Содержание
- 2. Immune system disorders Weakened immune response: Primary immunodeficiency Secondary immunodeficiency Excessive immune response: Allergic reactions Autoimmune
- 3. Antigen - any substance that can stimulate immune system Allergen – any substance that can induce
- 4. Allergy classification by P. G. H. Gell and R. R. A. Coombs Type I hypersensitivity -
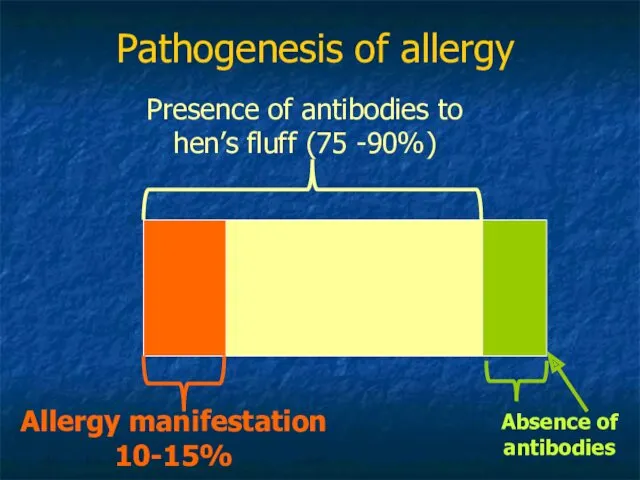
- 5. Pathogenesis of allergy Absence of antibodies Presence of antibodies to hen’s fluff (75 -90%) Allergy manifestation
- 6. Immune and Allergic reactions Similar features: protection of the organism from genetically foreign ones similar mechanisms
- 7. Hereditary Predisposition to Allergy increased permeability of barriers ↑ activity of T-helpers, ↑ synthesis of IgE
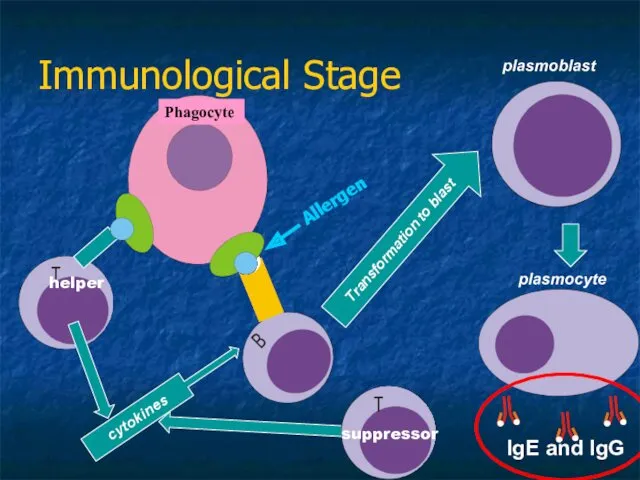
- 8. Immunological Stage of Allergic Reaction revealing the allergen presentation of the allergen to lymphocytes Ig synthesis
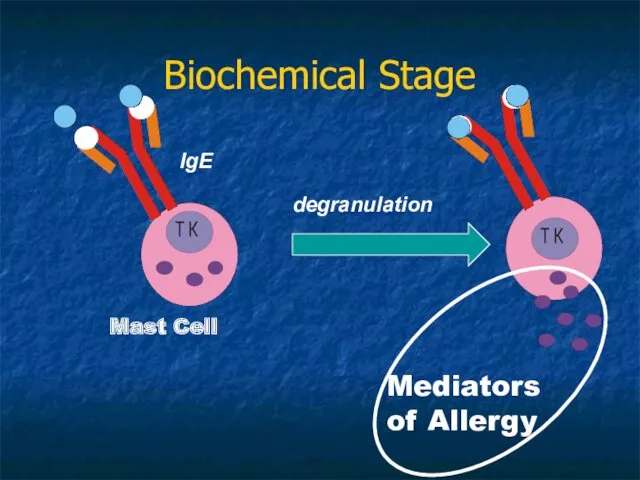
- 9. Biochemical Stage of Allergic Reaction allergen interaction with specific antibodies or sensitized lymphocytes; release or synthesis
- 10. The stage of allergy clinical manifestation (type 1) Local signs: Itching, pain, rashes Nasal congestion ?
