Содержание
- 2. Learning Objectives Define the major steps in designing a customer-driven marketing strategy: market segmentation, targeting, differentiation,
- 3. Learning Objectives Explain how companies identify attractive market segments and choose a market-targeting strategy. Discuss how
- 4. First Stop: P&G: Competing with Itself — and Winning P&G brands compete directly with each other.
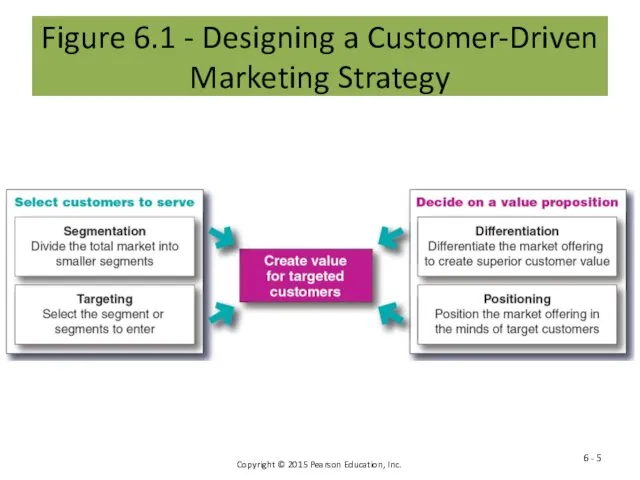
- 5. Figure 6.1 - Designing a Customer-Driven Marketing Strategy 6 -
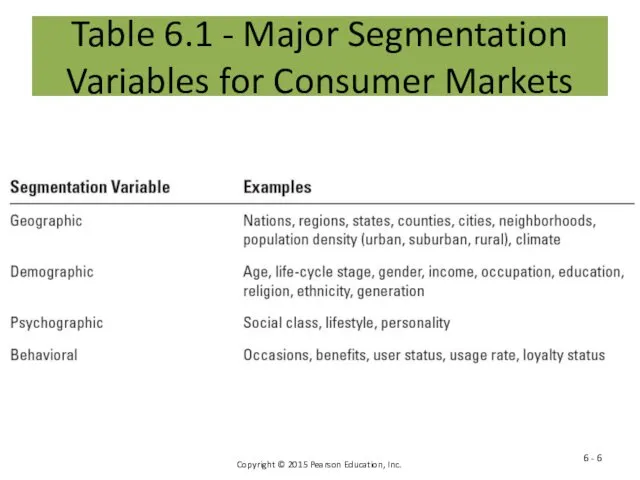
- 6. Table 6.1 - Major Segmentation Variables for Consumer Markets 6 -
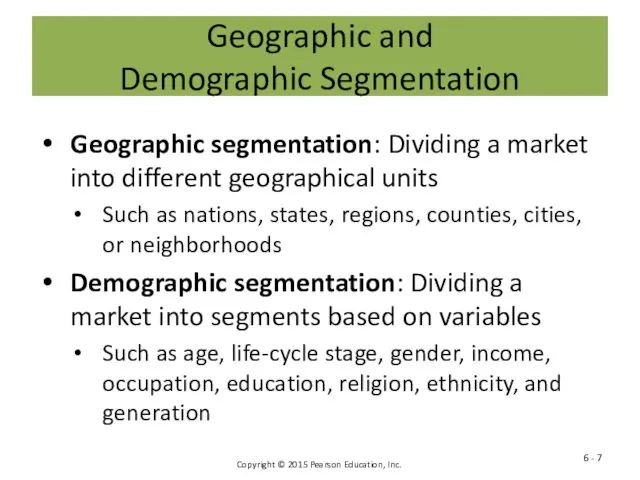
- 7. Geographic and Demographic Segmentation Geographic segmentation: Dividing a market into different geographical units Such as nations,
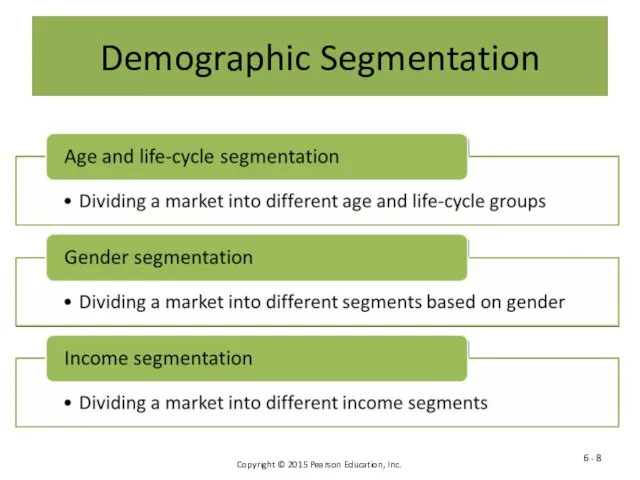
- 8. Demographic Segmentation 6 -
- 9. Psychographic Segmentation Marketers segment their markets using variables such as: Social class Consumer lifestyles Consumer personality
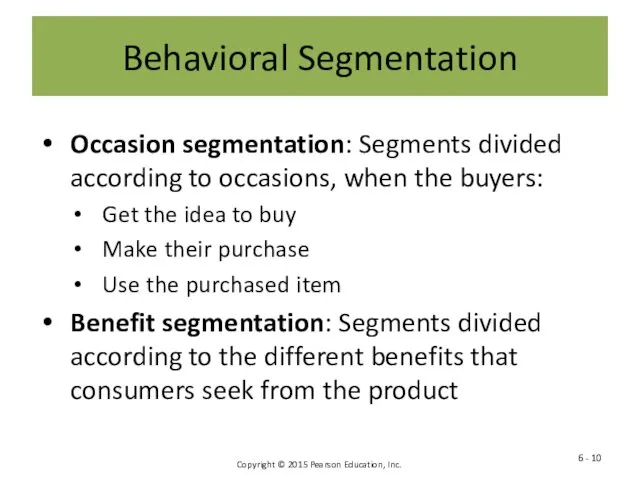
- 10. Behavioral Segmentation Occasion segmentation: Segments divided according to occasions, when the buyers: Get the idea to
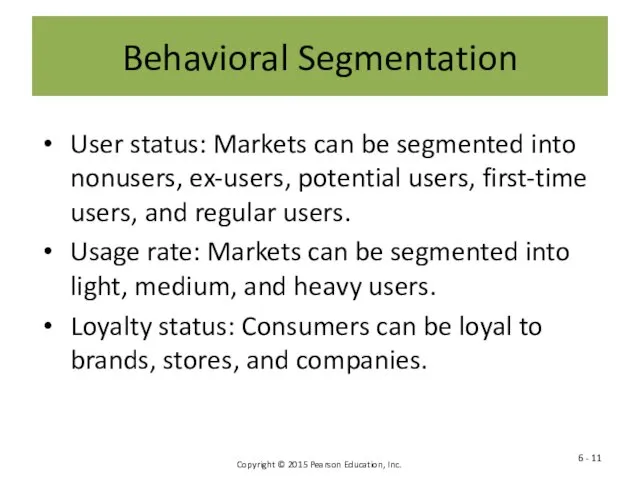
