Содержание
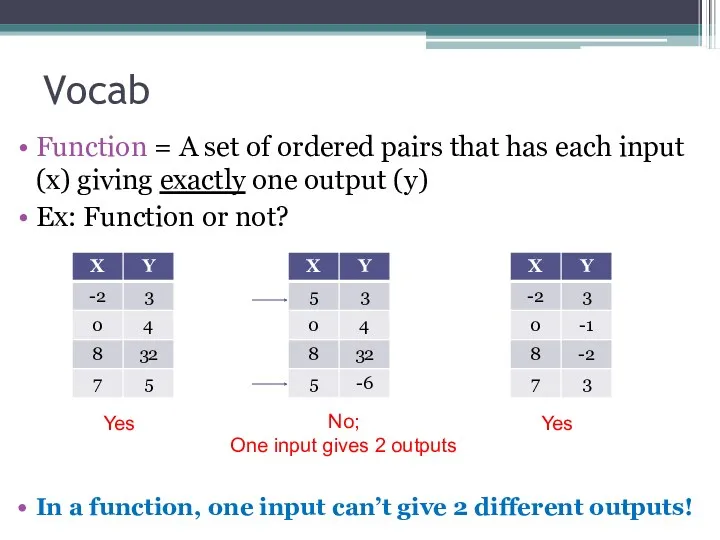
- 2. Vocab Function = A set of ordered pairs that has each input (x) giving exactly one
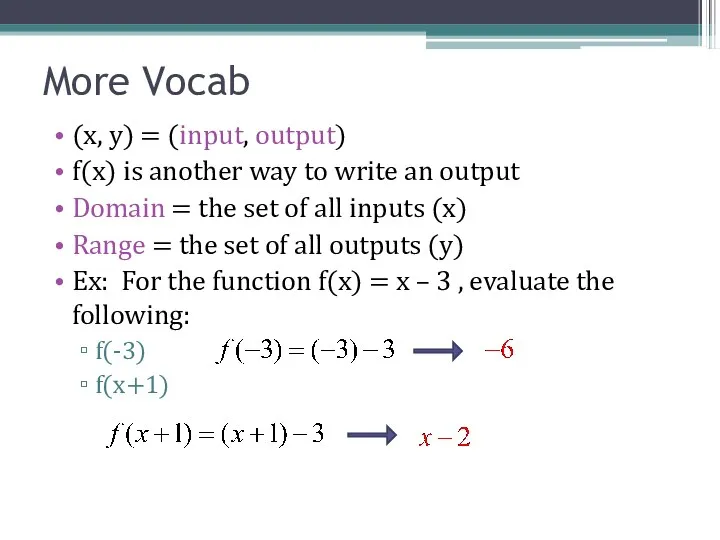
- 3. (x, y) = (input, output) f(x) is another way to write an output Domain = the
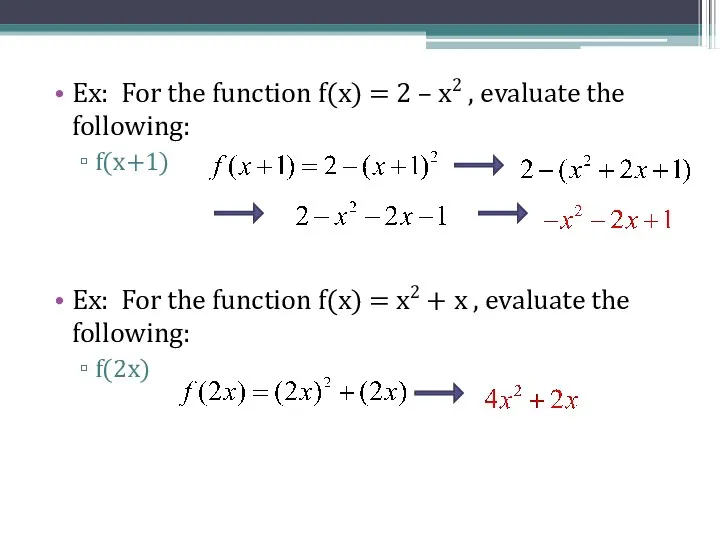
- 4. Ex: For the function f(x) = 2 – x2 , evaluate the following: f(x+1) Ex: For
- 5. Ex: For the function f(x) = x2 – 2x + 3, evaluate the following: f(x+h)
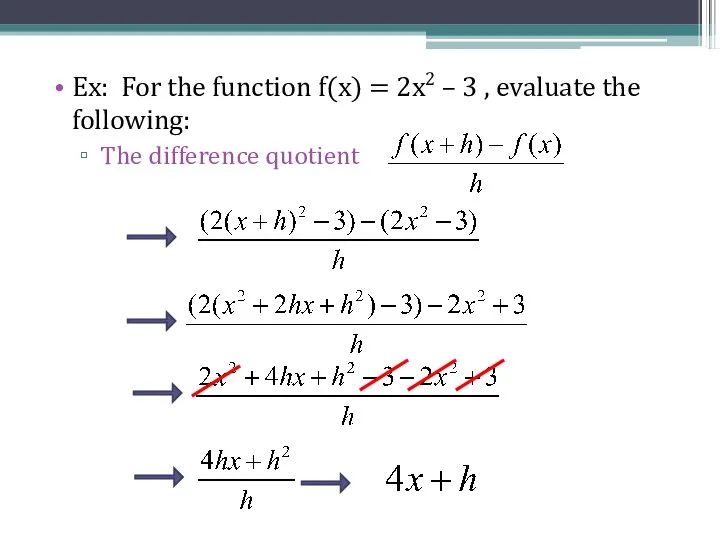
- 6. Ex: For the function f(x) = 2x2 – 3 , evaluate the following: The difference quotient
- 7. f(x) = 5x + 6. Find f(x – 3). 5x – 3 5x + 3 5x
- 8. f(x) = 2x – x2 . Find f(x + 1). -x2 + 1 -x2 + 2x
- 9. Ex: The function below is a piecewise function. Find f(0) and f(1). Since 0 f(0) =
- 10. y = x2 means y is a function of x Y is not a function of
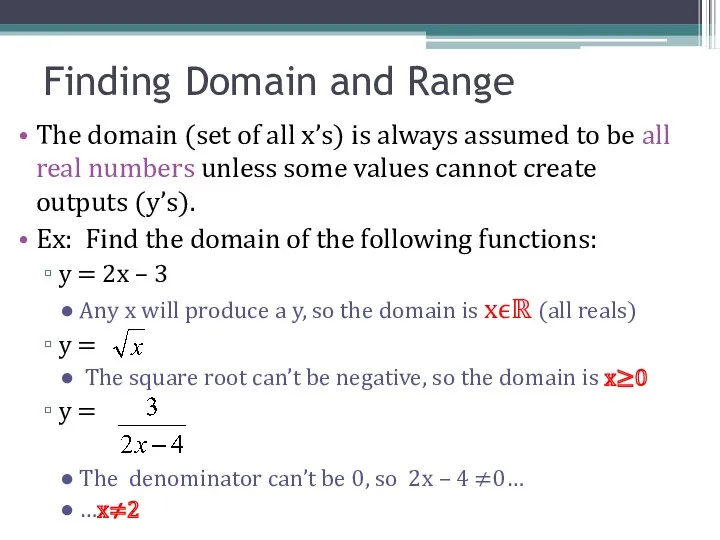
- 11. The domain (set of all x’s) is always assumed to be all real numbers unless some
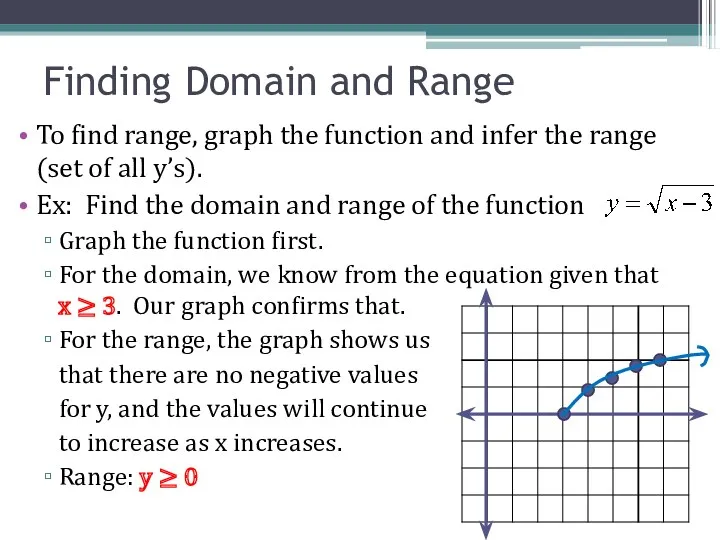
- 12. To find range, graph the function and infer the range (set of all y’s). Ex: Find
- 13. What is the domain? xϵℝ -2≤x≤2 x≥0 -2
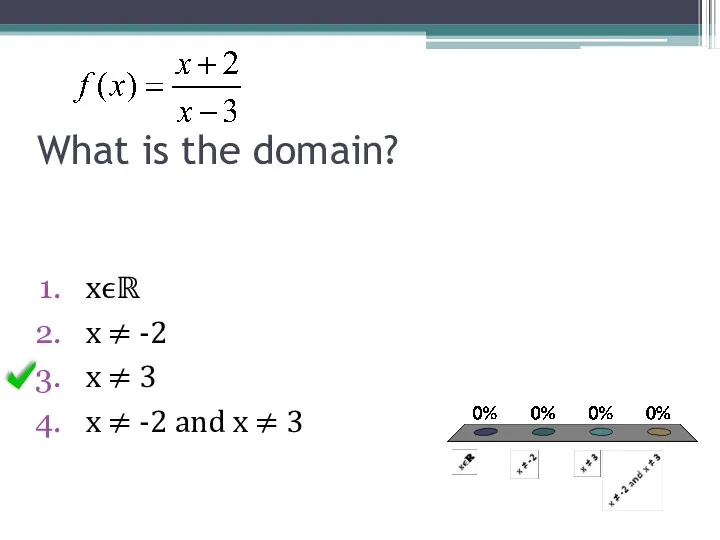
