Содержание
- 2. Discuss how firms analyze foreign markets Outline the process by which firms choose their mode of
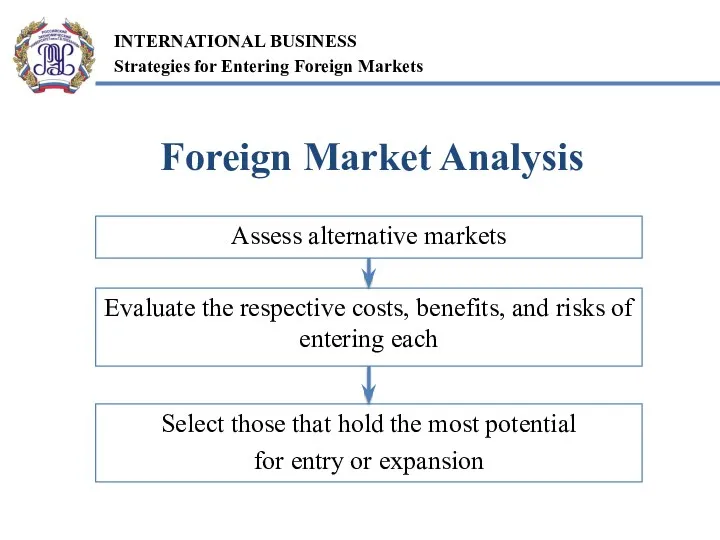
- 3. Foreign Market Analysis Assess alternative markets Evaluate the respective costs, benefits, and risks of entering each
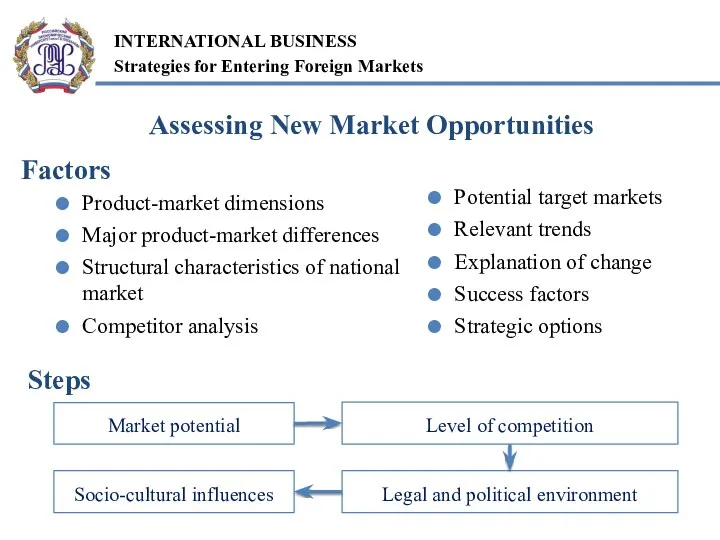
- 4. Factors Product-market dimensions Major product-market differences Structural characteristics of national market Competitor analysis Potential target markets
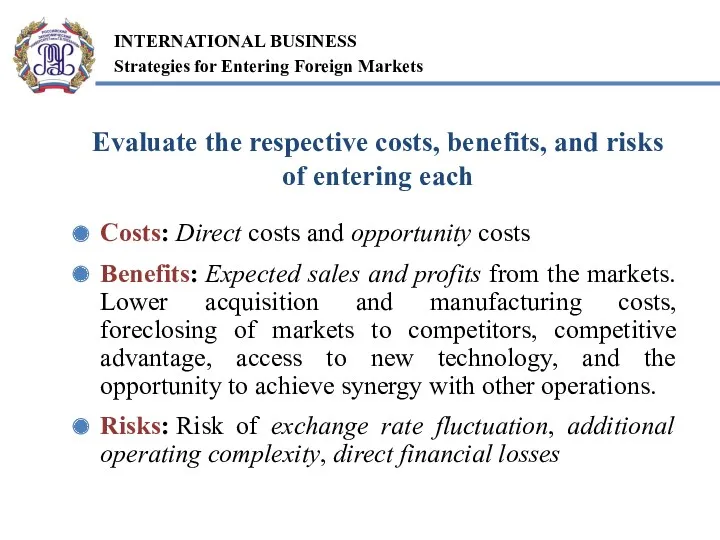
- 5. Evaluate the respective costs, benefits, and risks of entering each Costs: Direct costs and opportunity costs
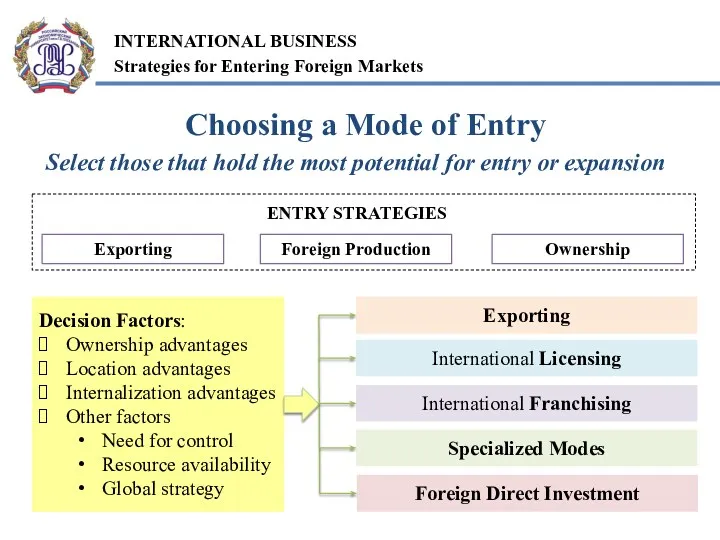
- 6. Choosing a Mode of Entry Select those that hold the most potential for entry or expansion
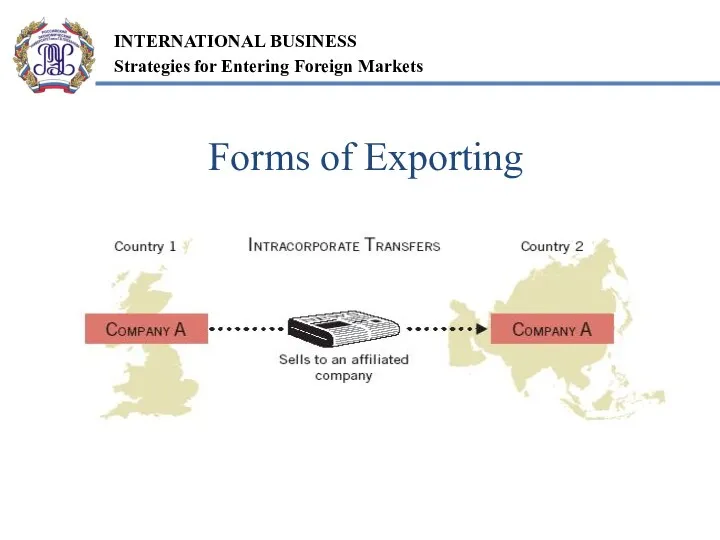
- 7. Motivations Proactive Reactive Forms Indirect exporting Direct exporting Intracorporate transfers Relatively low financial exposure Permit gradual
- 8. Forms of Exporting
- 9. Licensing Licensor leases the rights to use intellectual property Earns new revenues with low investment Licensee
- 10. Low financial risks Low-cost way to assess market potential Avoid tariffs, NTBs, restrictions on foreign investment
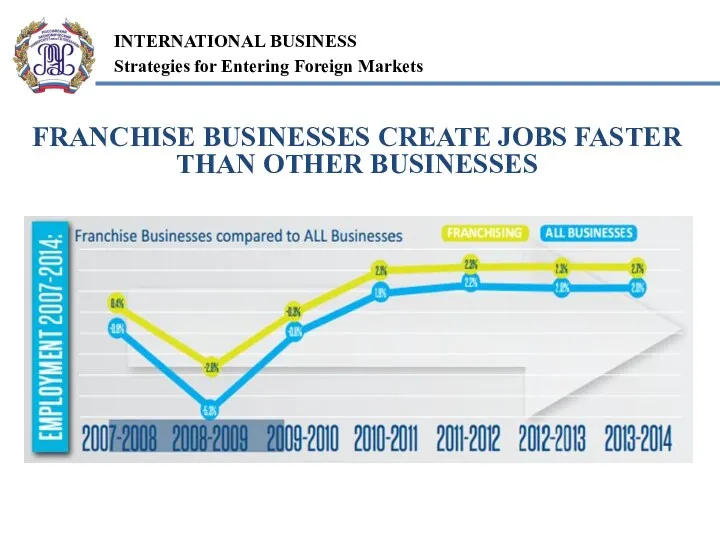
