Содержание
- 2. The Market Forces of Supply and Demand Supply and demand are the two words that economists
- 3. Markets A market is a group of buyers and sellers of a particular good or service.
- 4. Markets Buyers determine demand. Sellers determine supply.
- 5. Market Type: A Competitive Market A competitive market is a market. . . with many buyers
- 6. Competition: Perfect and Otherwise Products are the same Numerous buyers and sellers so that each has
- 7. Competition: Perfect and Otherwise Monopoly One seller, and seller controls price Oligopoly Few sellers Not always
- 8. Competition: Perfect and Otherwise Monopolistic Competition Many sellers Slightly differentiated products Each seller may set price
- 9. Demand Quantity demanded is the amount of a good that buyers are willing and able to
- 10. Law of Demand The law of demand states that there is an inverse relationship between price
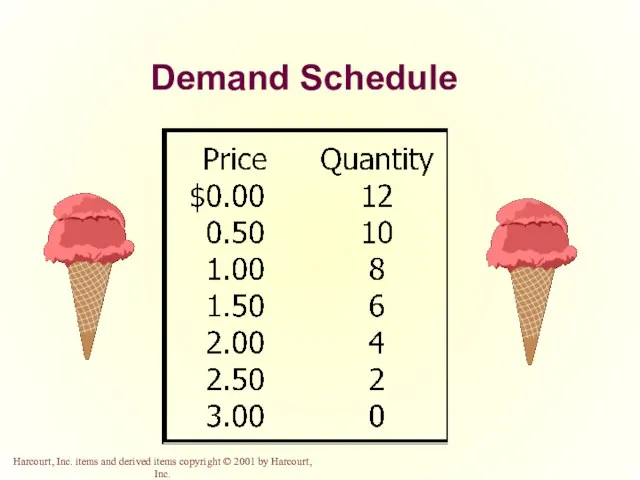
- 11. Demand Schedule The demand schedule is a table that shows the relationship between the price of
- 12. Demand Schedule
- 13. Determinants of Demand Market price Consumer income Prices of related goods Tastes Expectations
