Содержание
- 2. Plan Ascariasis Echinococcosis Alveococcosis Opisthorchiasis Amoebiasis Filariasis Paragonimoz Fascioliasis scheme of parasite development, principles of diagnosis
- 3. Ascariasis Etiology The cause of human infection is the use of fecal-contaminated vegetables or water containing
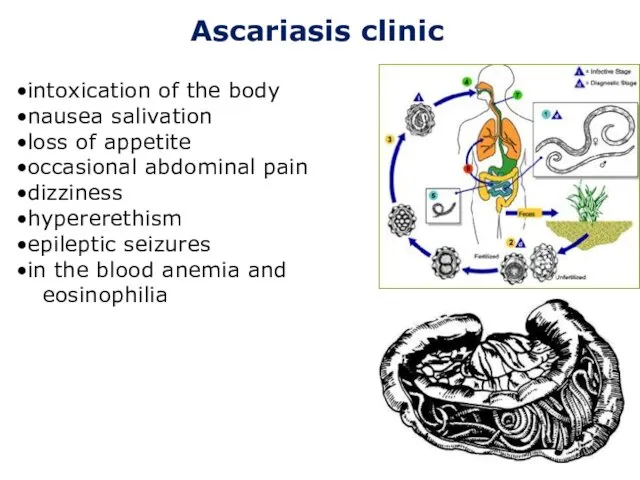
- 4. Ascariasis clinic intoxication of the body nausea salivation loss of appetite occasional abdominal pain dizziness hypererethism
- 5. Complications Peritonitis inflammation of biliary tract acute appendicitis intestinal obstruction Treatment In cases of surgical complications,
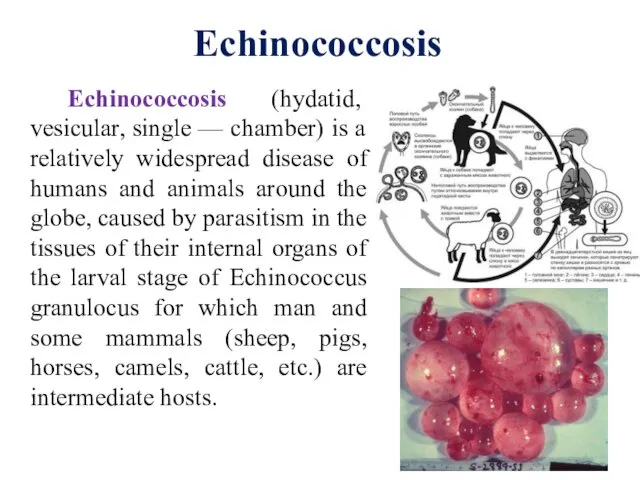
- 6. Echinococcosis (hydatid, vesicular, single — chamber) is a relatively widespread disease of humans and animals around
- 7. Clinical manifestations Stages 1) No symptoms 2) Manifestations allergic rash complaints of feeling of heaviness, pressure
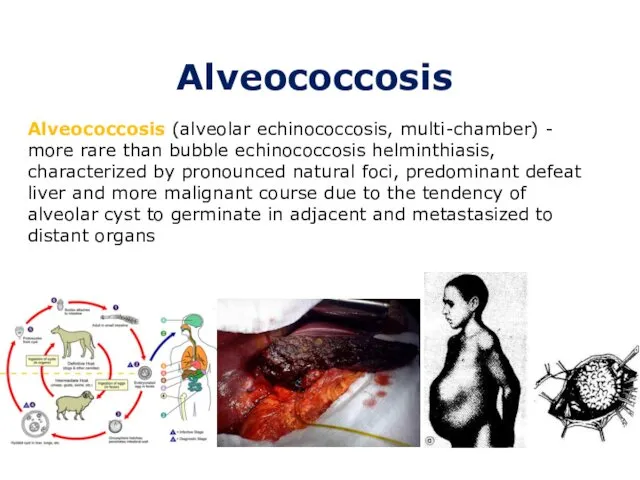
- 8. Alveococcosis Alveococcosis (alveolar echinococcosis, multi-chamber) - more rare than bubble echinococcosis helminthiasis, characterized by pronounced natural
- 9. The larva of the helminth has the form of a node consisting of a set of
- 10. Clinic Risk groups: 25-30 years old persons No symptoms in start period Symptoms the appearance of
- 11. Complications pronounced jaundice, ascites, splenomegaly, biochemical signs of liver failure Diagnostics determination of alpha-fetoprotein Treatment radical
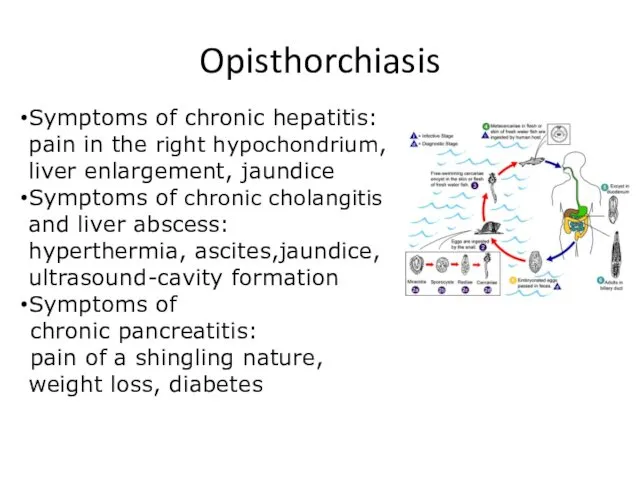
- 12. Opisthorchiasis Symptoms of chronic hepatitis: pain in the right hypochondrium, liver enlargement, jaundice Symptoms of chronic
- 13. Surgical treatment Puncture and drainage of abscesses of the liver and biliary ducts under ultrasound control
- 14. Amoebiasis clinic Intestinal amoebiasis: fever, weakness, malaise, frequent stool with mucus, blood, in the amoeba feces
- 15. Surgical treatment Resection of the affected area of the colon Opening and drainage of liver, lungs,
