Содержание
- 2. Learning Goals Explain the importance of information to the company Define the marketing information system Outline
- 3. Learning Goals Explain the importance of information to the company Define the marketing information system Outline
- 4. Case Study New Coke New Coke product failure Poor sales Over 1,500 phone calls a day
- 5. Learning Goals Explain the importance of information to the company Define the marketing information system Outline
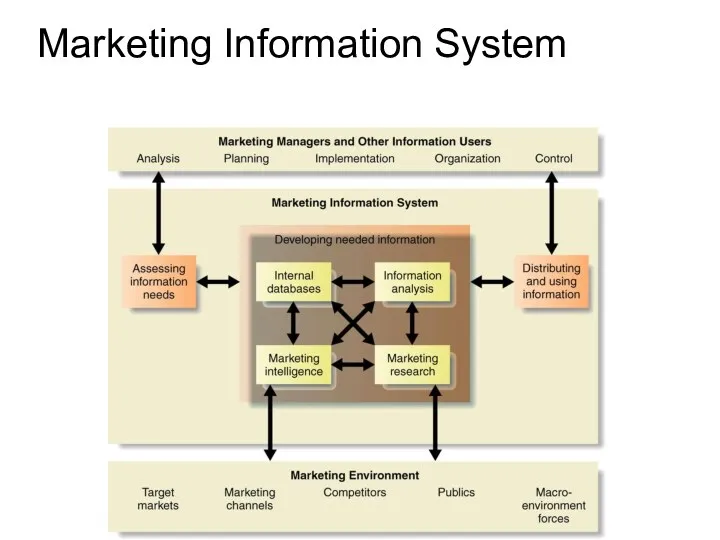
- 6. Marketing Information System Marketing Information System (MIS) Consists of people, equipment, and procedures to gather, sort,
- 7. Marketing Information System
- 8. Marketing Information System Interacts with information users to assess information Develops needed information from internal and
- 9. PeopleSoft markets databases to optimize customer relationship management
- 10. Assessing Marketing Information Needs The MIS serves company managers as well as external partners The MIS
- 11. Developing Marketing Information Internal data is gathered via customer databases, financial records, and operations reports Advantages
- 12. This ad is targeted to businesses to reinforce the importance of a good internal data for
- 13. Developing Marketing Information Marketing intelligence is the systematic collection and analysis of publicly available information about
- 14. Sources of Competitive Intelligence Company employees Internet Garbage Published information Competitor’s employees Trade shows Benchmarking Channel
- 15. Developing Marketing Information Marketing research is the systematic design, collection, analysis, and reporting of data relevant
- 16. Greenfield Online runs a teen panel for feedback to clients on this important market
- 17. Learning Goals Explain the importance of information to the company Define the marketing information system Outline
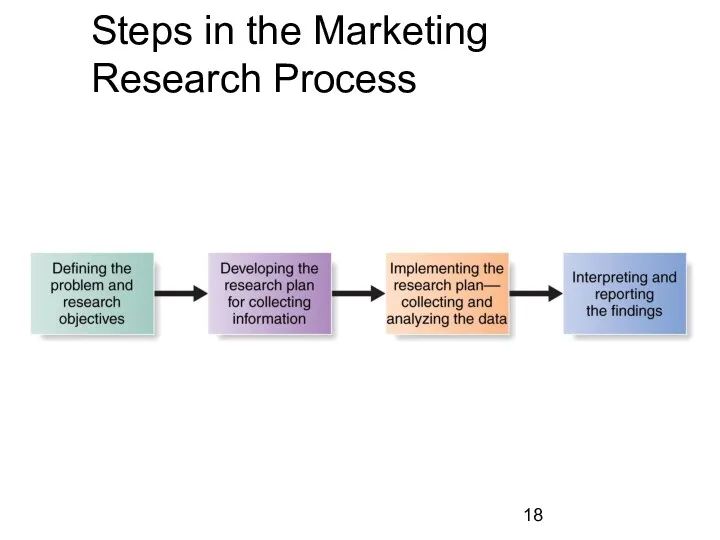
- 18. Steps in the Marketing Research Process
- 19. Step 1: Defining the problem and research objectives The manager and the researcher must work together.