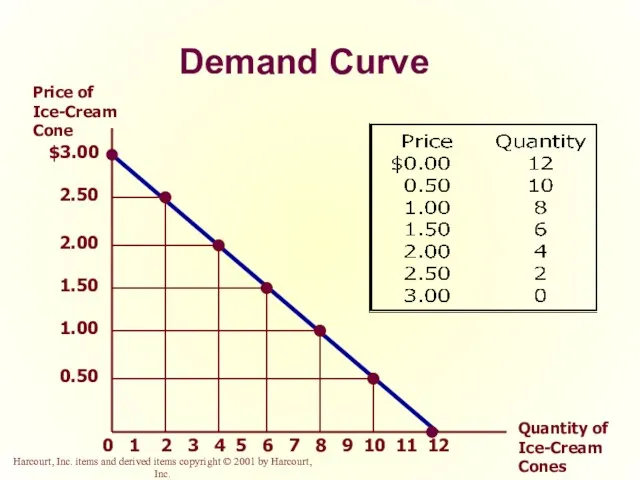
- 14. Demand Curve The demand curve is the downward-sloping line relating price to quantity demanded.
- 15. Demand Curve $3.00 2.50 2.00 1.50 1.00 0.50 2 1 3 4 5 6 7 8
- 16. Ceteris Paribus Ceteris paribus is a Latin phrase that means all variables other than the ones
- 17. Market Demand Market demand refers to the sum of all individual demands for a particular good
- 18. Determinants of Demand Market price Consumer income Prices of related goods Tastes Expectations
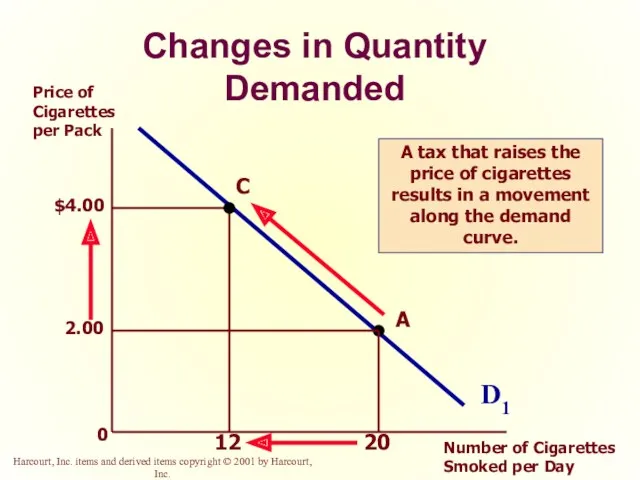
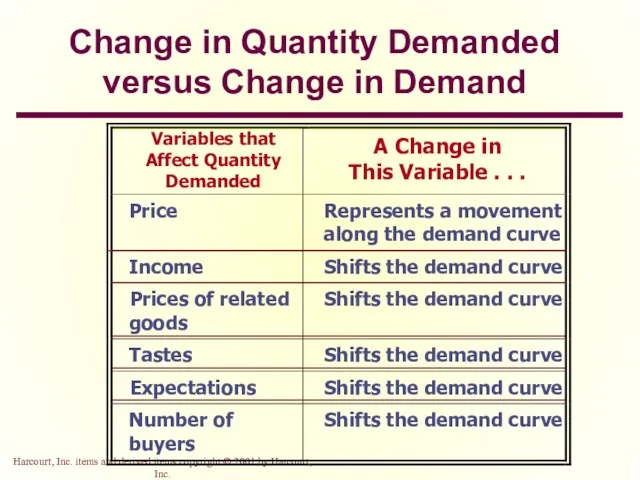
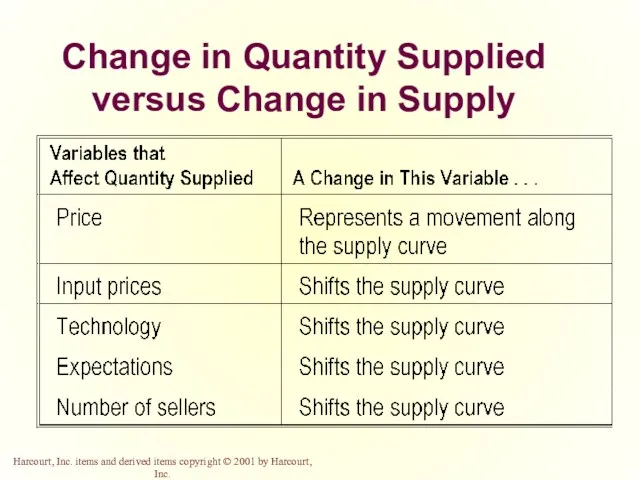
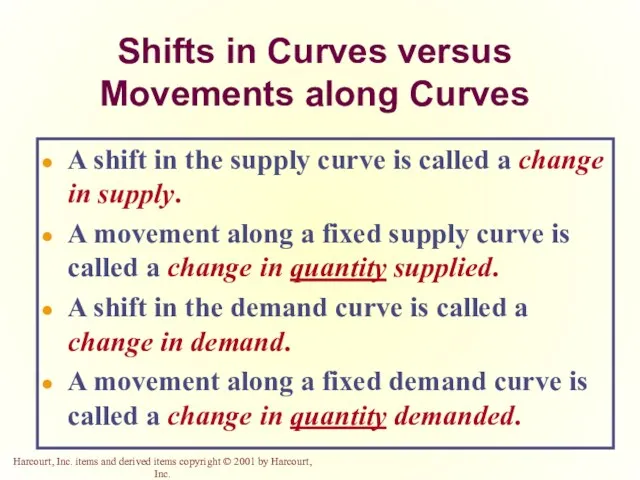
- 19. Change in Quantity Demanded versus Change in Demand Change in Quantity Demanded Movement along the demand
- 20. Changes in Quantity Demanded 0 D1 Price of Cigarettes per Pack Number of Cigarettes Smoked per
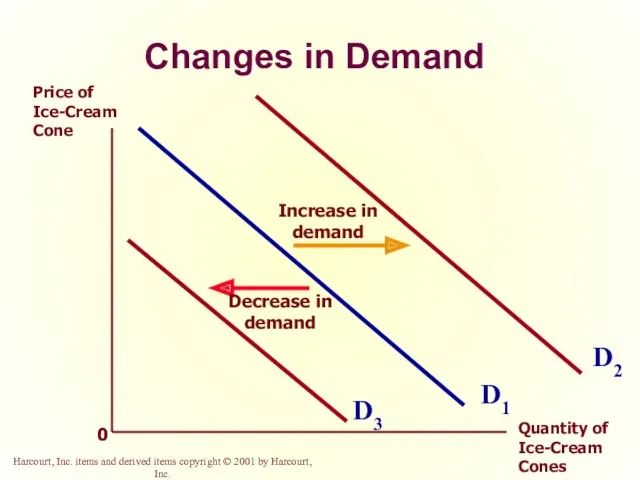
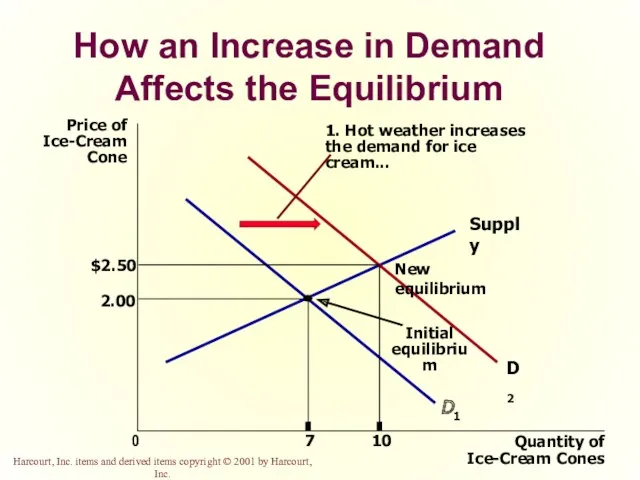
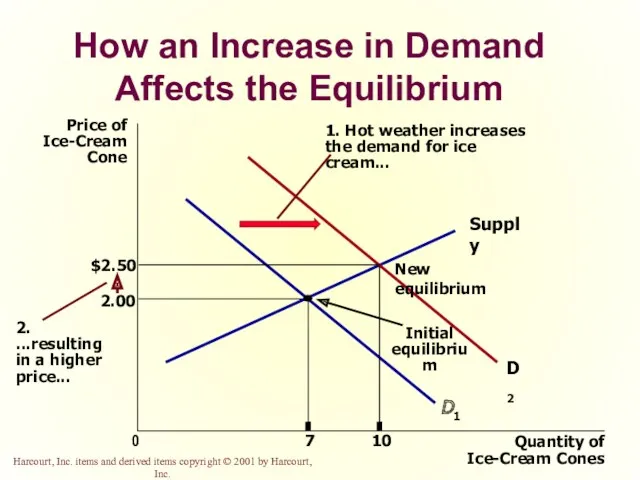
- 21. Change in Quantity Demanded versus Change in Demand Change in Demand A shift in the demand
