Содержание
- 2. Introduction to Brands and Products Brand and product concepts Local, international, and global brands Product design
- 3. Basic Product Concepts A product is a good, service, or idea Tangible Attributes Intangible Attributes Product
- 4. Buyer Orientation Buyer orientation Amount of effort expended Level of risk Buyer involvement Buyer orientation framework
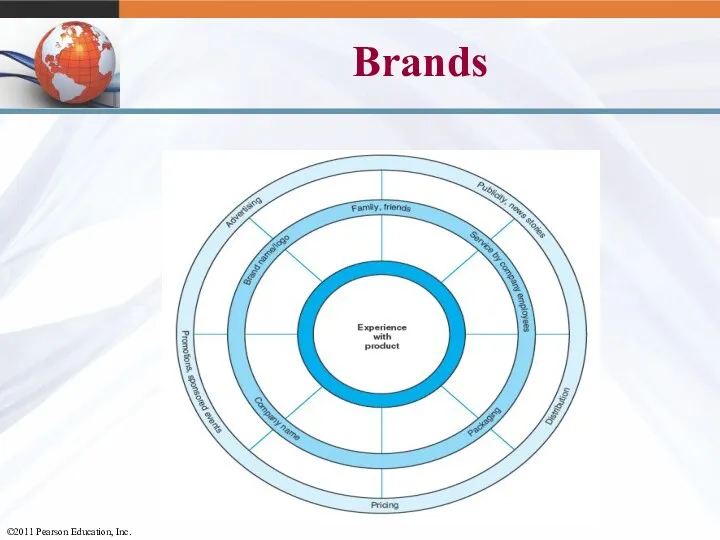
- 5. Brands Bundle of images and experiences in the customer’s mind A promise made by a particular
- 6. Brands
- 7. Brand Equity The added value that accrues to a product as a result of investments in
- 8. Brand Equity Benefits Greater loyalty Less vulnerability to marketing actions Less vulnerability to marketing crises Larger
- 9. Local Products and Brands Brands that have achieved success in a single national market Sometimes a
- 10. International Products and Brands Offered in several markets in a particular region ‘Euro-brands’ Honda 5-door hatchback
- 11. Global Products and Brands Global products meet the wants and needs of a global market and
- 12. Global Products and Brands “A multinational has operations in different countries. A global company views the
- 13. Global Brand Characteristics Quality signal—allows a company to charge premium price in a highly competitive market
- 14. Global Products and Brands Global brands are not the same as global products mp3 player= product
- 15. Branding Strategies Combination or tiered branding allows marketers to leverage a company’s reputation while developing a
- 16. Brand Extension Brand acts as an umbrella for new products Example: The Virgin Group Virgin Entertainment:
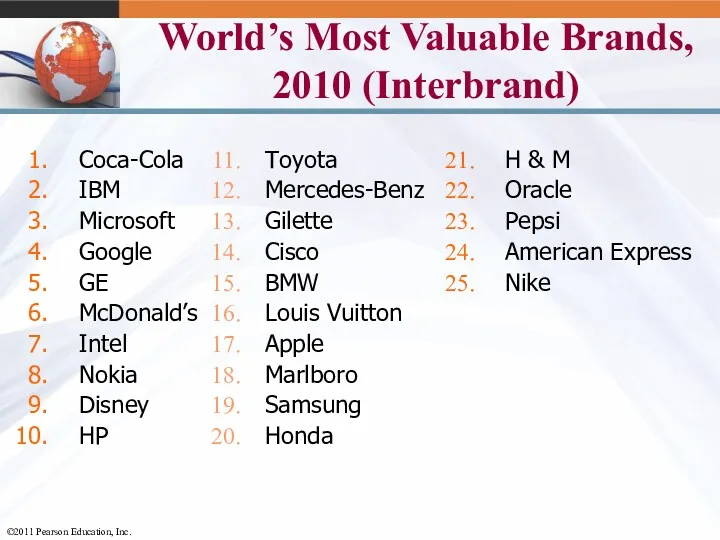
- 17. World’s Most Valuable Brands, 2010 (Interbrand) Coca-Cola IBM Microsoft Google GE McDonald’s Intel Nokia Disney HP
- 18. Private Label Branding Large retailers are moving increasingly into their own brand They try to obtain
- 19. Global Brand Development Questions to ask when management seeks to build a global brand: Does this
- 20. Global Brand Development Global Brand Leadership Using organizational structures, processes, and cultures; to allocate brand-building resources
- 21. Global Brand Development Suggestions to establish global brand leadership: Create a compelling value proposition Think about
