Содержание
- 2. Learning Objectives After studying this chapter, you should be able to: Explain the importance of information
- 3. Chapter Outline Assessing Marketing Information Needs Developing Marketing Information Marketing Research Analyzing Marketing Information Distributing and
- 4. A marketing information system (MIS) consists of people, equipment, and procedures to gather, sort, analyze, evaluate,
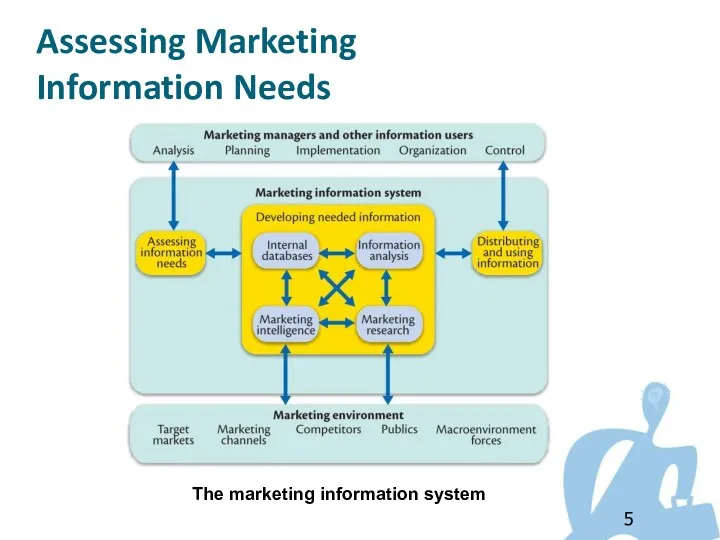
- 5. Assessing Marketing Information Needs The marketing information system
- 6. Assessing Marketing Information Needs MIS provides information to the company’s marketing and other managers and external
- 7. A good MIS balances the information users would like to have against what they need and
- 8. Marketers can obtain information from: Internal data Marketing intelligence Marketing research Developing Marketing Information
- 9. Internal Data Internal databases are electronic collections of consumer and market information obtained from data sources
- 10. Advantages: Can be accessed more quickly Less expensive Disadvantages: Incomplete information Wrong form for decision making
- 11. Marketing Intelligence Marketing intelligence is the systematic collection and analysis of publicly available information about competitors
- 12. Marketing research is the systematic design, collection, analysis, and reporting of data relevant to a specific
- 13. Steps in the marketing research process Defining the problem and research objectives Developing the research plan
- 14. Defining the Problem and Research Objectives Types of objectives: Exploratory research Descriptive research Causal research Marketing
- 15. Defining the Problem and Research Objectives Exploratory research is the gathering of preliminary information that will
- 16. Developing the Research Plan The research plan Outlines sources of existing data Spells out the specific
- 17. Developing the Research Plan The research plan is a written proposal that includes: Management problem Research
- 18. Developing the Research Plan Secondary data consists of information that already exists somewhere, having been collected
- 19. + Advantages: Speed Cost Provides data that a company cannot collect on its own Gathering Secondary
- 20. Primary Data Collection Research approaches Contact methods Sampling plan Research instruments Marketing Research
