Содержание
- 2. Lecture Plan
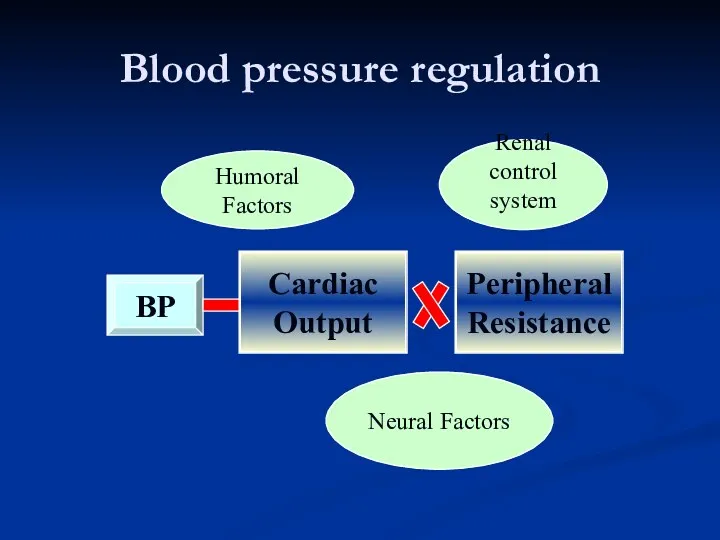
- 3. Blood pressure regulation Renal control system Neural Factors Humoral Factors
- 4. Blood pressure regulation The increase of BP: sympathetic nervous system humoral factors (rennin-angiotensin-aldosterone system, vasopressine, glucocorticoids)
- 5. Blood pressure regulation The decrease of BP : baroreceptor reflexes from aorta arch and carotid sinuses.
- 6. Rapid pressure control Nervous reflexes mechanisms Baroreceptors control BP in posture change, exercise, and moderate temperature
- 7. Rapid pressure control Hormonal mechanisms Norepinephrine/epinephrine – vasoconstriction, increased heart rate Vasopressin - vasoconstriction. Renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system
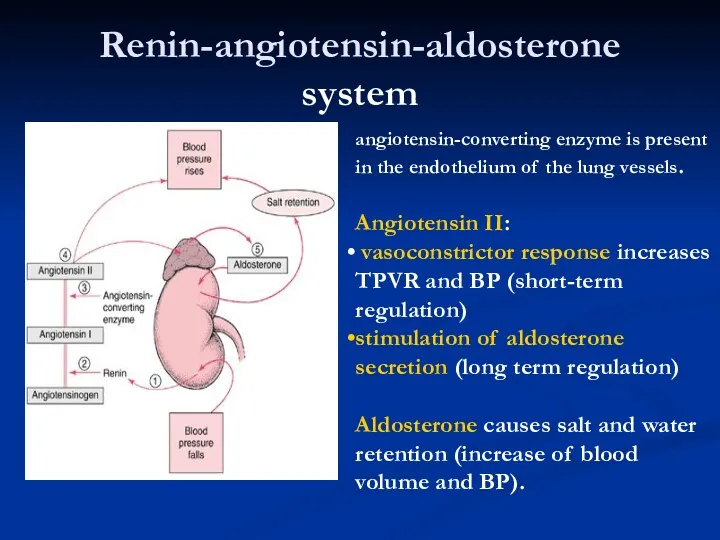
- 8. Renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system angiotensin-converting enzyme is present in the endothelium of the lung vessels. Angiotensin II: vasoconstrictor
- 9. Long-term regulation of BP Renal regulation Water resorption - aldosterone and vasopressin Sodium retention - aldosterone.