- 22. Global Brand Development Develop a consistent planning process Assign specific responsibility for managing branding issues Execute
- 23. Local versus Global Products and Brands: A Needs-Based Approach Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs
- 24. 10- Asian Hierarchy of Needs
- 25. Country of Origin as Brand Element Perceptions about and attitudes toward particular countries often extend to
- 26. Country of Origin as Brand Element For many products, the “made in” label matters a great
- 27. Packaging Consumer Packaged Goods refers to products whose packaging is designed to protect or contain the
- 28. 10- Labeling Provides consumers with various types of information Regulations differ by country regarding various products
- 29. Aesthetics Global marketers must understand the importance of visual aesthetics Aesthetic styles (degree of complexity found
- 30. Product Warranties Express Warranty is a written guarantee that assures the buyer is getting what they
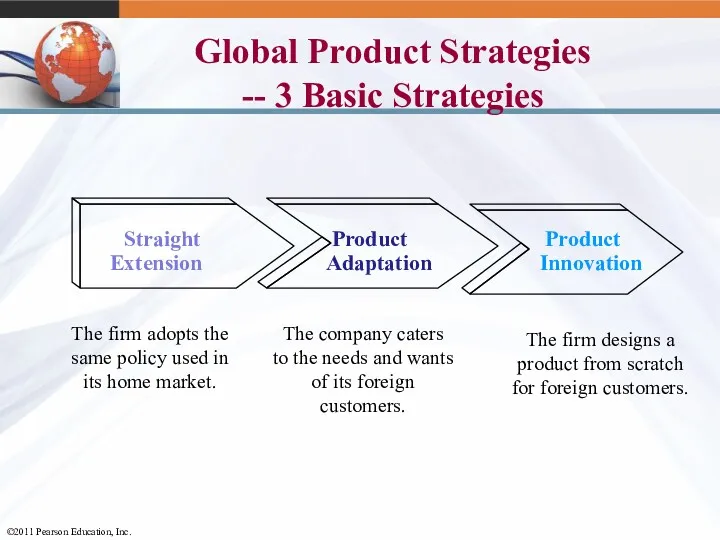
- 31. Global Product Strategies -- 3 Basic Strategies Straight Extension Product Product Adaptation Innovation The firm adopts
- 32. Extend, Adapt, Create: Strategic Alternatives in Global Marketing Extension – offering product virtually unchanged in markets
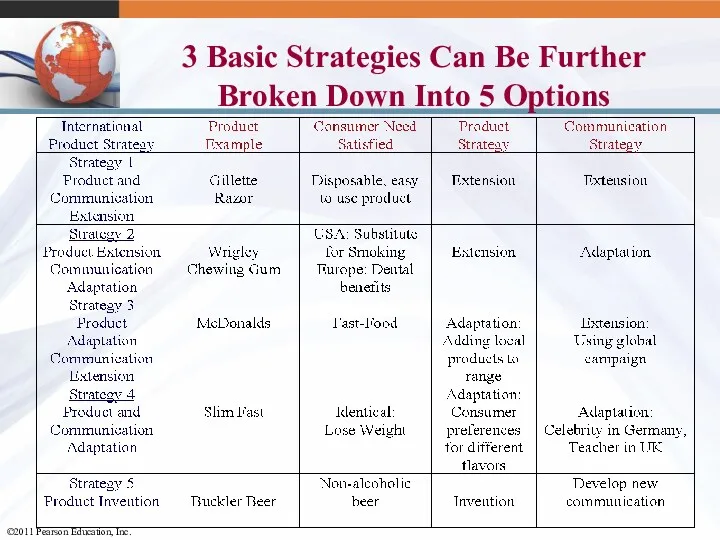
- 33. 3 Basic Strategies Can Be Further Broken Down Into 5 Options
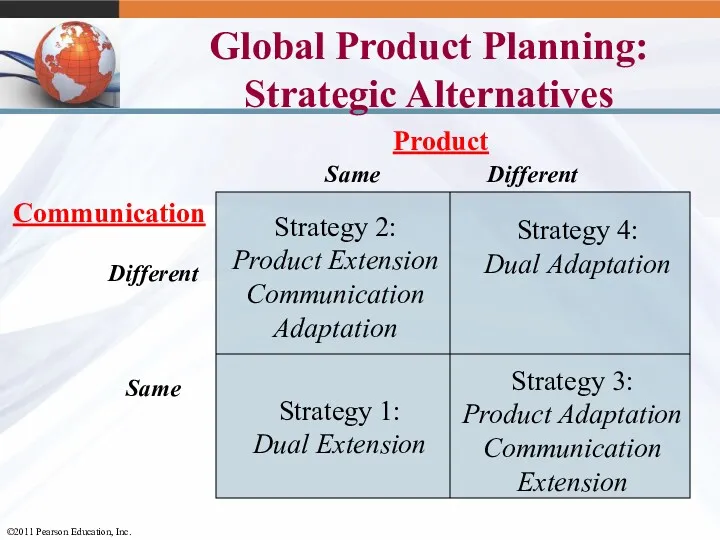
- 34. Global Product Planning: Strategic Alternatives Product Same Different Communication Different Same Strategy 1: Dual Extension Strategy
- 35. Product Invention Strategy 5: Important for reaching mass markets in less industrialized nations and certain segments
- 36. How to Choose a Strategy? Two errors that management makes in choosing a strategy NIH (Not
- 37. How to Choose a Strategy? The product itself, defined in terms of the function or need
- 38. Standardization versus Customization Although the products sold abroad generally are not identical to their domestic counterparts,
- 39. New Products in Global Marketing Pursue opportunities in competitive arenas of global marketplace Focus on one
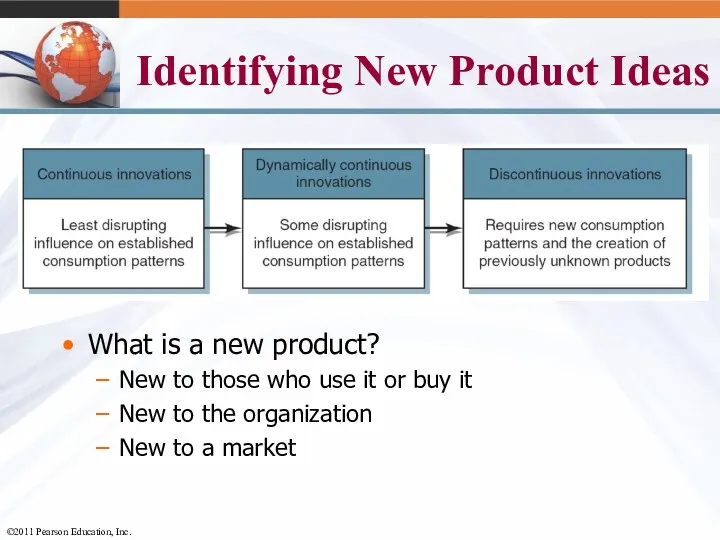
- 40. Identifying New Product Ideas What is a new product? New to those who use it or
- 41. The International New Product Department How big is the market for this product at various prices?
- 43. Скачать презентацию


































