Содержание
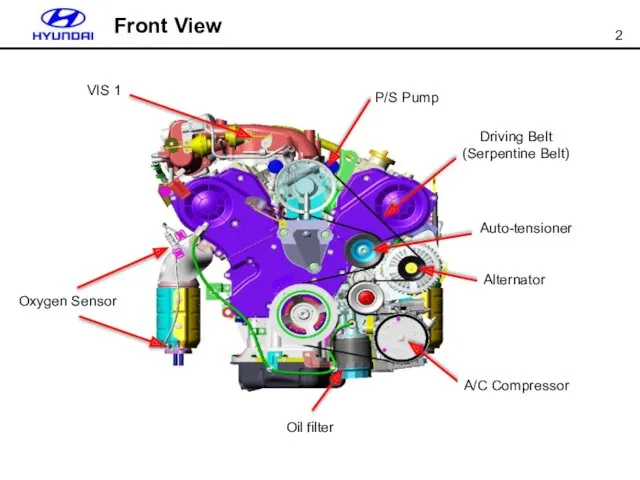
- 2. P/S Pump Auto-tensioner Driving Belt (Serpentine Belt) Alternator A/C Compressor Oil filter VIS 1 Oxygen Sensor
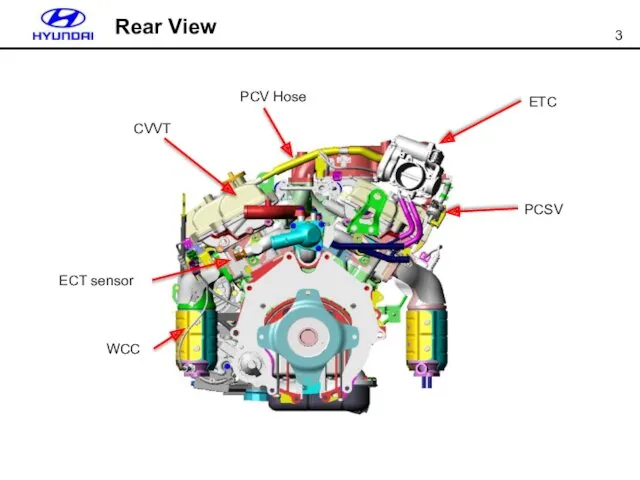
- 3. ETC PCSV PCV Hose CVVT WCC ECT sensor Rear View
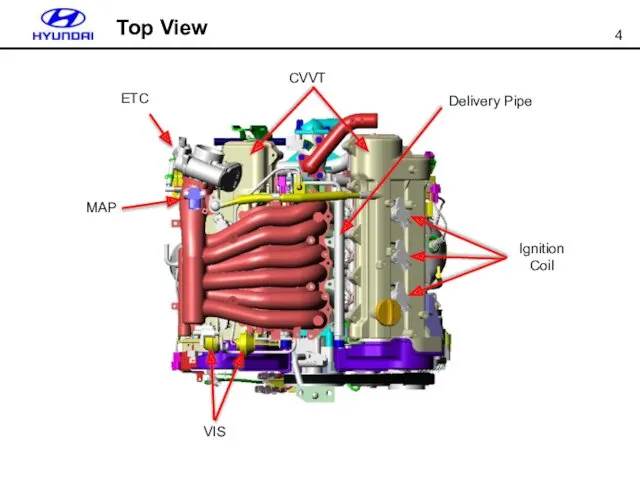
- 4. Ignition Coil Delivery Pipe ETC VIS MAP CVVT Top View
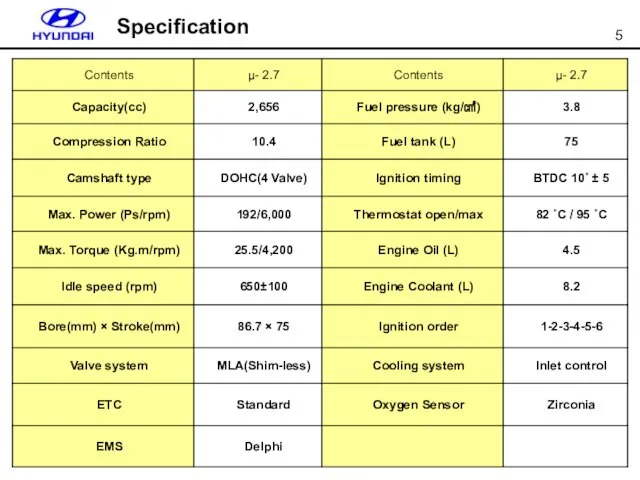
- 5. Specification
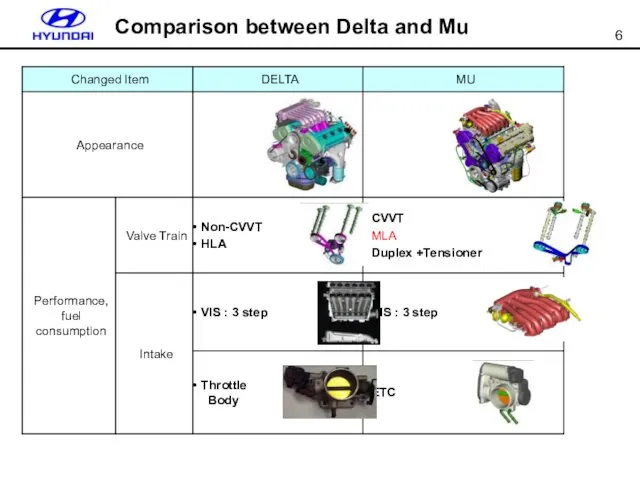
- 6. Comparison between Delta and Mu
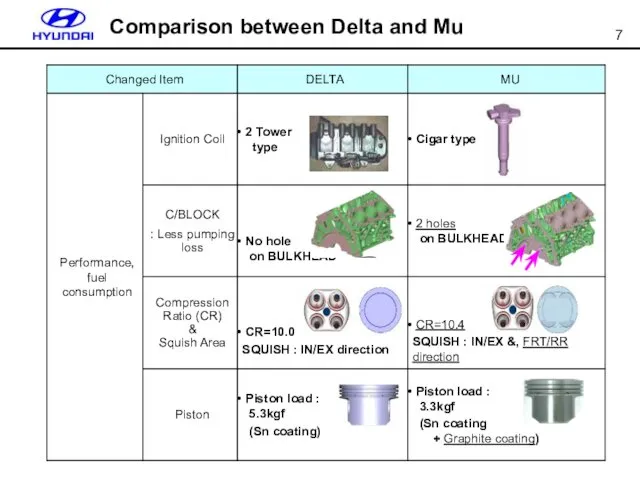
- 7. Comparison between Delta and Mu
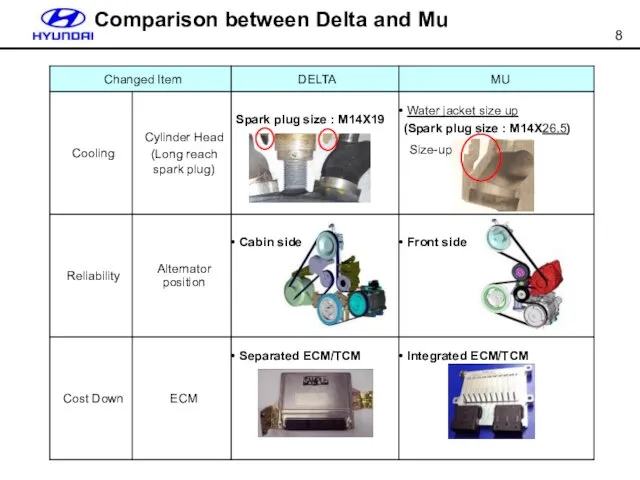
- 8. Comparison between Delta and Mu Size-up
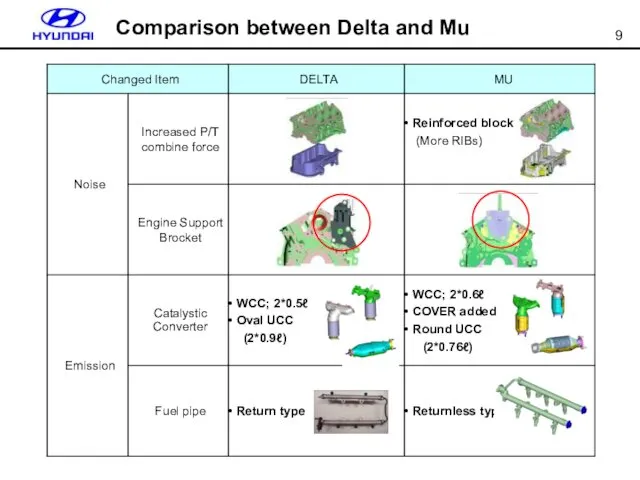
- 9. Comparison between Delta and Mu
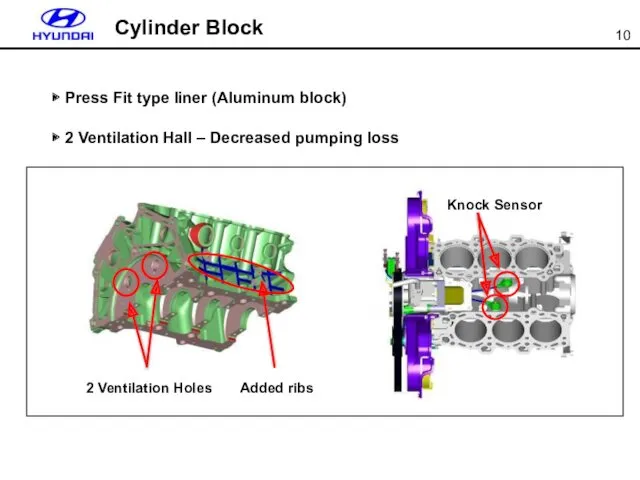
- 10. ▶ Press Fit type liner (Aluminum block) ▶ 2 Ventilation Hall – Decreased pumping loss 2
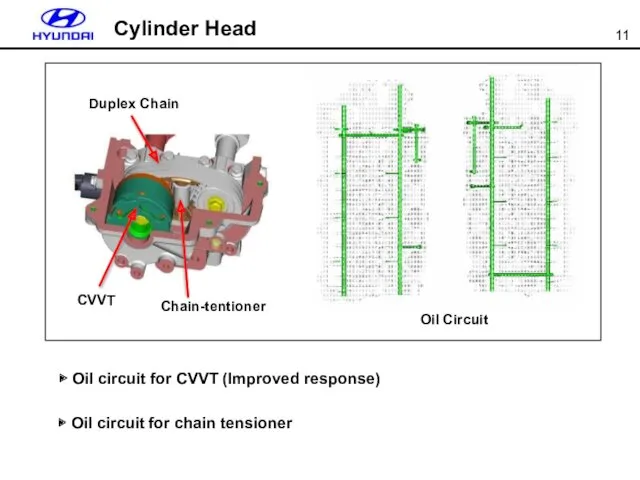
- 11. ▶ Oil circuit for CVVT (Improved response) ▶ Oil circuit for chain tensioner Oil Circuit Cylinder
