Содержание
- 2. The National Organic Program (NOP) Mission: Ensure the integrity of USDA organic products throughout the world
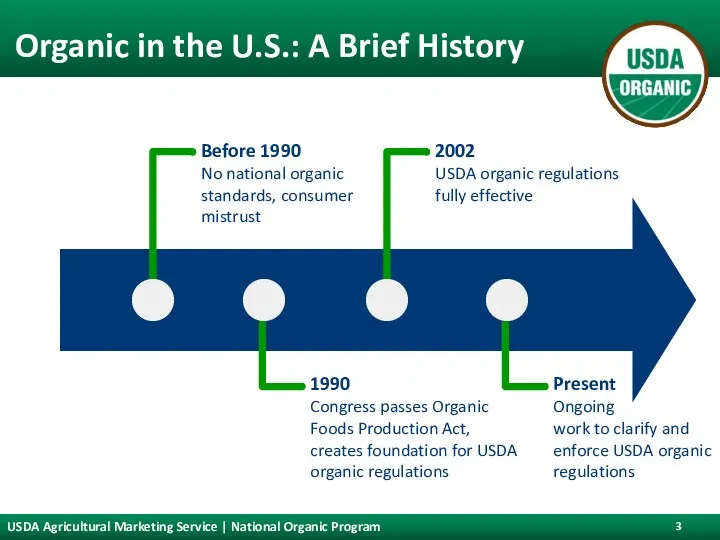
- 3. Organic in the U.S.: A Brief History USDA Agricultural Marketing Service | National Organic Program
- 4. Quick Facts About NOP Oversight Responsibility: 75+ certifying agents worldwide 30,000+ certified organic operations in over
- 5. What Does the Program Do? Develop and maintain organic standards Accredit and oversee third party organic
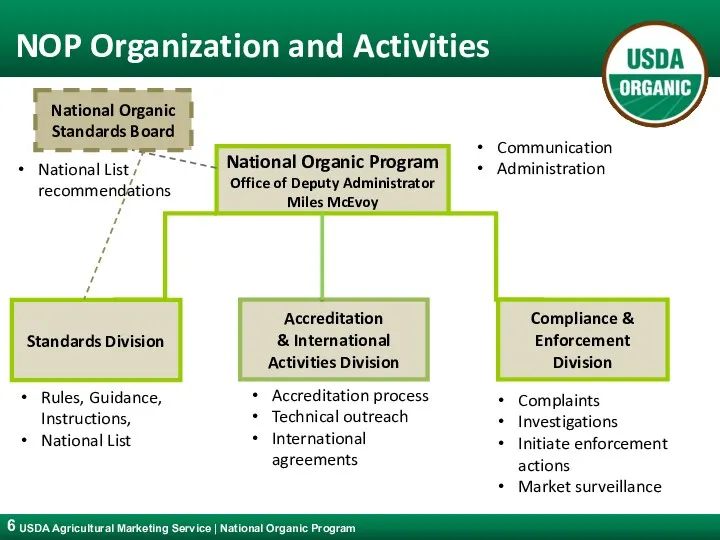
- 6. NOP Organization and Activities National Organic Program Office of Deputy Administrator Miles McEvoy Standards Division Accreditation
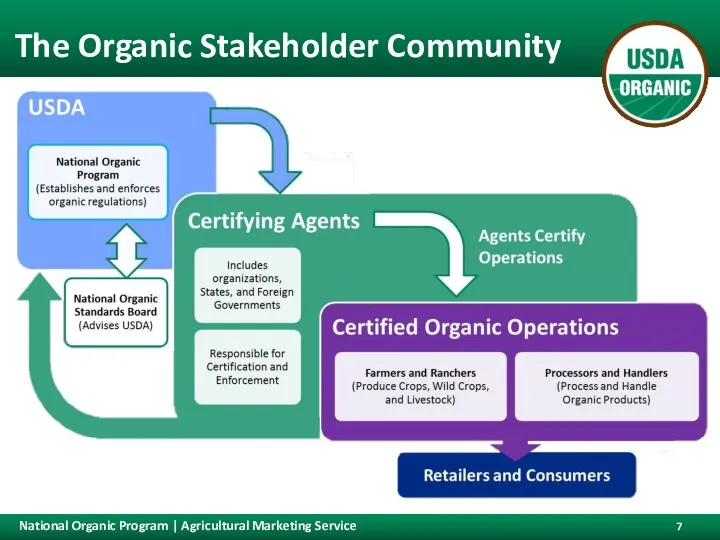
- 7. The Organic Stakeholder Community There are three primary levels to the organic integrity framework. USDA’s National
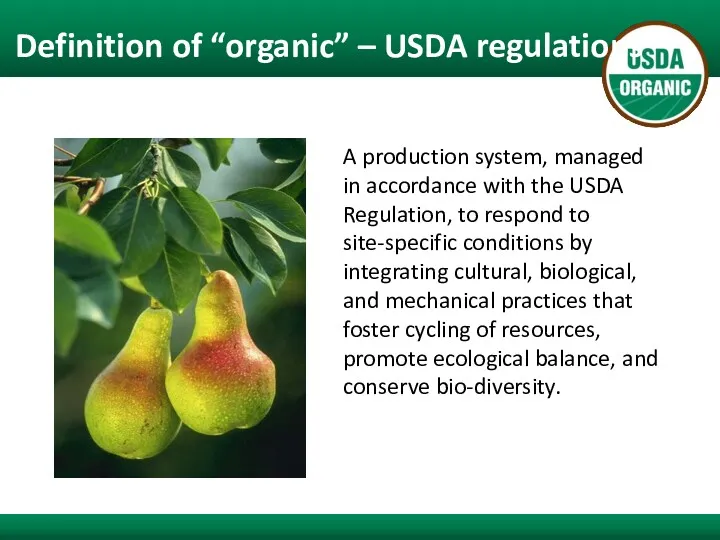
- 8. Definition of “organic” – USDA regulations A production system, managed in accordance with the USDA Regulation,
- 9. Scope of USDA Organic Standards The USDA organic standards cover the product from farm to table,
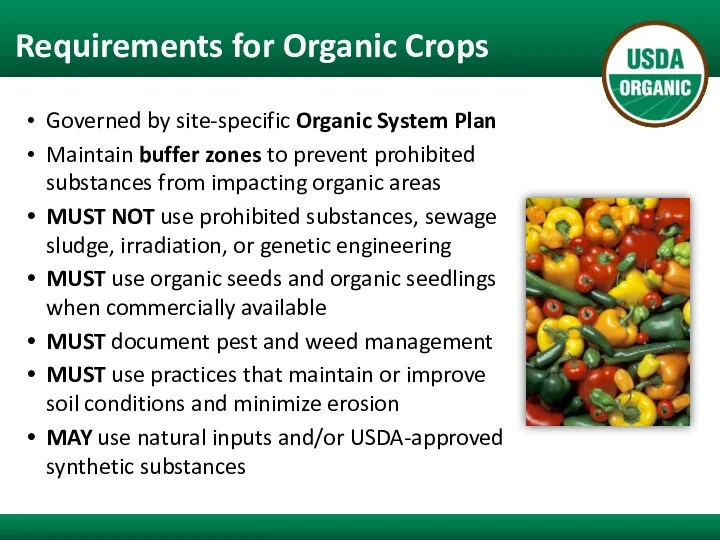
- 10. Requirements for Organic Crops Governed by site-specific Organic System Plan Maintain buffer zones to prevent prohibited
- 11. Requirements for Livestock Operations Governed by Organic System Plan Provide access to the outdoors and good
- 12. Requirements for Processors and Handlers Governed by an Organic System Plan Prevent the commingling or contamination
- 13. Allowed and Prohibited Substances The National List of Allowed and Prohibited Substances is part of the
- 14. Standards Division: Key Activities Key Activities Develop new rules and coordinate clearance Develop and maintain Regulatory
- 15. Accreditation Activities NOP oversees the work of certifiers, which certify over 30,000 certified organic operations. audits,
