Содержание
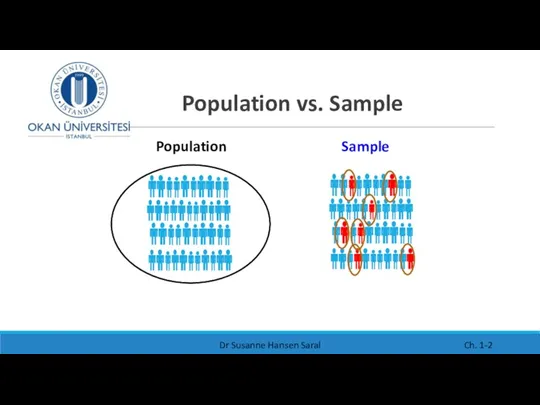
- 2. Population vs. Sample Dr Susanne Hansen Saral Ch. 1- Population Sample
- 3. Statistical key definitions POPULATION A population is the collection of all items of interest under investigation.
- 4. Statistical key definitions SAMPLE A sample is an observed subset of the population n represents the
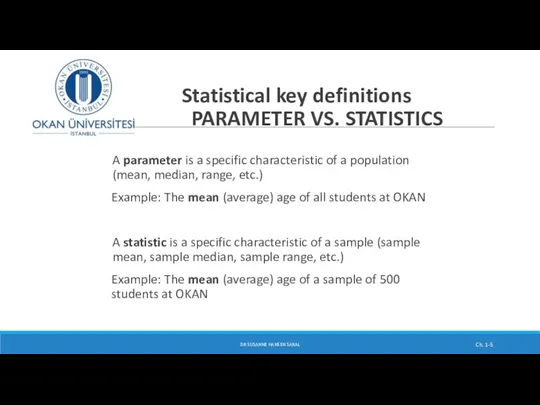
- 5. Statistical key definitions PARAMETER VS. STATISTICS A parameter is a specific characteristic of a population (mean,
- 6. Why do we collect samples instead of investigating the entire population? Populations usually are infinite and
- 7. Why do we collect samples instead of investigating the entire population? Populations are usually infinite. Therefore
- 8. Randomness (Turkish: Rasgelelik) Our final objective in statistics is to make valid and reliable statements about
- 9. Main sampling techniques Simple random sampling Systematic sampling Both techniques respect randomness and therefore provide reliable
- 10. Random Sampling Simple random sampling is a procedure in which: Each member/item in the population is
- 11. Sampling error In statistics we make decision about a population based on sample data, because the
- 12. Inferential statistics Drawing conclusion about a population based a sample information. DR SUSANNE HANSEN SARAL Ch.
- 13. Inferential statistics To draw conclusions about the population based on a sample we need to collect
- 14. What is data? Data = information Data can be numbers: Size of a hotel bill, number
- 15. Data and context Data are useless without a context. When we deal with data we need
- 16. Data and context Data values are useless without their context Consider the following: Amazon.com may collect
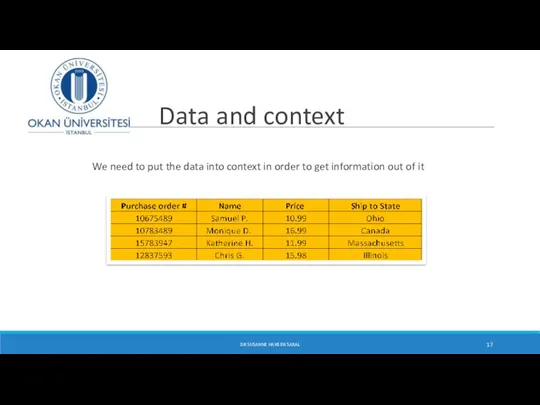
- 17. Data and context We need to put the data into context in order to get information
- 18. What is statistics? It is a basic study of transforming data into information : how to
- 19. Where does data come from? Market research Survey (online questionnaires, paper questionnaires, etc.) Interviews Research experiments
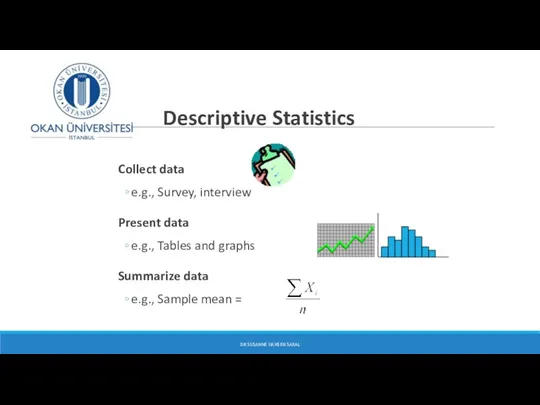
- 20. Descriptive Statistics Collect data e.g., Survey, interview Present data e.g., Tables and graphs Summarize data e.g.,
- 21. Create your account in Khan Academy Go to www.khanacademy.org create an account with your email address
- 23. Скачать презентацию














 Вписанная и описанная окружности
Вписанная и описанная окружности Нахождение дроби от числа
Нахождение дроби от числа Задачи на построение. Геометрия. 7 класс
Задачи на построение. Геометрия. 7 класс Знакомство с задачами
Знакомство с задачами Решение уравнений. 2 класс. УМК Гармония
Решение уравнений. 2 класс. УМК Гармония Неопределённый интеграл, его свойства . Непосредственное интегрирование. Метод замены переменной в неопределенном интеграле
Неопределённый интеграл, его свойства . Непосредственное интегрирование. Метод замены переменной в неопределенном интеграле Знакомим дошкольников с часами
Знакомим дошкольников с часами Развёртка прямоугольного параллелепипеда. Урок 143
Развёртка прямоугольного параллелепипеда. Урок 143 Кубизм в архитектуре. Оригами
Кубизм в архитектуре. Оригами Фалес Милетский. Нахождение расстояния до недоступного предмета
Фалес Милетский. Нахождение расстояния до недоступного предмета Сложение чисел с разными знаками» (проверочная работа)
Сложение чисел с разными знаками» (проверочная работа) Площадь криволинейной трапеции и интеграл
Площадь криволинейной трапеции и интеграл Решение систем, содержащих уравнения второй степени
Решение систем, содержащих уравнения второй степени Осевая и центральная симметрия 8 класс
Осевая и центральная симметрия 8 класс Умножение и деление обыкновенных дробей
Умножение и деление обыкновенных дробей Своя игра. 5 класс
Своя игра. 5 класс Луч и угол
Луч и угол Презентация Занимательная геометрия
Презентация Занимательная геометрия Презентация Веселая математика с Винни-Пухом
Презентация Веселая математика с Винни-Пухом Прямоугольный параллелепипед
Прямоугольный параллелепипед Измерение углов. Транспортир. 5 класс
Измерение углов. Транспортир. 5 класс Математика вокруг нас: форма, размер, цвет
Математика вокруг нас: форма, размер, цвет Конспект урока по математике Составные задачи 1 класс. (Программа Петерсон Л.Г.)
Конспект урока по математике Составные задачи 1 класс. (Программа Петерсон Л.Г.) Презентация по математике на тему Какие бывают алгоритмы
Презентация по математике на тему Какие бывают алгоритмы Дидактическая игра Круги и квадраты (презентация)
Дидактическая игра Круги и квадраты (презентация) Подготовка к ВПР. Математика 3 задание. Арифметический метод
Подготовка к ВПР. Математика 3 задание. Арифметический метод Заниматика №3
Заниматика №3 Способы решения логических задач
Способы решения логических задач