- 12. ▶ Changed Water Jacket : Improved a cooling efficiency ( Increased valve durability) * LRSP :
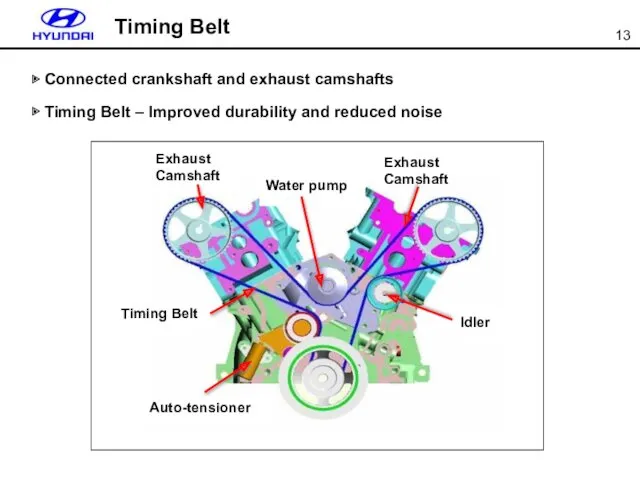
- 13. ▶ Connected crankshaft and exhaust camshafts ▶ Timing Belt – Improved durability and reduced noise Timing
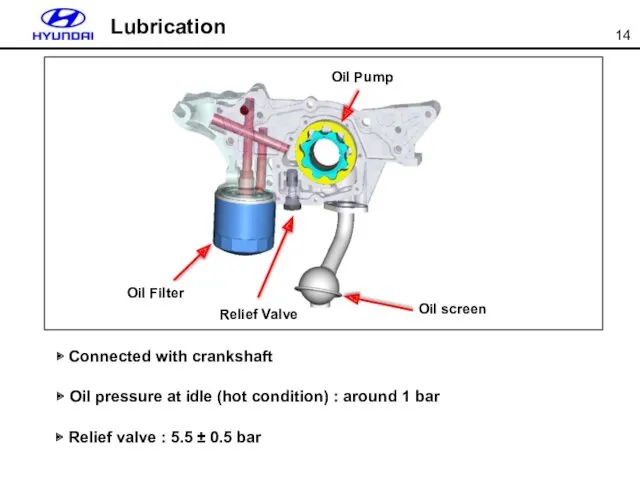
- 14. ▶ Connected with crankshaft ▶ Oil pressure at idle (hot condition) : around 1 bar ▶
- 15. ▶ - When replacing engine oil, washer must be replaced together (Supplied oil filter and washer
- 16. Camshaft cap LI1 IN : I EX : E CAP No. LH : L RH :
- 17. 0 120 240 -120 -240 EXHAUST INTAKE 45CA OVERLAP 51CA CVVT – Valve Timing
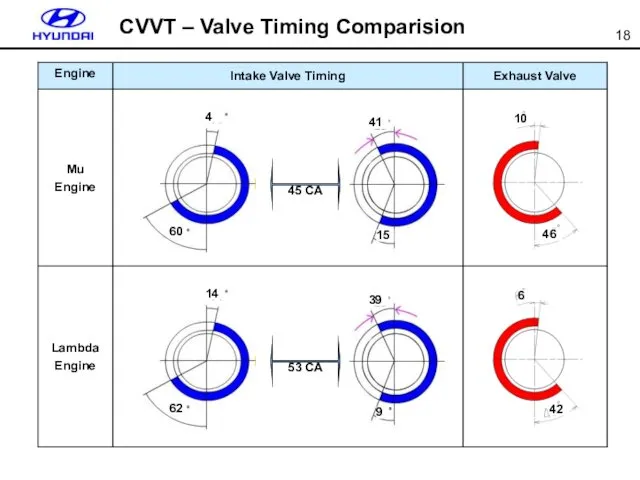
- 18. 45 CA 4 60 41 15 10 46 CVVT – Valve Timing Comparision 53 CA 14
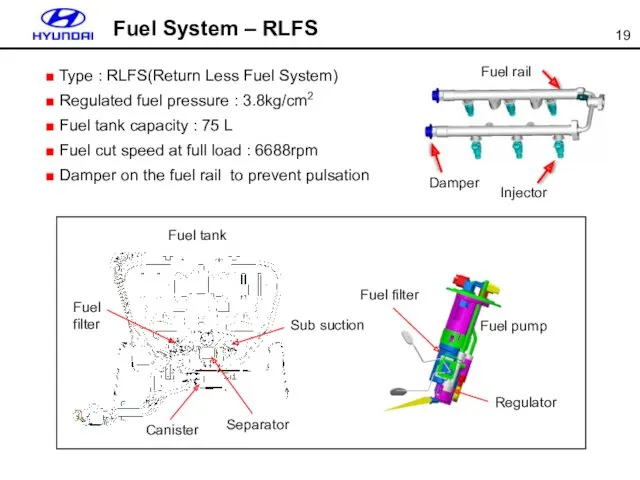
- 19. Fuel System – RLFS Fuel filter Regulator Fuel pump Damper Fuel rail Injector Sub suction Separator
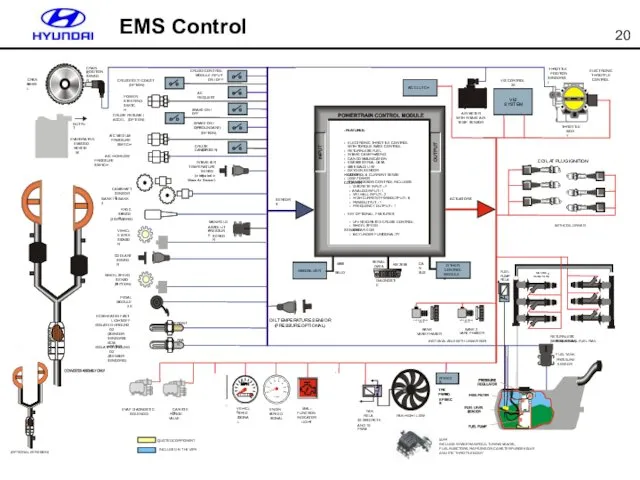
- 20. EMS Control
- 21. EMS General Specification
- 22. Cooling Fan Control Control logic ■ Fan logic of a vehicle without A/CON is equal to
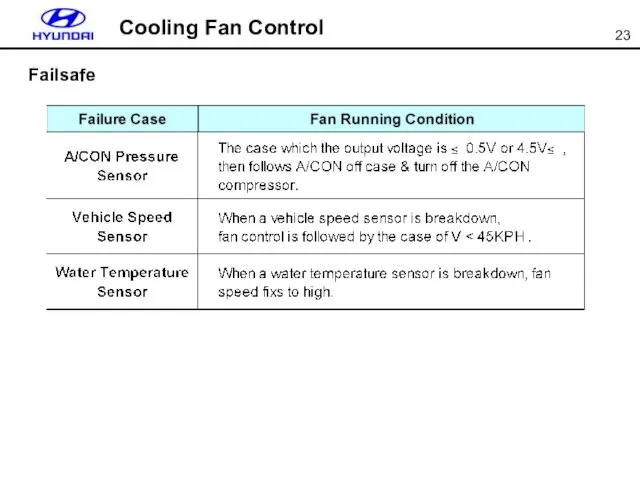
