Содержание
- 2. Learning Outcomes Outcome 1. Calculate and interpret the correlation between two variables. Outcome 2. Determine whether
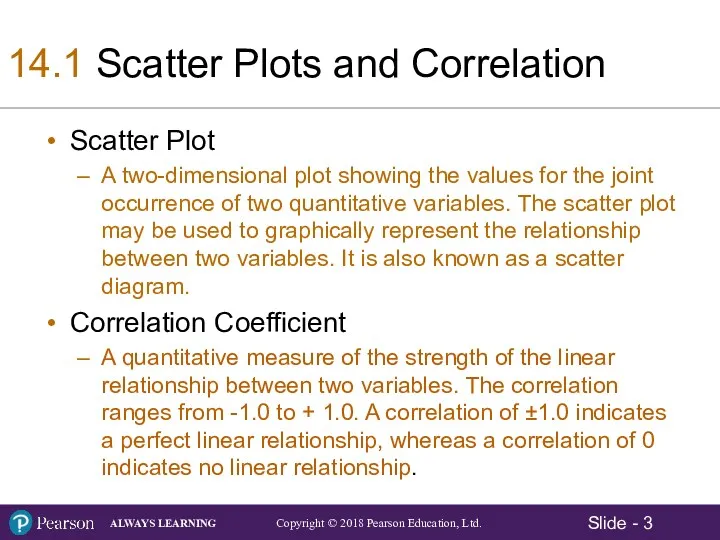
- 3. 14.1 Scatter Plots and Correlation Scatter Plot A two-dimensional plot showing the values for the joint
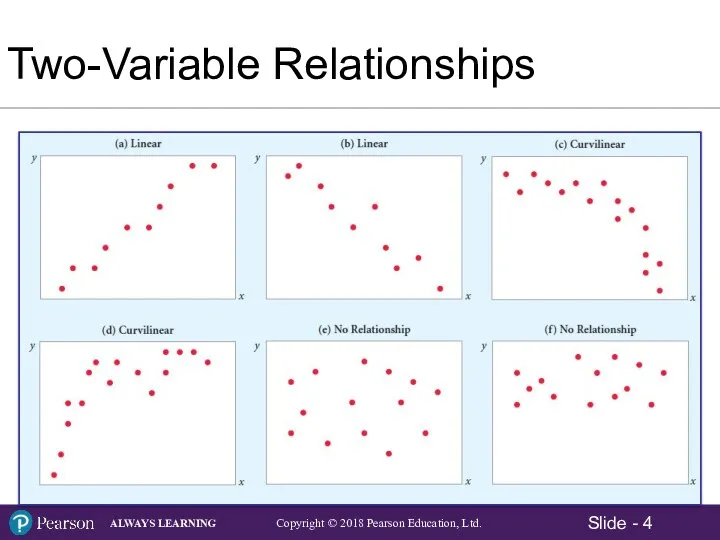
- 4. Two-Variable Relationships
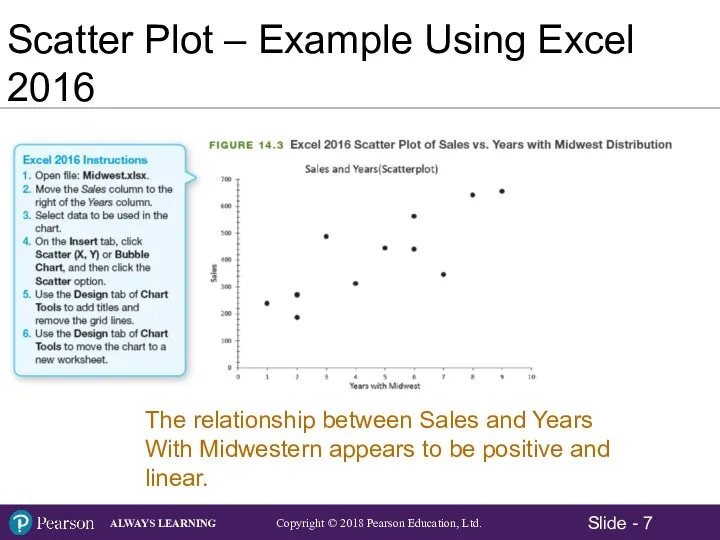
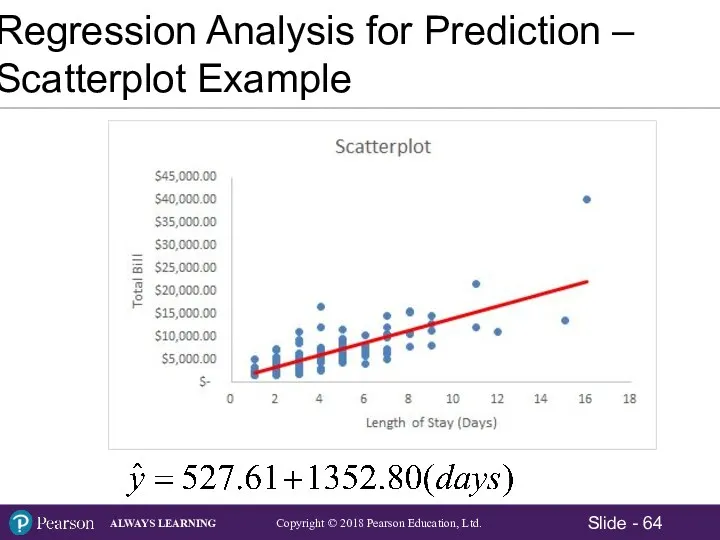
- 5. Scatter Plot – Example Using Excel 2016 The director of marketing for Midwest Distribution Company is
- 6. Scatter Plot – Example Using Excel 2016 Sample Data: Sales and Years With Midwestern
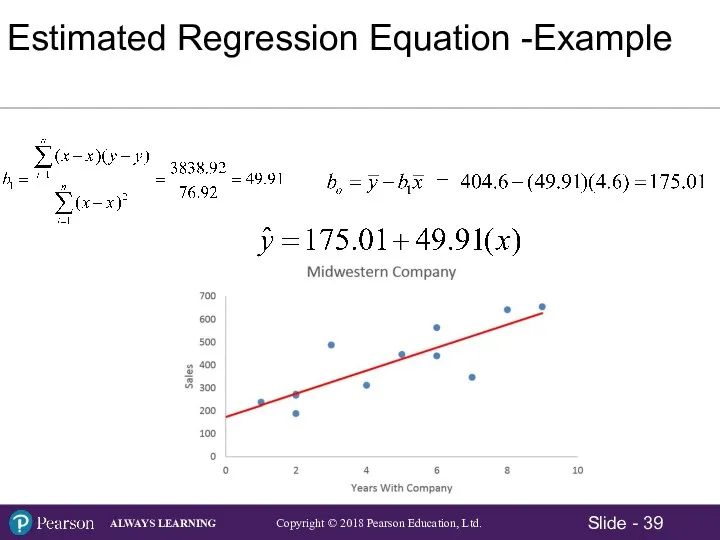
- 7. Scatter Plot – Example Using Excel 2016 The relationship between Sales and Years With Midwestern appears
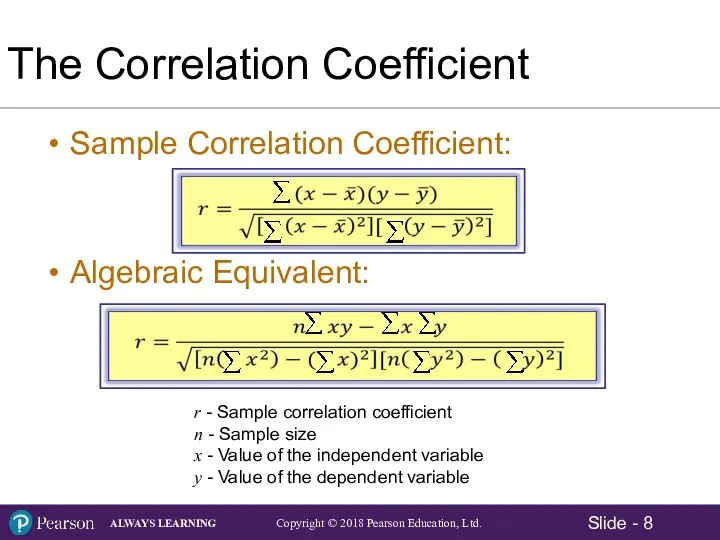
- 8. The Correlation Coefficient Sample Correlation Coefficient: Algebraic Equivalent: r - Sample correlation coefficient n - Sample
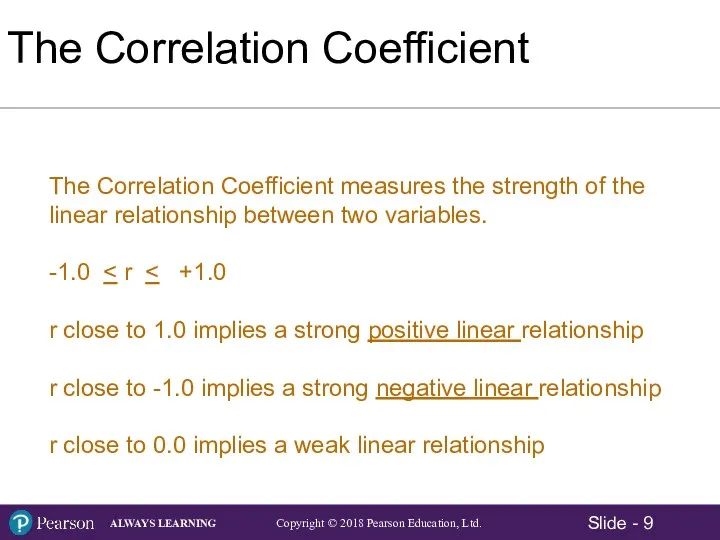
- 9. The Correlation Coefficient The Correlation Coefficient measures the strength of the linear relationship between two variables.
