Содержание
- 2. 12- Introduction Chapter topics: Channel objectives Distribution channels–consumer and industrial Global retailing Physical distribution, supply chains,
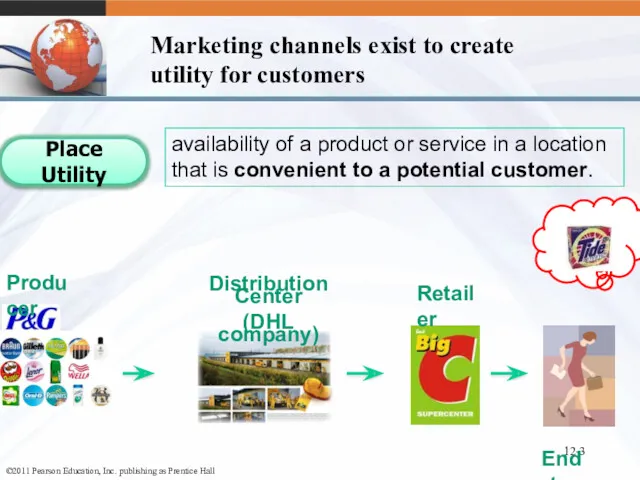
- 3. 12- availability of a product or service in a location that is convenient to a potential
- 4. 12- Time Utility availability of a product or service when desired by a customer.
- 5. 12- Form Utility availability of product processed, prepared, in proper condition and/or ready to use. availability
- 6. 12- Distribution Channels: Terminology and Structure Distribution is the physical flow of goods through channels Channels
- 7. 12- Distribution Channels: Terminology and Structure Distributor – wholesale intermediary that typically carries product lines or
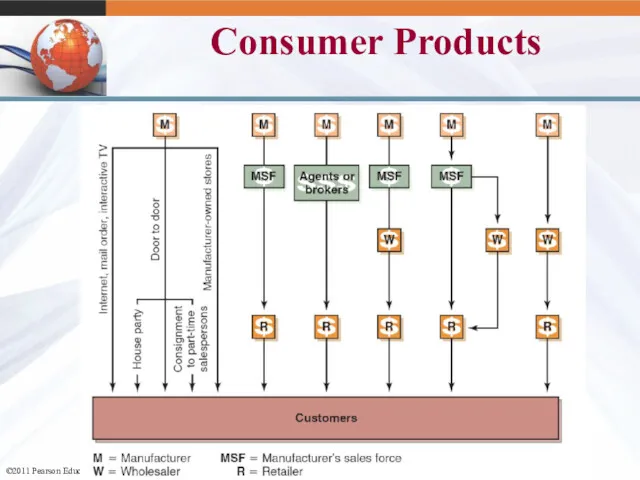
- 8. 12- Consumer Products
- 9. 12- Peer-to-Peer Selling The Internet and other related media are dramatically altering distribution Interactive TV may
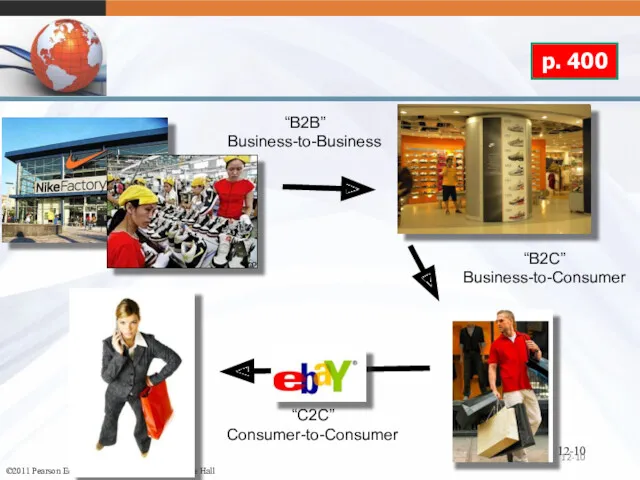
- 10. 12- 12- © 2007 McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc., McGraw-Hill/Irwin “B2B” Business-to-Business “B2C” Business-to-Consumer “C2C” Consumer-to-Consumer p. 400
- 11. 12- Door-to-Door Selling Mature form in the U.S. Growing popularity in China—AIG insurance, Mary Kay, Tupperware,
- 12. 12- Consumer Channels Manufacturer-owned stores/ independent franchisee stores Walt Disney opening 600 new stores globally Apple