- 23. Cooling Fan Control Failsafe
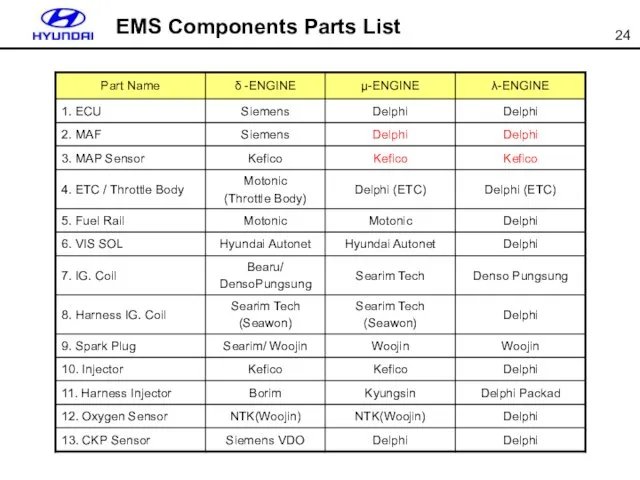
- 24. EMS Components Parts List
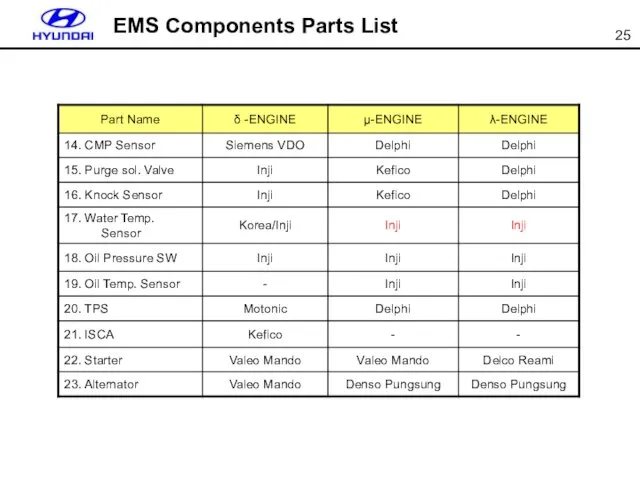
- 25. EMS Components Parts List
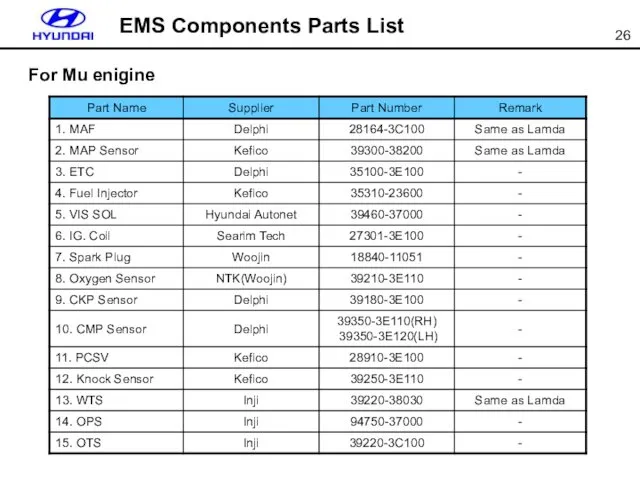
- 26. EMS Components Parts List For Mu enigine
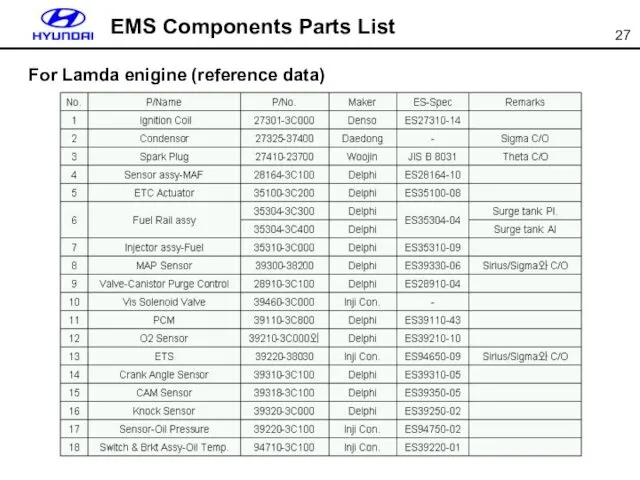
- 27. EMS Components Parts List For Lamda enigine (reference data)
- 28. PCM MAF Sensor Outputs Injector IAT Sensor WTS CKP Sensor CMP Sensor Inputs TPS ETC Relays(Main/Pump/Fan)
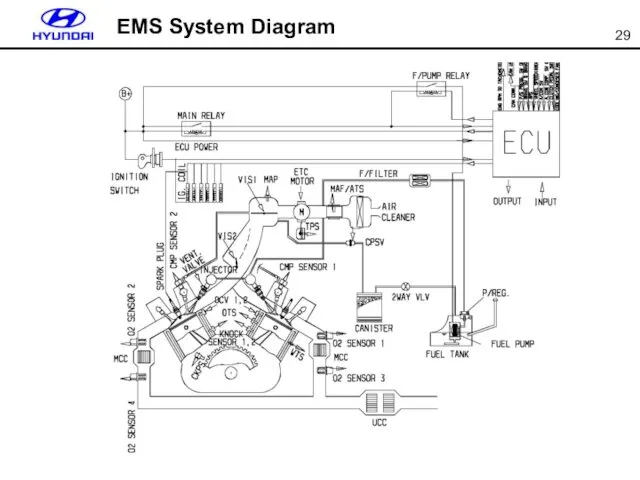
- 29. EMS System Diagram
- 30. CMPS CKPS WTS KNOCK Sensor OPS MAPS OTS O2 Sensor PCSV VIS SOL #2 ETC IG
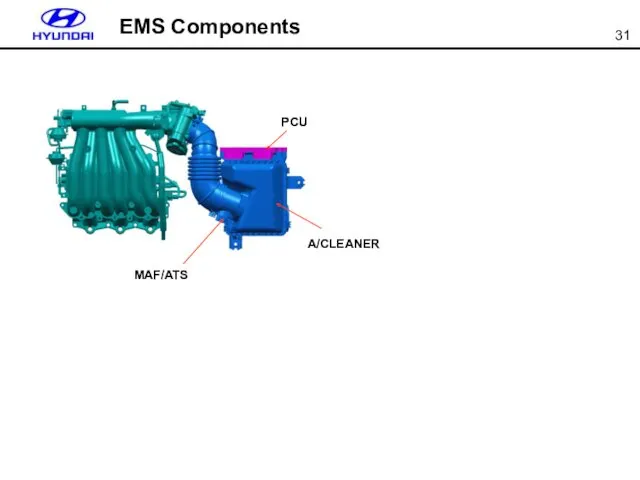
- 31. EMS Components
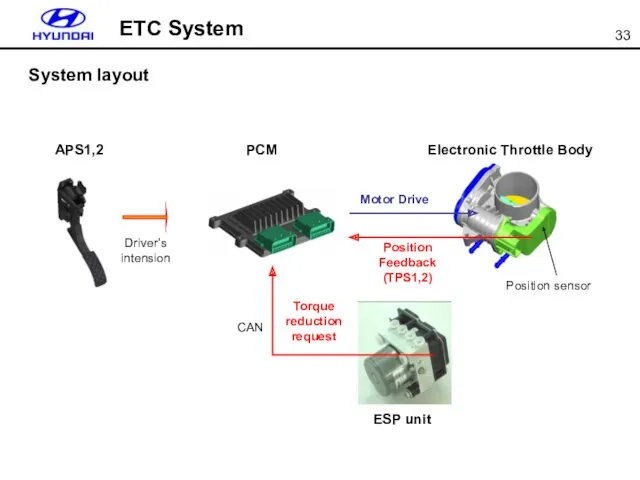
- 32. ETC( Electronic Throttle Control) system consists of ETC DC motor, throttle body, throttle position sensor and
- 33. Position sensor Motor Drive Position Feedback (TPS1,2) PCM APS1,2 Electronic Throttle Body Driver’s intension ETC System
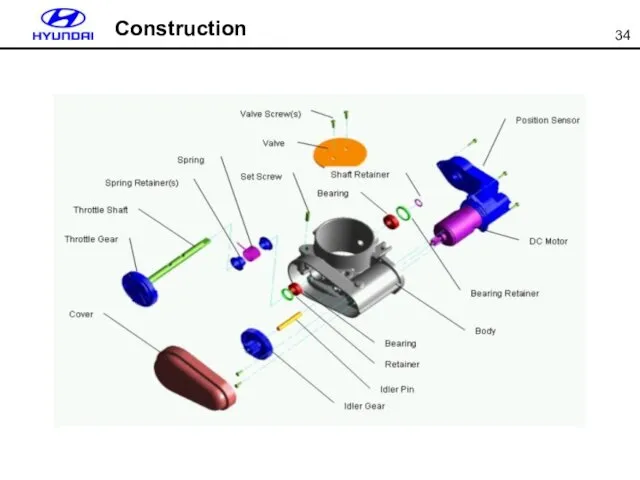
- 34. Construction
