Содержание
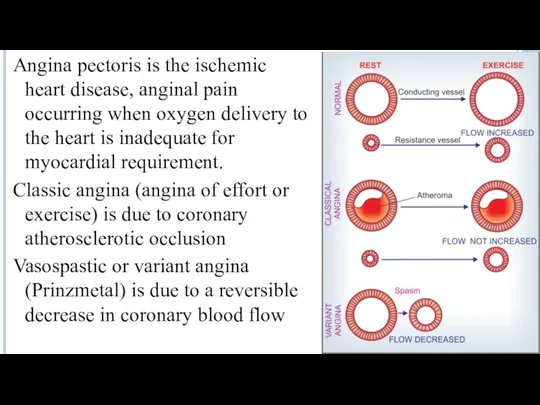
- 2. Angina pectoris is the ischemic heart disease, anginal pain occurring when oxygen delivery to the heart
- 3. Drug strategies in classic and vasospastic angina involve: ↑ oxygen delivery by ↓ vasospasm ↓ cardiac
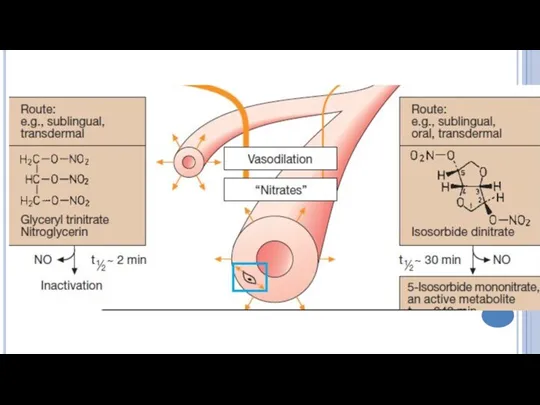
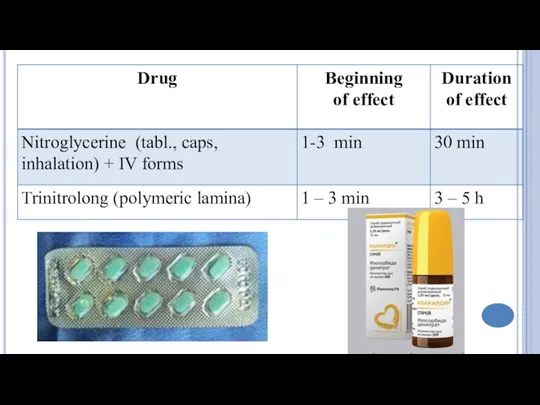
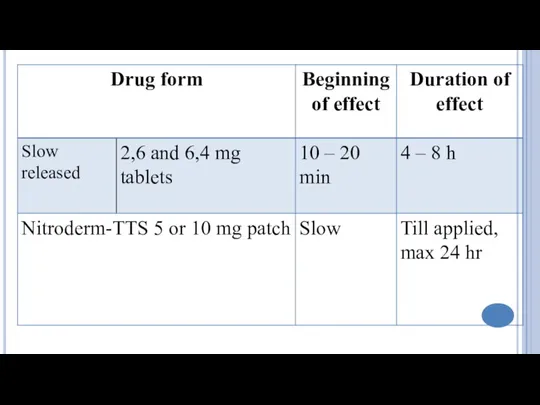
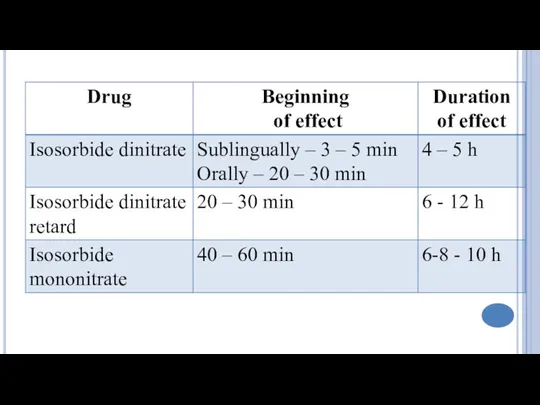
- 4. Classification Nitrates Short acting: Nitroglycerine Long acting: Isosorbide dinitrate (short acting by sublingual route), Isosorbide mononitrate
- 5. Potassium channels activator: Nicorandil Amiodarone Β-adrenoblockers Bradycardic drugs: Ivabradine, Falipamile Myotropic drugs dilating coronary vessels: Dipiridamole
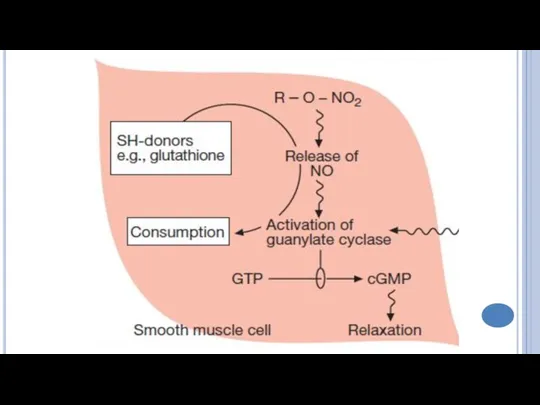
- 7. The mechanism of action of Nitroglycerine Nitroglycerine releases nitric oxide, which forms S-nitrosothioles. These substances activate
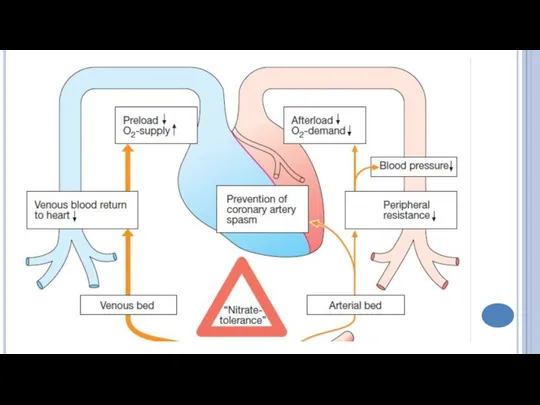
- 9. Hemodynamic changes Dilation of the peripheral veins → decrease of venous return to the heart→ ↓
- 11. Increase in blood supply to the ischemic myocardial area because: Dilation of major coronary arteries; Decrease
- 12. Indications for use: Relief of angina attack. Prevention of attacks. Acute myocardial infarction. Adverse effects Hypotension,
- 16. AMIODARONE Antianginal activity. Blocks α and β аr, glucagon’s receptors, ↓ heart rate, ↓ arterial blood
- 17. It is administered once every 24 h. Effect develops slowly , after several weeks. It can
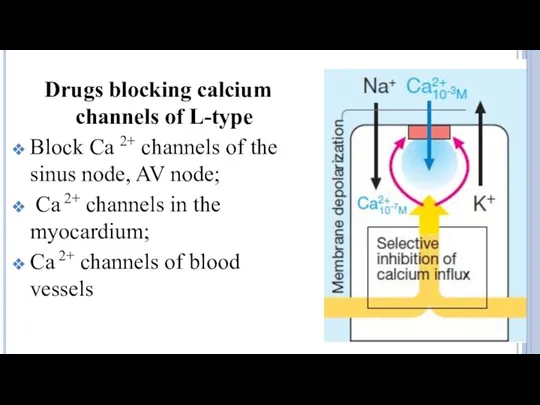