- 13. 12- Consumer Products Piggyback Marketing Channel innovation that has grown in popularity One manufacturer distributes product
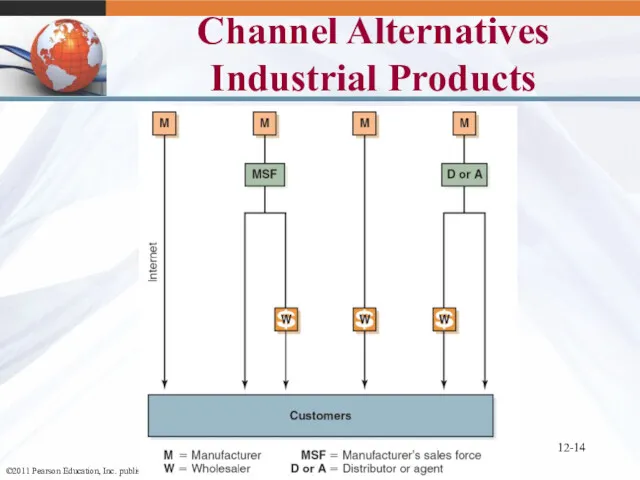
- 14. 12- Channel Alternatives Industrial Products
- 15. 12- Establishing Channels Direct involvement – the company establishes its own sales force or operates its
- 16. 12- Retailing in Developing Countries Consumers purchase food, soft drinks and other items at “Mom &
- 17. 12- Working with Channel Intermediaries Select distributors – don’t let them select you Look for distributors
- 18. 12- Working with Channel Intermediaries Support market entry by committing money, managers, and proven marketing ideas
- 19. 12- Global Retailing Department stores Specialty retailers Supermarkets Convenience stores Discount stores and warehouse clubs Hypermarkets
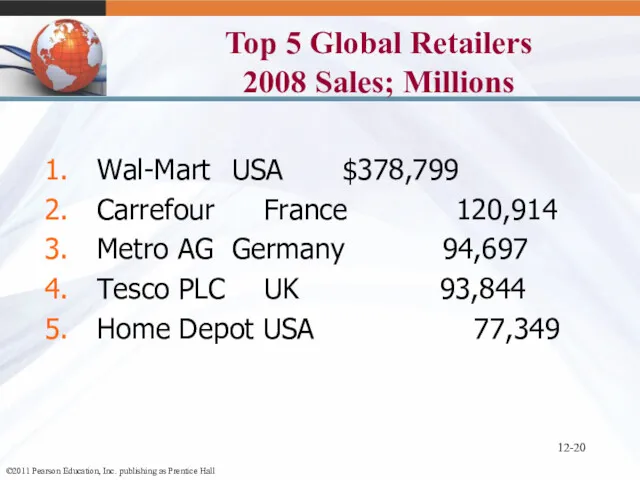
- 20. 12- Top 5 Global Retailers 2008 Sales; Millions Wal-Mart USA $378,799 Carrefour France 120,914 Metro AG
- 21. 12- Global Retailing Environmental Factors Saturation in the home country market Recession or other economic factors
- 22. 12- Classifying Global Retailers
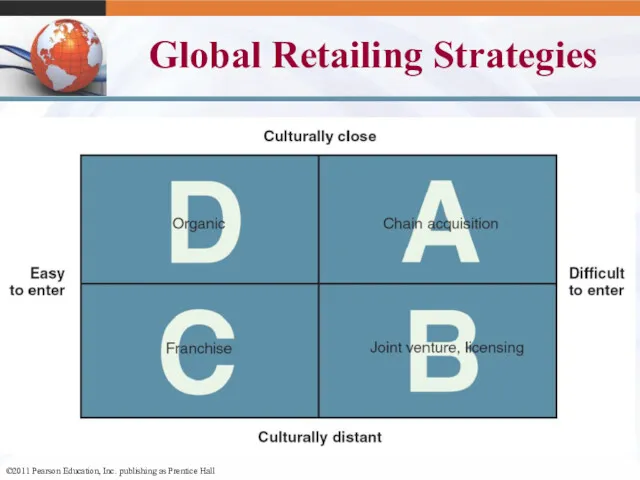
- 23. 12- Global Retailing Strategies Organic growth Company uses its own resources to open a store on
- 24. 12- Global Retailing Strategies Chain Acquisition A market entry strategy that entails purchasing a company with
- 25. 12- Global Retailing Strategies