- 20. Step 1: Defining the Problem & Research Objectives Example: American Airlines Case: American Airlines is constantly
- 21. Defining the Problem & Research Objectives Example: American Airlines Case The marketing manager contacted a major
- 22. Defining the Problem & Research Objectives Example: American Airlines Case (cont.) American Airlines looking for new
- 23. Defining the Problem & Research Objectives Example: American Airlines Case (cont.) Research Objectives: What are the
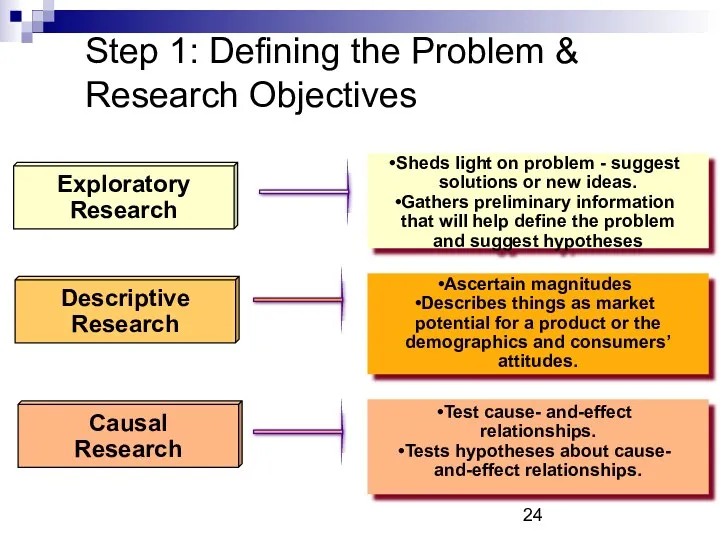
- 24. Step 1: Defining the Problem & Research Objectives Exploratory Research Descriptive Research Causal Research
- 25. Step 2: Developing the Research Plan Research plan is a written document which outlines the type
- 26. Secondary Data Secondary data sources: Government information Internal, commercial, and online databases Publications Advantages: Obtained quickly
- 27. Developing the Research Plan: Data Sources
- 28. Secondary data on female spending has prompted marketing changes at retailers Source: Business Week
- 29. Evaluate the Following when Judging Data Quality Relevance Accuracy Currency Impartiality
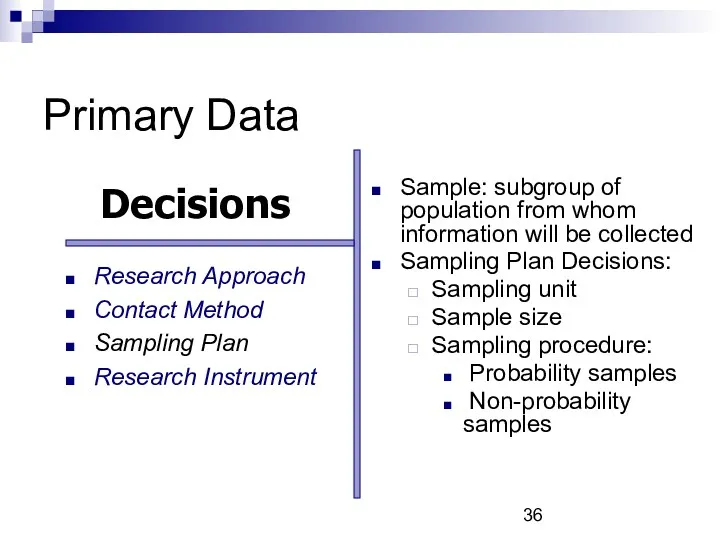
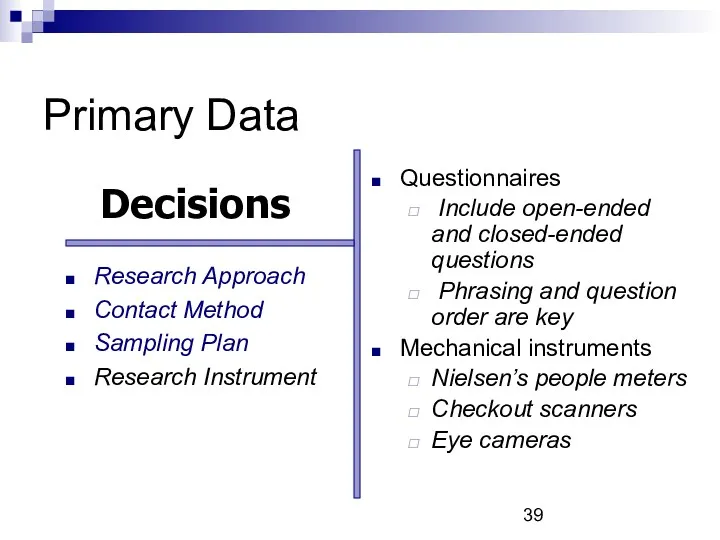
- 30. Primary Data Primary research decisions: Research approaches Contact methods Sampling plan Research instruments
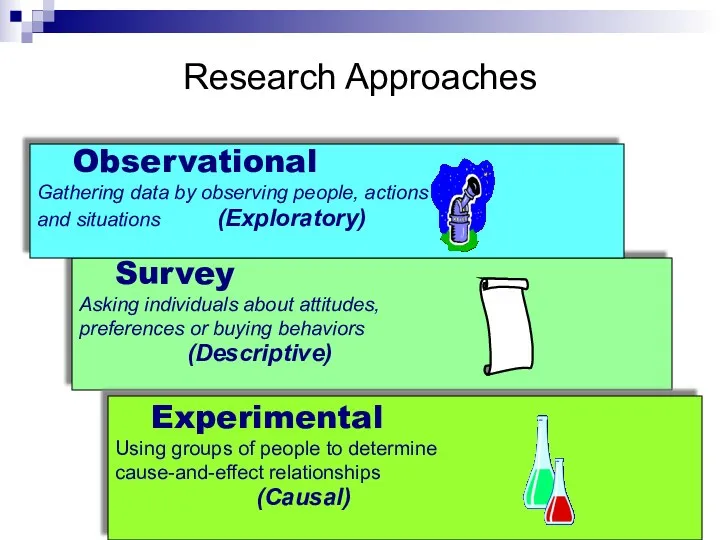
- 31. Primary Data Observation research using people or machines Discovers behavior but not motivations Survey research Effective
- 32. Research Approaches
- 33. Primary Data Key Contact Methods include: Mail surveys Telephone surveys Personal interviewing: Individual or focus group
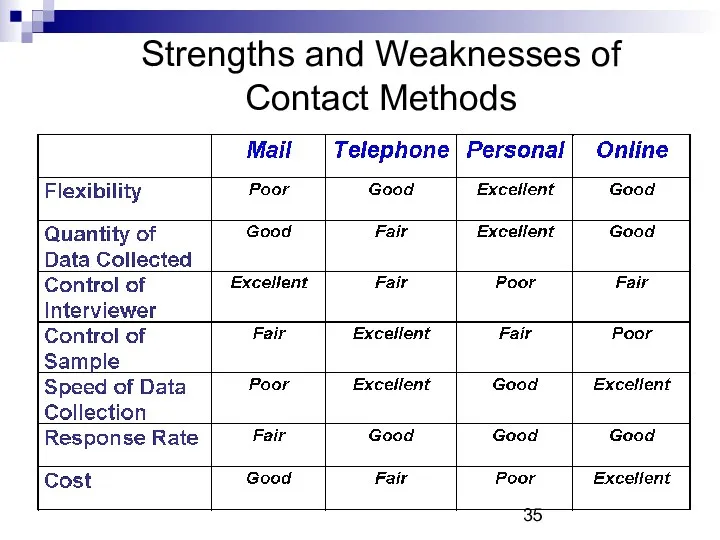
- 34. Strengths and Weaknesses of Contact Methods Relate to: Flexibility Sample control Data quantity Cost Interviewer effects
- 35. Strengths and Weaknesses of Contact Methods
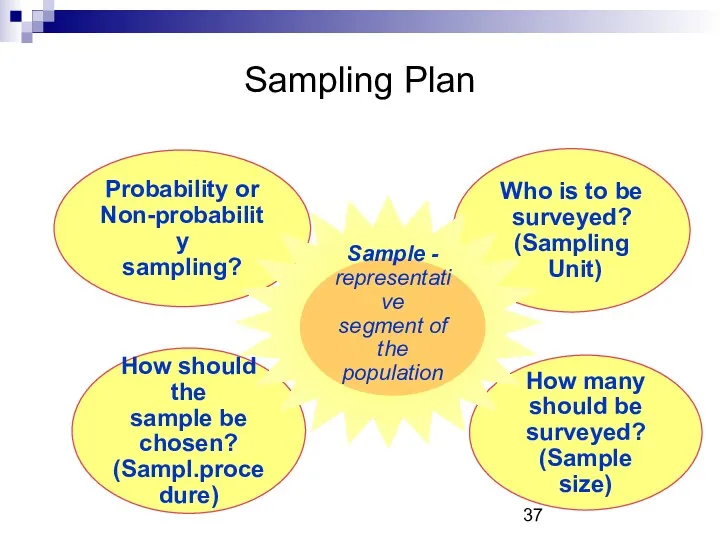
- 36. Primary Data Sample: subgroup of population from whom information will be collected Sampling Plan Decisions: Sampling
- 37. Sampling Plan Who is to be surveyed? (Sampling Unit) How many should be surveyed? (Sample size)