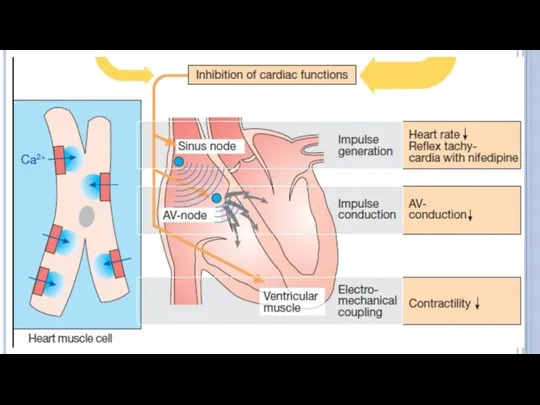
- 18. Drugs blocking calcium channels of L-type Block Ca 2+ channels of the sinus node, AV node;
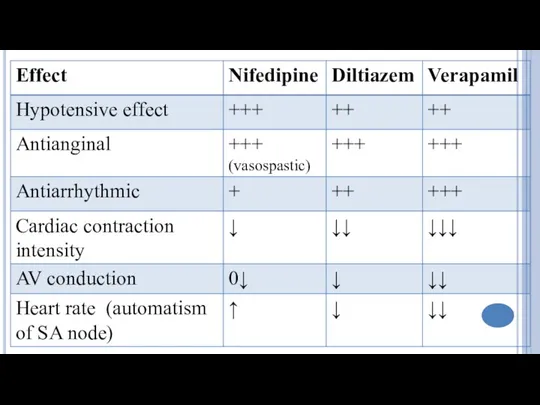
- 19. Verapamil , Diltiazem ↓depolarization (automaticity) in the sinus and AV nodes, ↑ERP; ↓HR, intensity of heart
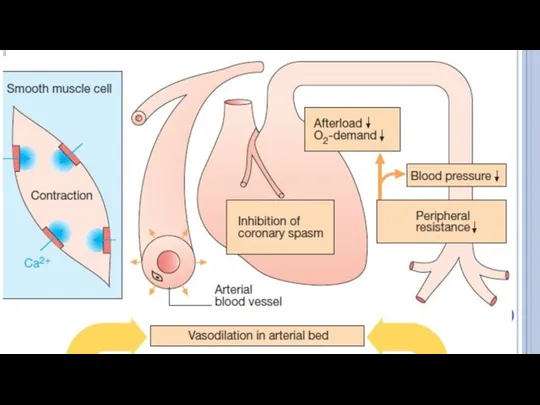
- 21. Nifedipine, Amlodipine Dilate large arteries and arterioles, ↓blood pressure, afterload and O2 demand; Dilate coronary vessels,
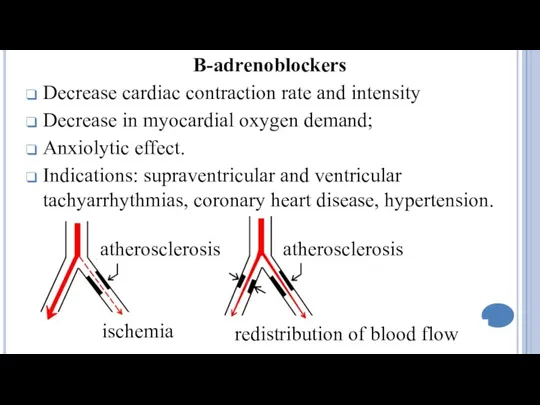
- 24. B-adrenoblockers Decrease cardiac contraction rate and intensity Decrease in myocardial oxygen demand; Anxiolytic effect. Indications: supraventricular
- 25. Ivabradine Selectively blocks Na + and K+ channels of the sinoatrial node, prolongs slow diastolic depolarization,
- 26. Dypiridamole It causes the suppression of adenosine reuptake (by myocardium or erythrocytes); inhibits adenosine desamidase enzyme.
- 27. Trimetazidine is the cardioprotective drug Inhibits 3-ketoacil-KOA thiolase enzyme isoform, inhibits the oxidation of fatty acids;
- 29. Скачать презентацию














 Организация занятий физической культурой школьников, отнесённых к специальной медицинской группе
Организация занятий физической культурой школьников, отнесённых к специальной медицинской группе Гормоны. Механизм действия гормонов белковой и пептидной природы
Гормоны. Механизм действия гормонов белковой и пептидной природы Дезинфекционные мероприятия при оказании медицинской помощи в условиях коронавирусной инфекции