- 11. Type 1 Allergic Reactions (anaphylactic, reaginic) Allergic asthma Conjunctivitis Allergic rhinitis ("hay fever") Anaphylactic shock Angionevrotic
- 12. Immunological Stage Transformation to blast cytokines Phagocyte helper suppressor IgE and IgG Allergen
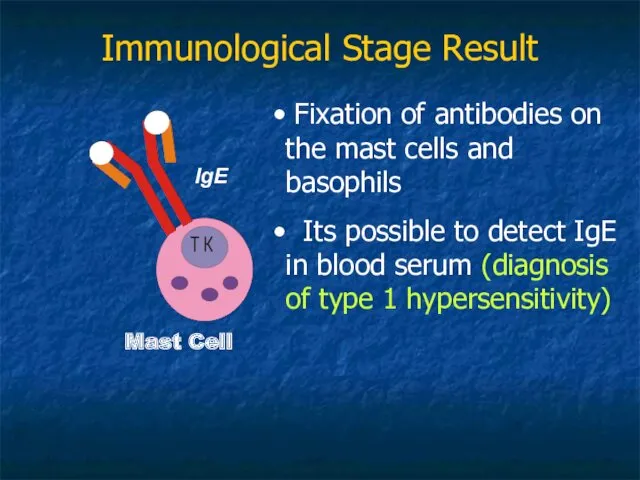
- 13. Immunological Stage Result Mast Cell Fixation of antibodies on the mast cells and basophils Its possible
- 14. Biochemical Stage Mast Cell Mediators of Allergy
- 15. Classification of Allergy Mediators Primary (pre-stored) Histamine Heparine Serotonine Secondary (new synthesis) Prostaglandins Leukotrienes Cytokines
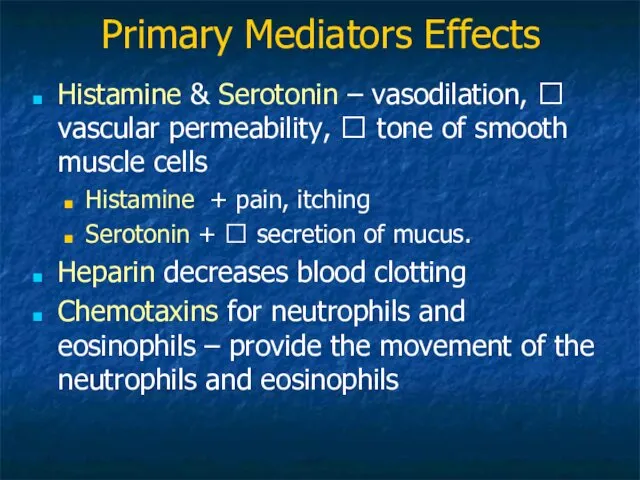
- 16. Primary Mediators Effects Histamine & Serotonin – vasodilation, ? vascular permeability, ? tone of smooth muscle
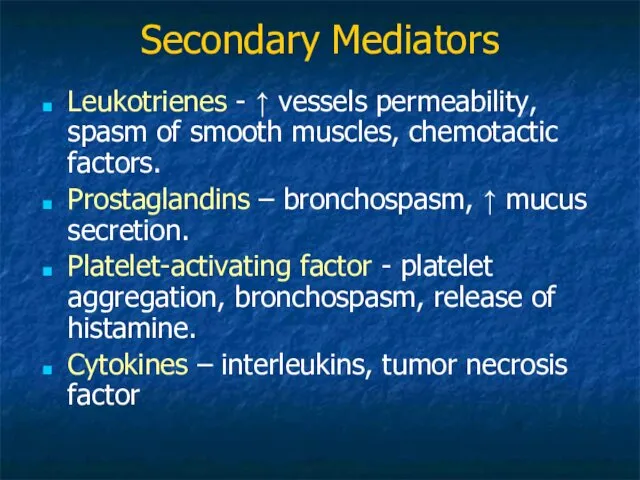
- 17. Secondary Mediators Leukotrienes - ↑ vessels permeability, spasm of smooth muscles, chemotactic factors. Prostaglandins – bronchospasm,
- 18. Type 2 allergic reactions (antibody-dependent cytotoxicity) Transfusion reactions, autoimmune anemia, leukopenia, thrombocytopenia, thyroiditis. Transformation of own
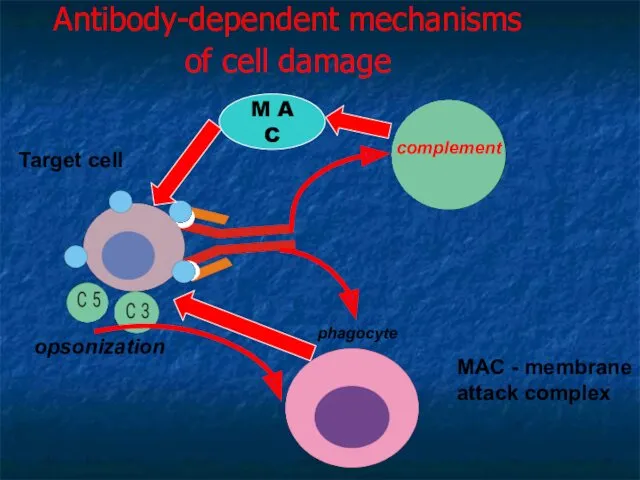
- 19. Antibody-dependent mechanisms of cell damage Target cell M A C opsonization MAC - membrane attack complex
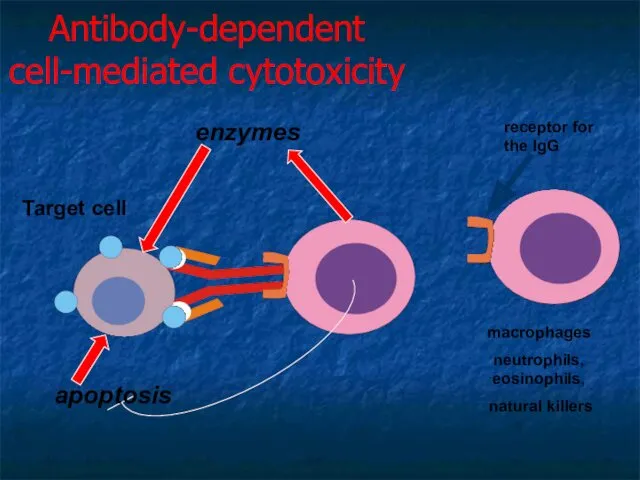
- 20. Antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity enzymes macrophages neutrophils, eosinophils, natural killers
- 21. Type 5 allergic reactions (stimulating reactions) Autoimmune thyroiditis Antibodies bind to TSH receptor on thyroid epithelial
- 22. Type 3 allergic reactions (immune complexes) Immune complex glomerulonephritis Serum sickness Arthus reaction (local reaction) Antigens
- 23. Features of type 3 hypersensitivity Circulation of immune complexes in blood (systemic diseases) IgG and IgM
- 24. Phases of the systemic immune-complex disease formation of antigen-antibody complexes in circulation; deposition of the immune
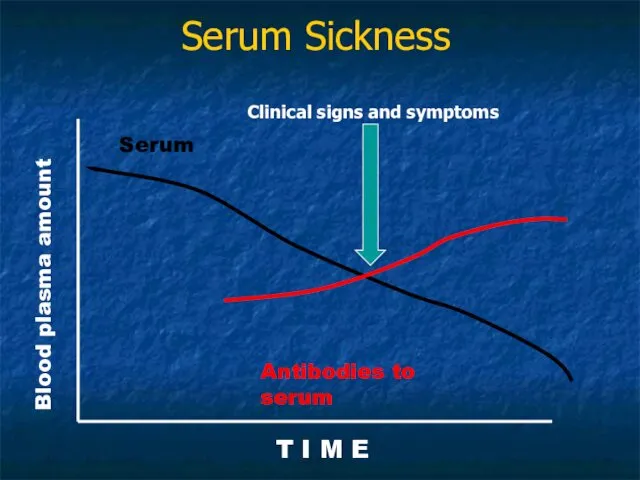
- 25. Serum Sickness Blood plasma amount T I M E Serum Antibodies to serum Clinical signs and
- 26. Pathogenic properties of immune complexes The amount of antigen - large enough to form immune complexes.