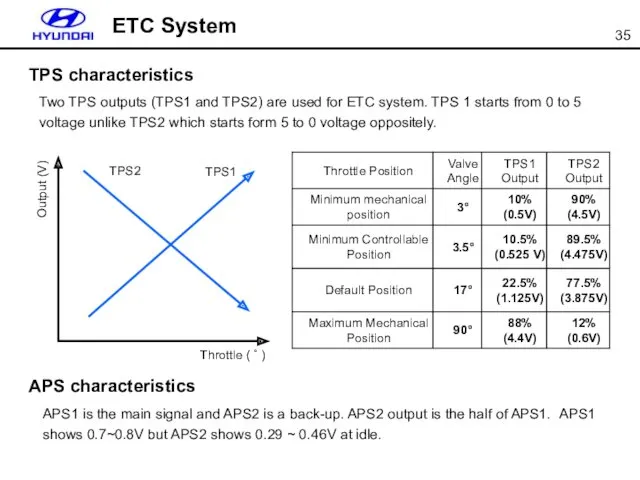
- 35. ETC System TPS characteristics Two TPS outputs (TPS1 and TPS2) are used for ETC system. TPS
- 36. ETC System - TPS Pin assignment
- 37. ETC System - APS APS 4 6 2 5 3 1 Pin assignment APS
- 38. Failsafe There are four main limphome functions in Delphi EMS - Forced idle - Limited performance
- 39. Failsafe Unlike forced idle, power management is followed mainly from TPS failure. Since now ECM doesn’t
- 40. ETC System - Initializing Every time when you make ignition on, ETC goes to initializing for
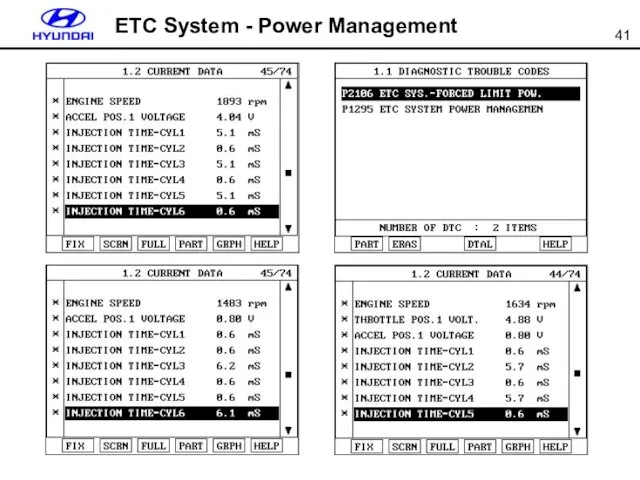
- 41. ETC System - Power Management
- 42. VIS (Variable Intake System) VIS-2 VIS-1 ■ VIS-1 : for low/middle rpm range ■ VIS-2 :
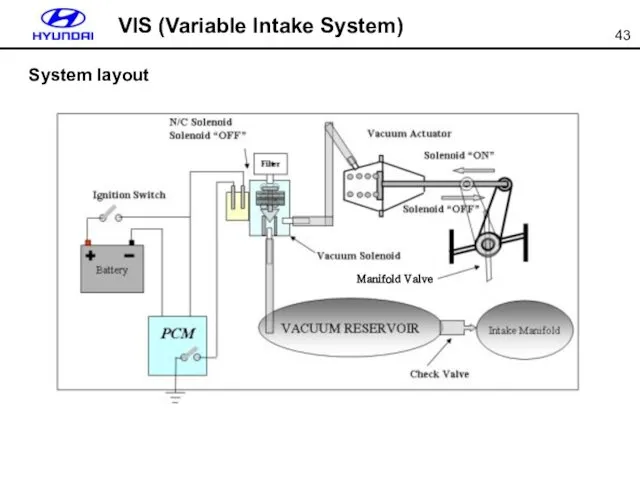
- 43. System layout VIS (Variable Intake System)
- 44. Solenoid Technical feature - Type : 3 way valve - Coil resistance : 32±3 Ω (at
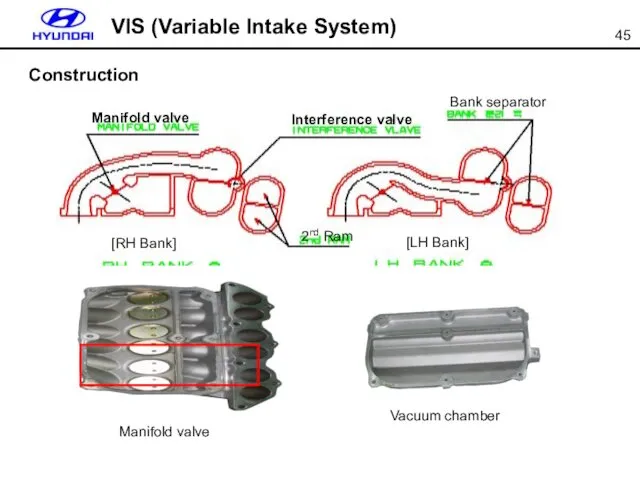
- 45. Construction VIS (Variable Intake System) Vacuum chamber Manifold valve
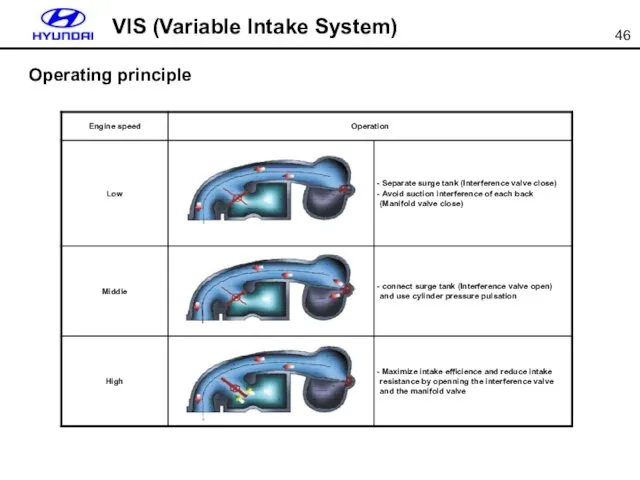