- 38. Sampling Plan Probability Sampling Simple random sample ğ every member of the population has an equal
- 39. Primary Data Questionnaires Include open-ended and closed-ended questions Phrasing and question order are key Mechanical instruments
- 40. Eye Cameras Eye cameras track the consumer’s eyes as they look at marketing materials Applications print
- 41. Discussion Question A digital camera manufacturer wants to determine what is most important to older (50+)
- 42. Step 3: Implementing the Research Plan Data is collected by the company or an outside firm
- 43. Step 4: Interpreting and Reporting the Findings The research interprets the finding, draws conclusions and reports
- 44. American Airlines Case: Main Survey Findings The chief reasons for using in-flight phone service are: emergencies,
- 45. American Airlines Case: Main Survey Findings (cont.) The promotion of in-flight phone service would win American
- 46. Good Marketing Research Is scientific Is creative Uses multiple methods Realizes the interdependence of models &
- 47. Marketing Research Industry $ 9 Billion a year is spent on marketing/advertising/public opinion research services around
- 48. Marketing Research Industry in Turkey Syndicated Services (MR data gathering and reporting) AC Nielsen: Retail Measurement
- 49. Analyzing Marketing Information Information gathered in internal databases and through marketing intelligence and marketing research may
- 50. Customer Relationship Management Customer relationship management (CRM) software helps manage information by integrating customer data from
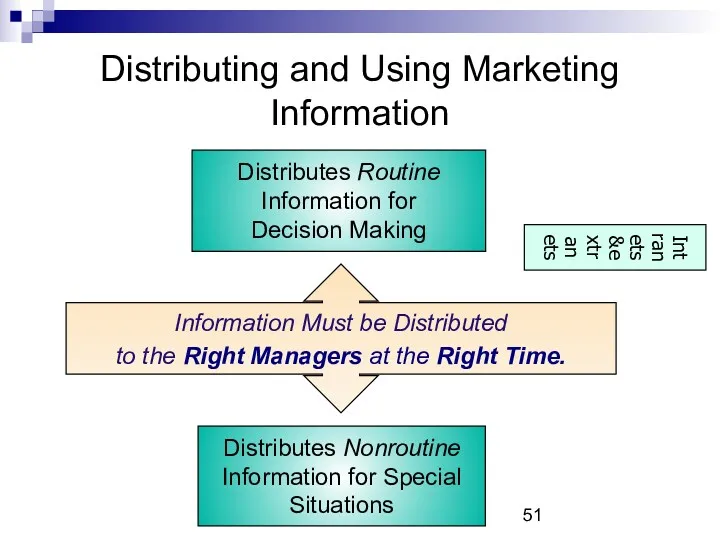
- 51. Distributing and Using Marketing Information Information Must be Distributed to the Right Managers at the Right
- 52. Other Considerations Marketing research in small businesses and not-for-profit organizations International marketing research Public policy and
- 53. Market Research Companies AC Nielsen AC Nielsen helps define the problem by packaging data around common
- 54. Market Research Companies AC Nielsen
- 56. Скачать презентацию











