- 22. Changes in Demand 0 D1 Price of Ice-Cream Cone Quantity of Ice-Cream Cones D3 D2 Increase
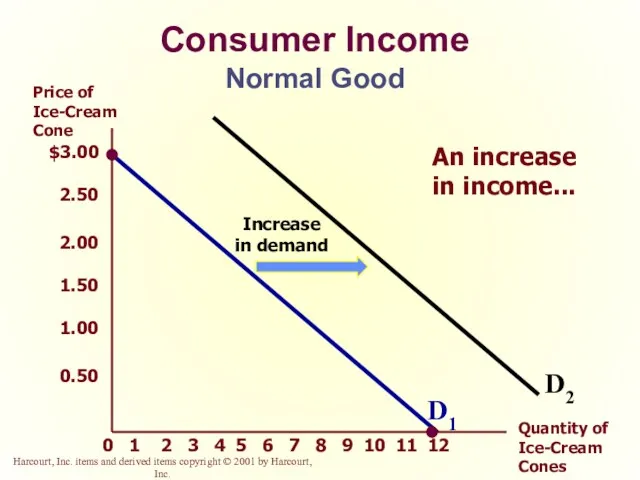
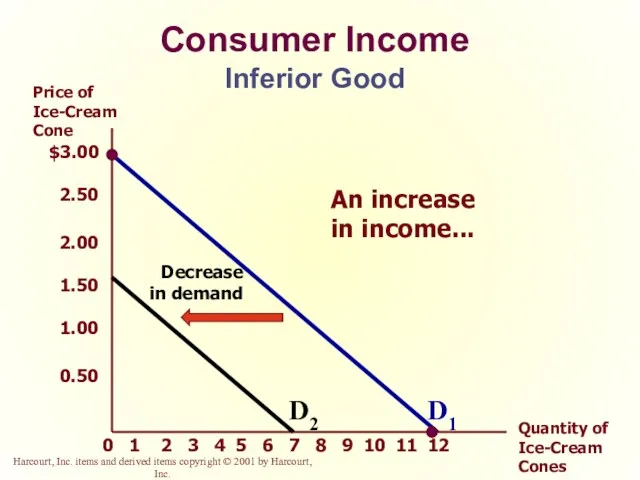
- 23. Consumer Income As income increases the demand for a normal good will increase. As income increases
- 24. Consumer Income Normal Good $3.00 2.50 2.00 1.50 1.00 0.50 2 1 3 4 5 6
- 25. Consumer Income Inferior Good $3.00 2.50 2.00 1.50 1.00 0.50 2 1 3 4 5 6
- 26. Prices of Related Goods Substitutes & Complements When a fall in the price of one good
- 27. Change in Quantity Demanded versus Change in Demand
- 28. Supply Quantity supplied is the amount of a good that sellers are willing and able to
- 29. Law of Supply The law of supply states that there is a direct (positive) relationship between
- 30. Determinants of Supply Market price Input prices Technology Expectations Number of producers
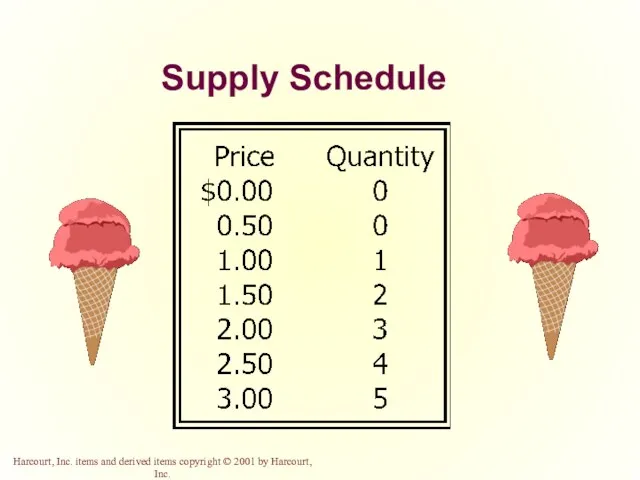
- 31. Supply Schedule The supply schedule is a table that shows the relationship between the price of
- 32. Supply Schedule
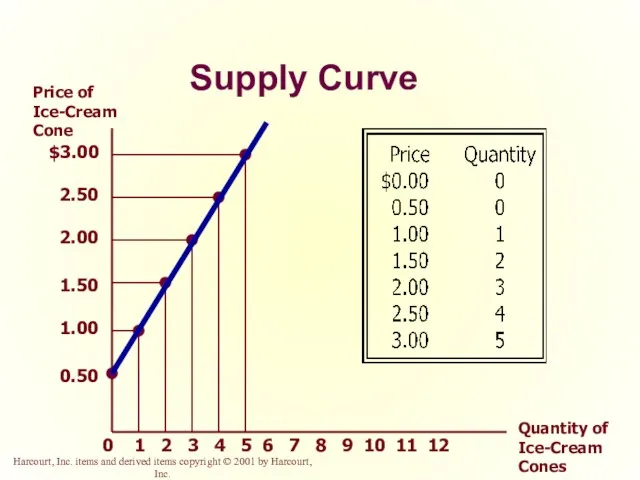
- 33. Supply Curve The supply curve is the upward-sloping line relating price to quantity supplied.