- 11. Behavioral Segmentation User status: Markets can be segmented into nonusers, ex-users, potential users, first-time users, and
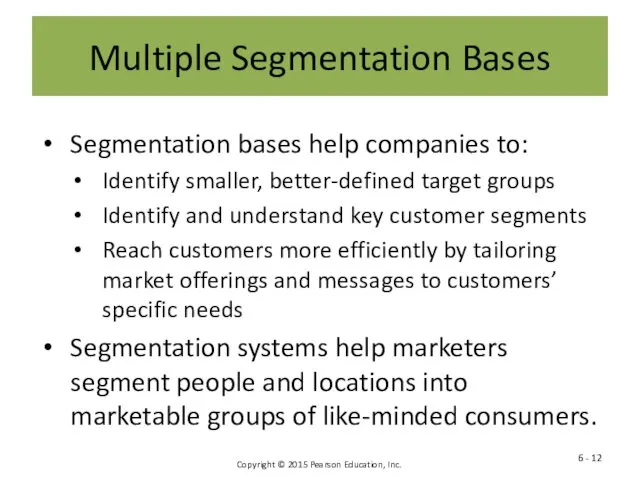
- 12. Multiple Segmentation Bases Segmentation bases help companies to: Identify smaller, better-defined target groups Identify and understand
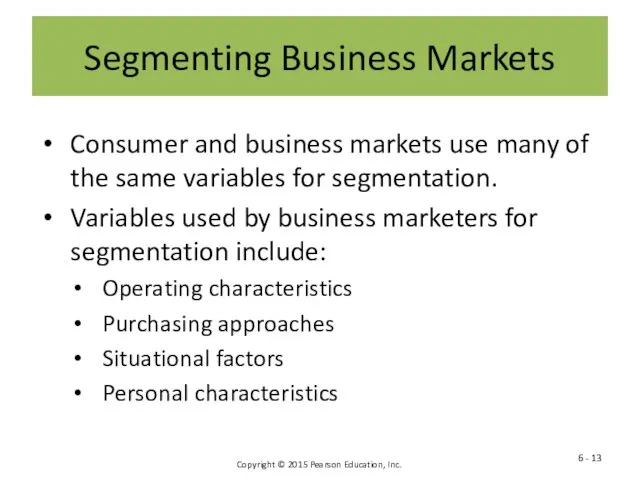
- 13. Segmenting Business Markets Consumer and business markets use many of the same variables for segmentation. Variables
- 14. Segmenting International Markets Variables include: Geographic location Economic factors Political and legal factors Cultural factors Intermarket
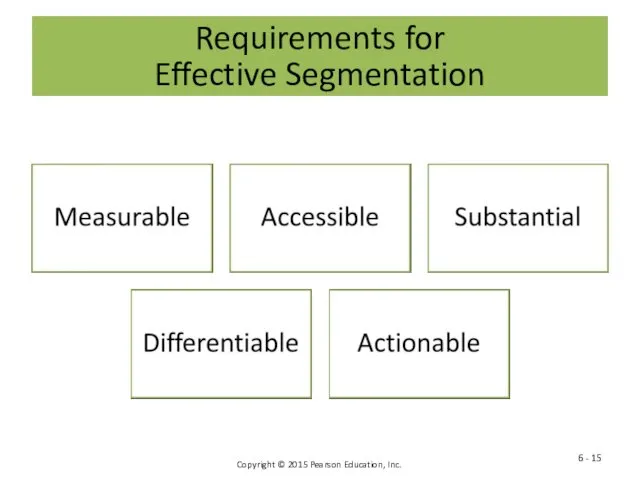
- 15. Requirements for Effective Segmentation 6 -
- 16. Market Targeting Evaluating the various segments based on: Segment size and growth Segment structural attractiveness Company
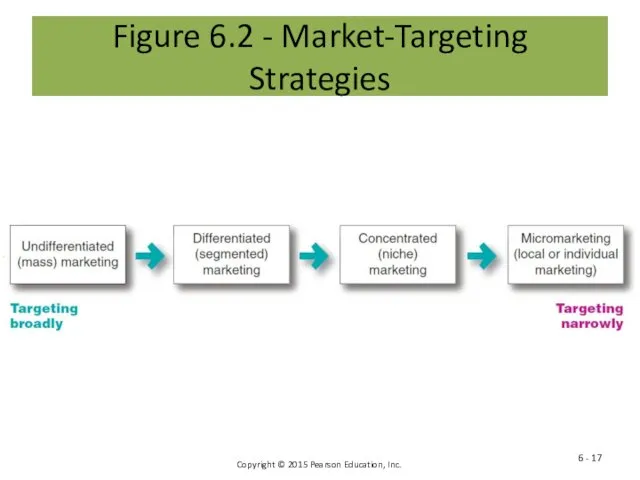
- 17. Figure 6.2 - Market-Targeting Strategies 6 -
- 18. Choosing a Targeting Strategy Factors to consider Company resources Product variability Product’s life-cycle stage Market variability
- 19. Socially Responsible Target Marketing Controversy and concern of target marketing Vulnerable or disadvantaged consumers are targeted
- 20. Differentiation and Positioning Firms must decide which segments to target and on the value proposition. Product