- 46. Operating principle VIS (Variable Intake System)
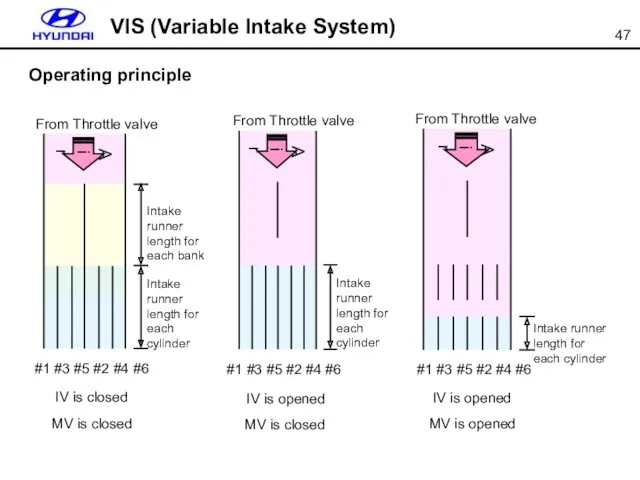
- 47. IV is closed MV is closed IV is opened MV is closed IV is opened MV
- 48. Control logic Initial position ? Both valve for IV & MV is closed(at no power supply)
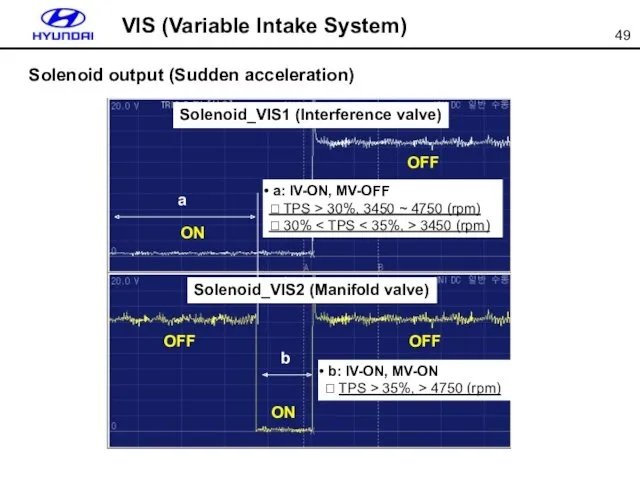
- 49. Solenoid output (Sudden acceleration) Solenoid_VIS1 (Interference valve) ON OFF OFF ON Solenoid_VIS2 (Manifold valve) a b
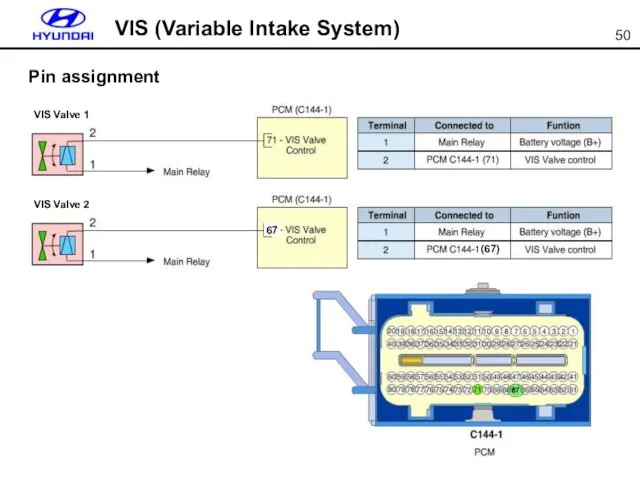
- 50. VIS (Variable Intake System) Pin assignment
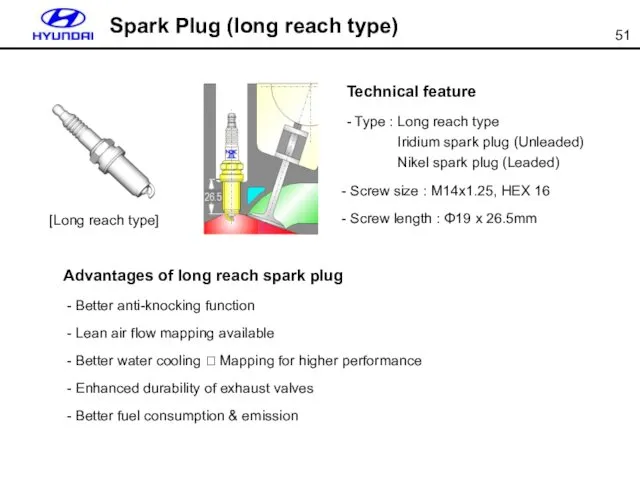
- 51. Spark Plug (long reach type) Advantages of long reach spark plug - Better anti-knocking function -
- 52. CKP Sensor - Output voltage : 0.4V~200V - Available engine rpm : 55~7000 rpm - Air
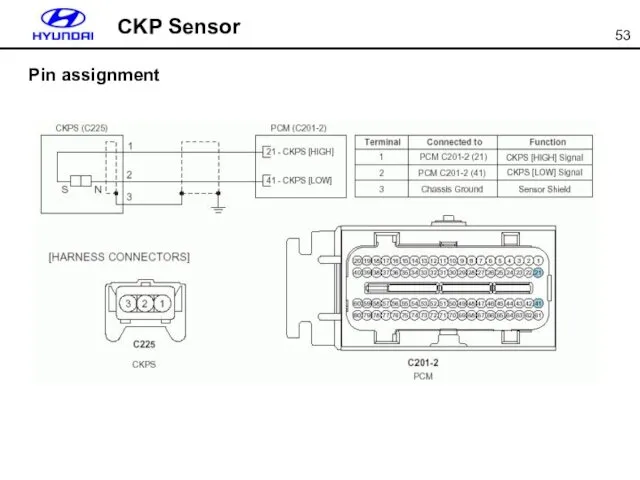
- 53. CKP Sensor Pin assignment
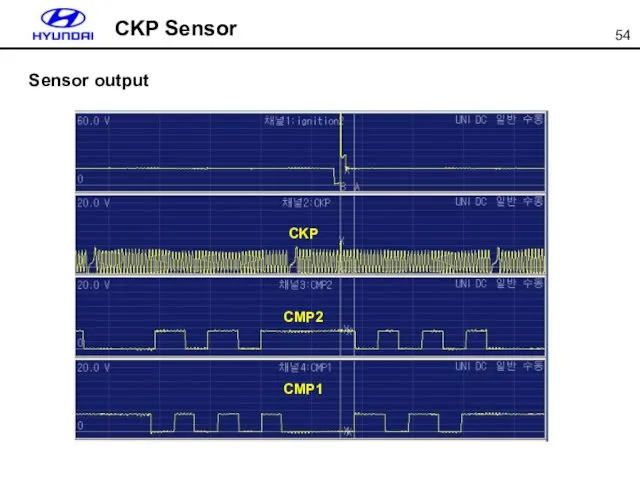
- 54. CKP Sensor Sensor output CKP CMP2 CMP1
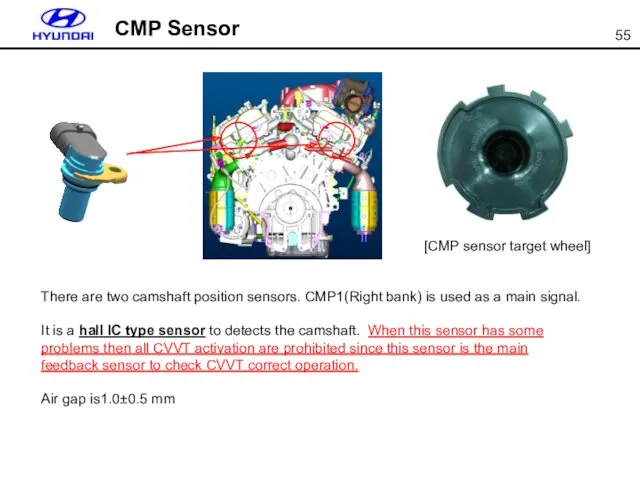
- 55. CMP Sensor There are two camshaft position sensors. CMP1(Right bank) is used as a main signal.