- 16. International Trade The United States has trade arrangements with several nations to facilitate the exchange of
- 17. Global Organic Food Market in 2014 According to findings in The World of Organic Agriculture: Statistics
- 18. Compliance and Enforcement Division Key Activities: Investigate complaints, work with operations to achieve compliance where possible
- 19. Purposes of Enforcement Purpose: To protect the integrity of the organic standards so as to facilitate
- 20. NOP Communications Email notification service Quarterly Newsletter “Organic Integrity” “Hot Topics” Website Postings Fact Sheets, Questions
- 21. Organic Literacy Initiative
- 22. National Organic Standards Board
- 23. National Organic Standards Board (NOSB) 15 member board governed by the Federal Advisory Committee Act (FACA)
- 24. Thank you Joe Dickson
- 25. National List The NOSB recommends substances on the National List by a 2/3 majority; NOSB members
- 27. Скачать презентацию



















 Ооо Леруа мерлен восток. Аудитор: группа компаний SRG
Ооо Леруа мерлен восток. Аудитор: группа компаний SRG Маркетинг и продвижение программ на рынке образовательных услуг. Опыт и рекомендации
Маркетинг и продвижение программ на рынке образовательных услуг. Опыт и рекомендации Компания История семьи
Компания История семьи Проект организации работы кафе на 60 мест в Онгудайском районе
Проект организации работы кафе на 60 мест в Онгудайском районе Комплекты постельного белья в мужских расцветках
Комплекты постельного белья в мужских расцветках E- suhtlus. Анализ блога педагога начальных классов Епимаховой Юлии Ивановны
E- suhtlus. Анализ блога педагога начальных классов Епимаховой Юлии Ивановны Информационная работа в организации
Информационная работа в организации Ресторан Черное и белое
Ресторан Черное и белое Работа с возражениями
Работа с возражениями Современные виды коммуникаций. Инновационные подходы в работе с клиентами