- 34. Supply Curve $3.00 2.50 2.00 1.50 1.00 0.50 2 1 3 4 5 6 7 8
- 35. Market Supply Market supply refers to the sum of all individual supplies for all sellers of
- 36. Determinants of Supply Market price Input prices Technology Expectations Number of producers
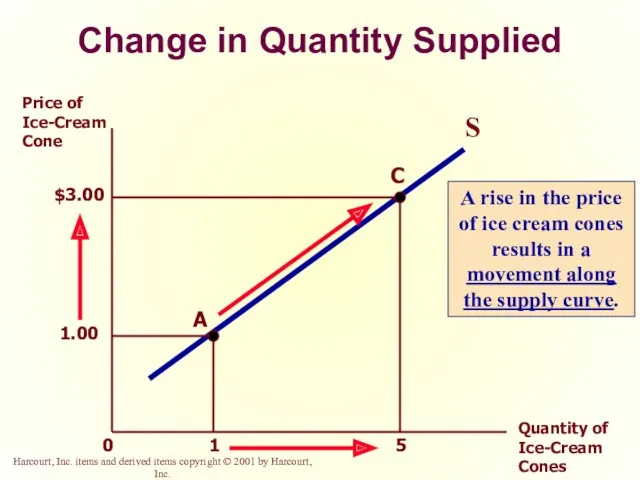
- 37. Change in Quantity Supplied versus Change in Supply Change in Quantity Supplied Movement along the supply
- 38. Change in Quantity Supplied 1 5 Price of Ice-Cream Cone Quantity of Ice-Cream Cones 0 S
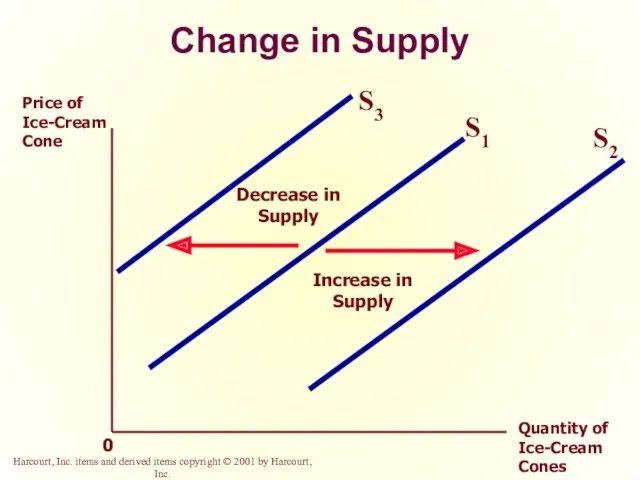
- 39. Change in Quantity Supplied versus Change in Supply Change in Supply A shift in the supply
- 40. Change in Supply Price of Ice-Cream Cone Quantity of Ice-Cream Cones 0 S1
- 41. Change in Quantity Supplied versus Change in Supply
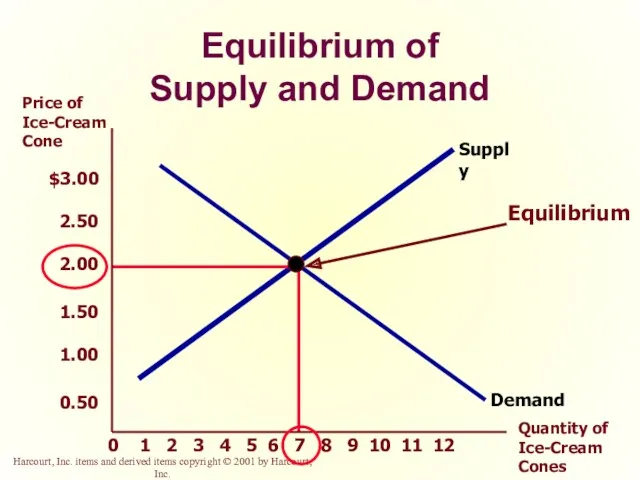