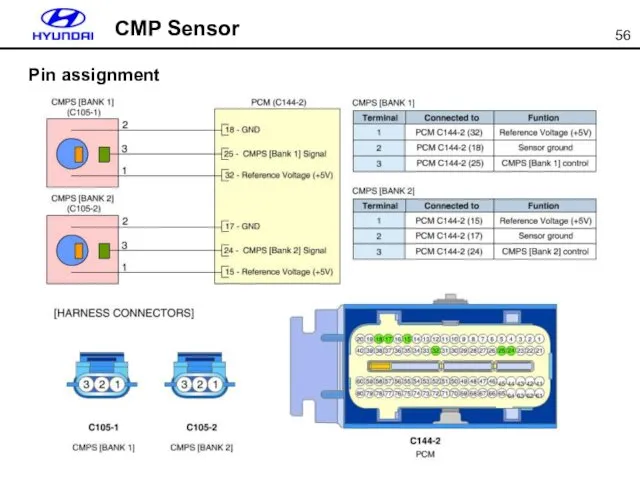
- 56. CMP Sensor Pin assignment
- 57. Technical Feature - Type : NTC thermistor - Operating Temp.: -40℃~130℃ - Resistance : -20℃ :
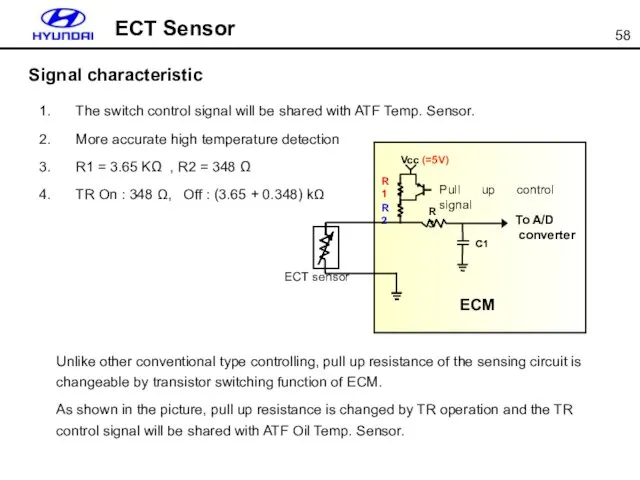
- 58. ECT Sensor The switch control signal will be shared with ATF Temp. Sensor. More accurate high
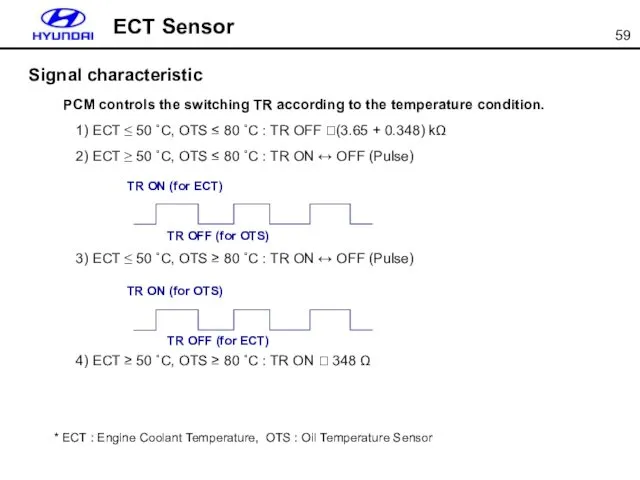
- 59. PCM controls the switching TR according to the temperature condition. 1) ECT ≤ 50 ˚C, OTS
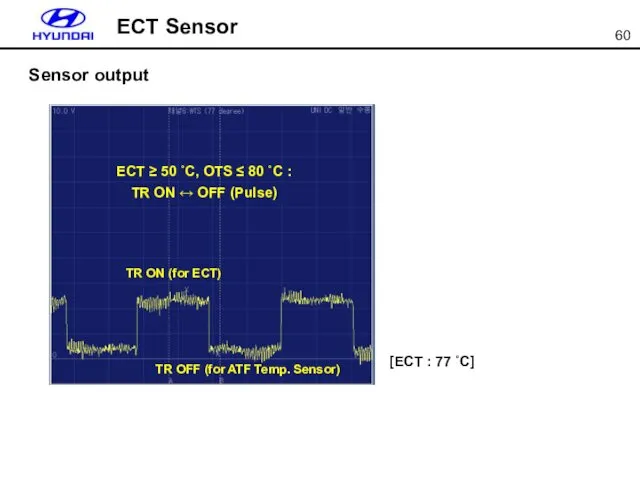
- 60. ECT Sensor Sensor output ECT ≥ 50 ˚C, OTS ≤ 80 ˚C : TR ON ↔
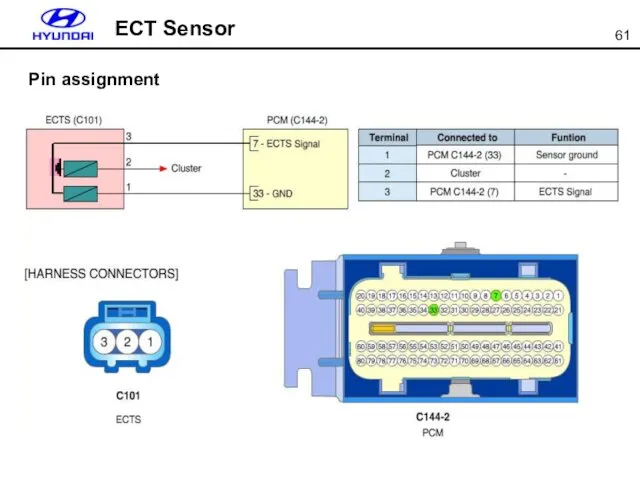
- 61. ECT Sensor Pin assignment
- 62. MAF sensor outputs frequency (Hz) according to the intake air amount. Frequency generator is assembled in
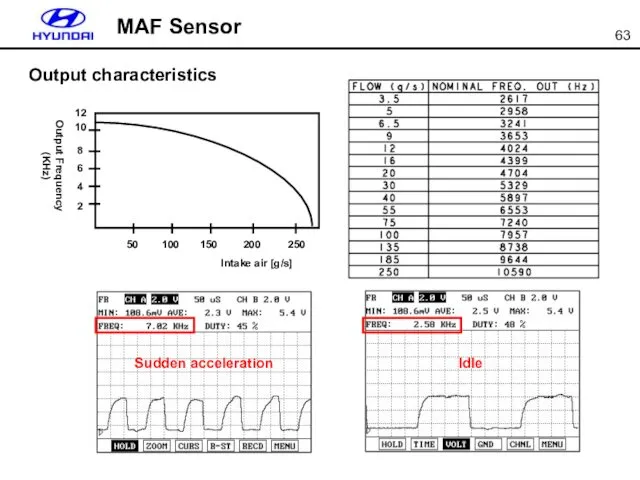
- 63. MAF Sensor Output characteristics Sudden acceleration Idle
- 64. When MAP sensor is normal : replaced by MAP sensor When MAP sensor is failed :
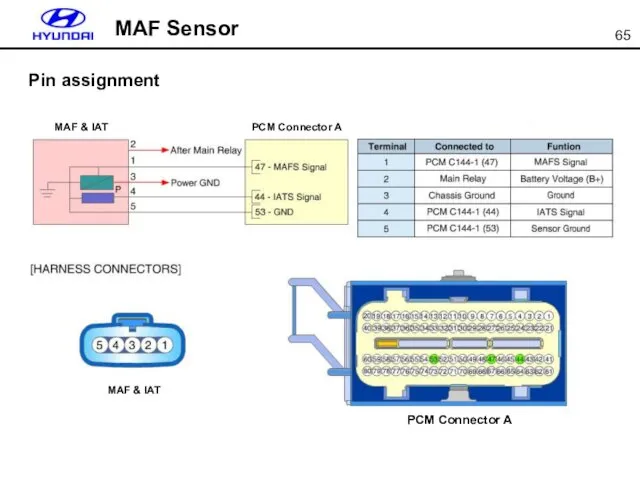
- 65. MAF Sensor Pin assignment
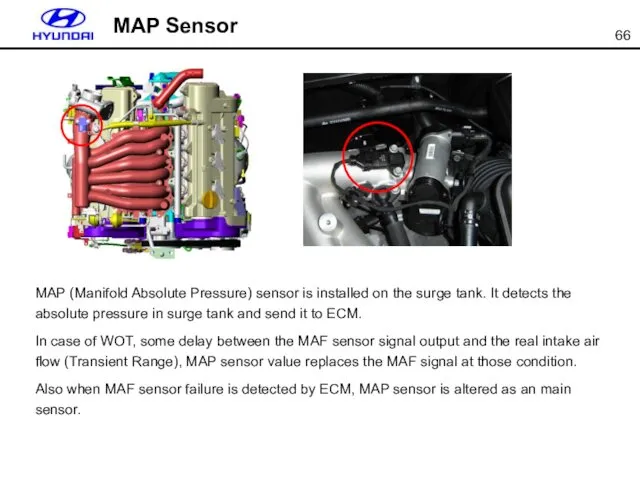
- 66. MAP Sensor MAP (Manifold Absolute Pressure) sensor is installed on the surge tank. It detects the
- 67. Cover Bush O-Ring NTC Thermistor Housing Ass’y MAP Sensor Sensor Type : Piezo Resistive Pressure range
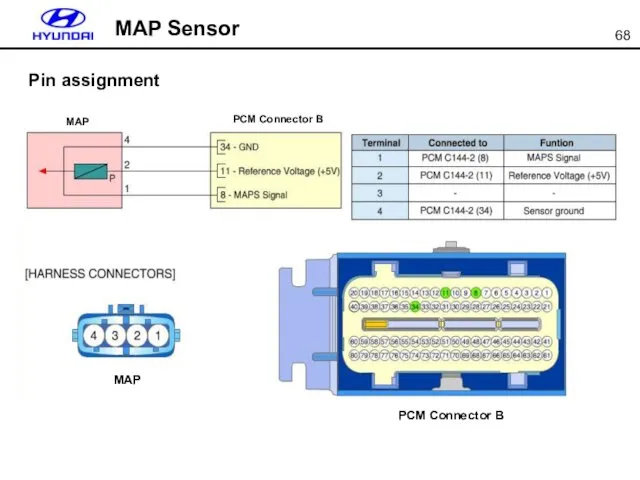
- 68. MAP Sensor Pin assignment
- 69. MAP Sensor When ECM reaches a transient range such as sudden acceleration or deceleration, MAF value
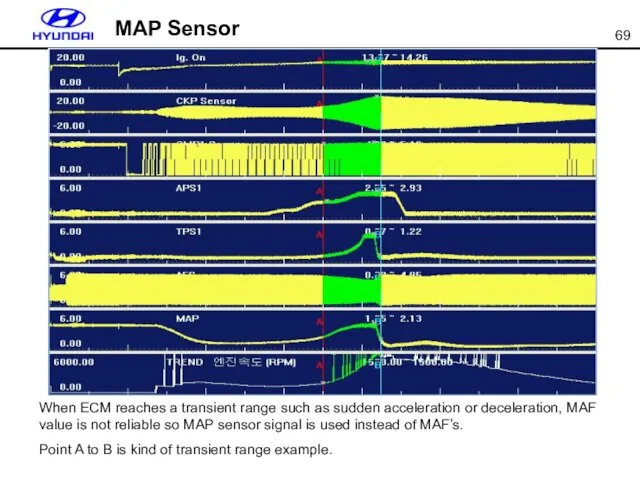
- 70. MAP Sensor Failsafe [[When MAP sensor connector is open]
- 71. Technical features EV6 (Kefico) : 4 Hole, 2 Spray Flow rate: 150g/min Spray Pattern - Cone
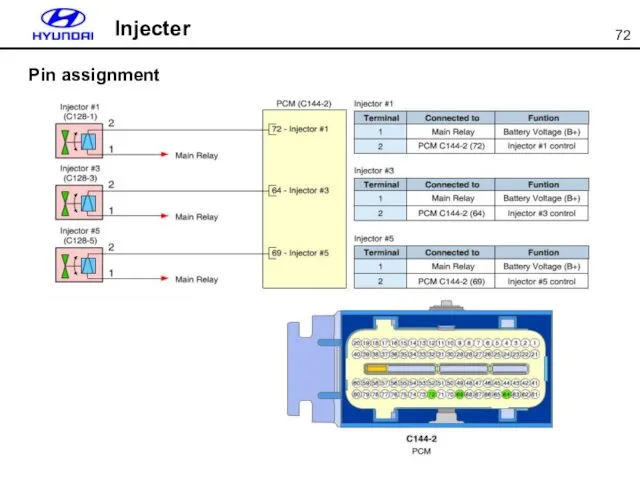
- 72. Injecter Pin assignment
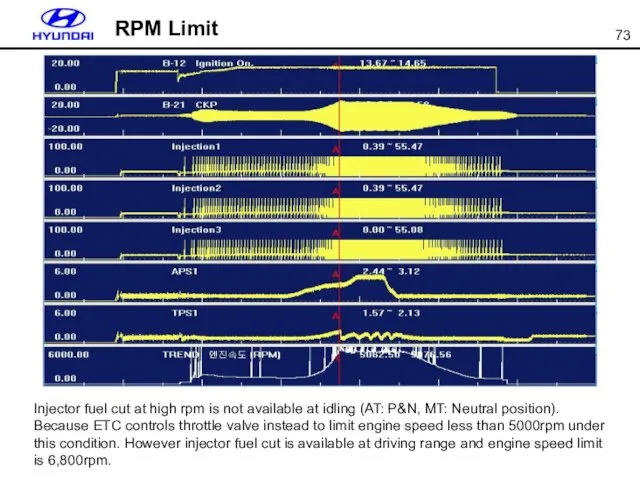
- 73. RPM Limit Injector fuel cut at high rpm is not available at idling (AT: P&N, MT:
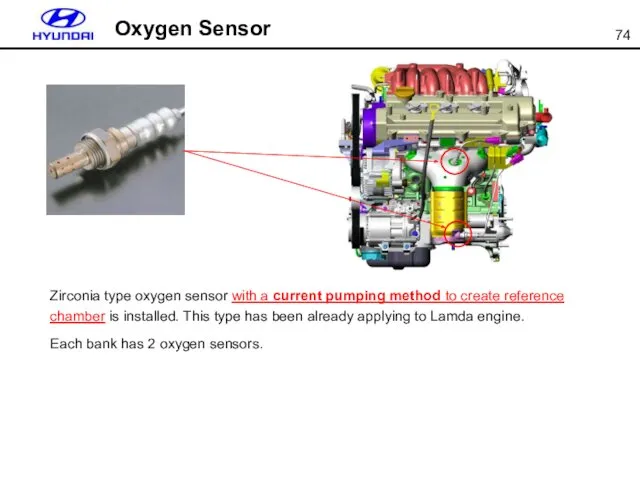
