Содержание
- 2. Appendicitis: appendicitis is a sudden inflammation of the appendix. Appendicitis is one of the most common
- 3. Appendicitis is more common in males than in females, and incidence peaks in the late teens
- 4. Etiology Infectious theory Obstruction theory Neuroproliferation theory Venous congestion theory
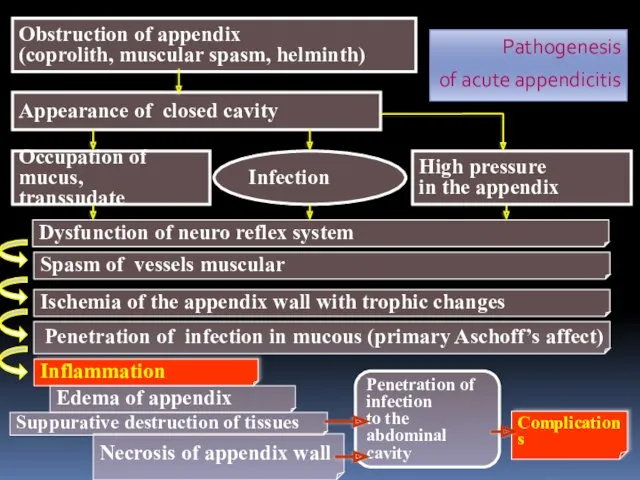
- 5. Obstruction of appendix (coprolith, muscular spasm, helminth) Appearance of closed cavity Occupation of mucus, transsudate Infection
- 6. Clinical manifestation The clinical signs and symptoms depend on the pathologic phase of appendicitis at examenation.
- 7. Later symptoms Loss of appetite Nausea Vomiting Constipation Rectal tenderness Chills and shaking
- 8. Abdominal pain Abdominal pain is a nonspecific symptom that may be associated with a multitude of
- 9. Abdominal pain can be caused by toxins, infection, biliary tract disease, liver disease, renal disease, bladder