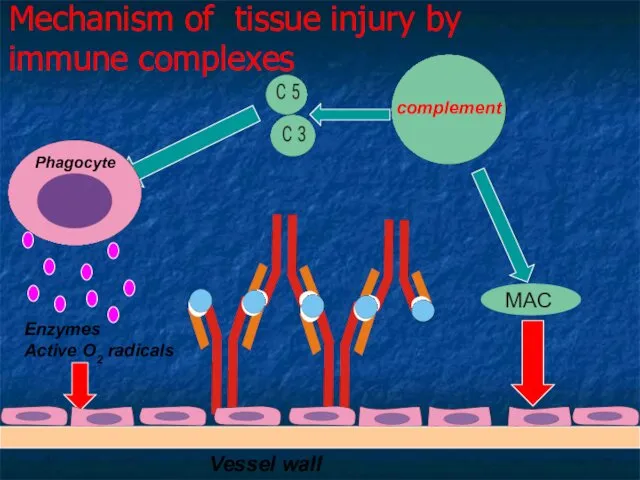
- 27. Mechanism of tissue injury by immune complexes Vessel wall Enzymes Active O2 radicals
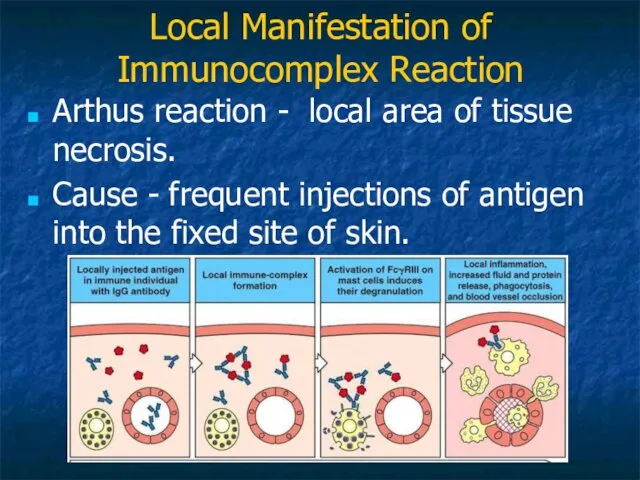
- 28. Local Manifestation of Immunocomplex Reaction Arthus reaction - local area of tissue necrosis. Cause - frequent
- 29. Type 4 allergic reactions (cell-mediated, delayed) Tuberculin test (Mantoux reaction ) Tuberculosis and leprosy Transplant rejection
- 30. Type 4 hypersensitivity Immunological stage - production of sensitized T-lymphocytes Cell injury is mediated by phagocytes
- 31. Mechanisms of tissue injury T-killers (perforins, granzymes) phagocytes (active oxygen radicals) lysosomal enzymes granulomatous (specific) inflammation
- 32. Pseudoallergy distinctive features Sensitization (immunologic) phase is absent Symptoms can occur at the first exposure. The
- 33. Pseudo-allergy mechanisms Non-immune degranulation of mast cells (histamine – liberating substances). The alternative pathway of complement
- 34. The mechanisms of self reactivity prevention Selection and deletion of self-reactive T-cells and B-cells. Peripheral suppression
- 35. Mechanisms of autoimmune diseases Damage of physiological isolation (nervous system, a crystalline lens, thyroid gland). Altering
- 36. General mechanisms of autoimmune pathology Direct antibody mediated effects (diabetes mellitus, autoimmune hemolytic anemia) T cell
- 37. Hyposensitization The patient is gradually vaccinated with progressively larger doses of the allergen. Mechanism: Increase of
- 39. Скачать презентацию
























 Приобретенные пороки сердца
Приобретенные пороки сердца Всемирный день памяти умерших от СПИДа
Всемирный день памяти умерших от СПИДа Контроль за нервно-психическим развитием детей третьего года жизни
Контроль за нервно-психическим развитием детей третьего года жизни Подходы к повышению эффективности лечения больных артериальной гипертонией с целью профилактики ее осложнений
Подходы к повышению эффективности лечения больных артериальной гипертонией с целью профилактики ее осложнений Артериальная гипотензия
Артериальная гипотензия Жүрек қан тамырлар жүйесін зерттеу