- 74. Oxygen Sensor Zirconia type oxygen sensor with a current pumping method to create reference chamber is
- 75. Oxygen Sensor When ECM supply current through signal output line which is about 7 ~ 10
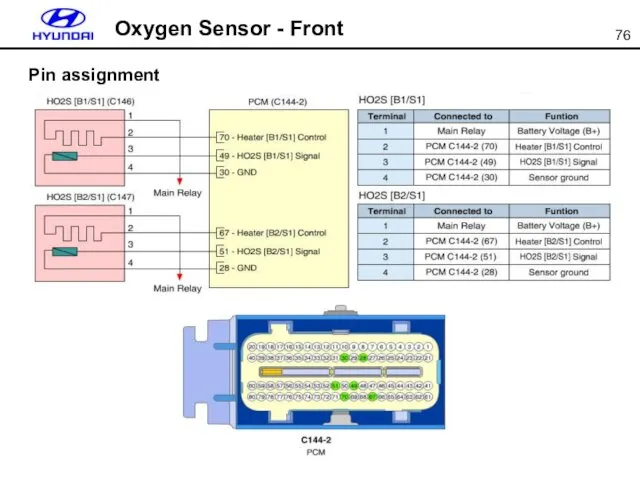
- 76. Oxygen Sensor - Front Pin assignment
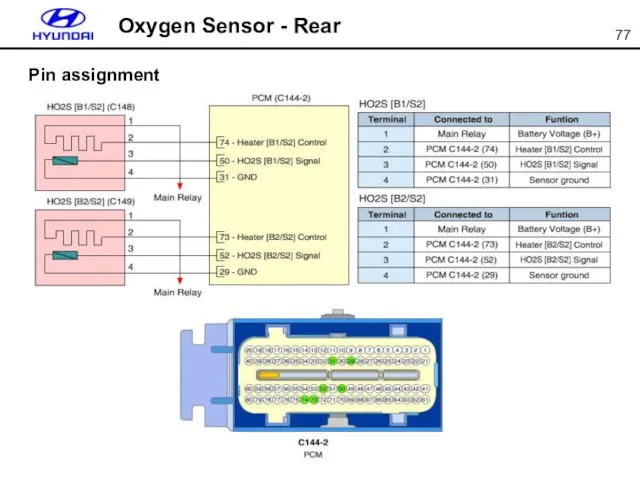
- 77. Oxygen Sensor - Rear Pin assignment
- 78. Oxygen Sensor Even reference chamber is created by electrically, oxygen sensor waveform is same as the
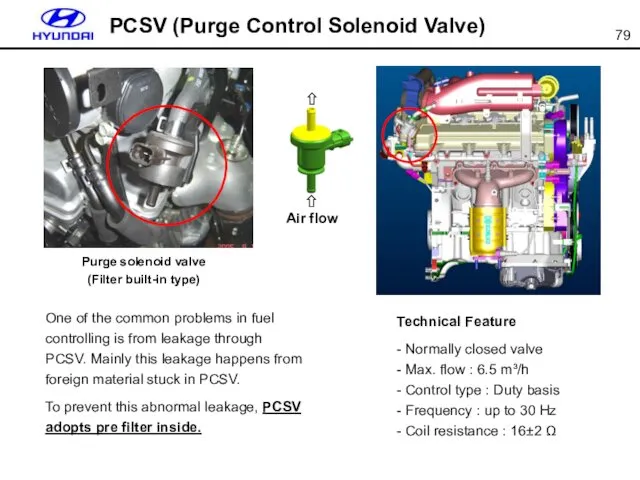
- 79. PCSV (Purge Control Solenoid Valve) Purge solenoid valve (Filter built-in type) One of the common problems
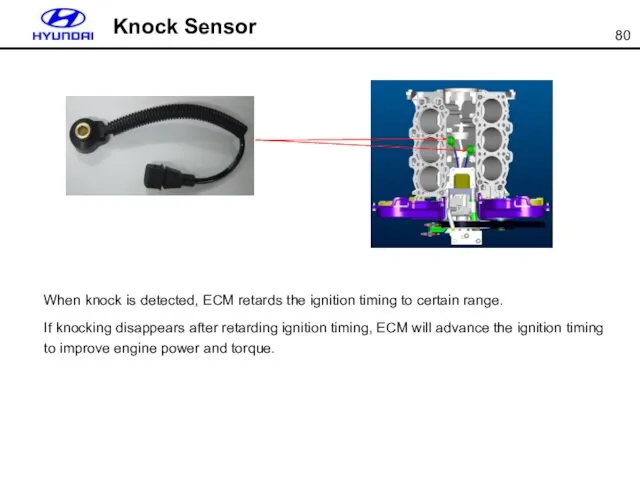
- 80. Knock Sensor When knock is detected, ECM retards the ignition timing to certain range. If knocking
- 81. Knock Sensor Sensor output 1.6V [Knock sensor output at engine idle]
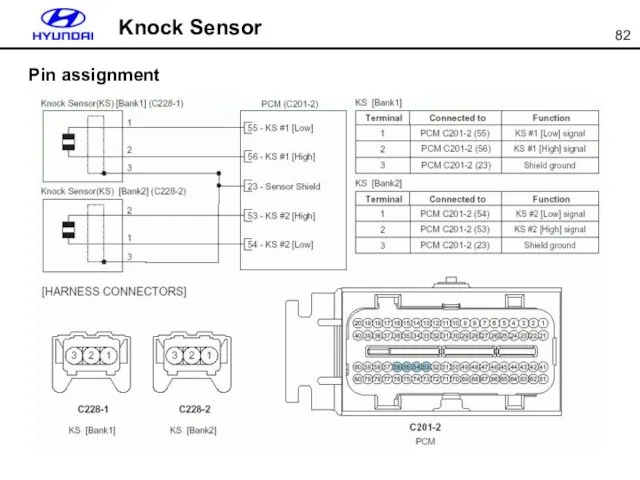
- 82. Knock Sensor Pin assignment
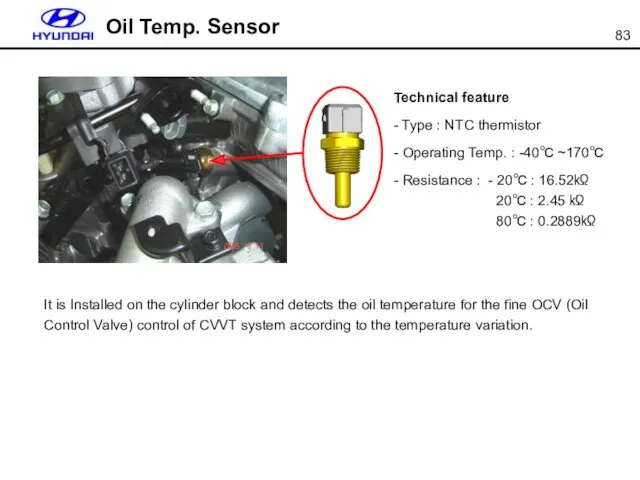
- 83. Oil Temp. Sensor Technical feature - Type : NTC thermistor - Operating Temp. : -40℃ ~170℃
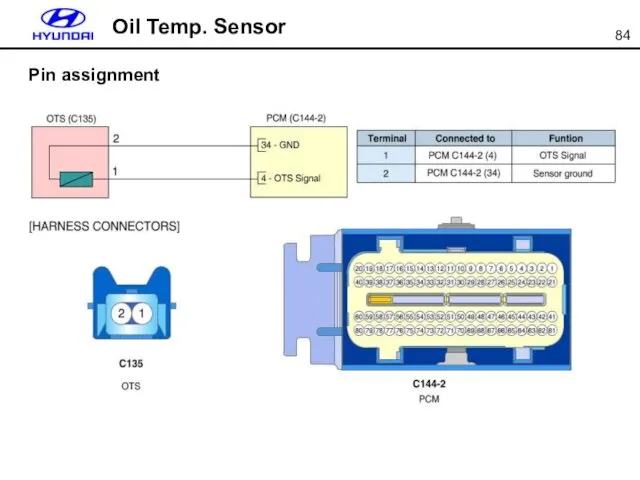
- 84. Oil Temp. Sensor Pin assignment
- 86. Скачать презентацию






















![MAP Sensor Failsafe [[When MAP sensor connector is open]](/_ipx/f_webp&q_80&fit_contain&s_1440x1080/imagesDir/jpg/96005/slide-69.jpg)



![Knock Sensor Sensor output 1.6V [Knock sensor output at engine idle]](/_ipx/f_webp&q_80&fit_contain&s_1440x1080/imagesDir/jpg/96005/slide-80.jpg)
 Advertisement. Packing
Advertisement. Packing Мировые тренды на керамическую плитку
Мировые тренды на керамическую плитку Исследование рыночного спроса на продукцию предприятия
Исследование рыночного спроса на продукцию предприятия Вихідні відомості журналу
Вихідні відомості журналу Каталог мастер-классов Пасха
Каталог мастер-классов Пасха Квалификационная (дипломная) работа Проведение исследования поведения потребителей на рынке (на примере ИП Ларшина Е.А.)