- 10. During physical examination, the health care provider will try to determine if the pain is localized
- 11. In addition, the health care provider will try to relate the abdominal tenderness to other general
- 13. Differential diagnosis 1. Gastroenteritis 2. Diverticulitis 3. Mesenteric adenitis 4. Intussusception 5. Hemolytic – uremic syndrome
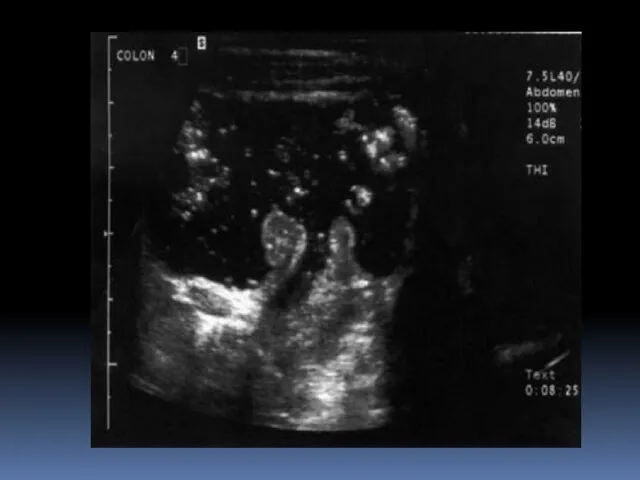
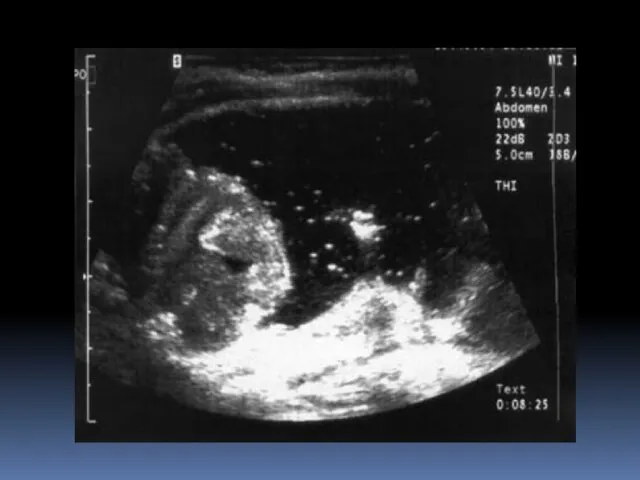
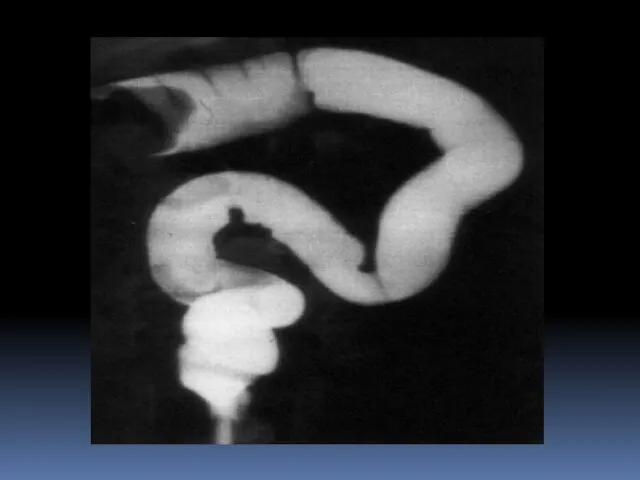
- 18. Signs and tests CT scan revealing thickening of the inflamed area colonoscopy sigmoidoscopy barium enema abdominal
- 22. Complications Peritonitis Wound infection Intra-abdominal abscess Intestinal obstruction
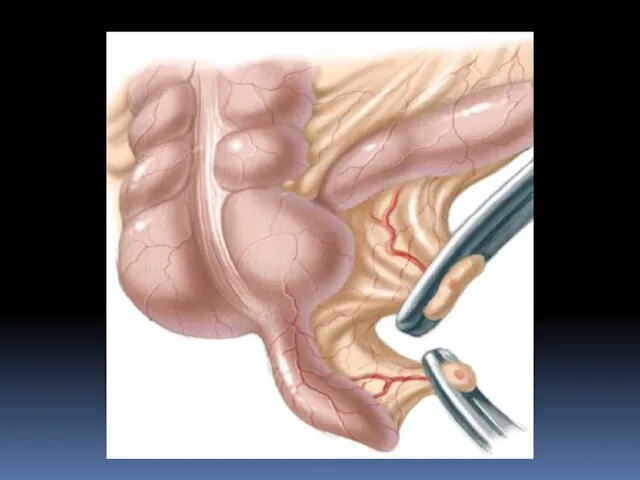
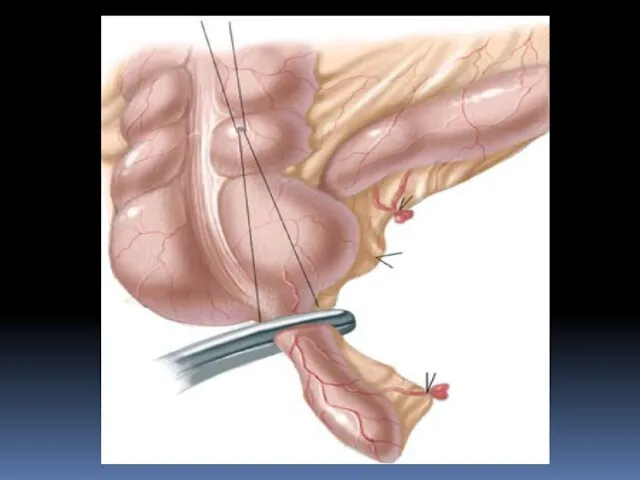
- 23. Treatment complications Acute diverticulitis requires antibiotic therapy. Recurrent attacks or presence of perforation (hole), fistula (abnormal
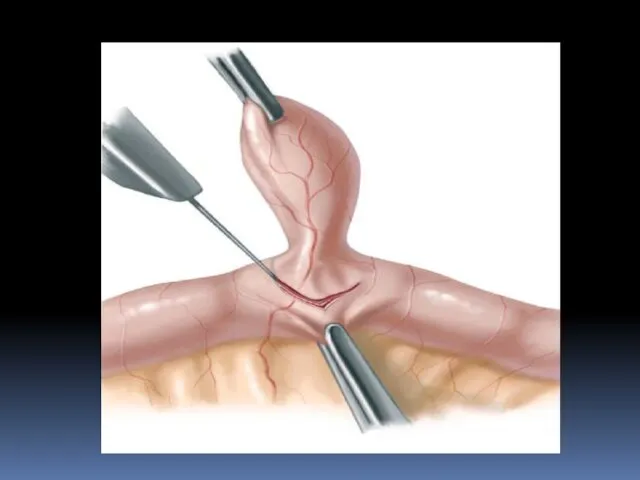
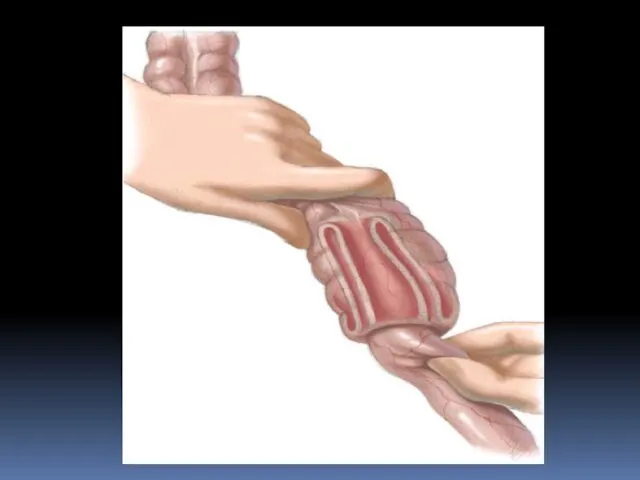
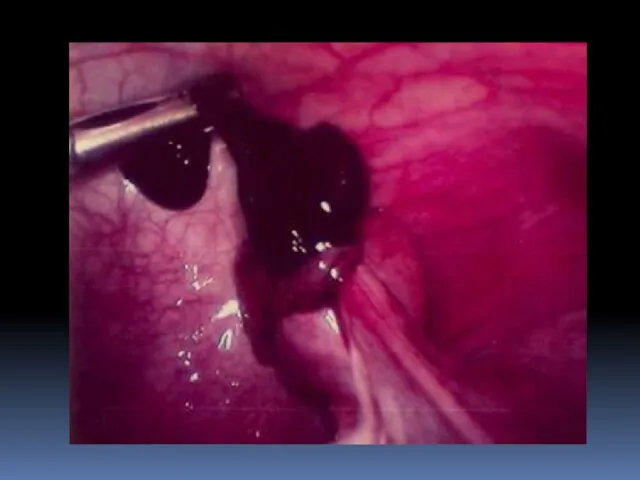