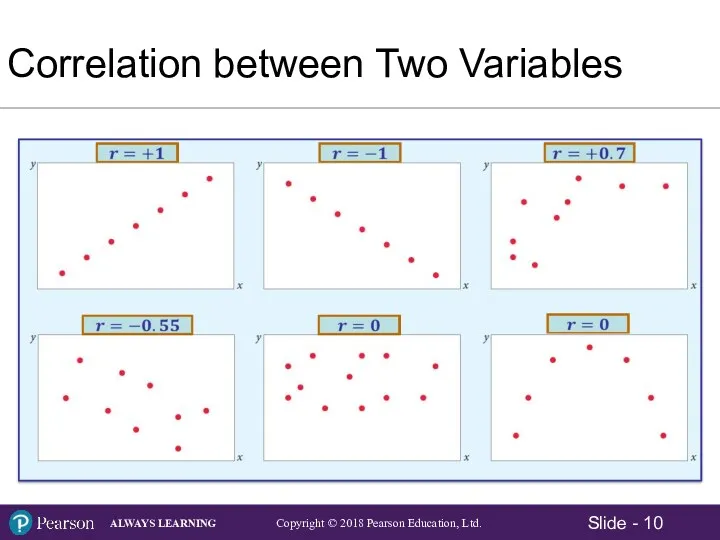
- 10. Correlation between Two Variables
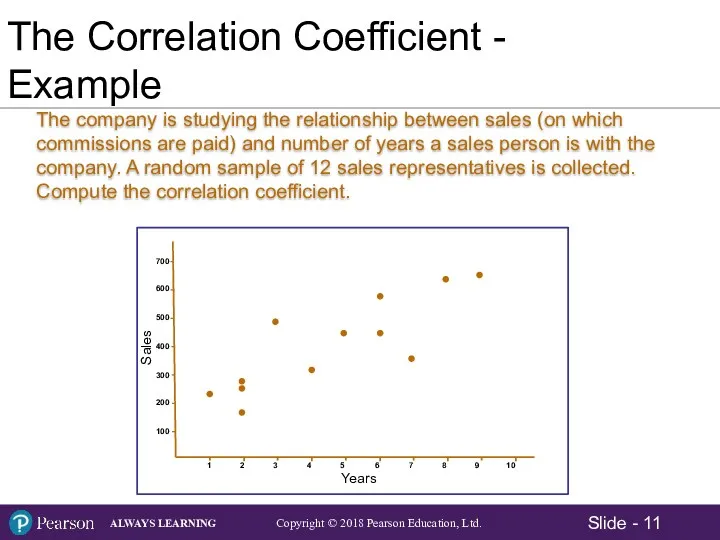
- 11. The Correlation Coefficient - Example The company is studying the relationship between sales (on which commissions
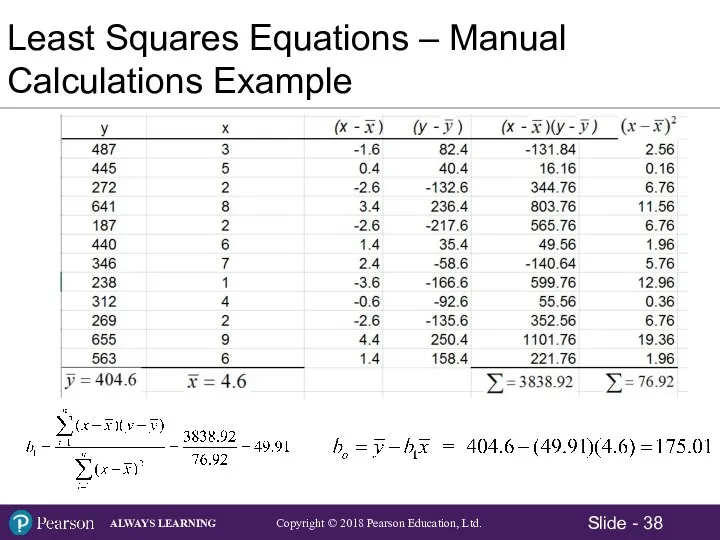
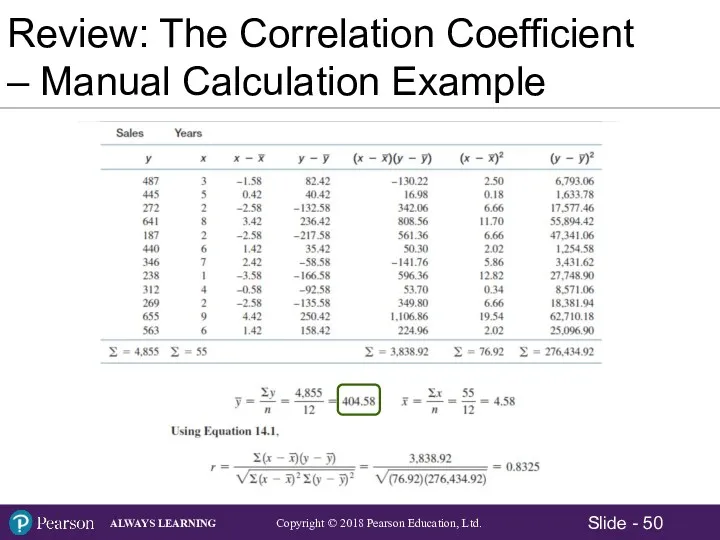
- 12. The Correlation Coefficient – Manual Calculation Example
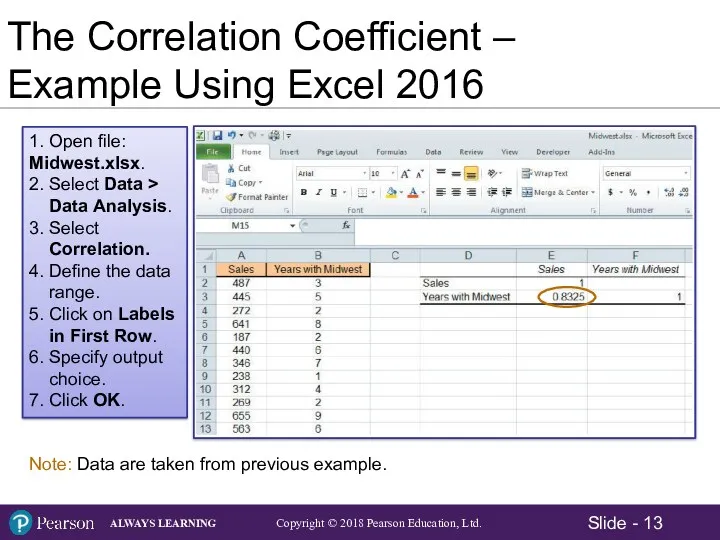
- 13. 1. Open file: Midwest.xlsx. 2. Select Data > Data Analysis. 3. Select Correlation. 4. Define the
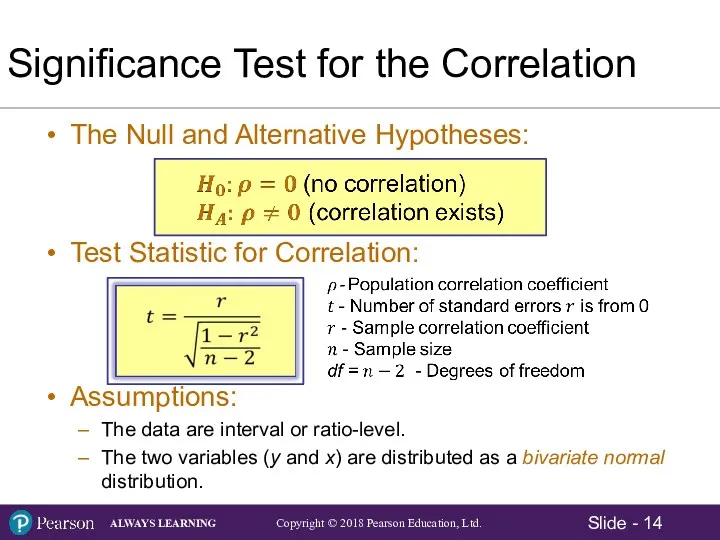
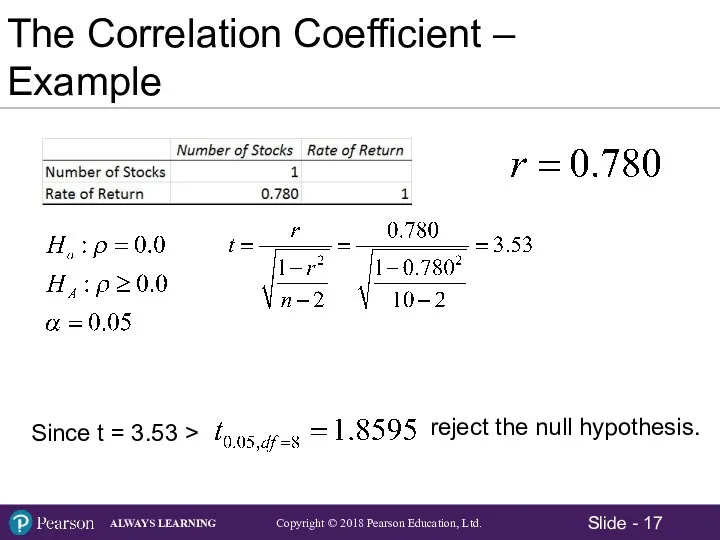
- 14. Significance Test for the Correlation The Null and Alternative Hypotheses: Test Statistic for Correlation: Assumptions: The
