Содержание
- 2. 2. English Literature Introductory Course. The Theory of Literature 3. American Literature
- 3. To introduce students to a variety of literary works Formal GOAL To help students to learn
- 4. To define worthwhile literary works/ literature Informal GOAL
- 5. worthwhile vs. worthless
- 6. creates a lasting impression worthwhile literature may be provocative, beautiful, uncanny, meaningful, reverberating long after the
- 7. leaves your head the moment you finish it worthless literature once you finish reading immediately start
- 8. stretches the readers’ imagination worthwhile literature We like to use our imagination!
- 9. does not stretch your imagination worthless literature predictable, stale, easily anticipated, nothing new.
- 10. presents an aesthetically pleasing experience worthwhile literature We may be stunned by the work’s “beauty”, its
- 11. does not strike the reader as beautiful in any way worthless literature
- 12. worthwhile vs. worthless worthwhile Creates a lasting impression Stretches the readers’ imagination Presents an aesthetically pleasing
- 13. Fiction
- 14. 1. Plot 2. Setting 3. Characterization 4. Theme 5. Point of View 6. Symbolism 7. Style
- 15. 1. Plot 2. Setting 3. Characterization 4. Theme 5. Point of View 6. Symbolism 7. Style
- 16. Plot refers to the sequence of events which give focus to a story and which shape
- 17. Plot = story line = plotline = narrative structure
- 18. Plot is a guiding principle for the author and an ordering control for the reader
- 19. A plot in a story can take a number of forms 1) traditional straightline plot 2)
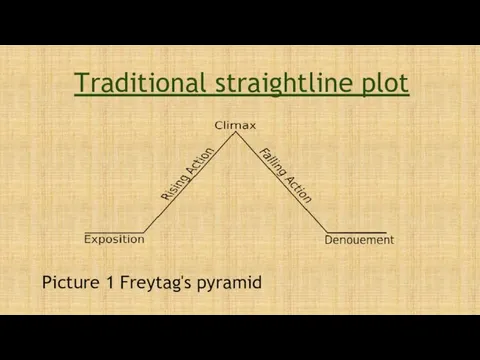
- 20. Traditional straightline plot moves chronologically from beginning to end as things happen one after another
- 21. Traditional straightline plot Picture 1 Freytag's pyramid
- 22. Modern plot techniques which may move forward and back through the storyline as a story progresses
- 23. Modern plot techniques flashback and foreshadowing
- 24. 1. Plot 2. Setting 3. Characterization 4. Theme 5. Point of View 6. Symbolism 7. Style
- 25. Setting refers to the where and the when of a literary work time and place !!!!!!!
- 26. 1. Plot 2. Setting 3. Characterization 4. Theme 5. Point of View 6. Symbolism 7. Style
- 27. Characterization is the process by which a writer brings the characters in a story to life
- 28. Characters According to the development of these traits in the process of a story According to
- 29. According to the number of traits a character possesses flat (can be summed up by one
- 30. According to the development of characters in the process of a story static (remaining the same
- 31. 1. Plot 2. Setting 3. Characterization 4. Theme 5. Point of View 6. Symbolism 7. Style
- 32. Theme is its meaning, its central insight, concept, controlling idea
- 33. 1. Plot 2. Setting 3. Characterization 4. Theme 5. Point of View 6. Symbolism 7. Style
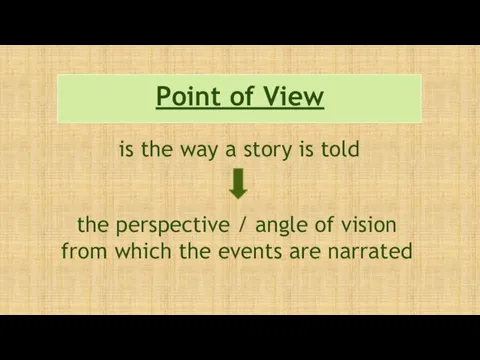
- 34. Point of View is the way a story is told the perspective / angle of vision
- 35. sometimes the author tells the story sometimes the characters do sometimes the narrator knows all about
- 36. ? Who is telling the story? How much is the character able to know?