- 11. FRANCHISE BUSINESSES CREATE JOBS FASTER THAN OTHER BUSINESSES
- 12. EMPLOYMENT DISTRIBUTION by sector, 2014
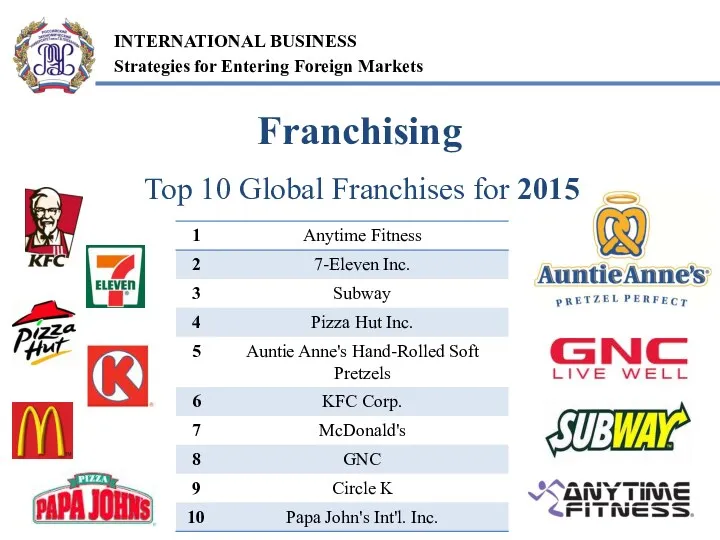
- 13. Top 10 Global Franchises for 2015 Franchising
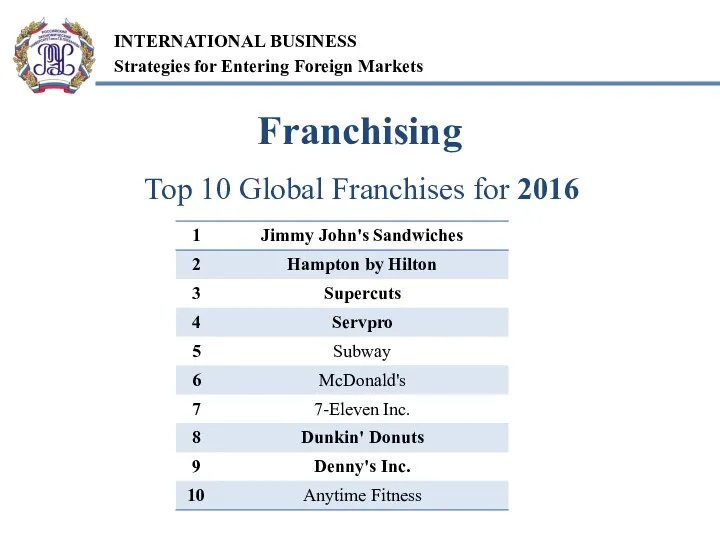
- 14. Top 10 Global Franchises for 2016 Franchising
- 15. High profit potential Maintain control over operations Acquire knowledge of local market Avoid tariffs and NTBs
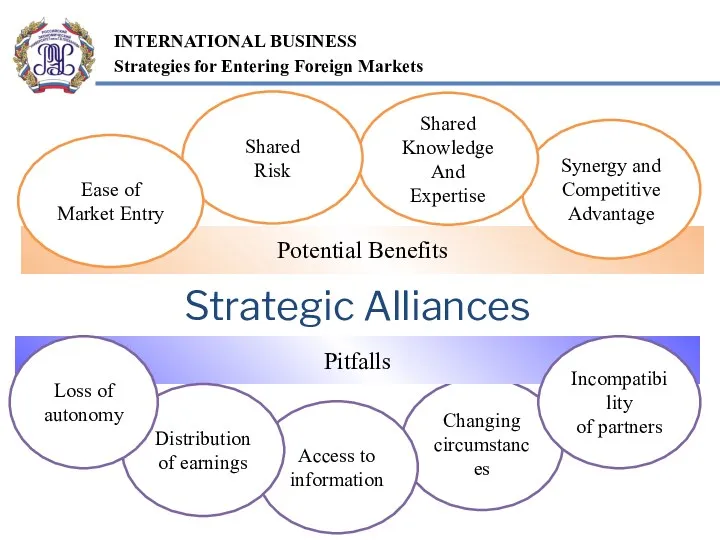
- 16. A strategic alliance is a business arrangement whereby two or more firms choose to cooperate for
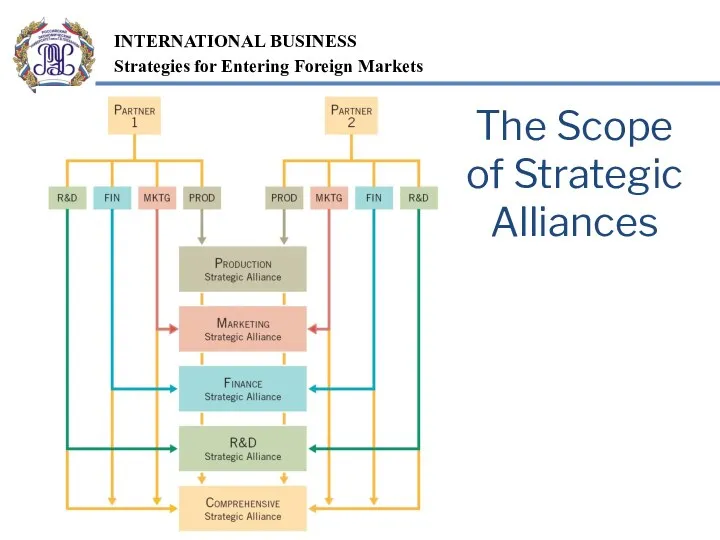
- 17. The Scope of Strategic Alliances
- 18. Approaches to Joint Management Shared management agreements Delegated arrangements Assigned arrangements Each partner fully and actively
- 19. Changing circumstances Strategic Alliances Potential Benefits Pitfalls Access to information Distribution of earnings Loss of autonomy
- 20. Contract manufacturing Turnkey project Management contract Specialized Entry Modes Advantages Focus firm’s resources on its area
- 22. Скачать презентацию









 Технологии Delphia. Диагностическая платформа Zetetic
Технологии Delphia. Диагностическая платформа Zetetic Вэлнэс - перспективы развития