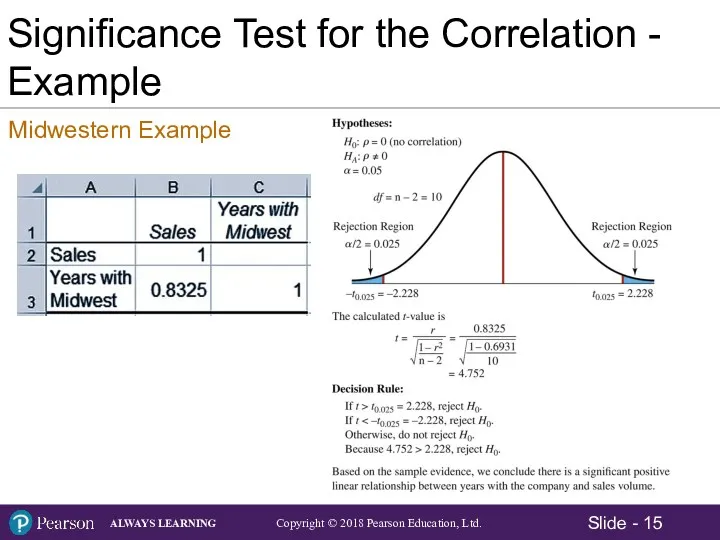
- 15. Significance Test for the Correlation - Example Midwestern Example
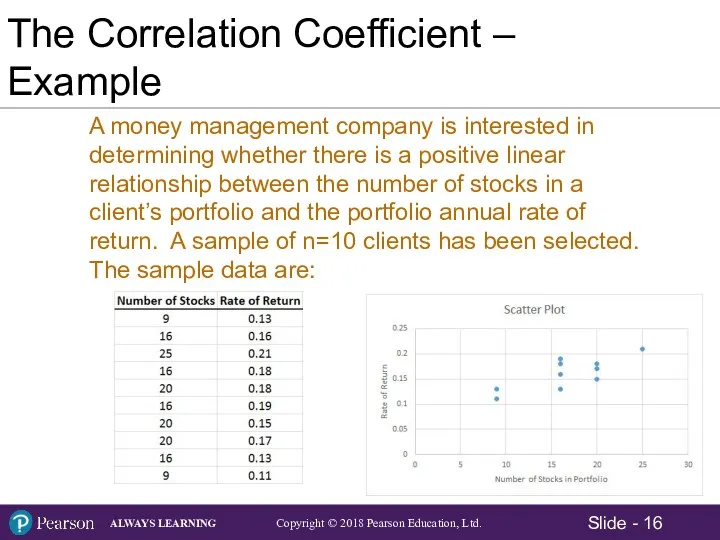
- 16. The Correlation Coefficient – Example A money management company is interested in determining whether there is
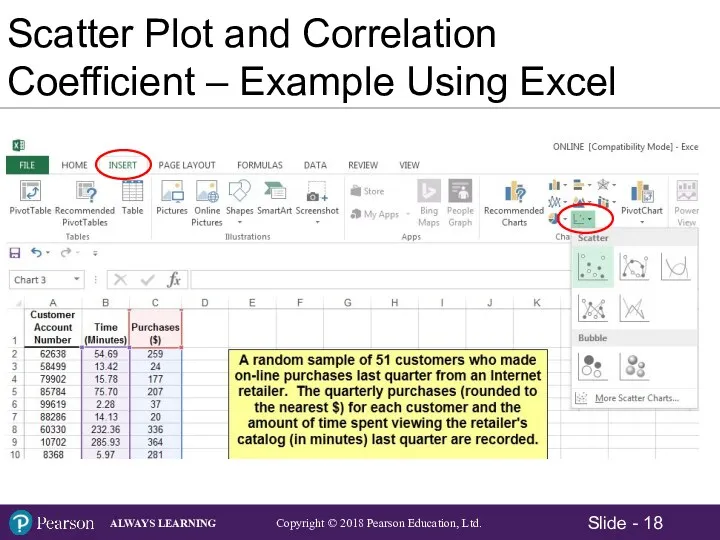
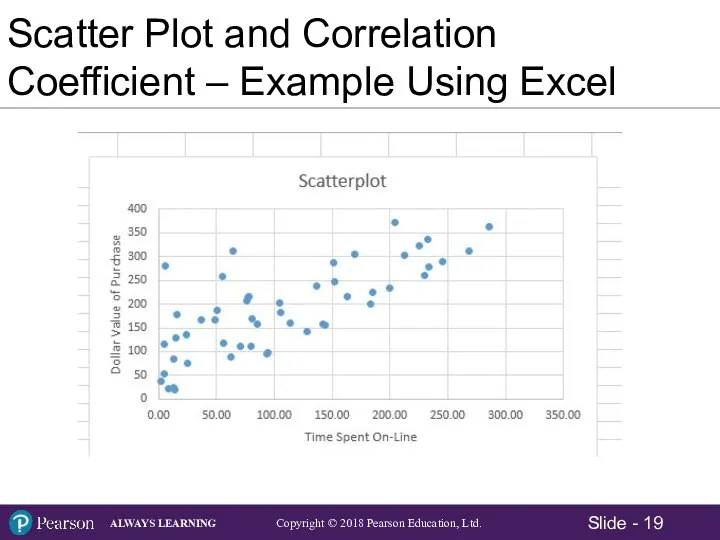
- 19. Scatter Plot and Correlation Coefficient – Example Using Excel
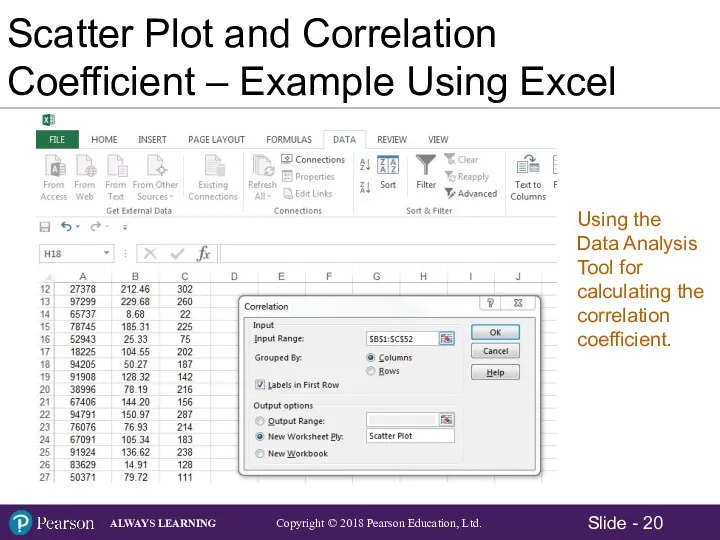
- 20. Scatter Plot and Correlation Coefficient – Example Using Excel Using the Data Analysis Tool for calculating
- 22. Correlation Analysis - Summary Step 1: Specify the population parameter of interest Step 2: Formulate the
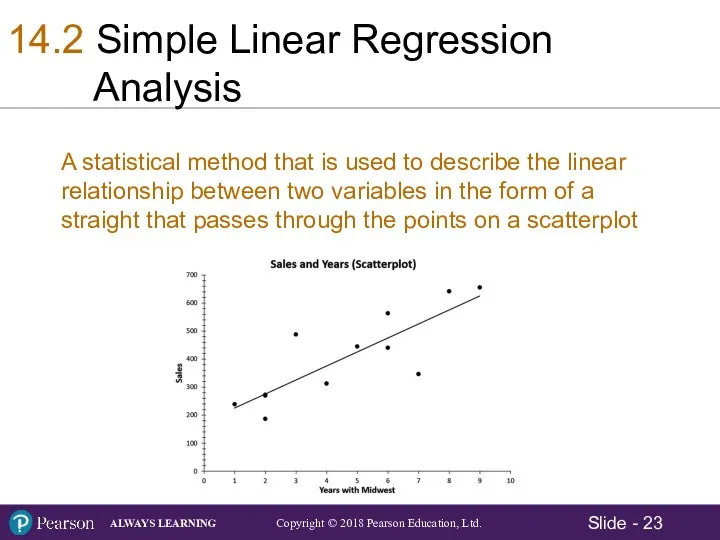