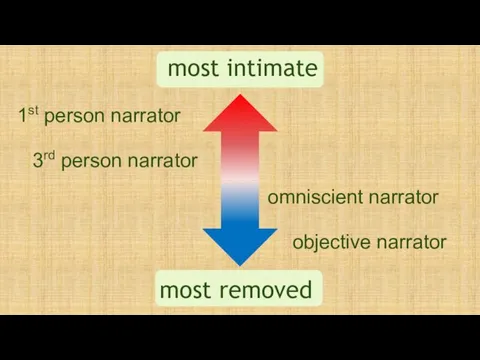
- 37. most intimate most removed 1st person narrator 3rd person narrator omniscient narrator objective narrator
- 38. 1st person narrator - “I” the author writes from inside of the characters as a participant
- 39. 3rd person narrator - “s/he” the author becomes a non-participant, moving to the side of and
- 40. omniscient narrator the author is a non-participant again, but is able to see into and have
- 41. objective narrator the author writes from the objective perspective (the writer disappears entirely and becomes a
- 42. 1. Plot 2. Setting 3. Characterization 4. Theme 5. Point of View 6. Symbolism 7. Style
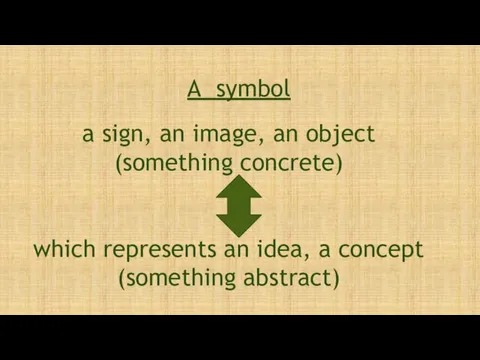
- 43. A symbol a sign, an image, an object (something concrete) which represents an idea, a concept
- 44. Traditional symbols
- 45. Literary symbols
- 46. Poetry
- 47. Poets try to say the most in the fewest words (S.Lyne)
- 49. Скачать презентацию










































 Поэты пушкинской поры Диск
Поэты пушкинской поры Диск Народное страдание и скорбь в поэме А.Ахматовой Реквием
Народное страдание и скорбь в поэме А.Ахматовой Реквием Татар теленнән лексик КВН
Татар теленнән лексик КВН Книги Дмитрия Сергеевича Лихачёва (1906 — 1999)
Книги Дмитрия Сергеевича Лихачёва (1906 — 1999) Презентация по чтению для 1 класса Специальные знаки.
Презентация по чтению для 1 класса Специальные знаки. Поэзия сердца
Поэзия сердца Агафонова Наталія Володимирівна
Агафонова Наталія Володимирівна Священномученик Андроник, архиепископ Пермский и Кунгурский
Священномученик Андроник, архиепископ Пермский и Кунгурский О подвигах, о доблести, о славе
О подвигах, о доблести, о славе Фабула или пересказ содержания. Жак Лурселль. Авторская энциклопедия фильмов
Фабула или пересказ содержания. Жак Лурселль. Авторская энциклопедия фильмов Мой кумир Ильин Илья Александрович
Мой кумир Ильин Илья Александрович Урок по чувашскому языку Кун йĕрки
Урок по чувашскому языку Кун йĕрки Әҙәби уҡыу дәрестәренә эштәр
Әҙәби уҡыу дәрестәренә эштәр Родная природа в стихотворениях поэтов ХХ века
Родная природа в стихотворениях поэтов ХХ века Даниэль Дефо (ок.1660- 1731)
Даниэль Дефо (ок.1660- 1731) Развитие дизайна и его значение в жизни современного общества
Развитие дизайна и его значение в жизни современного общества Презентация к вводному уроку литературы в 10 классе
Презентация к вводному уроку литературы в 10 классе Дитрих Букстехуде
Дитрих Букстехуде презентация к уроку чтения И.Суриков Детство
презентация к уроку чтения И.Суриков Детство Оформление списка литературы и источников. 10 класс
Оформление списка литературы и источников. 10 класс В світі казки чарівної
В світі казки чарівної Нововавилонское царство
Нововавилонское царство Истоки теории Родиона Раскольникова в романе Ф.М. Достоевского Преступление и наказание. 10 класс
Истоки теории Родиона Раскольникова в романе Ф.М. Достоевского Преступление и наказание. 10 класс Сергей Есенин. Подготовка к ЕГЭ, задания В8-В12, С3-С4
Сергей Есенин. Подготовка к ЕГЭ, задания В8-В12, С3-С4 Амедео Модильяни
Амедео Модильяни Лев Толстой Война и мир 1 том
Лев Толстой Война и мир 1 том О.Е. Клер
О.Е. Клер Литература Серебряного века
Литература Серебряного века