- 14. What is the domain? xϵℝ x ≠ -2 x ≠ 3 x ≠ -2 and x
- 15. What is the range? yϵℝ y ≠ 5 y y ≥ -5
- 16. Ch. 1 – Functions and Their Graphs 1.3 – More Functions
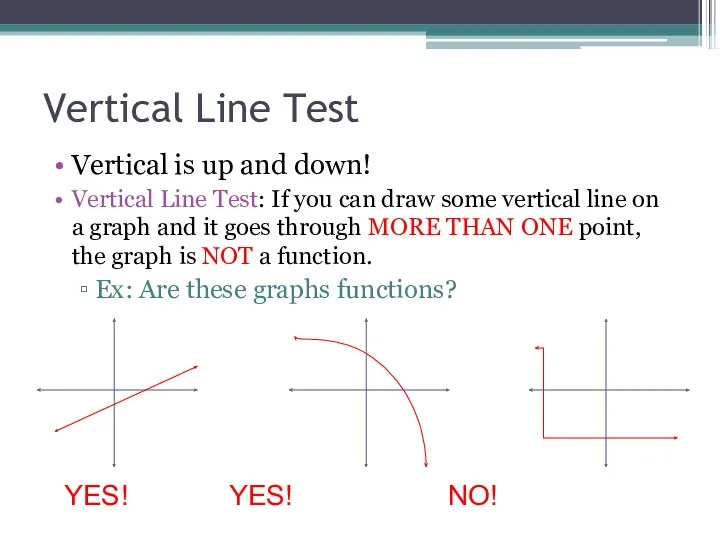
- 17. Vertical Line Test Vertical is up and down! Vertical Line Test: If you can draw some
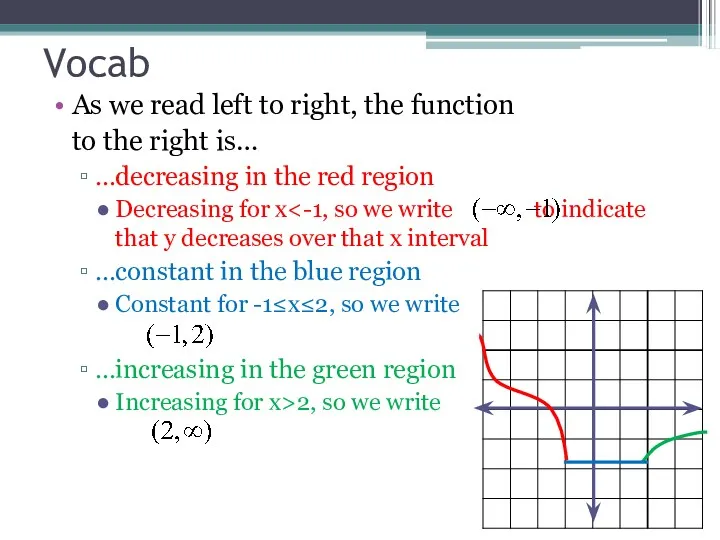
- 18. Vocab As we read left to right, the function to the right is… …decreasing in the
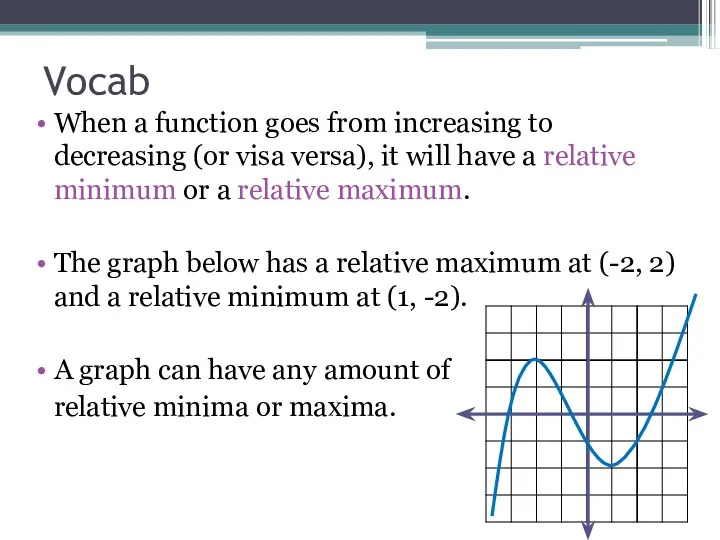
- 19. Vocab When a function goes from increasing to decreasing (or visa versa), it will have a
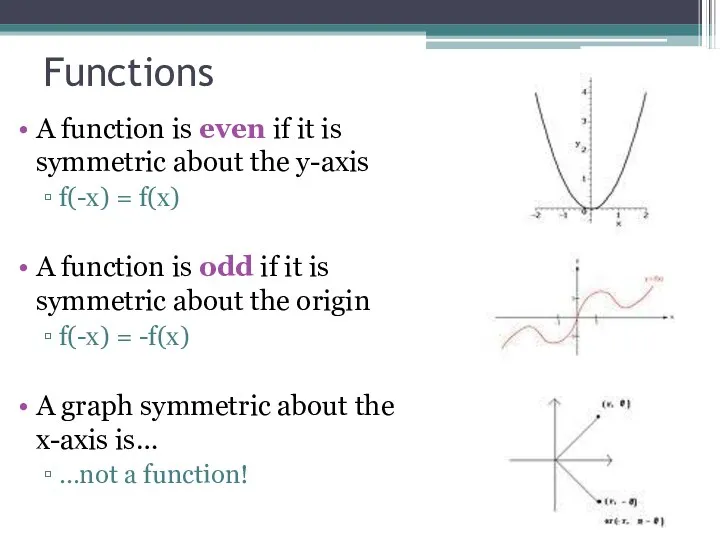
- 20. Functions A function is even if it is symmetric about the y-axis f(-x) = f(x) A
- 21. The function y = 4x2 – 2 is… Even Odd None of the above Not a
- 22. The function y = 1/x is… Even Odd None of the above Not a function
- 23. The function y = x3 – x is… Even Odd None of the above Not a
- 25. Скачать презентацию











 Предварительная обработка экспериментальных данных
Предварительная обработка экспериментальных данных Старинные измерения величин
Старинные измерения величин Задачи на смеси и сплавы
Задачи на смеси и сплавы Число и цифра 5. Состав Числа 5.