- 21. Research Approaches Observational research involves gathering primary data by observing relevant people, actions, and situations. Ethnographic
- 22. Research Approaches Survey research is the most widely used method and is best for descriptive information—knowledge,
- 23. Research Approaches Experimental research is best for gathering causal information Tries to explain cause-and-effect relationships. Marketing
- 24. Contact Methods Mail questionnaires Collect large amounts of information Low cost Less bias with no interviewer
- 25. Contact Methods Telephone interviewing Collects information quickly More flexible than mail questionnaires Interviewers can explain difficult
- 26. Contact Methods Mail, telephone, and personal interviewing Personal interviewing Individual interviewing Group interviewing Marketing Research
- 27. Contact Methods Personal interviewing Individual interviewing Involves talking with people at home or the office, on
- 28. Contact Methods Online marketing research Internet surveys Online panels Online experiments Online focus groups Marketing Research
- 29. Contact Methods Online marketing research Low cost Speed to administer Fast results Good for hard-to-reach groups
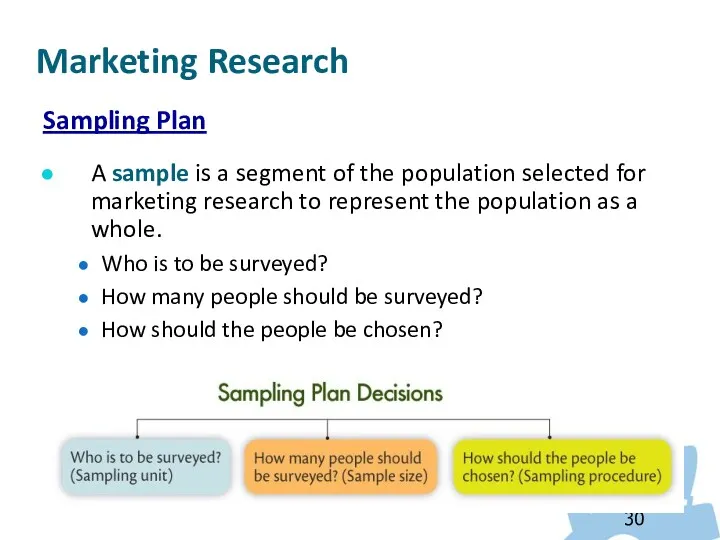
- 30. Sampling Plan A sample is a segment of the population selected for marketing research to represent
- 31. Marketing Research Sampling Plan Probability samples: Each population member has a known chance of being included
- 32. Marketing Research Research Instruments Questionnaires Mechanical devices
- 33. Marketing Research Research Instruments Questionnaires Most common Administered in person, by phone, or online Flexible Open-end
- 34. Marketing Research Research Instruments Closed-end questions include all the possible answers, and subjects are to make
- 35. Implementing the Research Plan Collecting data Processing the information Analyzing the information Issues to consider: What
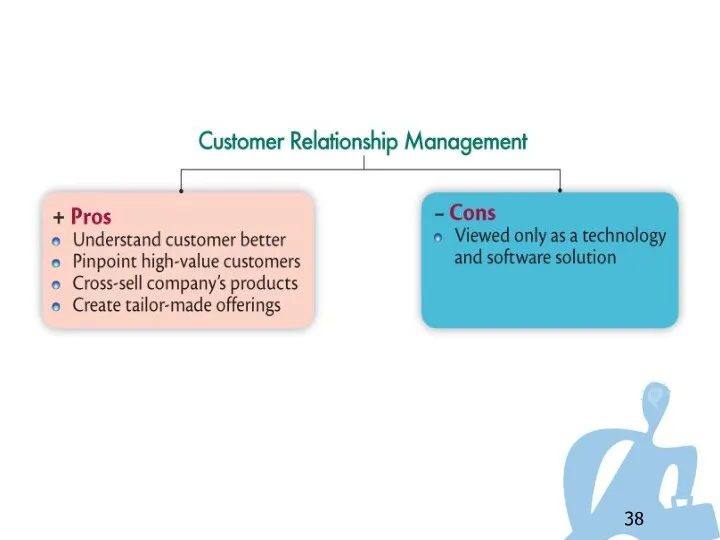
- 36. Customer Relationship Management (CRM) Consists of sophisticated software and analytical tools Integrates customer information from all
- 37. Customer Relationship Management (CRM) Data warehouses are comprehensive companywide electronic databases of finely-tuned, detailed customer information.