- 23. 14.2 Simple Linear Regression Analysis A statistical method that is used to describe the linear relationship
- 24. Simple Linear Regression Analysis When there are only two variables - a dependent variable, and an
- 25. Dependent and Independent Variables Dependent Variable – A variable whose values are thought to be a
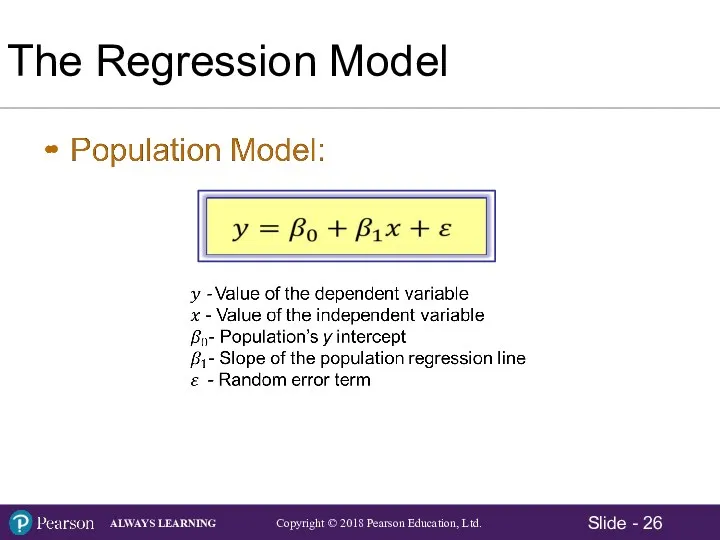
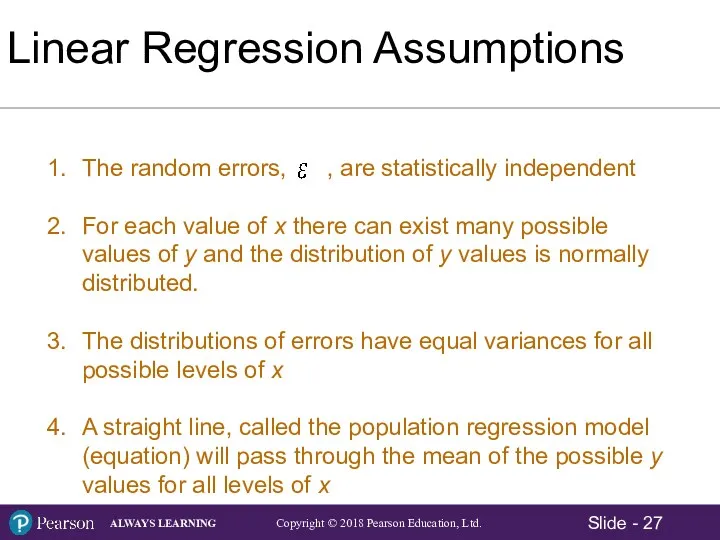
- 26. The Regression Model
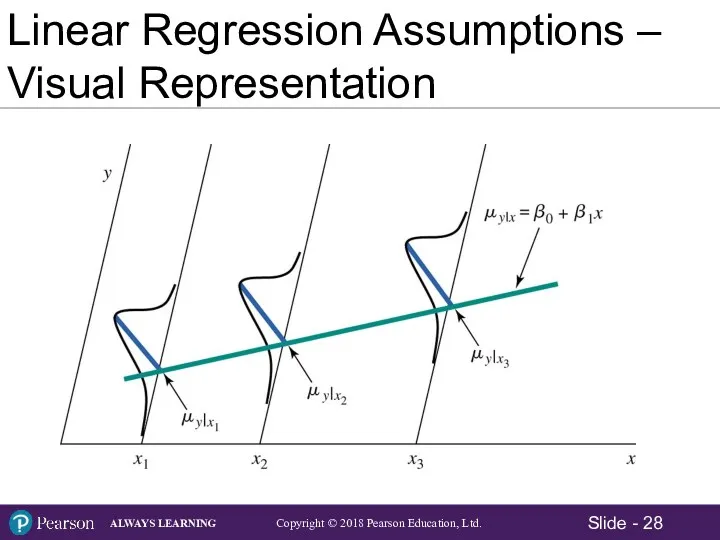
- 28. Linear Regression Assumptions – Visual Representation
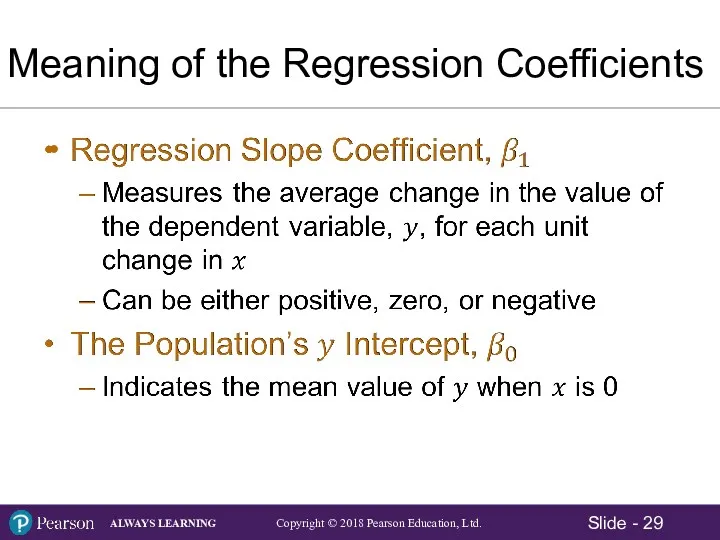
- 29. Meaning of the Regression Coefficients
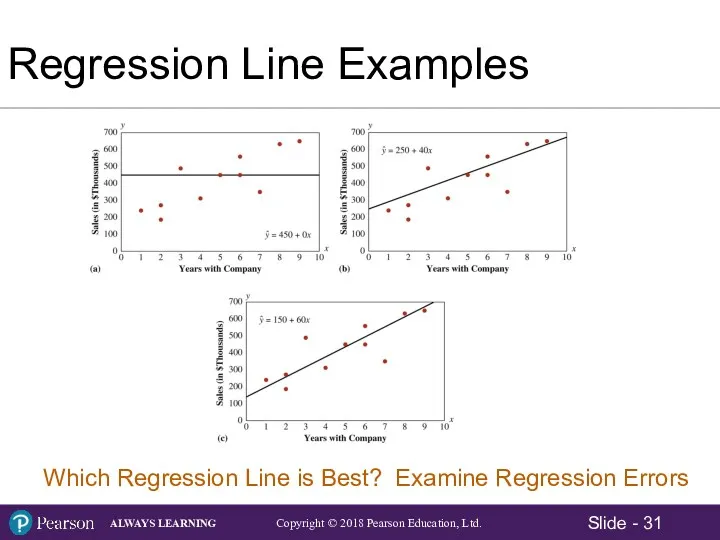
- 31. Regression Line Examples
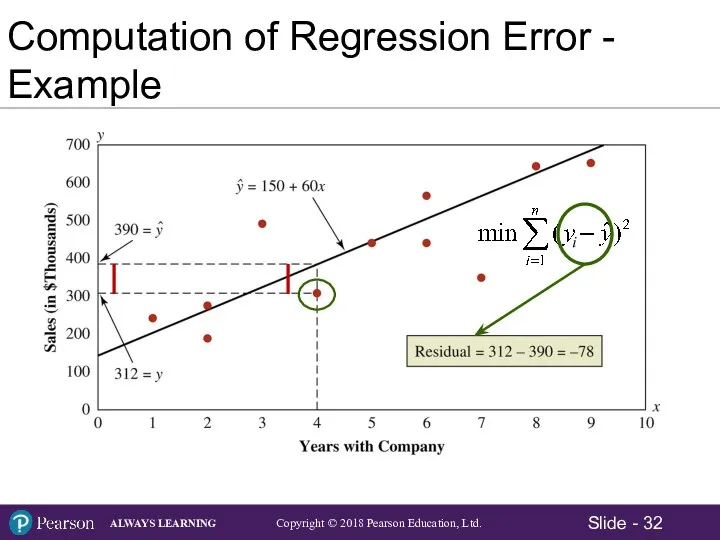
- 32. Computation of Regression Error - Example