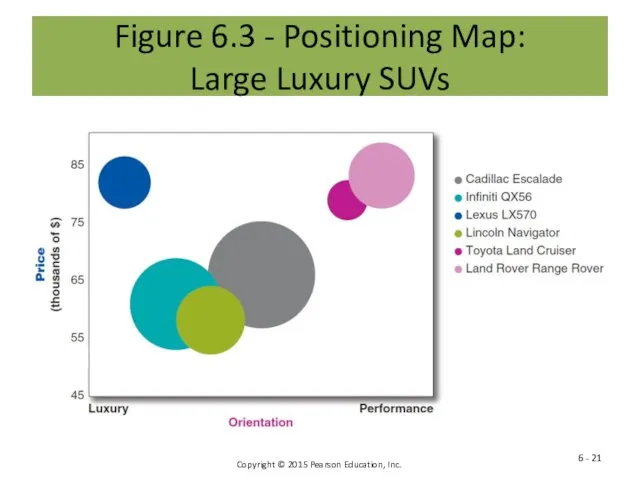
- 21. Figure 6.3 - Positioning Map: Large Luxury SUVs 6 -
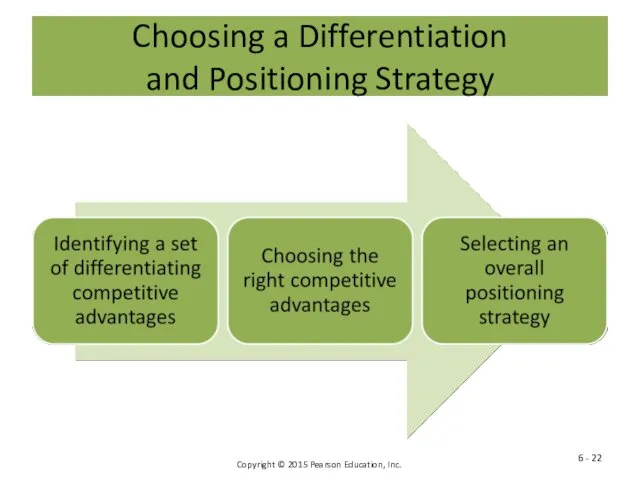
- 22. Choosing a Differentiation and Positioning Strategy 6 -
- 23. Identifying Possible Value Differences and Competitive Advantages Competitive advantage: An advantage over competitors gained by offering
- 24. Choosing the Right Competitive Advantages 6 -
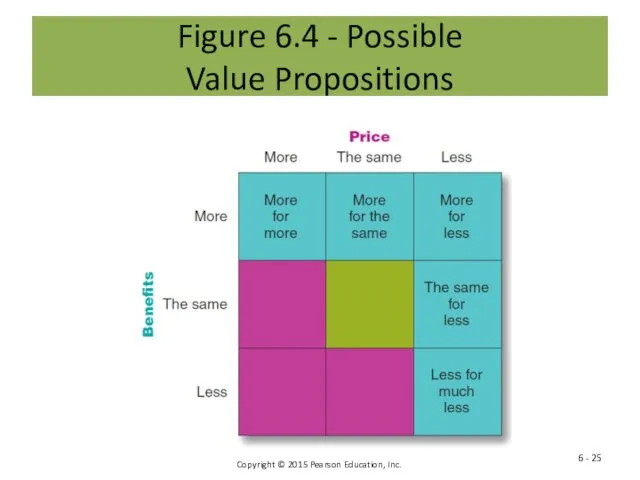
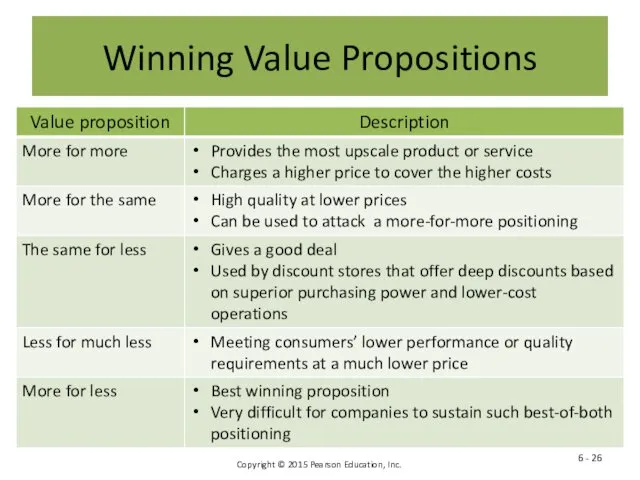
- 25. Figure 6.4 - Possible Value Propositions 6 -
- 26. Winning Value Propositions 6 -
- 27. Developing a Positioning Statement Positioning statement: Summarizes company or brand positioning Format: To (target segment and
- 28. Communicating and Delivering the Chosen Position All the company’s marketing mix efforts must support the positioning
- 29. Learning Objectives Define the major steps in designing a customer-driven marketing strategy: market segmentation, targeting, differentiation,
- 30. Learning Objectives Explain how companies identify attractive market segments and choose a market-targeting strategy. Discuss how
- 32. Скачать презентацию















 Набор Здоровье ваших костей. Компания NSP