- 39. Customer Relationship Management (CRM) Touch points: Every contact between the customer and company Customer purchases Sales
- 40. Information distribution involves entering information into databases and making it available in a time-useable manner. Intranet
- 41. Other Marketing Information Considerations Marketing Research in Small Businesses and Nonprofit Organizations Need information about their
- 42. Other Marketing Information Considerations Marketing Research in Small Businesses and Nonprofit Organizations Sources of marketing information:
- 43. Other Marketing Information Considerations Marketing Research in Small Businesses and Nonprofit Organizations Sources of marketing information:
- 44. Other Marketing Information Considerations International Marketing Research Additional and different challenges: Level of economic development Culture
- 46. Скачать презентацию








































 Project: Global Social Media Plan // March Topic: Tyre Change Format: image Date: Flexible Content
Project: Global Social Media Plan // March Topic: Tyre Change Format: image Date: Flexible Content Компания Тилайн
Компания Тилайн Бренд Мистер КВАККИ. Продукция детской косметики и бытовой химии
Бренд Мистер КВАККИ. Продукция детской косметики и бытовой химии Кондитерская BakeCake. Торты на заказ с доставкой
Кондитерская BakeCake. Торты на заказ с доставкой Поведенческие в Google
Поведенческие в Google Принципы продаж. Ошибки, техники, приемы
Принципы продаж. Ошибки, техники, приемы Краткая характеристика табака
Краткая характеристика табака Групповой коучинг по продаже товаров через интернет: Разбогатей или сдохни!
Групповой коучинг по продаже товаров через интернет: Разбогатей или сдохни! ЖК Ultra City 2.0 в Санкт-Петербурге от Северный город
ЖК Ultra City 2.0 в Санкт-Петербурге от Северный город Товар в системе маркетинга
Товар в системе маркетинга Система товародвижения в маркетинге
Система товародвижения в маркетинге Корпорация Apple
Корпорация Apple Коммерческое предложение Интернет для бизнеса
Коммерческое предложение Интернет для бизнеса Бриф на брошюру Бунге Про
Бриф на брошюру Бунге Про Сварочные аппараты REDVERG
Сварочные аппараты REDVERG Сфера туризма. Методы формирования спроса и маркетинговые инструменты
Сфера туризма. Методы формирования спроса и маркетинговые инструменты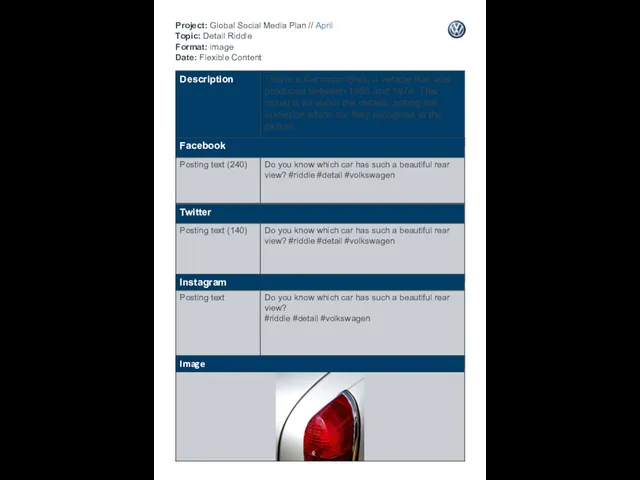 Project: Global Social Media Plan // April Topic: Detail Riddle Format: image Date: Flexible Content
Project: Global Social Media Plan // April Topic: Detail Riddle Format: image Date: Flexible Content Виды маркетинга
Виды маркетинга Сетевая акция Литературный фантик
Сетевая акция Литературный фантик Специальная программа для сотрудников корпоративного клиента АО Тюменьэнерго по услугам сотовой связи МегаФон
Специальная программа для сотрудников корпоративного клиента АО Тюменьэнерго по услугам сотовой связи МегаФон Совершенствование маркетинговой деятельности компании (на примере ООО Импульс)
Совершенствование маркетинговой деятельности компании (на примере ООО Импульс) Organization of Service on residential floors
Organization of Service on residential floors Автоматизированные информационные системы в промышленности. Электронные системы КОДЕКС
Автоматизированные информационные системы в промышленности. Электронные системы КОДЕКС Компания Брозэкс
Компания Брозэкс Форсаж. Матричный проект
Форсаж. Матричный проект ООО Виктория Эксклюзивные украшения. Ручная работа
ООО Виктория Эксклюзивные украшения. Ручная работа Product placement в компьютерных играх
Product placement в компьютерных играх Менеджмент и маркетинг. Слагаемые успеха в бизнесе
Менеджмент и маркетинг. Слагаемые успеха в бизнесе