Число и цифра 5. Состав Числа 5. Показательная функция, ее свойства и график
Показательная функция, ее свойства и график Алгоритм деления многозначного числа на однозначное
Алгоритм деления многозначного числа на однозначное открытый урок по математика 3 класс система Занкова
открытый урок по математика 3 класс система Занкова Статистика. Цели проекта
Статистика. Цели проекта Сложение однозначных чисел с переходом через десяток вида … +4
Сложение однозначных чисел с переходом через десяток вида … +4 Геометрия. Подготовка к ОГЭ
Геометрия. Подготовка к ОГЭ Cложение и вычитание алгебраических дробей с разными знаменателями. 8 класс
Cложение и вычитание алгебраических дробей с разными знаменателями. 8 класс Урок математики по теме: Единицы времени
Урок математики по теме: Единицы времени презентация к уроку математики в 3 классе по теме: Угол. Виды углов. Сравнение углов
презентация к уроку математики в 3 классе по теме: Угол. Виды углов. Сравнение углов Окружность и круг в задачах повышенного уровня сложности по планиметрии в КИМ на ЕГЭ по математике
Окружность и круг в задачах повышенного уровня сложности по планиметрии в КИМ на ЕГЭ по математике Решение систем уравнений способом сложения
Решение систем уравнений способом сложения Деление числа на произведение
Деление числа на произведение Многогранники и круглые тела
Многогранники и круглые тела Уравнения, сводящиеся к квадратным
Уравнения, сводящиеся к квадратным Презентация к уроку математики
Презентация к уроку математики Системы уравнений с несколькими неизвестными. Метод замены неизвестных
Системы уравнений с несколькими неизвестными. Метод замены неизвестных Цилиндр. Понятие цилиндрической поверхности
Цилиндр. Понятие цилиндрической поверхности Математика представляет собой могущественный инструмент познания природы
Математика представляет собой могущественный инструмент познания природы Вписанные и описанные окружности. (9 класс)
Вписанные и описанные окружности. (9 класс) Давайте посчитаем. Устный счёт. 2класс. Математика
Давайте посчитаем. Устный счёт. 2класс. Математика Средняя линия треугольника
Средняя линия треугольника Урок-сказка по математике, 1 класс.
Урок-сказка по математике, 1 класс. Модуль числа
Модуль числа Окружность и круг в задачах повышенного уровня сложности по планиметрии в КИМ на ЕГЭ по математике
Окружность и круг в задачах повышенного уровня сложности по планиметрии в КИМ на ЕГЭ по математике