Вэлнэс - перспективы развития Карта гостя. Дисконтная туристская система, созданная с целью увеличения въездного туристского потока Свердловской области
Карта гостя. Дисконтная туристская система, созданная с целью увеличения въездного туристского потока Свердловской области Добро пожаловать в мир zepter. Мир здоровья, стиля и красоты
Добро пожаловать в мир zepter. Мир здоровья, стиля и красоты Project: Global Social Media Plan // May Topic: Getting better and better. Format: Image Date: Flexible Content
Project: Global Social Media Plan // May Topic: Getting better and better. Format: Image Date: Flexible Content Коллекция двухсторонних зеркал от TianDe
Коллекция двухсторонних зеркал от TianDe Мультимедийные лонгриды, как новый формат онлайн-журналистики
Мультимедийные лонгриды, как новый формат онлайн-журналистики Эволюция концепции маркетинга
Эволюция концепции маркетинга Resolve guard cabin issues with Guard Cabin Manufacturers
Resolve guard cabin issues with Guard Cabin Manufacturers Общая теория маркетинга. Понятие и сущность маркетинга
Общая теория маркетинга. Понятие и сущность маркетинга Как продавать не товары, а решения для повышения конкурентоспособности компании
Как продавать не товары, а решения для повышения конкурентоспособности компании Lammi-Kivitalot Oy высококачественные дома