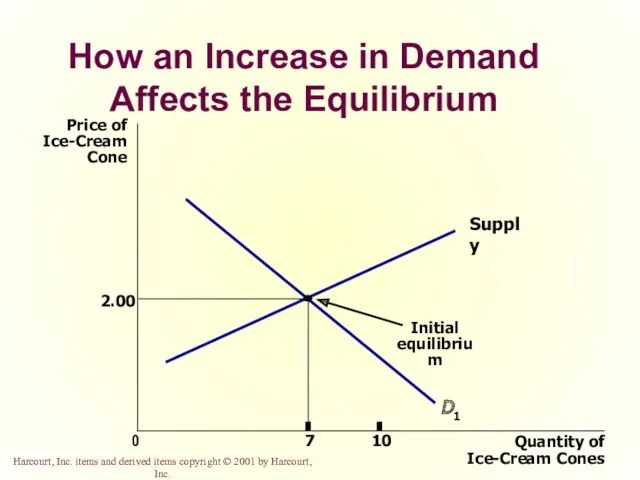
- 42. Supply and Demand Together Equilibrium Price The price that balances supply and demand. On a graph,
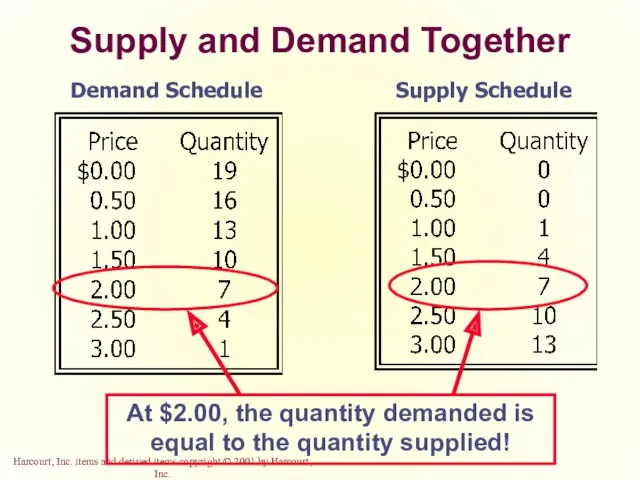
- 43. Supply and Demand Together Demand Schedule Supply Schedule At $2.00, the quantity demanded is equal to
- 44. Price of Ice-Cream Cone Quantity of Ice-Cream Cones Equilibrium of Supply and Demand 2 1 3
- 45. Price of Ice-Cream Cone Quantity of Ice-Cream Cones 2 1 3 4 5 6 7 8
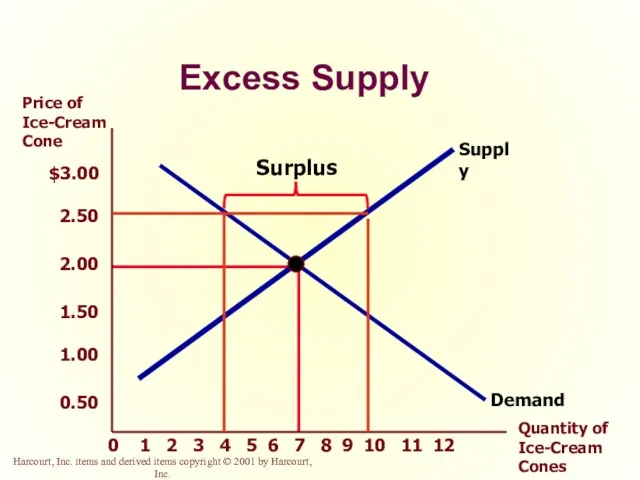
- 46. Surplus When the price is above the equilibrium price, the quantity supplied exceeds the quantity demanded.
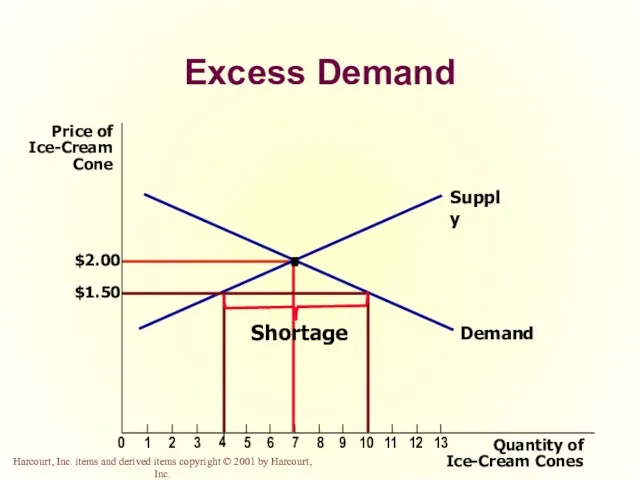
- 47. Excess Demand Quantity of Ice-Cream Cones Price of Ice-Cream Cone $2.00 0 1 2 3 4
- 48. Shortage When the price is below the equilibrium price, the quantity demanded exceeds the quantity supplied.