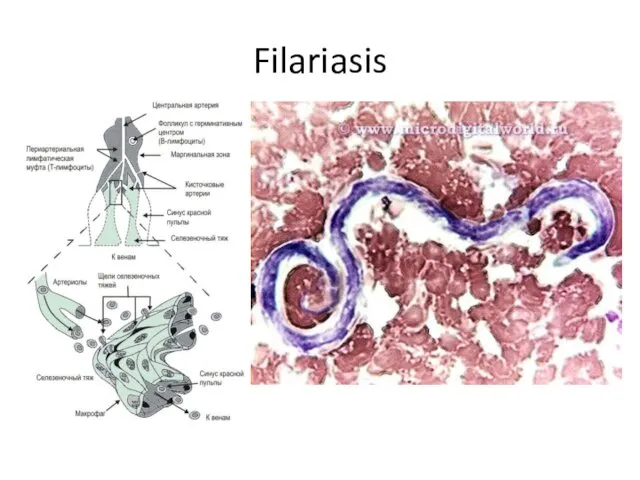
- 16. Filariasis
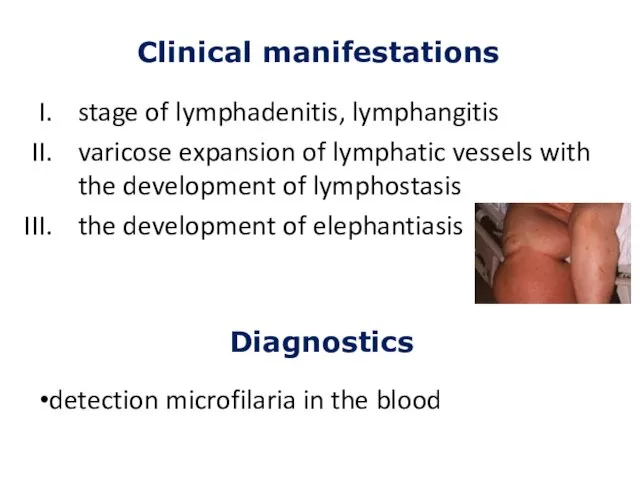
- 17. stage of lymphadenitis, lymphangitis varicose expansion of lymphatic vessels with the development of lymphostasis the development
- 18. Conservative treatment of filariasis ditrazin citrate (banozic, hetrazan) to 0.1 g 3 times a day for
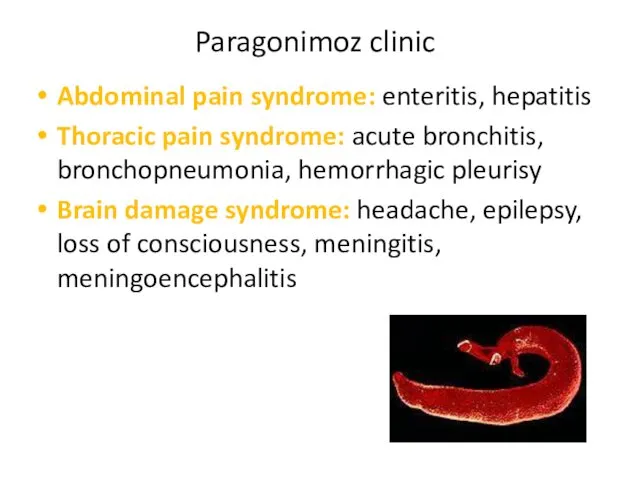
- 19. Paragonimoz clinic Abdominal pain syndrome: enteritis, hepatitis Thoracic pain syndrome: acute bronchitis, bronchopneumonia, hemorrhagic pleurisy Brain
- 20. Diagnostic In laparoscopy - fibrinous purulent effusion Fluoroscopy of the lungs – diffuse small and large-focal
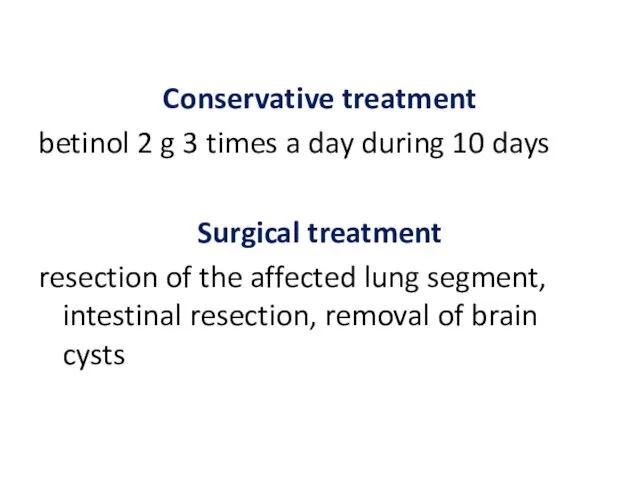
- 21. Conservative treatment betinol 2 g 3 times a day during 10 days Surgical treatment resection of
- 22. Observe basic personal hygiene measures It is good to wash your hands before eating, as well
- 23. According to who, every year infectious and parasitic diseases take 15 – 16 million lives, most
- 25. Скачать презентацию









 Листериялар. Морфология, физиология, листериялар антигені. Экологиясы. Әйелдер патологиясындағы маңызы
Листериялар. Морфология, физиология, листериялар антигені. Экологиясы. Әйелдер патологиясындағы маңызы Prezentatsia_po_biologii_na_temu_Znachenie_pischi_i_eyo_sostav__8_klass
Prezentatsia_po_biologii_na_temu_Znachenie_pischi_i_eyo_sostav__8_klass Внутренняя картина болезни и ее взаимосвязь между психоэмоциональным состоянием у лиц с сахарным диабетом 2 типа
Внутренняя картина болезни и ее взаимосвязь между психоэмоциональным состоянием у лиц с сахарным диабетом 2 типа Лекарственные средства, вызывающие тонические сокращения миометрия матки
Лекарственные средства, вызывающие тонические сокращения миометрия матки Объективный статус при осмотре ребенка
Объективный статус при осмотре ребенка Современные проблемы профилактики ХНИЗ