- 26. 12- Supply Chain Definitions Logistics The management process that integrates the activities of all companies to
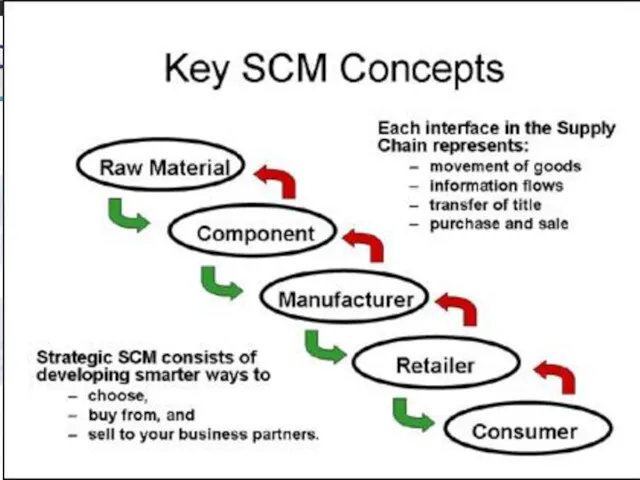
- 27. 12- Supply Chain Definitions Supply chain Includes all the firms that perform support activities by generating
- 28. 12-
- 29. 12- Key Logistics Activities Customer service Inventory MGT Logistics communications Order processing Material handling Packaging Demand
- 30. 12- Physical Distribution, Supply Chains, and Logistics Management Order Processing includes order entry in which the
- 31. 12- Wal-Mart operates 78 huge distribution centers in US and another 37 around the globe.
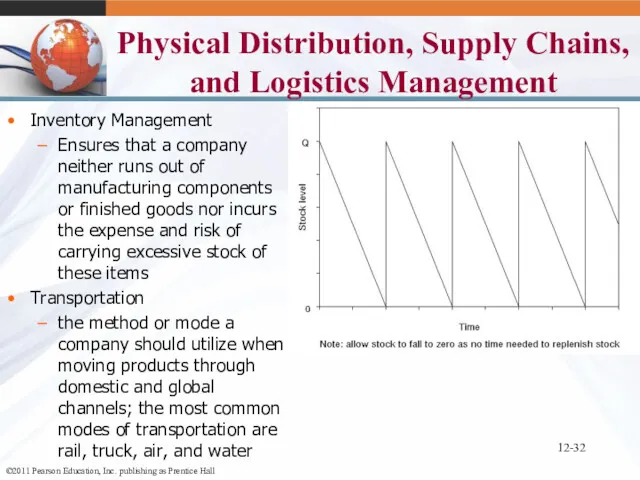
- 32. 12- Physical Distribution, Supply Chains, and Logistics Management Inventory Management Ensures that a company neither runs
- 33. 12- Transportation Channel Strategy – analyzing each shipping mode to determine which mode, or combination of
- 34. SKIP TOPICS Page 408-417 12-
- 36. Скачать презентацию

























 Advertisement. Packing
Advertisement. Packing Мировые тренды на керамическую плитку
Мировые тренды на керамическую плитку Исследование рыночного спроса на продукцию предприятия
Исследование рыночного спроса на продукцию предприятия Вихідні відомості журналу
Вихідні відомості журналу Каталог мастер-классов Пасха
Каталог мастер-классов Пасха Квалификационная (дипломная) работа Проведение исследования поведения потребителей на рынке (на примере ИП Ларшина Е.А.)