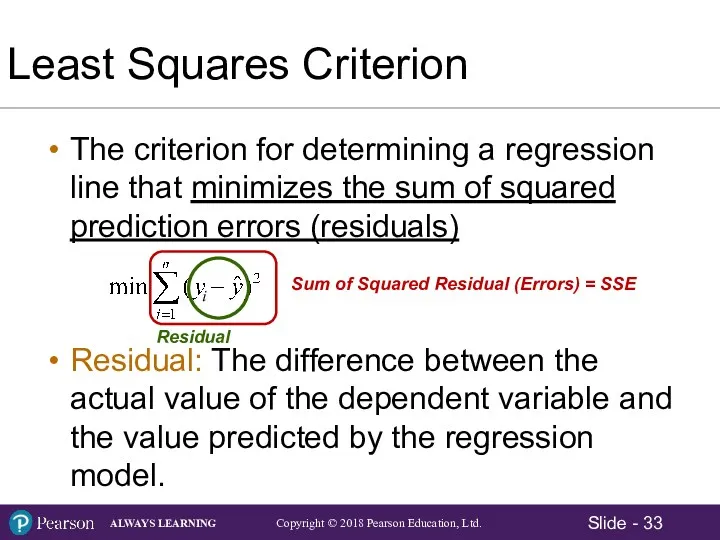
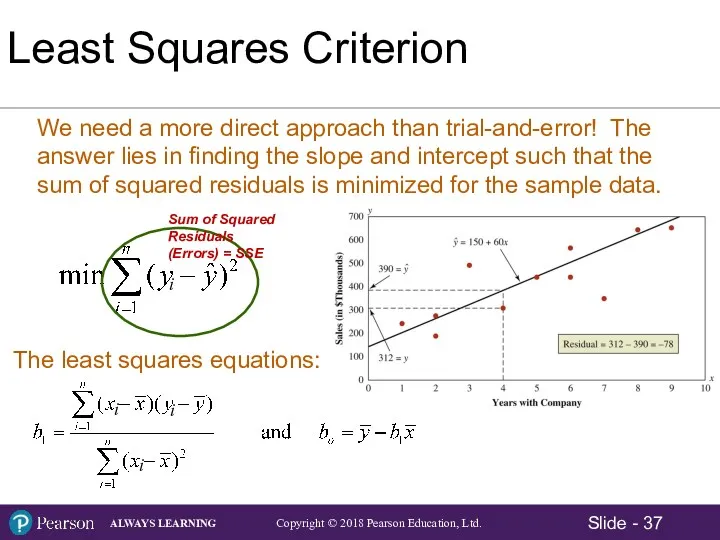
- 33. Least Squares Criterion The criterion for determining a regression line that minimizes the sum of squared
- 34. Sum of Squared Residuals (Errors) =
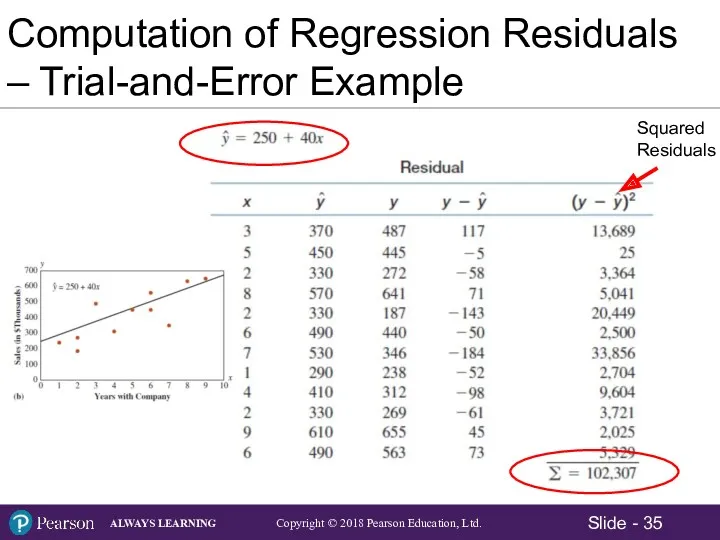
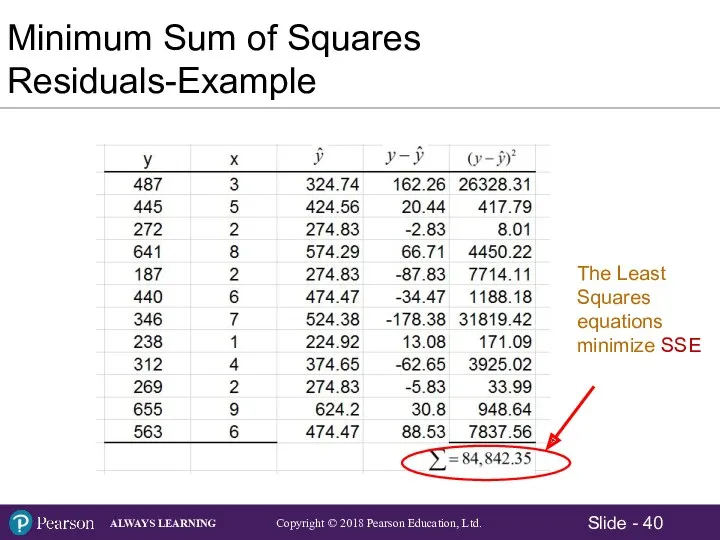
- 37. i i i i Sum of Squared Residuals (Errors) = SSE
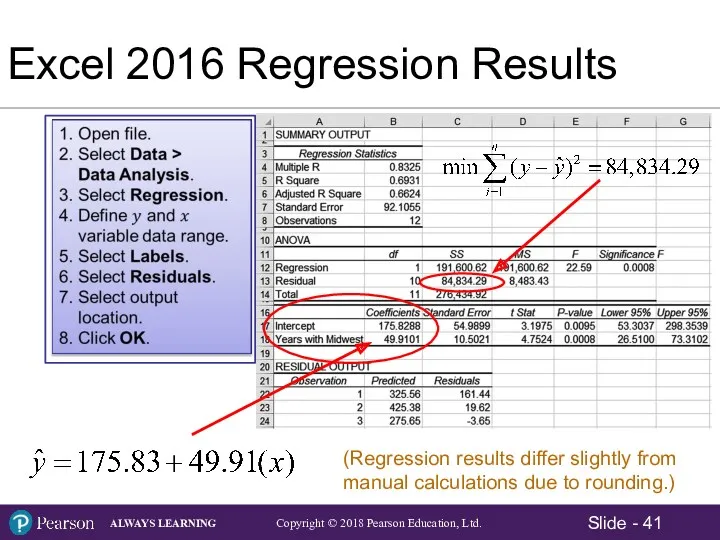
- 41. Excel 2016 Regression Results
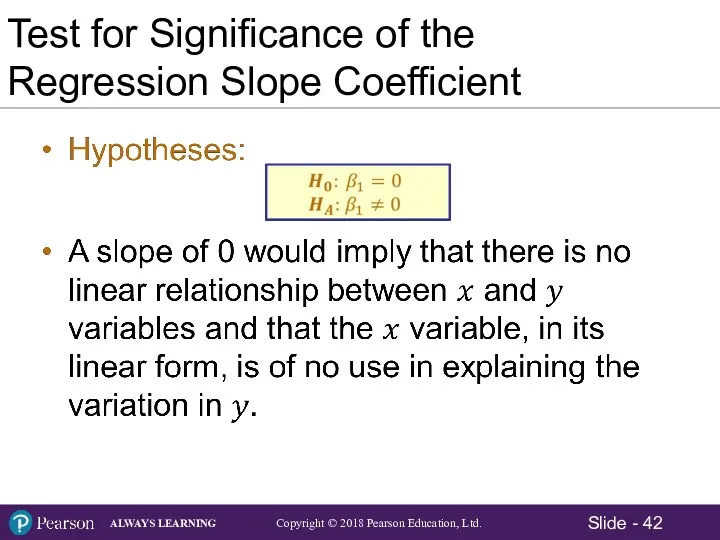
- 42. Test for Significance of the Regression Slope Coefficient
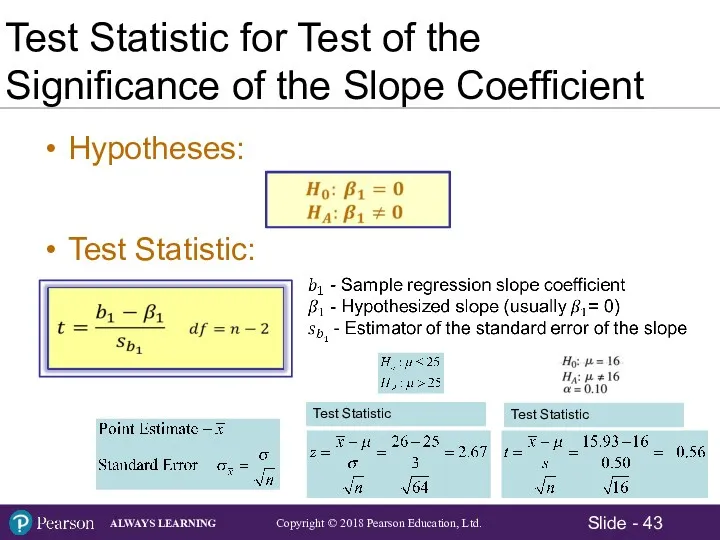
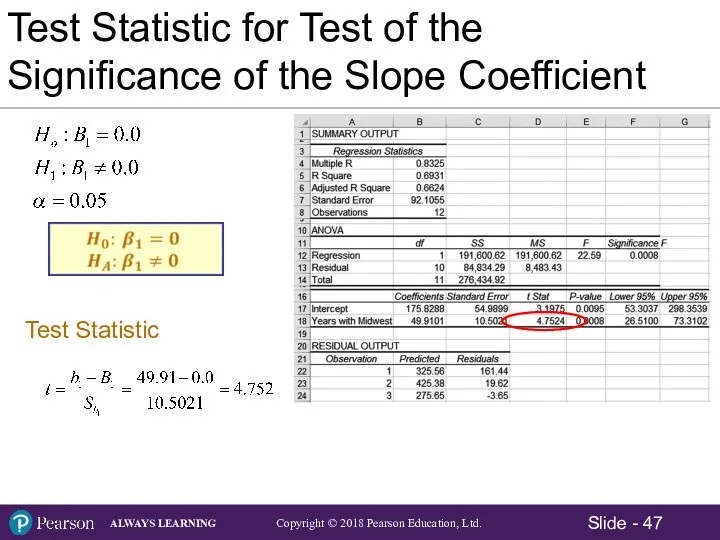
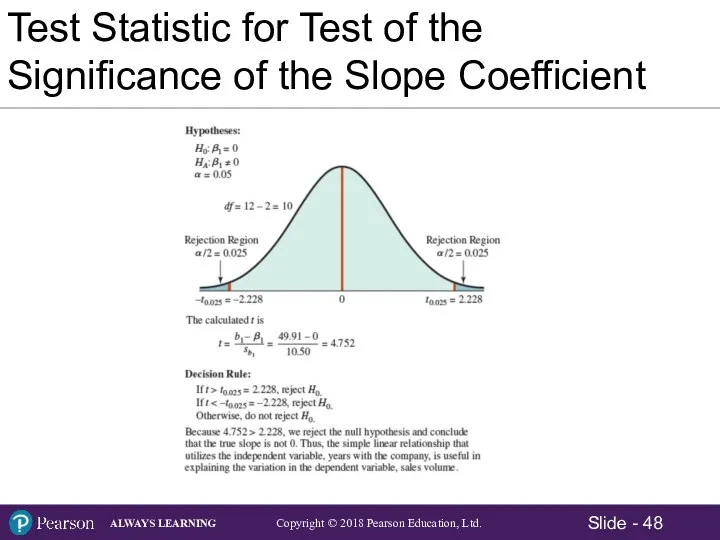
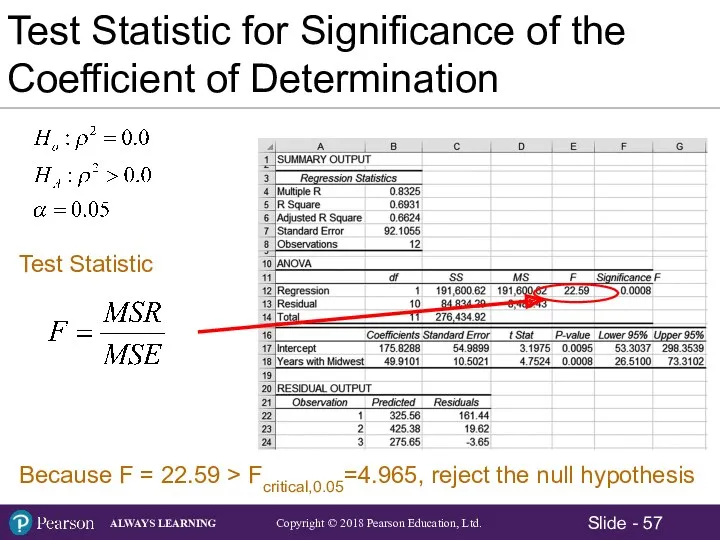