Lammi-Kivitalot Oy высококачественные дома Модели потребительского поведения
Модели потребительского поведения Новогодний гастротур в страну Арго
Новогодний гастротур в страну Арго Обзор конкурентов. Salice
Обзор конкурентов. Salice Линейка продуктов Frontol
Линейка продуктов Frontol Программа Профсоюз+
Программа Профсоюз+ Продукция компании Ellumex
Продукция компании Ellumex Продвижение профиля в Instgram в 2019 году
Продвижение профиля в Instgram в 2019 году The marketing environment. (Chapter 3)
The marketing environment. (Chapter 3) Работа регионального оператора по обращению с отходами
Работа регионального оператора по обращению с отходами Как удержать клиента. Курс Онлайн партнер Оriflame
Как удержать клиента. Курс Онлайн партнер Оriflame Euphoria Hotels. Пора менять привычки к отдыху
Euphoria Hotels. Пора менять привычки к отдыху Компания Atomy
Компания Atomy Айдиго. Каталог продукции
Айдиго. Каталог продукции Использование двухфакторной модели мотивации Ф.Герцберга в компании Макдоналдс
Использование двухфакторной модели мотивации Ф.Герцберга в компании Макдоналдс Ежедневник сотрудника филиала ВТБ МС-3
Ежедневник сотрудника филиала ВТБ МС-3 Гарантия на автомобили с пробегом
Гарантия на автомобили с пробегом