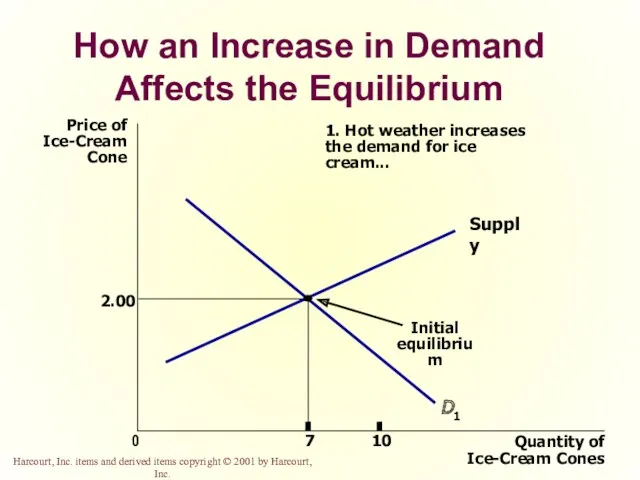
- 49. Three Steps To Analyzing Changes in Equilibrium Decide whether the event shifts the supply or demand
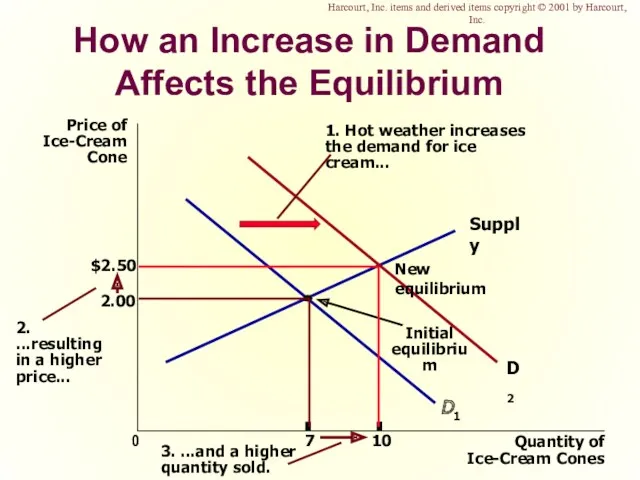
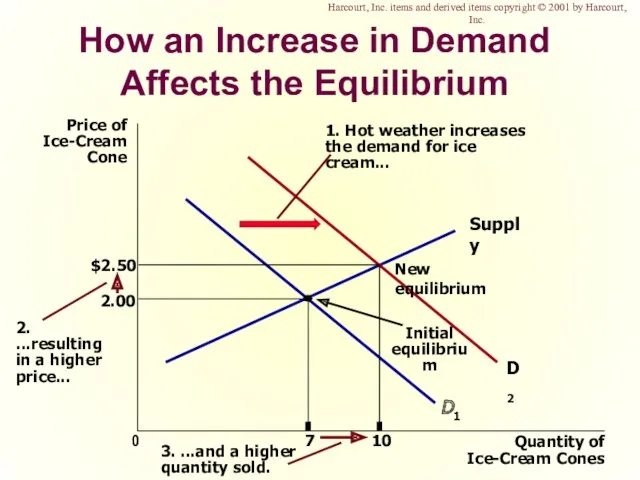
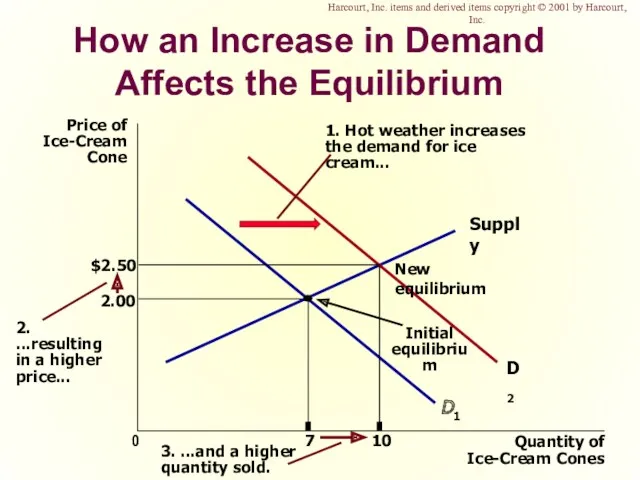
- 50. How an Increase in Demand Affects the Equilibrium Price of Ice-Cream Cone 2.00 0 7 Quantity
- 51. Shifts in Curves versus Movements along Curves A shift in the supply curve is called a
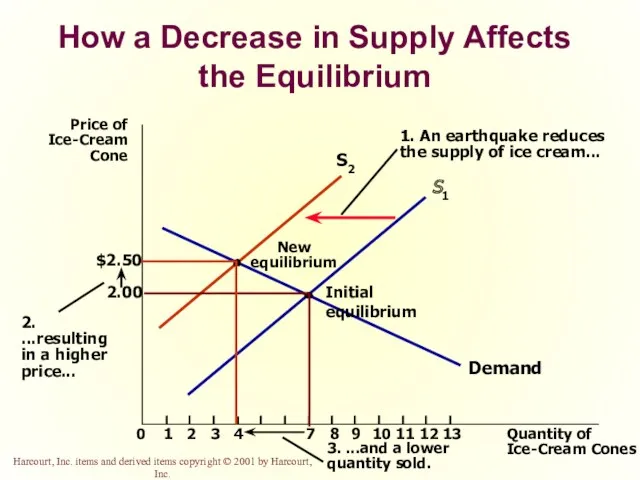
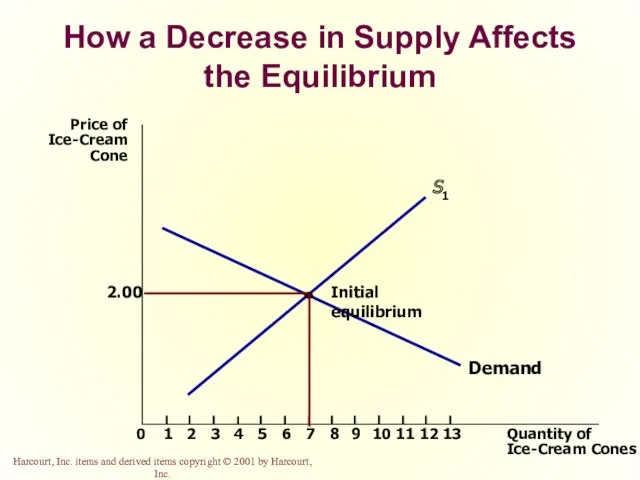
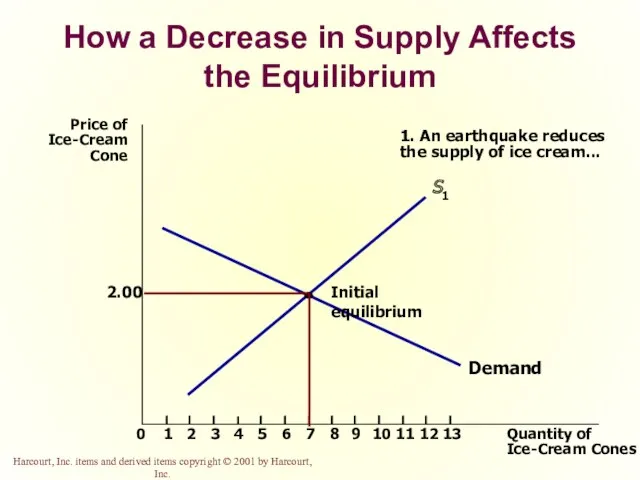
- 52. How a Decrease in Supply Affects the Equilibrium Price of Ice-Cream Cone 2.00 0 1 2
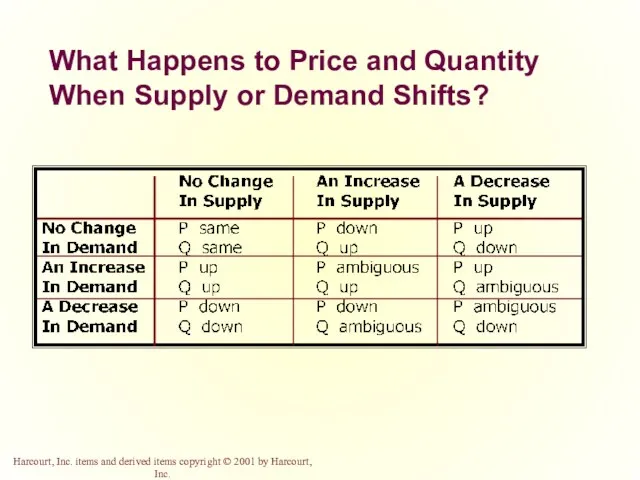
- 53. What Happens to Price and Quantity When Supply or Demand Shifts?
- 54. Summary Economists use the model of supply and demand to analyze competitive markets. The demand curve
- 55. Summary According to the law of demand, as the price of a good rises, the quantity
- 56. Summary The supply curve shows how the quantity of a good supplied depends upon the price.
- 57. Summary In addition to price, other determinants of quantity supplied include input prices, technology, and expectations.
- 58. Summary Supply and demand together determine the prices of the economy’s goods and services. In market
- 60. How an Increase in Demand Affects the Equilibrium
- 61. How an Increase in Demand Affects the Equilibrium
- 62. How an Increase in Demand Affects the Equilibrium
- 63. How an Increase in Demand Affects the Equilibrium
- 64. How an Increase in Demand Affects the Equilibrium Harcourt, Inc. items and derived items copyright ©