Жүрек қан тамырлар жүйесін зерттеу Професійні захворювання серцевого м’яза
Професійні захворювання серцевого м’яза Қазақстан Республикасында медицина және фармацевтік өнеркәсіптерді дамытудың мемлекеттік бағдарламасы
Қазақстан Республикасында медицина және фармацевтік өнеркәсіптерді дамытудың мемлекеттік бағдарламасы The Tooth structure Modal verbs
The Tooth structure Modal verbs Искусственное вскармливание детей первого года жизни
Искусственное вскармливание детей первого года жизни Дифференциальная диагностика и лечение кишечной диспепсии
Дифференциальная диагностика и лечение кишечной диспепсии Сестринский процесс при заболеваниях новорожденных
Сестринский процесс при заболеваниях новорожденных Медицинская арахноэнтомология
Медицинская арахноэнтомология Особенности применения лекарственных средств при сочетанном и повторном применении
Особенности применения лекарственных средств при сочетанном и повторном применении Козье молоко в детских смесях питания
Козье молоко в детских смесях питания Проявления на слизистой полости рта специфических инфекций
Проявления на слизистой полости рта специфических инфекций Организация паллиативной помощи населению Вологодской области. Проблемы и пути их решения
Организация паллиативной помощи населению Вологодской области. Проблемы и пути их решения Кишечный шов
Кишечный шов Синие пороки сердца
Синие пороки сердца Преэклампсия: классификация, клиника, диагностика, лечение
Преэклампсия: классификация, клиника, диагностика, лечение Понятие здоровье и болезнь. Этика и деонтология в медицине
Понятие здоровье и болезнь. Этика и деонтология в медицине Детский церебральный паралич связанный с мозгом : причины, формы болезни и лечение. (ДЦП)
Детский церебральный паралич связанный с мозгом : причины, формы болезни и лечение. (ДЦП) Общий уход
Общий уход Внутрибольничные инфекции в стоматологической практике
Внутрибольничные инфекции в стоматологической практике Система охорони здоров’я у Німеччині
Система охорони здоров’я у Німеччині Диабеттік нефропатия диагнозын анықтау, емдеу
Диабеттік нефропатия диагнозын анықтау, емдеу Хронический пульпит
Хронический пульпит Физиология системы кровообращения и работы сердца
Физиология системы кровообращения и работы сердца