Дезинфекционные мероприятия при оказании медицинской помощи в условиях коронавирусной инфекции Морфологія та фізіологія шкіри. Основи діагностики та методи обстеження. Принципи загального та місцевого лікування хвороб шкіри
Морфологія та фізіологія шкіри. Основи діагностики та методи обстеження. Принципи загального та місцевого лікування хвороб шкіри Диффузные болезни соединительной ткани: системная красная волчанка, узелковой периартериит, склеродермия,дерматомиозит
Диффузные болезни соединительной ткани: системная красная волчанка, узелковой периартериит, склеродермия,дерматомиозит Обессивно-компульсивные расстройства. Тактика ведения. Лечение, профилактика
Обессивно-компульсивные расстройства. Тактика ведения. Лечение, профилактика Терапия. Задача. Диагноз: Инфекционный эндокардит трикуспидального клапана
Терапия. Задача. Диагноз: Инфекционный эндокардит трикуспидального клапана Хронічне обструктивне захворювання легень
Хронічне обструктивне захворювання легень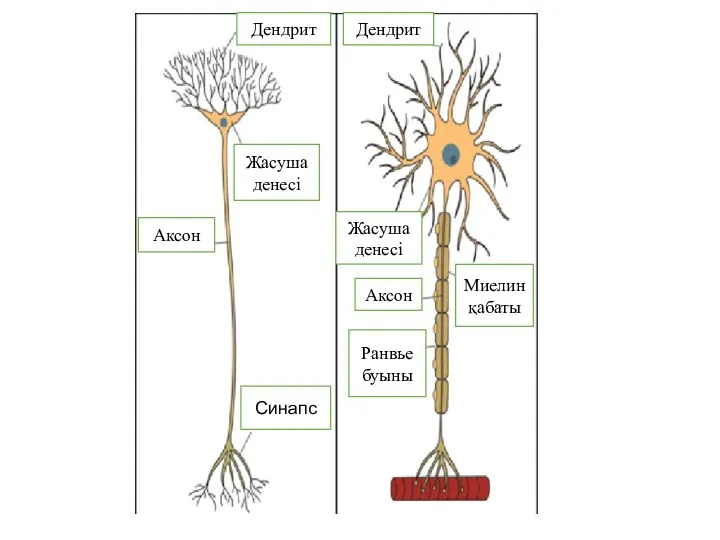 Миеленді, миеленсіз аксондарда жүйке импульстарының туындауы және өткізілуі. Өткізу жылдамдығы
Миеленді, миеленсіз аксондарда жүйке импульстарының туындауы және өткізілуі. Өткізу жылдамдығы Пломбировочные материалы в стоматологии
Пломбировочные материалы в стоматологии Первая помощь при укусах животных
Первая помощь при укусах животных Жүкті әйелдерде балаларда және қарт адамдарда тыныс алу жүйесі паталогиясының ерекшеліктері
Жүкті әйелдерде балаларда және қарт адамдарда тыныс алу жүйесі паталогиясының ерекшеліктері Применение ротационной атерэктомии и внутрисосудистой визуализации при кальцинированных поражениях коронарных артерий