Набор Здоровье ваших костей. Компания NSP Солнцезащитные средства Мэри Кэй
Солнцезащитные средства Мэри Кэй Новогоднее предложение. Игрокс
Новогоднее предложение. Игрокс Рекламное агентство Мир рекламы
Рекламное агентство Мир рекламы Пресс-ланч, брифинг, пресс-тур и пресс-клуб
Пресс-ланч, брифинг, пресс-тур и пресс-клуб Веб-приложение для управления офисом и создания бронирований офисных рабочих мест
Веб-приложение для управления офисом и создания бронирований офисных рабочих мест Инновационные инсектоакарицидные препараты
Инновационные инсектоакарицидные препараты Творческий и инновационный подход при разработке проектов в торговом деле. Тема 5
Творческий и инновационный подход при разработке проектов в торговом деле. Тема 5 Методы рекрутинга
Методы рекрутинга Мастер по шугарингу. Базовое обучение
Мастер по шугарингу. Базовое обучение Лучшее детское мероприятие. Караоке- спектакль
Лучшее детское мероприятие. Караоке- спектакль Сбалансированная система показателей (BSC) группы компаний Протек. Производство лекарственных средств
Сбалансированная система показателей (BSC) группы компаний Протек. Производство лекарственных средств Фонд детского кино Сотворение
Фонд детского кино Сотворение Raspberry Pi India
Raspberry Pi India Основы продаж. Семь этапов продаж