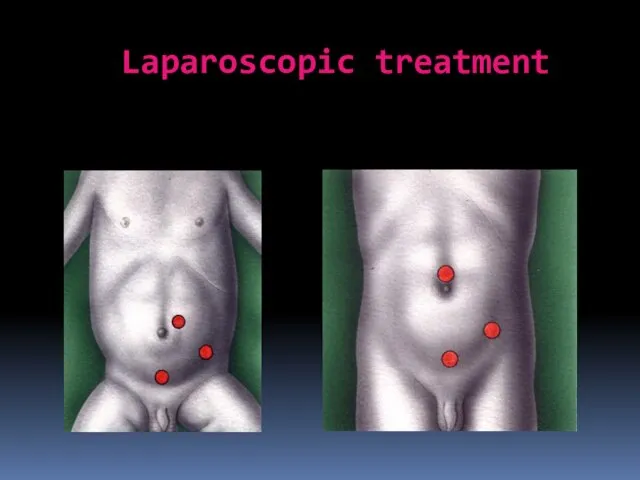
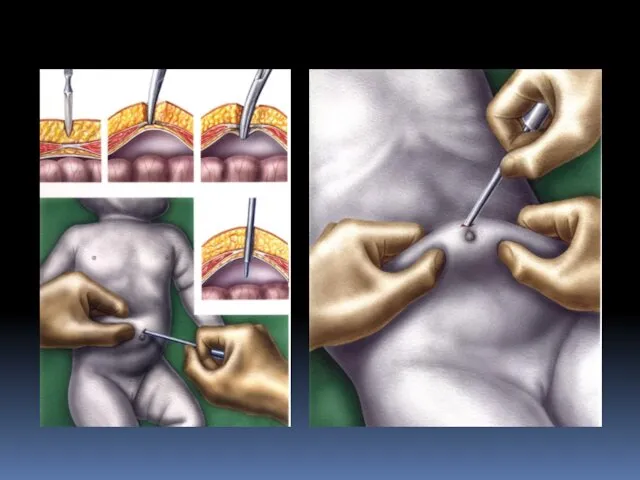
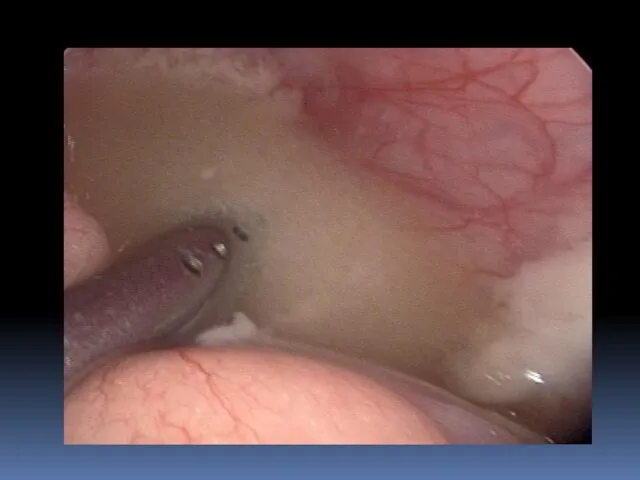
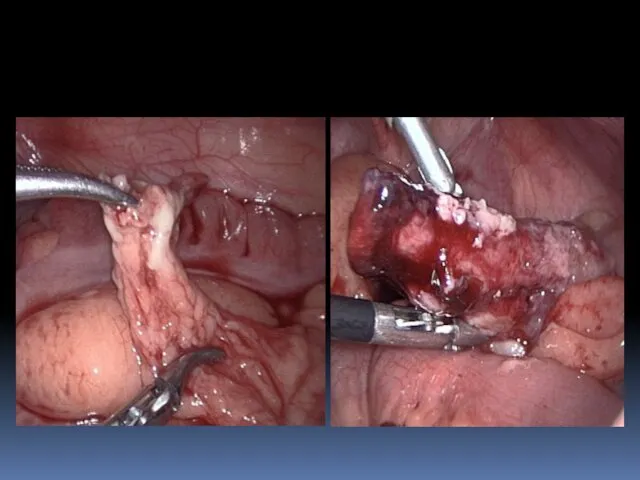
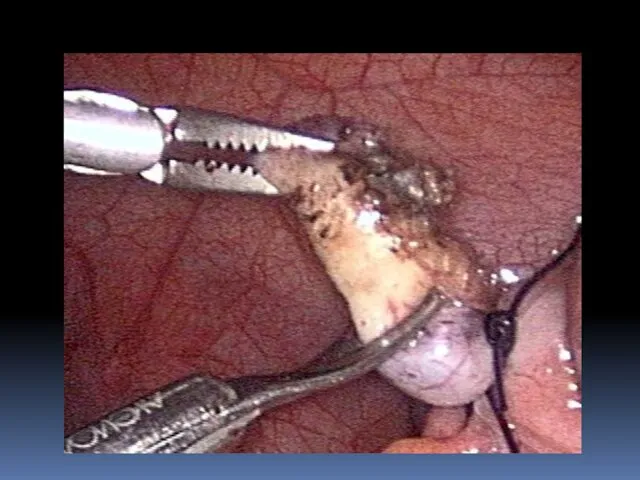
- 26. Laparoscopic treatment
- 33. Advances in peri-operative care and antibiotics have resulted in a zero mortality rate and low morbidity
- 35. Скачать презентацию














 Заболевания зрительного нерва и сетчатой оболочки. Патология глаз при общих соматических заболеваниях
Заболевания зрительного нерва и сетчатой оболочки. Патология глаз при общих соматических заболеваниях Реабилитация инсульта
Реабилитация инсульта Оказание первой медицинской помощи при кровотечениях. 5 класс
Оказание первой медицинской помощи при кровотечениях. 5 класс Механикалық зақым
Механикалық зақым Денсаулық - 2020
Денсаулық - 2020 Презентация по ЭКГ для ветеринарных врачей
Презентация по ЭКГ для ветеринарных врачей Общая фармакотерапевтическая характеристика противоопухолевых препаратов