Современные проблемы профилактики ХНИЗ Ауыз қуыс кілегей қабық ауруларына тағайындалатын дәрілік терпияның салыстырмалы сипаттамасы
Ауыз қуыс кілегей қабық ауруларына тағайындалатын дәрілік терпияның салыстырмалы сипаттамасы Есту қабілеті нашар, көз көруі бұзылған,сөйлеу қабілеті нашар науқастармен қарым-қатынас
Есту қабілеті нашар, көз көруі бұзылған,сөйлеу қабілеті нашар науқастармен қарым-қатынас Исследовательский проект на тему: Соль - вред или польза
Исследовательский проект на тему: Соль - вред или польза Туберкулез органов мочевой системы
Туберкулез органов мочевой системы Міри радіобіологічних ефектів
Міри радіобіологічних ефектів Медицинская статистика. Цели и задачи
Медицинская статистика. Цели и задачи Аномальные маточные кровотечения
Аномальные маточные кровотечения Выпот в полость перикарда
Выпот в полость перикарда Вирус Эбола
Вирус Эбола Классификация шизофрении
Классификация шизофрении Пищеварение. Нарушения экзокринной секреции поджелудочной железы
Пищеварение. Нарушения экзокринной секреции поджелудочной железы Ісіктер туралы жалпы ілім
Ісіктер туралы жалпы ілім Воспалительные заболевания женских половых органов
Воспалительные заболевания женских половых органов Инфекции, передающиеся половым путем
Инфекции, передающиеся половым путем Переливанням крові та донорство
Переливанням крові та донорство Қан физиологиясы
Қан физиологиясы Ерлердің жыныс мүшулурінін даму ақаулары
Ерлердің жыныс мүшулурінін даму ақаулары Помощь при рвоте, кормление тяжело больного пациента
Помощь при рвоте, кормление тяжело больного пациента Психоорганический синдром и когнитивные нарушения – взгляд психиатра
Психоорганический синдром и когнитивные нарушения – взгляд психиатра Морфологические основы почки
Морфологические основы почки Лимфоаденопатии. Дифференциальная диагностика
Лимфоаденопатии. Дифференциальная диагностика Гигиена органов пищеварения. Предупреждение желудочно-кишечных инфекций
Гигиена органов пищеварения. Предупреждение желудочно-кишечных инфекций