Слайд 2

Brief Biography
Born in February 11, 1847 in Milan, Ohio
Born as the
youngest of the seven children
Moved to Port Huron, Michigan at age 7
Did very poorly in school; teachers believed that he was stupid and had learning disability so his mother decided to home school him
Слайд 3

Brief Biography
As his mother home schooled him, he slowly began to
take interest in chemistry
During his childhood, Edison spent most of his time reading scientific and technical books
He learned how to operate a telegram in a young age
At age sixteen, he was skilled enough to become a telegrapher
Слайд 4
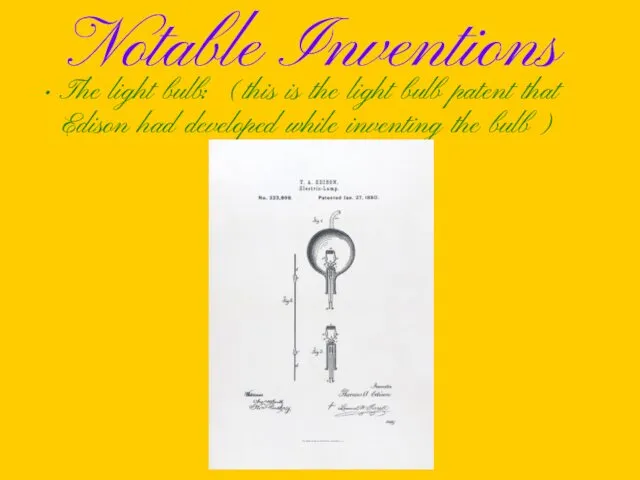
Notable Inventions
The light bulb: (this is the light bulb patent that
Edison had developed while inventing the bulb)
Слайд 5

Notable Inventions: Light Bulbs
Contrary to popular belief, Edison didn’t really invent
the electric light bulb. However, he was credited for inventing incandescent light.
The first test of his light bulb took place in 1879.
Much of Edison’s earliest light bulbs had many flaws. They burned out shortly, were very expensive, and had higher electric current drawn.
These factors made the bulbs difficult to apply on a large scale commercially.
Below is one of Edison’s earliest light bulbs produced. This light bulb was the carbon-filament.
Слайд 6

Notable Inventions: Light bulb
Edison tried to improve these factors. He finally
made his light bulbs high resistance lamps that are capable of withstanding very high vacuum. This helped produce better lighting and lasted longer than his earliest bulbs.
In 1878, Edison developed his own electric company with his financers. A year later, he publicly demonstrated how his light bulb worked. During this time he famously said “We will make electricity so cheap that only the rich will burn candles.”
Слайд 7
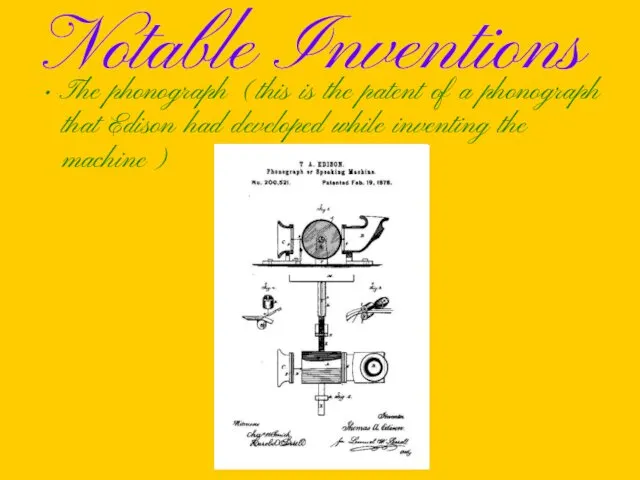
Notable Inventions
The phonograph (this is the patent of a phonograph that
Edison had developed while inventing the machine)
Слайд 8

Notable Inventions: Phonograph
As the first inventor of the phonograph, Thomas Edison
had achieved the principle of recording and reproducing sound.
Before his achieved his fame for the light bulb, Edison initially focused on telegraphic devices like the phonograph.
The first phonograph that he invented was recorded in a tinfoil around a grooved cylinder.
This gave the phonograph a very poor sound quality.
Слайд 9