Применение ротационной атерэктомии и внутрисосудистой визуализации при кальцинированных поражениях коронарных артерий Модель современной медицинской сестры
Модель современной медицинской сестры Еңбек гигиенасы зертханасының қазіргі кездегі құрал-жабдықтары
Еңбек гигиенасы зертханасының қазіргі кездегі құрал-жабдықтары Гепатит А. Патогенез, классификация, эпидемиология, клиника
Гепатит А. Патогенез, классификация, эпидемиология, клиника Медикаментозная терапия при лихорадке
Медикаментозная терапия при лихорадке Радионуклидная диагностика в кардиологии
Радионуклидная диагностика в кардиологии Биологиялық дозиметрия (электрондық парамагниттік резонанс және тағы басқалары) және олардың тәжірибеде қолданылуы
Биологиялық дозиметрия (электрондық парамагниттік резонанс және тағы басқалары) және олардың тәжірибеде қолданылуы Гельминтозы. Морфологическая классификация
Гельминтозы. Морфологическая классификация Функциональные пробы печени
Функциональные пробы печени Өкпеден қан кету
Өкпеден қан кету Курація хворого з гострою серцевою недостаністю
Курація хворого з гострою серцевою недостаністю Лечебное питание
Лечебное питание Развитие у пациентов с рассеянным склерозом прогрессирующей мультифокальной лейкоэнцефалопатии (ПМЛ)
Развитие у пациентов с рассеянным склерозом прогрессирующей мультифокальной лейкоэнцефалопатии (ПМЛ) ВИЧ-положительная женщина на приеме у педиатра
ВИЧ-положительная женщина на приеме у педиатра Редкие формы ранних токсикозов
Редкие формы ранних токсикозов Ингалянты и их влияние на организм
Ингалянты и их влияние на организм