Квалификационная (дипломная) работа Проведение исследования поведения потребителей на рынке (на примере ИП Ларшина Е.А.) Хирургиялық стоматологиядағы менеджмент және маркетинг
Хирургиялық стоматологиядағы менеджмент және маркетинг Microbus love
Microbus love Оздоровительный туризм Вьетнама
Оздоровительный туризм Вьетнама Маркетинг в социальных сетях
Маркетинг в социальных сетях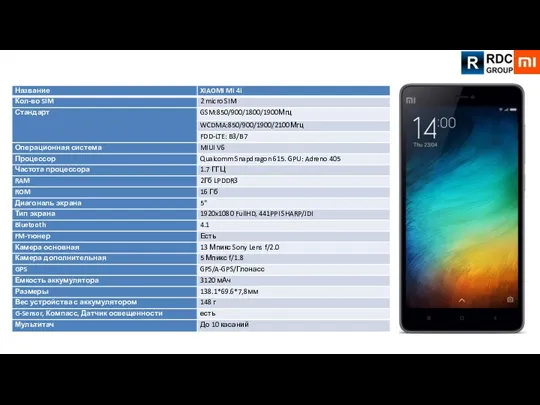 XIAOMI Redmi Note 3, XIAOMI Redmi 3 Pro, XIAOMI Redmi 2 Pro
XIAOMI Redmi Note 3, XIAOMI Redmi 3 Pro, XIAOMI Redmi 2 Pro Динамика корпоративного развития Bosch
Динамика корпоративного развития Bosch Тауар саны бойынша градация
Тауар саны бойынша градация Міжнародна реклама
Міжнародна реклама Marketing strategy for the U.S. market
Marketing strategy for the U.S. market Товарная политика аптеки в фармацевтическом маркетинге
Товарная политика аптеки в фармацевтическом маркетинге Интернет в офис. Коммерческое предложение от Билайн Бизнес
Интернет в офис. Коммерческое предложение от Билайн Бизнес Комплекс Med Planta (Cosmofarma, Италия)
Комплекс Med Planta (Cosmofarma, Италия) OZON. Статусы заказа
OZON. Статусы заказа Изменения в ассортименте моторных масел petro-canada для легкового транспорта
Изменения в ассортименте моторных масел petro-canada для легкового транспорта Фирменный стиль
Фирменный стиль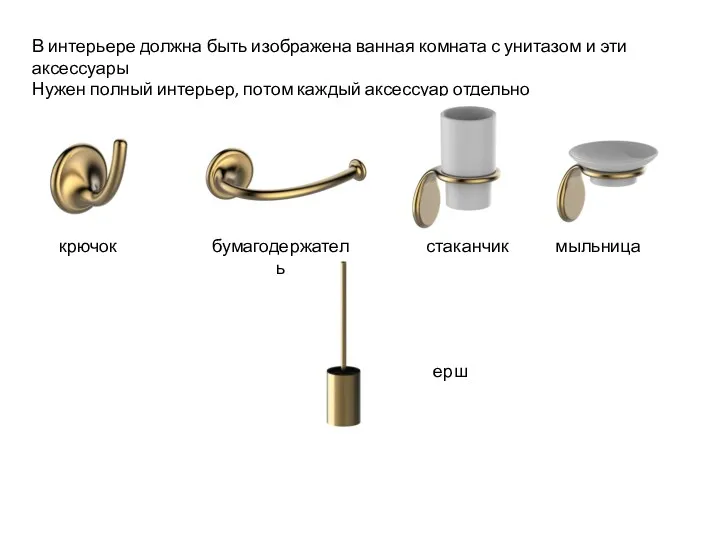 Корректировки. аксессуары для ванной Oldie
Корректировки. аксессуары для ванной Oldie ЖК Новая Ливадия
ЖК Новая Ливадия Методы оценки кривых спроса
Методы оценки кривых спроса Медиаплан по продвижению интернет-магазина Mediapark.uz в связи с Covid-19
Медиаплан по продвижению интернет-магазина Mediapark.uz в связи с Covid-19 Процесс управления маркетинговой деятельностью компании
Процесс управления маркетинговой деятельностью компании Marketing strategy
Marketing strategy Описания Шоу программ
Описания Шоу программ