- 65. How an Increase in Demand Affects the Equilibrium Harcourt, Inc. items and derived items copyright ©
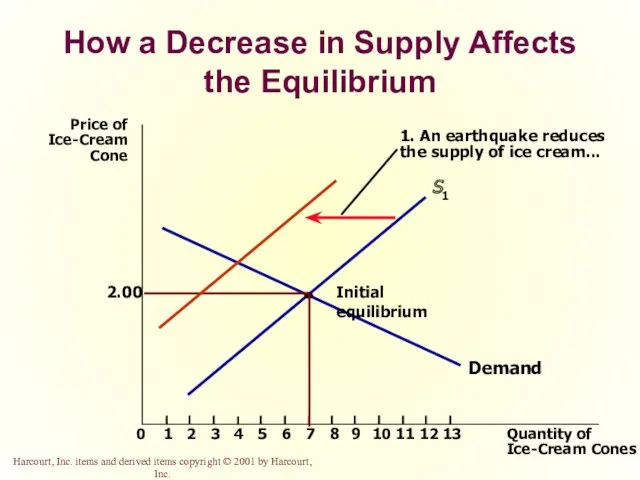
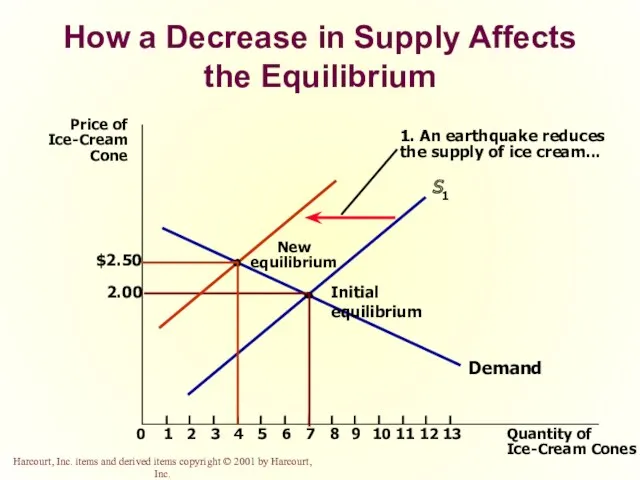
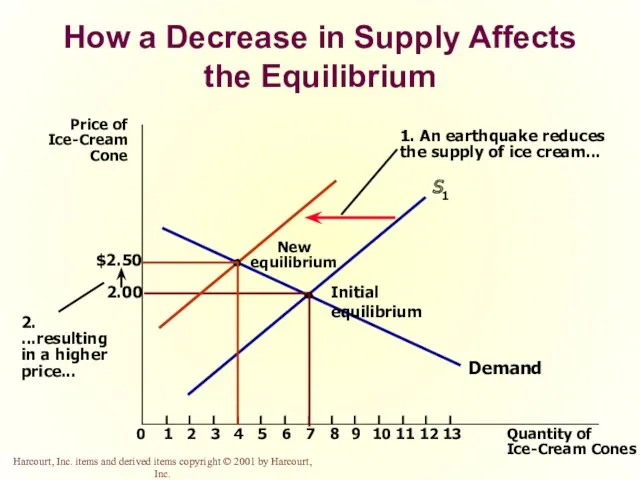
- 66. How a Decrease in Supply Affects the Equilibrium
- 67. How a Decrease in Supply Affects the Equilibrium
- 68. How a Decrease in Supply Affects the Equilibrium
- 69. How a Decrease in Supply Affects the Equilibrium
- 70. How a Decrease in Supply Affects the Equilibrium
- 72. Скачать презентацию






































 Электронный обмен данными (EDI)
Электронный обмен данными (EDI) Товар. Категории представлений товаров
Товар. Категории представлений товаров Тренинг группы А. Продукты компании HERBALIFE
Тренинг группы А. Продукты компании HERBALIFE Зарождение идеи Zara
Зарождение идеи Zara Текст рекламного объявления
Текст рекламного объявления Школа проектов - дети в науке. Поможем вашему ребенку стать успешным. Запуск – январь 2019 г
Школа проектов - дети в науке. Поможем вашему ребенку стать успешным. Запуск – январь 2019 г Супермаркет Виктория. Информация по бонусной карте сети Моя Виктория
Супермаркет Виктория. Информация по бонусной карте сети Моя Виктория Личный бренд – маркетинг предпринимателя в социальных сетях
Личный бренд – маркетинг предпринимателя в социальных сетях Матрицы принятия решений. Матрица БКГ (BCG Matrix)
Матрицы принятия решений. Матрица БКГ (BCG Matrix) Міжнародний досвід розвитку систем управління якістю. Вітчизняні системи управління якістю. (Тема 2)