Общая фармакотерапевтическая характеристика противоопухолевых препаратов Бесплодный брак. Итоги работы кабинета бесплодия
Бесплодный брак. Итоги работы кабинета бесплодия Сестринский уход при повреждениях органа зрения. Лекция 8
Сестринский уход при повреждениях органа зрения. Лекция 8 Гемостаз
Гемостаз Иммуннобиологические препараты
Иммуннобиологические препараты Организационная структура службы медицины катастроф, режимы ее функционирования, задачи в чрезвычайных ситуациях мирного времени
Организационная структура службы медицины катастроф, режимы ее функционирования, задачи в чрезвычайных ситуациях мирного времени Хирургическая инфекция
Хирургическая инфекция Пренатальная психология
Пренатальная психология Leptospirozlar
Leptospirozlar Предмет и содержание судебной медицины. Процессуальные и организационные основы судебномедицинской экспертизы
Предмет и содержание судебной медицины. Процессуальные и организационные основы судебномедицинской экспертизы Первая помощь при отсутствии сознания, остановке дыхания и кровообращения
Первая помощь при отсутствии сознания, остановке дыхания и кровообращения Шугаринг
Шугаринг Биопсийные исследования желудочно-кишечного тракта
Биопсийные исследования желудочно-кишечного тракта Чувствительность: общие понятия
Чувствительность: общие понятия ЯМР, ЭПР-ді медицинада қолдану
ЯМР, ЭПР-ді медицинада қолдану Санитарный надзор
Санитарный надзор Ринит. Синусит. Тонзиллит. Фарингит. Дифференциальная диагностика
Ринит. Синусит. Тонзиллит. Фарингит. Дифференциальная диагностика Хламидиоз у детей
Хламидиоз у детей Empreinte traditionnelle ou empreinte optique
Empreinte traditionnelle ou empreinte optique Правда о СПИДе. Часть 1
Правда о СПИДе. Часть 1 Ұзақ жаншылу синдромы кезіндегі жедел көмек
Ұзақ жаншылу синдромы кезіндегі жедел көмек Special issues. Guidelines for the use of antiretroviral agents in adults and adolescents
Special issues. Guidelines for the use of antiretroviral agents in adults and adolescents