 Свой электрик. Долгосрочная забота о клиентах
Свой электрик. Долгосрочная забота о клиентах Principles of Marketing. Creating Competitive Advantage
Principles of Marketing. Creating Competitive Advantage Пищевые герметичные контейнеры с уникальным замком
Пищевые герметичные контейнеры с уникальным замком Menu Italian Cuisine Victoria
Menu Italian Cuisine Victoria Коллектив танцевальной аэробики С нами танцуй
Коллектив танцевальной аэробики С нами танцуй Предложение по уникальному подарку
Предложение по уникальному подарку Продажи ГУДС
Продажи ГУДС Двери СТЕЛ и ДПН. Складская программа. ООО Торэкс Северо-Запад
Двери СТЕЛ и ДПН. Складская программа. ООО Торэкс Северо-Запад Ключевые сообщения и продуктовые характеристики ТМ JTI. ТОП 8 SKU
Ключевые сообщения и продуктовые характеристики ТМ JTI. ТОП 8 SKU Путь самурая. Привлечение клиентов с интернета
Путь самурая. Привлечение клиентов с интернета Smart технологиялар
Smart технологиялар Project: Global Social Media Plan // July Topic: T1 Stop Motion Format: Video Date: Flexible Content
Project: Global Social Media Plan // July Topic: T1 Stop Motion Format: Video Date: Flexible Content Міжнародна реклама
Міжнародна реклама Easyjet
Easyjet Акция 20+1, Петровская Слобода
Акция 20+1, Петровская Слобода Hotel Amanwana
Hotel Amanwana Secret Key Профессиональный эксперт в сохранении Вашей природной красоты
Secret Key Профессиональный эксперт в сохранении Вашей природной красоты SMM стратегия (название бренда/продукта)
SMM стратегия (название бренда/продукта) Маркетинговые коммуникации
Маркетинговые коммуникации Сеть фитнес-клубов Вертикаль
Сеть фитнес-клубов Вертикаль Маркетинговая стратегия СК Жемчужный
Маркетинговая стратегия СК Жемчужный Новое покрытие ткани в коллекции куртки весна 2017
Новое покрытие ткани в коллекции куртки весна 2017 Управление продуктовой политикой в международных компаниях
Управление продуктовой политикой в международных компаниях Как стать поставщиком X5. Заключение контракта
Как стать поставщиком X5. Заключение контракта Инструкции для приёмки и выдачи заказов (ПВЗ). Яндекс.Маркет
Инструкции для приёмки и выдачи заказов (ПВЗ). Яндекс.Маркет Кәсiпорынды тiркеу: офф-лайн, он-лайн
Кәсiпорынды тiркеу: офф-лайн, он-лайн Группа компаний. A1TIS Вместе сделаем лучше!
Группа компаний. A1TIS Вместе сделаем лучше! Товарная политика фирмы
Товарная политика фирмы