Современные виды коммуникаций. Инновационные подходы в работе с клиентами Совершенствование комплекса маркетинга промышленного предприятия (на примере ОАО 8 Марта)
Совершенствование комплекса маркетинга промышленного предприятия (на примере ОАО 8 Марта) Маркетинговые исследования. Сущность и задачи исследований
Маркетинговые исследования. Сущность и задачи исследований Торговая марка CITY MALL
Торговая марка CITY MALL Новая концентрация аромата Want
Новая концентрация аромата Want Программа лояльности для питомников и заводчиков
Программа лояльности для питомников и заводчиков Коммерческое предложение. Брендсон Медиа Групп - ведущее российское брендинговое агентство
Коммерческое предложение. Брендсон Медиа Групп - ведущее российское брендинговое агентство Жёсткие продажи
Жёсткие продажи Матрасы Аскона
Матрасы Аскона Термошкафы. Муфельные печи
Термошкафы. Муфельные печи Продукция компании Amway слишком дорогая
Продукция компании Amway слишком дорогая Этикетка кондитерского изделия как информационный ресурс в укреплении здоровья потребителя и как инструмент конкурентной борьбы
Этикетка кондитерского изделия как информационный ресурс в укреплении здоровья потребителя и как инструмент конкурентной борьбы Coral club. Ключевые компоненты для вашего организма на каждый день
Coral club. Ключевые компоненты для вашего организма на каждый день Виды товаров в аптеке по критериям спроса
Виды товаров в аптеке по критериям спроса Торговый кластер под размещение объектов торговли (48 магазинов)
Торговый кластер под размещение объектов торговли (48 магазинов) Франчайзинг как форма интеграции в сфере гостиничного и ресторанного бизнеса
Франчайзинг как форма интеграции в сфере гостиничного и ресторанного бизнеса Виды планировок магазина
Виды планировок магазина Travelling. Couchsurfing
Travelling. Couchsurfing Изготовление мебели в любом стиле для любых помещений из любых материалов
Изготовление мебели в любом стиле для любых помещений из любых материалов