 Організація обслуговування прийомів
Організація обслуговування прийомів Компания Merry Cherry. Вкусная и здоровая пища для детей
Компания Merry Cherry. Вкусная и здоровая пища для детей Насосні станції. Асортимент
Насосні станції. Асортимент On Vans Brand Story
On Vans Brand Story Бенчмаркинг как функция маркетинговых исследований
Бенчмаркинг как функция маркетинговых исследований Кастомизация. Каналы сбыта
Кастомизация. Каналы сбыта Revaluetech Ltd. Large scale uses for Polymer Composites made from post use mixed plastics
Revaluetech Ltd. Large scale uses for Polymer Composites made from post use mixed plastics Продажи. 7 шагов
Продажи. 7 шагов Nokia
Nokia Маркетинг отношений или совершенствуем точки контакта
Маркетинг отношений или совершенствуем точки контакта Heineken
Heineken Экспресс-анализ франчайзингового предложения Утилитсервис
Экспресс-анализ франчайзингового предложения Утилитсервис Квартал Красный кирпичник в Санкт-Петербурге для агентств
Квартал Красный кирпичник в Санкт-Петербурге для агентств Travelling. Couchsurfing
Travelling. Couchsurfing Визитная карточка (визитка)
Визитная карточка (визитка) Дисплеї і стойки Хот Вілс
Дисплеї і стойки Хот Вілс Ставропольский край. Развитие направлений ИБП и АКБ
Ставропольский край. Развитие направлений ИБП и АКБ Понятия и категории маркетинга
Понятия и категории маркетинга Архитектурные элементы интерьера квартиры
Архитектурные элементы интерьера квартиры Продажи Инсталляторов
Продажи Инсталляторов Продукция компании Amway слишком дорогая
Продукция компании Amway слишком дорогая Новые тарифы Tele2
Новые тарифы Tele2 Більше, ніж краса. AVON
Більше, ніж краса. AVON Компания KRASS
Компания KRASS What is promotion?
What is promotion? Особенности продажи и характеристика ассортимента сувениров и товаров народных художественных промыслов
Особенности продажи и характеристика ассортимента сувениров и товаров народных художественных промыслов Маркетинг ресторана который работает
Маркетинг ресторана который работает Раскрытие библиотечного фонда как способ популяризации книги и чтения
Раскрытие библиотечного фонда как способ популяризации книги и чтения