Основы продаж. Семь этапов продаж Оценка эффективности рекламной деятельности на телевидении
Оценка эффективности рекламной деятельности на телевидении Банкеты и конференции
Банкеты и конференции Новый фитнес с бассейном Вертикаль. Официальное открытие 2 сентября 2017. Успей стать членом клуба по самым низким ценам
Новый фитнес с бассейном Вертикаль. Официальное открытие 2 сентября 2017. Успей стать членом клуба по самым низким ценам Лофт — архитектурный стиль XX—XXI века
Лофт — архитектурный стиль XX—XXI века Wowspace Decor. Мебель в аренду на мероприятия, на выставку, на свадьбу и другие события
Wowspace Decor. Мебель в аренду на мероприятия, на выставку, на свадьбу и другие события Проект участника Science Fair
Проект участника Science Fair ЖК Эверест, г. Екатеринбург
ЖК Эверест, г. Екатеринбург Маркетинг и исследования в маркетинге
Маркетинг и исследования в маркетинге Делаем бизнес вместе в Фаберлик
Делаем бизнес вместе в Фаберлик Проектирование в системе комплект
Проектирование в системе комплект Обследование объекта недвижимости. Проверка качества произведенных работ
Обследование объекта недвижимости. Проверка качества произведенных работ Міжнародна маркетингова цінова політика
Міжнародна маркетингова цінова політика Набор ножей I Cook
Набор ножей I Cook