Notable Inventions: Phonograph
To improve better sound quality for the phonograph, Edison
concentrated more on the cylinder part of the phonograph since he believed that this provided more sound.
The invention of the phonograph had received a lot of attention from the public media. People began to use Edison’s phonographs to listen to music. By the 1890s, most American cities had at least one phonograph parlor.
Слайд 10
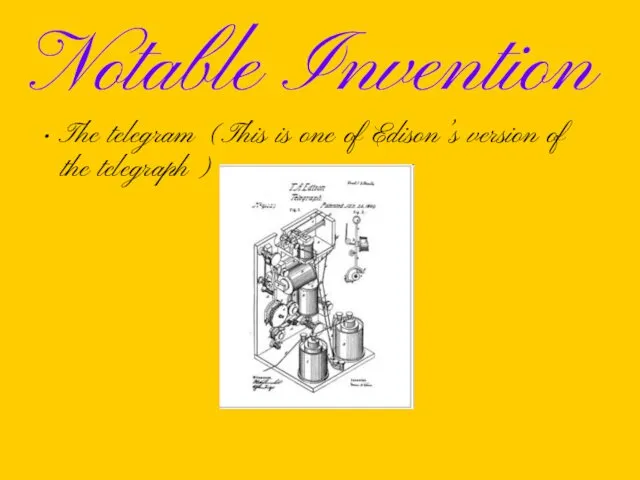
Notable Invention
The telegram (This is one of Edison’s version of the
telegraph)
Слайд 11
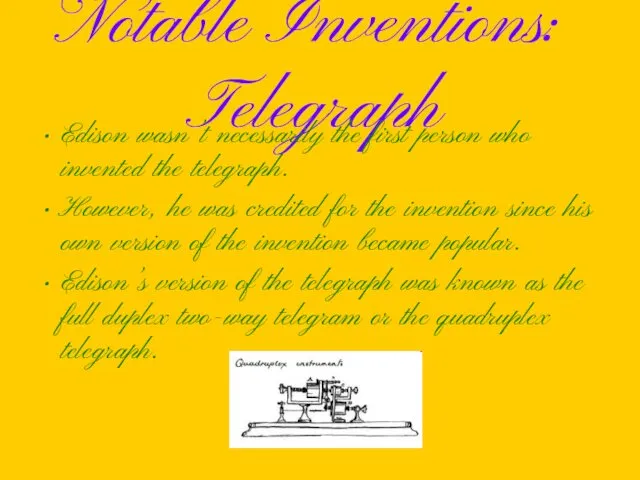
Notable Inventions: Telegraph
Edison wasn’t necessarily the first person who invented the
telegraph.
However, he was credited for the invention since his own version of the invention became popular.
Edison’s version of the telegraph was known as the full duplex two-way telegram or the quadruplex telegraph.
Слайд 12

Notable Inventions: Telegraph
The quadruplex telegraph allowed users to send four separate
signals to be transmitted and received at the same time. The signals goes by two directions.
Edison’s version of the telegraph didn’t succeed commercially due to a major problem of unable to send two signals simultaneously in opposite directions on the same wire.
However, other inventors like Julius Wilhelm Gintl and J.B. Stearns were able to solve the problem.











 Ф.И.Тютчев стихотворение Ноябрь
Ф.И.Тютчев стихотворение Ноябрь Шаинский Владимир Яковлевич
Шаинский Владимир Яковлевич Образ Гобсека у повісті О. де Бальзака
Образ Гобсека у повісті О. де Бальзака Басня. Особенности и история жанра. Проектная работа
Басня. Особенности и история жанра. Проектная работа Презентация Сказки Пушкина.
Презентация Сказки Пушкина. Людвиг ван Бетховен. Песня Сурок
Людвиг ван Бетховен. Песня Сурок Защитники земли русской. От богатырей к Александру Невскому. Открытый урок внеклассного чтения в 3 классе.
Защитники земли русской. От богатырей к Александру Невскому. Открытый урок внеклассного чтения в 3 классе. Презентация Направления и темы сочинения 2015 Тазиева Л.Ш.
Презентация Направления и темы сочинения 2015 Тазиева Л.Ш. Поэзия Серебряного века
Поэзия Серебряного века 200 лет со дня рождения М.Ю.Лермонтова
200 лет со дня рождения М.Ю.Лермонтова Ауыз әдебиеті мен поэзия
Ауыз әдебиеті мен поэзия Лара Фабиан
Лара Фабиан Тема праведничества в повести Н.С.Лескова Очарованный странник
Тема праведничества в повести Н.С.Лескова Очарованный странник Сравнение литературных сказок
Сравнение литературных сказок А.П. Платонов, рассказ Песчаная учительница
А.П. Платонов, рассказ Песчаная учительница Древнерусская литература. (9 класс)
Древнерусская литература. (9 класс) Марія Заньковецька (1854-1934)
Марія Заньковецька (1854-1934) Обитатели моря. Загадки для детей
Обитатели моря. Загадки для детей Презентация А.Н. Некрасов Дед Мазай и зайцы
Презентация А.Н. Некрасов Дед Мазай и зайцы Игорь Иванович Сикорский
Игорь Иванович Сикорский Большое сердце, как океан, никогда не замерзает. Иван Алексеевич Бунин, стихотворения
Большое сердце, как океан, никогда не замерзает. Иван Алексеевич Бунин, стихотворения Презентация Биография В.Г.Королено
Презентация Биография В.Г.Королено Эдуард Асадов
Эдуард Асадов Александр Сергеевич Пушкин Няне. Литературное чтение. 4 класс
Александр Сергеевич Пушкин Няне. Литературное чтение. 4 класс Друга світова війна у європейській поезії. Окуджава Булат Шалвович
Друга світова війна у європейській поезії. Окуджава Булат Шалвович Мир униженных и оскорбленных в романе Ф.М. Достоевского Преступление и наказание
Мир униженных и оскорбленных в романе Ф.М. Достоевского Преступление и наказание Интеллектуальная игра по русскому языку и литературе
Интеллектуальная игра по русскому языку и литературе Каким я вижу А.С. Пушкина в поэме Медный всадник?
Каким я вижу А.С. Пушкина в поэме Медный всадник?