Слайд 2
Heinrich Hermann Robert Koch (it. Heinrich Hermann Robert Koch; December 11, 1843, Clausthal
- Zellerfeld - may 27, 1910, Baden-Baden) - German microbiologist. Opened the Bacillus of anthrax, Vibrio cholerae and the tubercle Bacillus. For research of tuberculosis awarded the Nobel prize in physiology or medicine in 1905.

Слайд 3
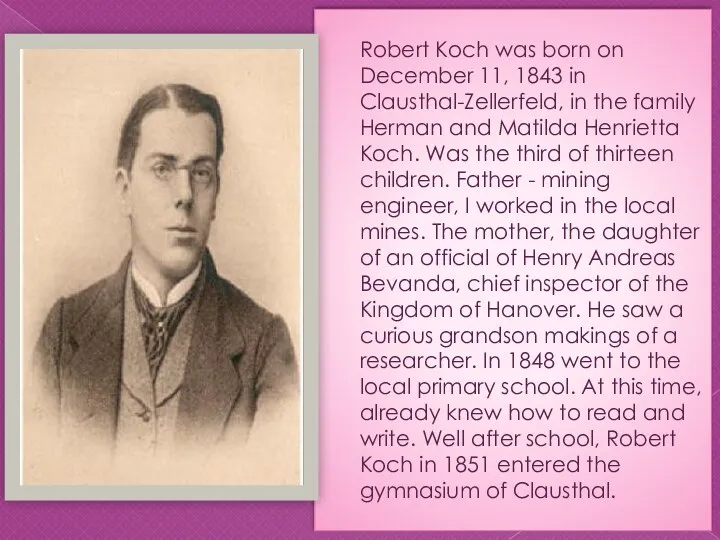
Robert Koch was born on December 11, 1843 in Clausthal-Zellerfeld, in the family
Herman and Matilda Henrietta Koch. Was the third of thirteen children. Father - mining engineer, I worked in the local mines. The mother, the daughter of an official of Henry Andreas Bevanda, chief inspector of the Kingdom of Hanover. He saw a curious grandson makings of a researcher. In 1848 went to the local primary school. At this time, already knew how to read and write. Well after school, Robert Koch in 1851 entered the gymnasium of Clausthal.
Слайд 4
In 1862 Koh graduated from high school and then arrives at the famous
scientific traditions of the Gottingen University. There he studies physics, botany, and then and medicine. The most important role in shaping the interest of the future of the great scientist to research played many of his professors, including anatomist Jacob Henle, physiologist Georg Meissner and Clinician Charles of Hesse. Гёттингенский университет имени Георга-Августа

Слайд 5
In 1866 Robert finished her studies in the University and receive a diploma.
From this time he starts working in various hospitals, and at the same time, unsuccessfully trying to organize a private practice in five different cities of Germany. Later he wants to become a military doctor or to travel around the world as a ship's doctor, while finally are not established in the city Require, where he began his medical practice as an assistant in the hospital for the insane. In 1867, he married Emma Adelfina Josephine Fraz.

Слайд 6
In 1870 begins the Franco-Prussian war, and work Koch in the hospital is
interrupted. Koh voluntarily becomes a doctor field hospital, in spite of strong short-sightedness. The new service, he gets a big practical experience in dealing with the treatment of infectious diseases, in particular cholera and typhoid. At the same time studying under a microscope algae and large microbes, improving his skills in microphotography.

Слайд 7
In 1871 Koch was demobilized. On dvadtsatisemiletny wife presented him with a microscope,
and since then Robert whole days spent at him. He loses all interest in private medical practice, and began to carry out research and experiments, which gets a large number of mice. In 1872 Koch is assigned to the district health officer in Wolstein. He found that around Volshteyna among cattle and sheep disseminated endemic disease, anthrax, which affects the lungs, causes carbuncles skin and change the lymph nodes.

Слайд 8
In 1881 Koch publishes the work "Methods of study of pathogenic organisms" ("Methods
for the Study of Pathogenic Organisms"), which describes a method of growing microbes on firm nutrient mediums. This method was essential to isolate and study the pure bacterial cultures. After that, between Koch and Pasteur - until this time leader in Microbiology - a fierce debate. After Koh published a highly critical reviews of the Pasteur research anthrax, leadership last staggered, and between the two outstanding scientists flashes enmity lasting several years. All this time they are locked in bitter disputes and discussions on the pages of magazines and in public speeches.