Міжнародний досвід розвитку систем управління якістю. Вітчизняні системи управління якістю. (Тема 2) Омега-3. Онлайн мастер-класс
Омега-3. Онлайн мастер-класс Beach Words
Beach Words Обзор конкурентов. Curiosity-mobile
Обзор конкурентов. Curiosity-mobile Сувенирная продукция, как маркетинговый инструмент рекламной кампании
Сувенирная продукция, как маркетинговый инструмент рекламной кампании Маркетинговые исследования и ситуационный анализ
Маркетинговые исследования и ситуационный анализ Комплексне обслуговування нерухомості. Геотаргетинг всі міста +обл. центри
Комплексне обслуговування нерухомості. Геотаргетинг всі міста +обл. центри Прайс-лист Рыболовные товары
Прайс-лист Рыболовные товары Обучающая презентация по продуктам Эвалар
Обучающая презентация по продуктам Эвалар Управление интегрированными коммуникациями
Управление интегрированными коммуникациями Конкурентные преимущества иван-чая
Конкурентные преимущества иван-чая Качество изделий: основные понятия
Качество изделий: основные понятия Кондитерская промышленность в России
Кондитерская промышленность в России Высококачественные, современные центрифуги. Компания Центромаш (3)
Высококачественные, современные центрифуги. Компания Центромаш (3) Радио Европа плюс Могилёв
Радио Европа плюс Могилёв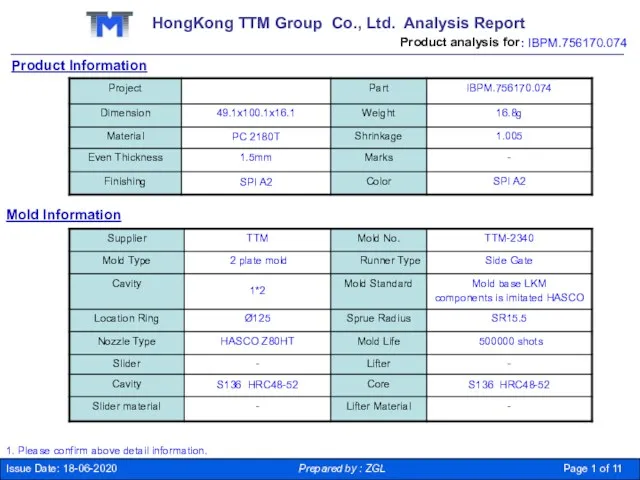 HongKong TTM Group Co
HongKong TTM Group Co Стажировки в зарубежных ИТ компаниях
Стажировки в зарубежных ИТ компаниях Zerts. Маркетинг план
Zerts. Маркетинг план Большая конференция по маркетинговой и продуктовой аналитике
Большая конференция по маркетинговой и продуктовой аналитике