BSU’s)
- 16. Preprocessor Sentence end detection (semicolon, period – ratio, time and decimal point, sentence ending respectively) Abbreviations
- 17. Morphological Analysis Task is to propose all possible parts of speech categories to each word taken
- 18. Function Words Function words (determiners, pronouns, prepositions, conjunctions..). Can be stored in a lexicon to get
- 19. Content Words Content words- infinite in number Needs Morphology – part of linguistics that describes word
- 20. Contextual Analysis Considers words in their context Reduces the list of their parts of speech categories
- 21. Letter to Sound Module LTS module is responsible for the automatic determination of the phonetic transciption
- 22. Letter to Sound Module Some of the cases to consider Consonants may be reduced or deleted
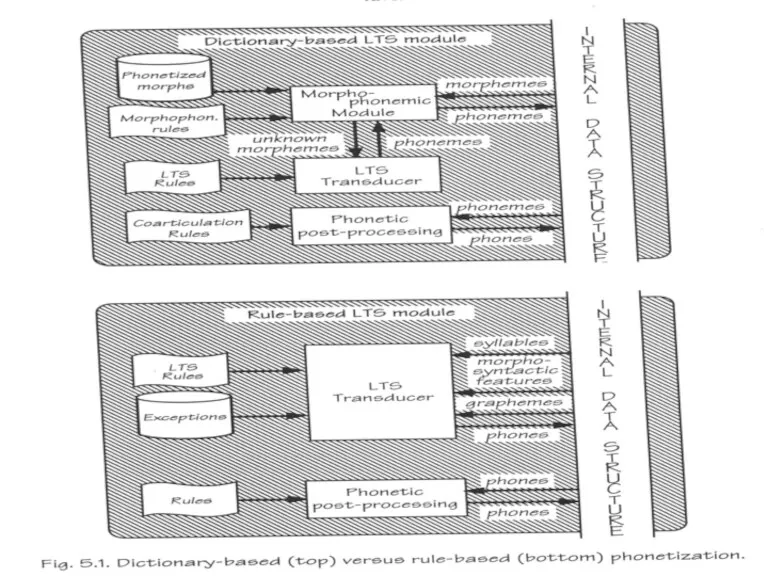
- 23. Two Basic Strategies Dictionary based and Rule-based
- 24. Dictionary Based Dictionary based consist of storing a maximum of phonological knowledge into a lexicon and
- 25. Rule Based Rule based strategy which transfers most of the phonological competence of dictionaries into a
- 26. Dictionary based and Rule based
- 27. Morpho-Phonemic Module in Dictionary based Morphophonology is concerned with phonological changes in the pronunciation of morphemes
- 28. Morpho-Phonemic Module in Dictionary based This module deals with the phonological changes and one distinguishes the
- 29. LTS Transducer This is the key component that transforms graphemes to phones in the rule based
- 30. Phonetic Post Processing In order to increase the intelligibility and the naturalness of synthetic speech, some
- 31. Syntactic Prosodic Parser Prosody refers to certain properties of the speech signal which are related to
- 33. Syntactic Prosodic parser Getting a speech with all those features is impossible. Focuses on obtaining an
- 34. Syntactic Prosodic Parser These prosodic groups are achieved by a recent very crude algorithm termed as
- 35. DSP Module Takes in the narrow phonetic transcription and gives out speech as output
- 36. Why we need TTS system There are several advantages of a high quality text to speech
- 38. Скачать презентацию





























 Правило постановки ударений в латинском языке
Правило постановки ударений в латинском языке Готский язык
Готский язык Как составить рабочую программу по предмету.
Как составить рабочую программу по предмету. Технологическая карта урока немецкого языка во 2-ом классе
Технологическая карта урока немецкого языка во 2-ом классе Части речи в китайском языке
Части речи в китайском языке Planning Birthday Party
Planning Birthday Party Презентация к уроку английского языка в 5 классе. Тема: Appearance and Traits of character
Презентация к уроку английского языка в 5 классе. Тема: Appearance and Traits of character Испанский
Испанский Порядковые числительные
Порядковые числительные Күзгі орманның көріністері. Ана тілі
Күзгі орманның көріністері. Ана тілі Учебное занятие_11кл_Подготовка к ЕГЭ-2015_устная часть
Учебное занятие_11кл_Подготовка к ЕГЭ-2015_устная часть Лучший IT проект Республиканский конкурс Bookworms Christmas Carol
Лучший IT проект Республиканский конкурс Bookworms Christmas Carol Китайский язык. Середина осени
Китайский язык. Середина осени Лингвистические проблемы курса Русский язык
Лингвистические проблемы курса Русский язык Holy places of Krasnenskiy District
Holy places of Krasnenskiy District Зв’язок слів у реченні. Урок №159
Зв’язок слів у реченні. Урок №159 Урок 40-41_Учимся читать
Урок 40-41_Учимся читать Публичный доклад по теме Система работы с одаренными детьми
Публичный доклад по теме Система работы с одаренными детьми Концептуальные основы научных исследований по теории и методике обучения ИЯ
Концептуальные основы научных исследований по теории и методике обучения ИЯ Прямое дополнение – второстепенный член предложения
Прямое дополнение – второстепенный член предложения We Learn Reading “Now let’s learn how to write this sound (– show them the way of writing the letter). Then I say,” Let’s do it together” and trace the letter and pronounce the letter sound. Do it several tim
We Learn Reading “Now let’s learn how to write this sound (– show them the way of writing the letter). Then I say,” Let’s do it together” and trace the letter and pronounce the letter sound. Do it several tim История латинского языка. Алфавит. Правила чтения
История латинского языка. Алфавит. Правила чтения Сказка на английском языке Репка
Сказка на английском языке Репка Разработка урока в 3 классе How to write an address on the envelope
Разработка урока в 3 классе How to write an address on the envelope Презентация к обобщающему уроку английского языка в 4 классе по теме: Жизнь в городе и селе.
Презентация к обобщающему уроку английского языка в 4 классе по теме: Жизнь в городе и селе. Комплекси
Комплекси If you are tired at the English lesson
If you are tired at the English lesson Современные школы семиотики
Современные школы семиотики