Квалификационная (дипломная) работа Проведение исследования поведения потребителей на рынке (на примере ИП Ларшина Е.А.) Хирургиялық стоматологиядағы менеджмент және маркетинг
Хирургиялық стоматологиядағы менеджмент және маркетинг Microbus love
Microbus love Оздоровительный туризм Вьетнама
Оздоровительный туризм Вьетнама Маркетинг в социальных сетях
Маркетинг в социальных сетях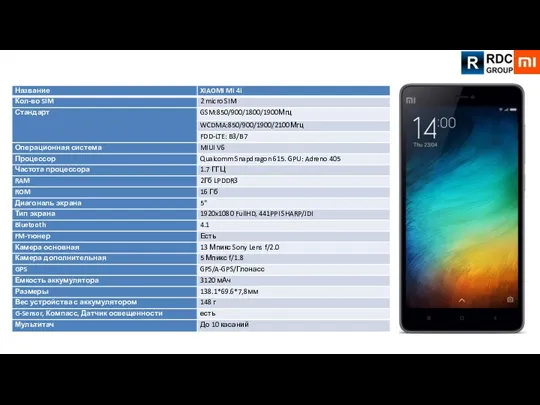 XIAOMI Redmi Note 3, XIAOMI Redmi 3 Pro, XIAOMI Redmi 2 Pro
XIAOMI Redmi Note 3, XIAOMI Redmi 3 Pro, XIAOMI Redmi 2 Pro Динамика корпоративного развития Bosch
Динамика корпоративного развития Bosch Тауар саны бойынша градация
Тауар саны бойынша градация Міжнародна реклама
Міжнародна реклама Marketing strategy for the U.S. market
Marketing strategy for the U.S. market Товарная политика аптеки в фармацевтическом маркетинге
Товарная политика аптеки в фармацевтическом маркетинге Интернет в офис. Коммерческое предложение от Билайн Бизнес
Интернет в офис. Коммерческое предложение от Билайн Бизнес Комплекс Med Planta (Cosmofarma, Италия)
Комплекс Med Planta (Cosmofarma, Италия) OZON. Статусы заказа
OZON. Статусы заказа Изменения в ассортименте моторных масел petro-canada для легкового транспорта
Изменения в ассортименте моторных масел petro-canada для легкового транспорта Фирменный стиль
Фирменный стиль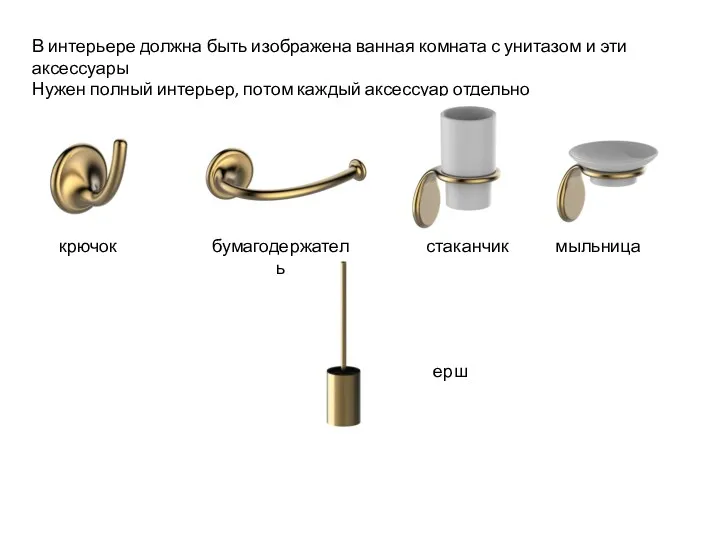 Корректировки. аксессуары для ванной Oldie
Корректировки. аксессуары для ванной Oldie ЖК Новая Ливадия
ЖК Новая Ливадия Методы оценки кривых спроса
Методы оценки кривых спроса Медиаплан по продвижению интернет-магазина Mediapark.uz в связи с Covid-19
Медиаплан по продвижению интернет-магазина Mediapark.uz в связи с Covid-19 Процесс управления маркетинговой деятельностью компании
Процесс управления маркетинговой деятельностью компании Marketing strategy
Marketing strategy Описания Шоу программ
Описания Шоу программ