- 43. Test Statistic for Test of the Significance of the Slope Coefficient Hypotheses: Test Statistic: Test Statistic
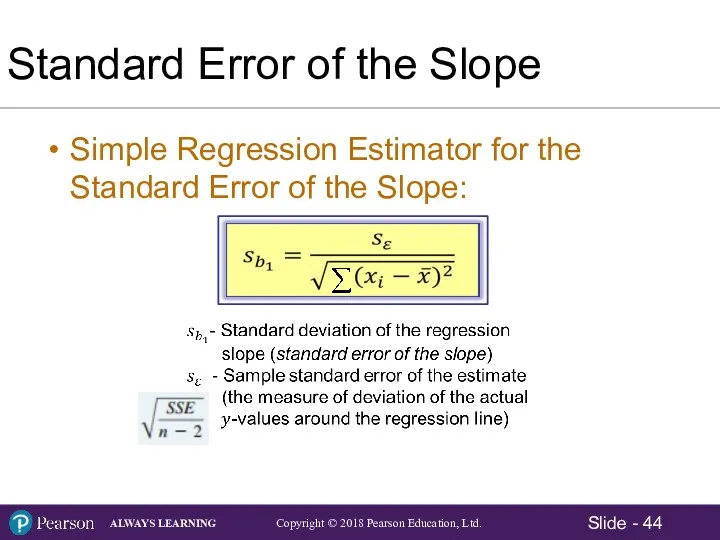
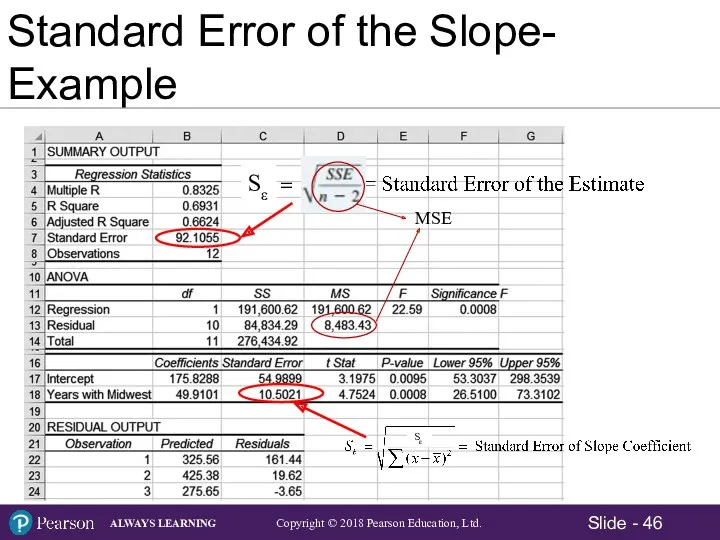
- 44. Standard Error of the Slope Simple Regression Estimator for the Standard Error of the Slope:
- 45. Standard Error of the Slope Large Standard Error Small Standard Error
- 46. Standard Error of the Slope- Example Sε Sε MSE
- 47. Test Statistic for Test of the Significance of the Slope Coefficient
- 48. Test Statistic for Test of the Significance of the Slope Coefficient
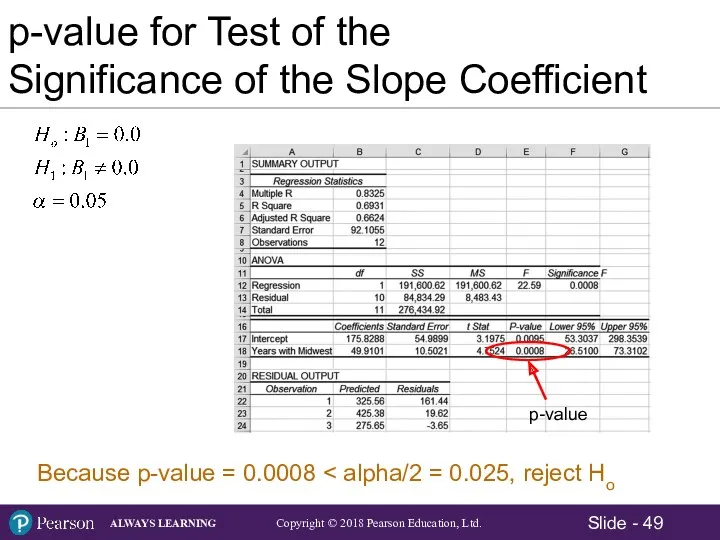
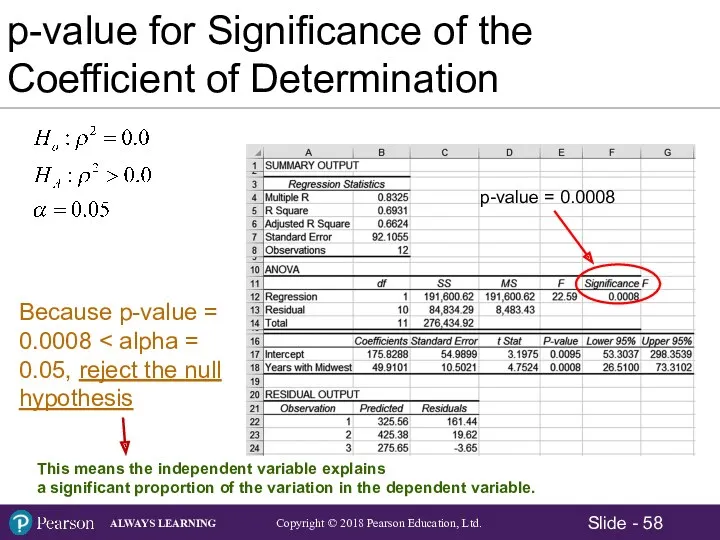
- 49. p-value for Test of the Significance of the Slope Coefficient
- 50. Review: The Correlation Coefficient – Manual Calculation Example