Слайд 9
TUBERCULOSIS.
Later Koch attempts to find the cause of tuberculosis, the disease at the
time of widespread and is the primary cause of death. The proximity of the clinic Charite , filled tuberculosis patients that makes it a task - it daily, early morning comes to the hospital where he receives material for research: a small amount of sputum or a few drops of blood of patients with tuberculosis. The Institute of Microbiology at Dorotheenstrasse in Berlin - here Robert Koch discovered the cause of tuberculosis.
Mycobactérium tuberculósis, Koch's Bacillus (ILO, BK)- type of mycobacteria described March 24, 1882 Robert Koch (March 24, who declared the world day against tuberculosis).

Слайд 10
In 1885 Koch became a Professor at the University of Berlin and Director
of the newly created Institute of hygiene. At the same time he continues the research of tuberculosis, focusing on finding ways to treat the disease.

Слайд 11
AWARDS.
In 1905, for "research and discoveries concerning the treatment of tuberculosis", Robert
Koch awarded the Nobel prize in physiology or medicine. In his Nobel lecture laureate said that if we look back at the path, "which has been passed in recent years in the fight against such widespread diseases as tuberculosis, we cannot fail to admit that there were taken the first important steps.











 Пушкинское поэтическое эхо
Пушкинское поэтическое эхо Ф. И. Тютчев Весенние воды
Ф. И. Тютчев Весенние воды И. А. Крылов
И. А. Крылов Cecilia Payne (1900-1979)
Cecilia Payne (1900-1979) Урок литературного чтения. Тема: В.Высоцкий Он не вернулся из боя, С.Баруздин Страшный клад.
Урок литературного чтения. Тема: В.Высоцкий Он не вернулся из боя, С.Баруздин Страшный клад. Александр Александрович Блок (1880- 1921)
Александр Александрович Блок (1880- 1921) А.Н. Некрасов. Несжатая полоса, Размышления у парадного подъезда, Вчерашний день, часу в шестом…
А.Н. Некрасов. Несжатая полоса, Размышления у парадного подъезда, Вчерашний день, часу в шестом… Наталія Королевська
Наталія Королевська Сравнительных психологический анализ героев произведения А.Н. Островского Гроза. Тихон и Катерина
Сравнительных психологический анализ героев произведения А.Н. Островского Гроза. Тихон и Катерина Повір у себе. Леся Мовчун Арфа для павучка (продовження). Урок №101
Повір у себе. Леся Мовчун Арфа для павучка (продовження). Урок №101 Высказывания известных писателей о космосе
Высказывания известных писателей о космосе Национальные цветовые символы России в цикле И.С. Шмелева Родное на материале рассказов Роcстани, Как я стал писателем
Национальные цветовые символы России в цикле И.С. Шмелева Родное на материале рассказов Роcстани, Как я стал писателем Презентация Приемыш
Презентация Приемыш Пою тебя, мой край родной. Валентин Викторович Зайцев
Пою тебя, мой край родной. Валентин Викторович Зайцев Изображение мира чиновничества в поэме Н.В.Гоголя Мертвые души (урок литературы, 9 класс)
Изображение мира чиновничества в поэме Н.В.Гоголя Мертвые души (урок литературы, 9 класс) Моя любимая сказка
Моя любимая сказка Презентация детского литературного творчества по пейзажной лирике. Написание синквейнов по теме Весна
Презентация детского литературного творчества по пейзажной лирике. Написание синквейнов по теме Весна Основные мотивы творчества А.А. Фета
Основные мотивы творчества А.А. Фета Первый отряд космонавтов СССР
Первый отряд космонавтов СССР 21 нче февраль - Халыкара туган тел көне
21 нче февраль - Халыкара туган тел көне Робинзон Крузо
Робинзон Крузо Конспект урока и презентация по теме Искусство Великого Новгорода в 10 классе
Конспект урока и презентация по теме Искусство Великого Новгорода в 10 классе Игорь Северянин и его современники
Игорь Северянин и его современники Джек Лондон. Моряк в седле
Джек Лондон. Моряк в седле Обобщающий урок по литературе для 6 класса
Обобщающий урок по литературе для 6 класса А.П. Чехов
А.П. Чехов Шоқан Уәлиханов қазақтың аса көрнекті ғалымы әрі ағартушысы
Шоқан Уәлиханов қазақтың аса көрнекті ғалымы әрі ағартушысы التهيئة mp4قام االتحاد
التهيئة mp4قام االتحاد