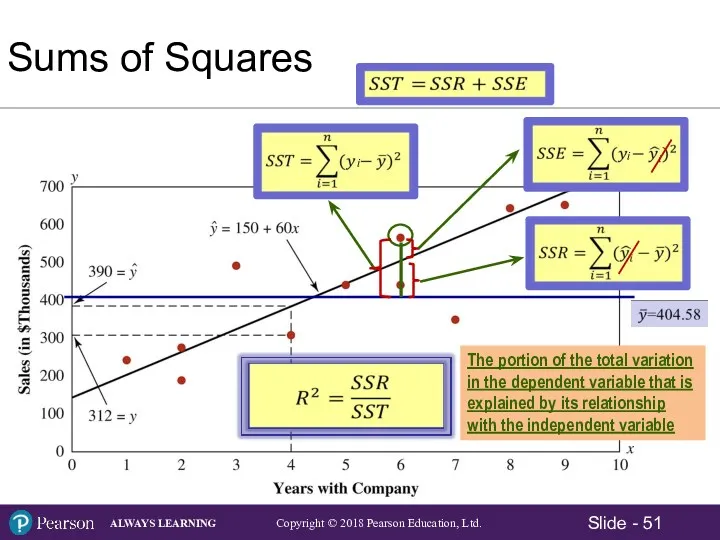
- 51. Sums of Squares The portion of the total variation in the dependent variable that is explained
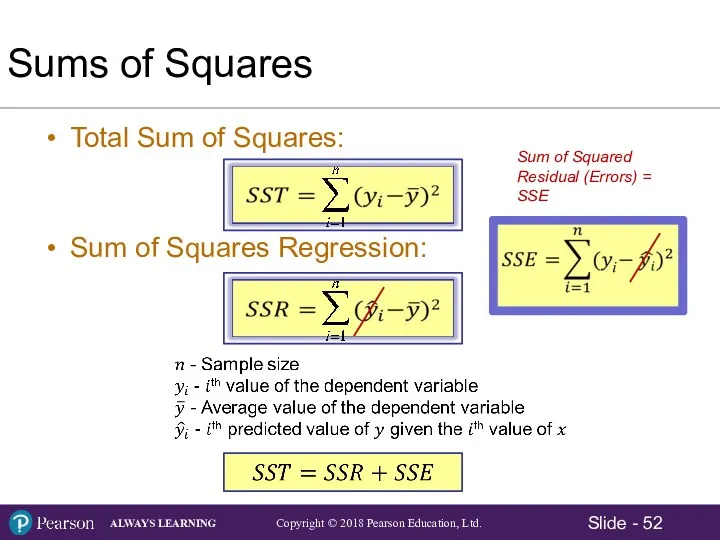
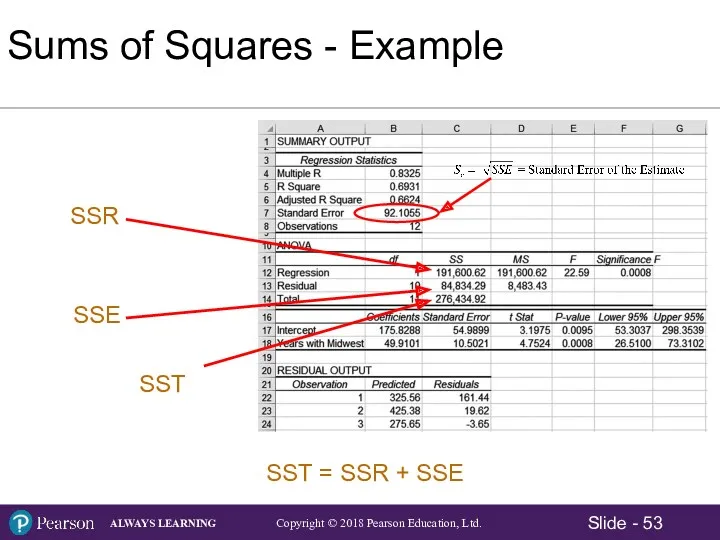
- 52. Sums of Squares Total Sum of Squares: Sum of Squares Regression: Sum of Squared Residual (Errors)
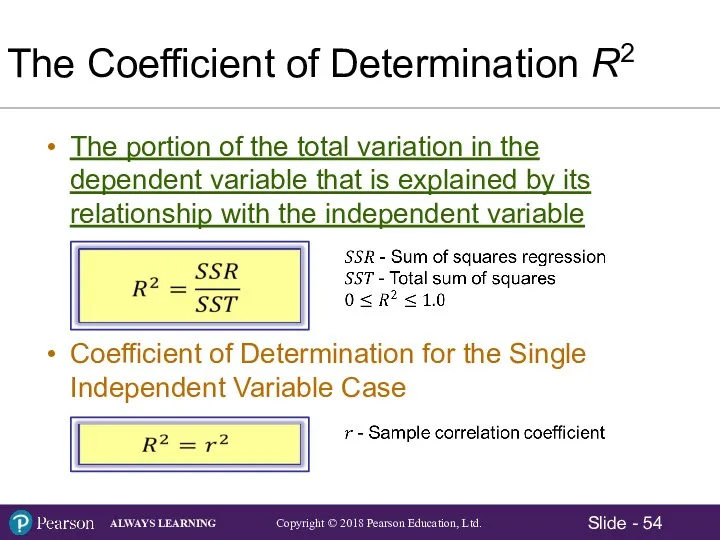
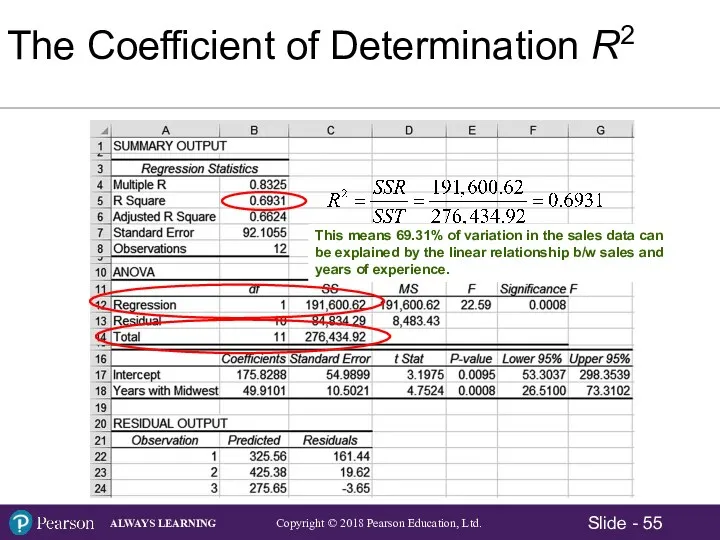
- 54. The Coefficient of Determination R2 The portion of the total variation in the dependent variable that
- 55. This means 69.31% of variation in the sales data can be explained by the linear relationship
- 58. This means the independent variable explains a significant proportion of the variation in the dependent variable.
- 59. 14.3 Uses for Regression Analysis Description – When we are primarily interested in analyzing the relationship
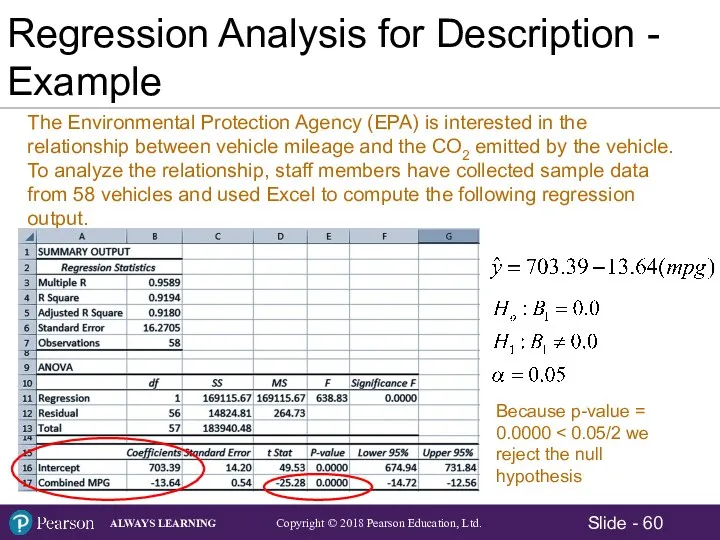
- 60. Regression Analysis for Description - Example
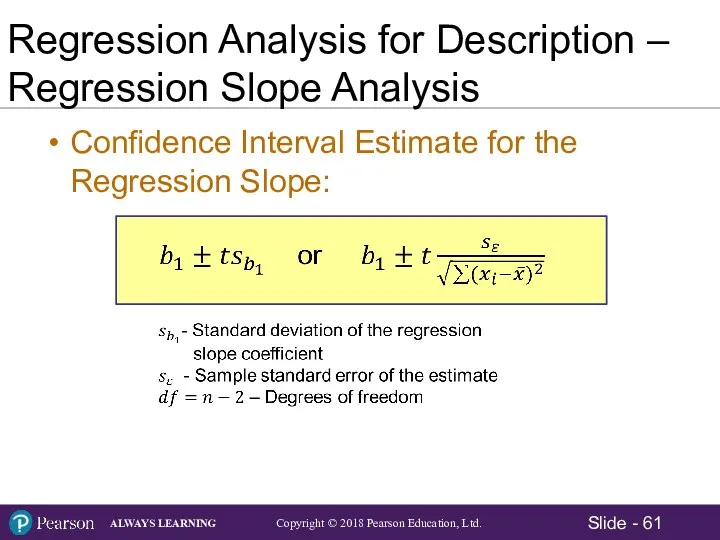
- 61. Regression Analysis for Description – Regression Slope Analysis Confidence Interval Estimate for the Regression Slope:
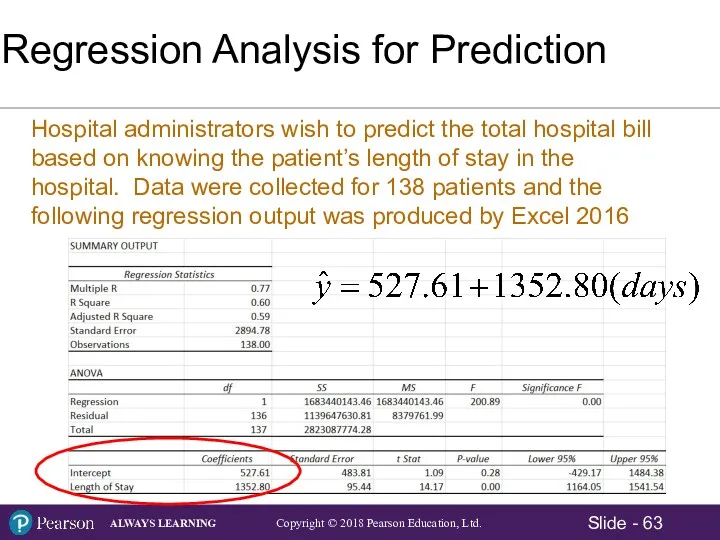
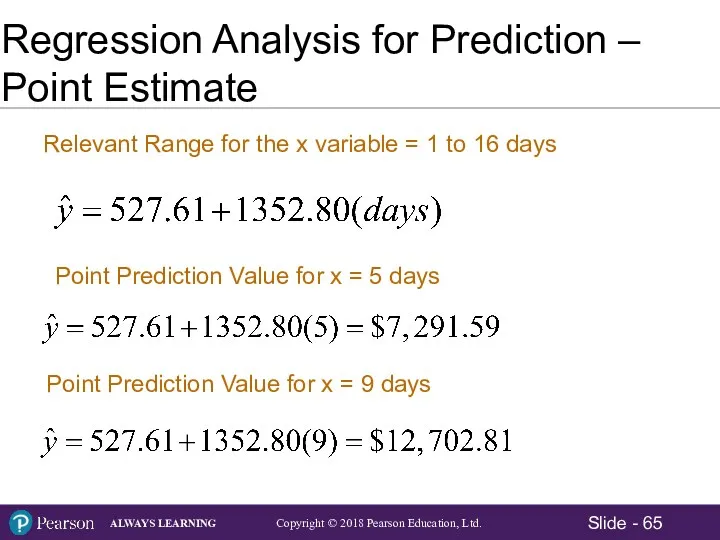
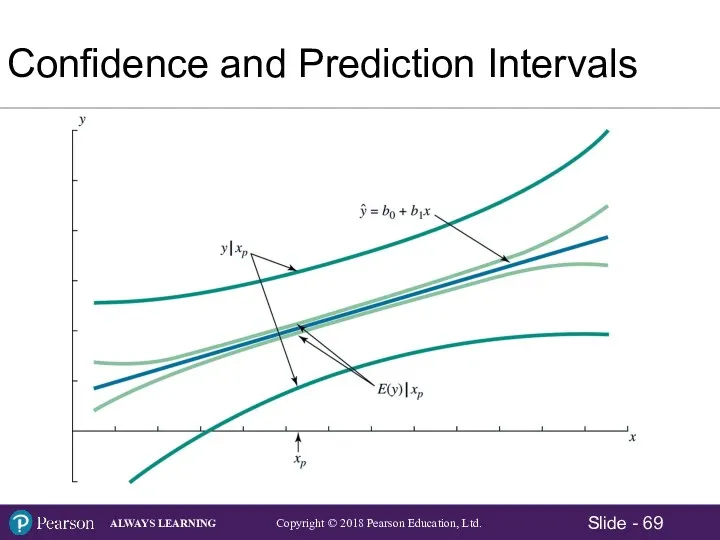
- 65. Regression Analysis for Prediction – Point Estimate Relevant Range for the x variable = 1 to
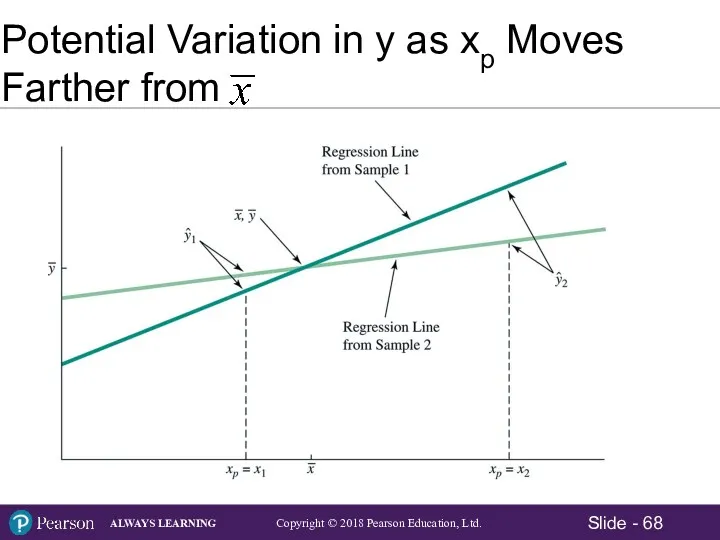
- 68. Potential Variation in y as xp Moves Farther from
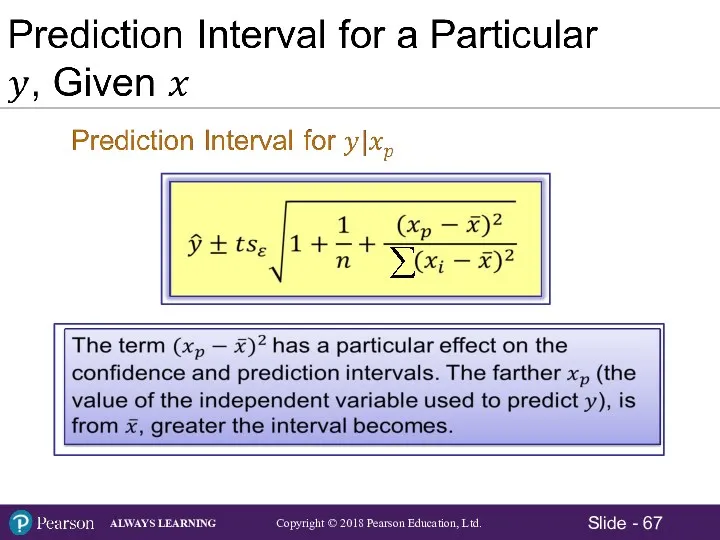
- 69. Confidence and Prediction Intervals
- 71. Скачать презентацию











 Конспект урока и презентация по математике в 4 классе
Конспект урока и презентация по математике в 4 классе Тоғызқұмалақ және математика
Тоғызқұмалақ және математика математика. устный счет
математика. устный счет Округление натуральных чисел
Округление натуральных чисел Решение алгебраических и трансцендентных уравнений
Решение алгебраических и трансцендентных уравнений Решение задач по планиметрии
Решение задач по планиметрии Классификация треугольников по углам
Классификация треугольников по углам Свойства правильных многогранников и их применение
Свойства правильных многогранников и их применение Алгебра логики
Алгебра логики Урок математики
Урок математики Ділення з остачею
Ділення з остачею Задачи на деление.
Задачи на деление. Дециметр (дм)
Дециметр (дм) Нахождение дроби от числа
Нахождение дроби от числа Урок повторения курса геометрии 7-9
Урок повторения курса геометрии 7-9 Свойства действий над числами
Свойства действий над числами Тест по математике Решение логических задач. 5 класс
Тест по математике Решение логических задач. 5 класс Преподавание алгебры в 7 классе с углубленным изучением математики
Преподавание алгебры в 7 классе с углубленным изучением математики Презентация к уроку математики по программе Перспективная начальная школа
Презентация к уроку математики по программе Перспективная начальная школа Билеты по геометрии. Переводной экзамен. 8 класс
Билеты по геометрии. Переводной экзамен. 8 класс Масса предметов. Килограмм
Масса предметов. Килограмм Урок математики с презентацией в 1 классе на тему:Закрепление изученного. Проверка знаний
Урок математики с презентацией в 1 классе на тему:Закрепление изученного. Проверка знаний Среднее арифметическое. Среднее значение величины
Среднее арифметическое. Среднее значение величины Умножение положительных и отрицательных чисел
Умножение положительных и отрицательных чисел Готовимся к ЕГЭ
Готовимся к ЕГЭ Фрагмент урока. Контрольный тест Числа больше 1000
Фрагмент урока. Контрольный тест Числа больше 1000 Аналіз характеристик КС на основі теорії марківських процесів. (Тема 5)
Аналіз характеристик КС на основі теорії марківських процесів. (Тема 5) Урок математики
Урок математики