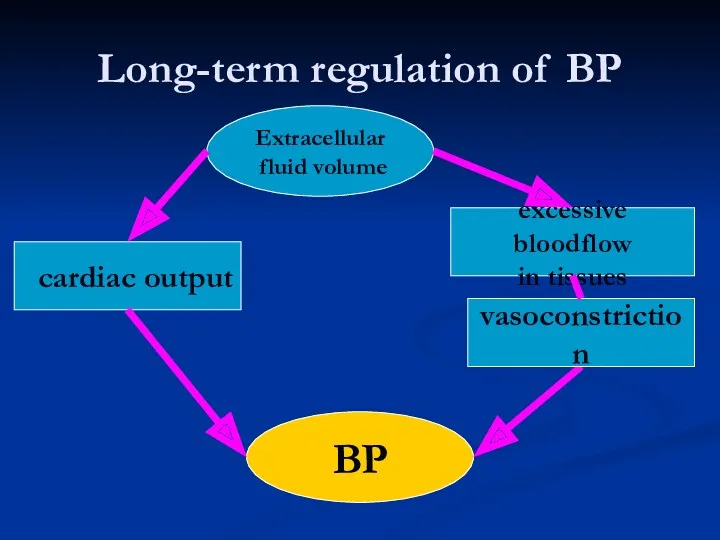
- 10. Long-term regulation of BP Extracellular fluid volume BP ⭡ cardiac output excessive bloodflow in tissues vasoconstriction
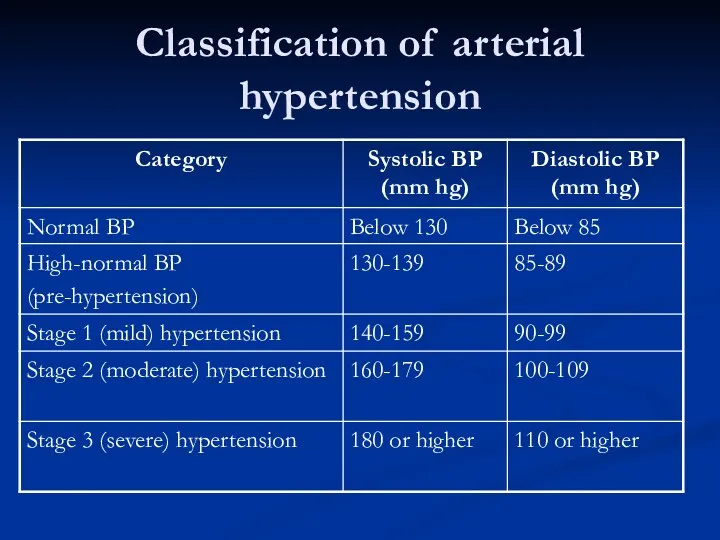
- 11. Classification of arterial hypertension
- 12. Arterial hypertension Primary hypertension (90%) - without evidence of other diseases multifactorial syndrome increased TPVR Secondary
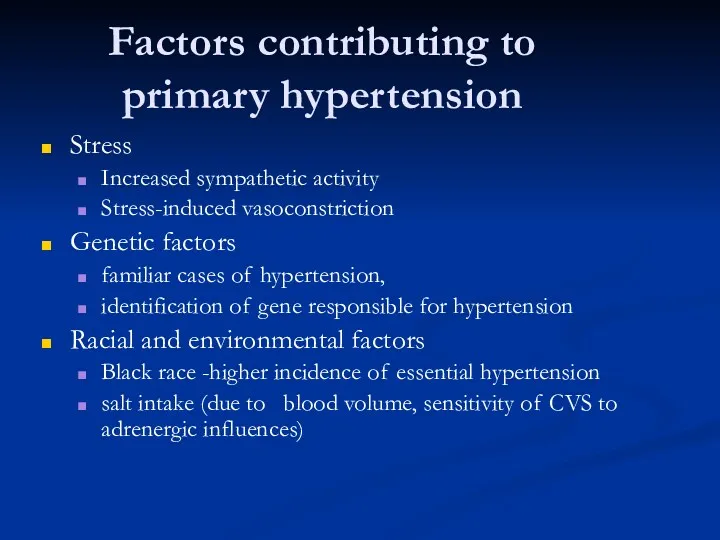
- 13. Factors contributing to primary hypertension Stress Increased sympathetic activity Stress-induced vasoconstriction Genetic factors familiar cases of
- 14. Risk factors modifying the course of essential hypertension age (in younger persons more severe) sex (premenopausal
- 15. Insulin resistance and hypertension part of syndrome X, or the metabolic syndrome which includes: central obesity,
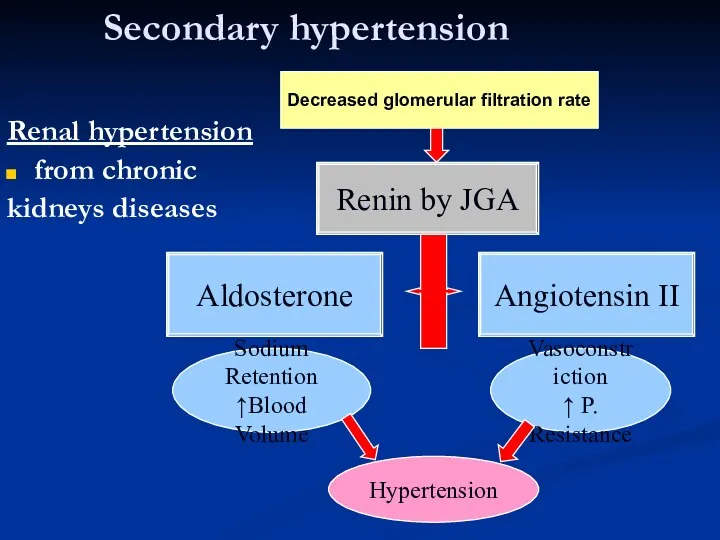
- 16. Secondary hypertension Renal hypertension from chronic kidneys diseases Renin by JGA Angiotensin II Vasoconstriction ↑ P.
- 17. Etiology of secondary hypertension ↑secretion of aldosterone Cushing’s syndrome/disease - ↑ glucocorticoid secretion. Phaeochromocytoma - tumour
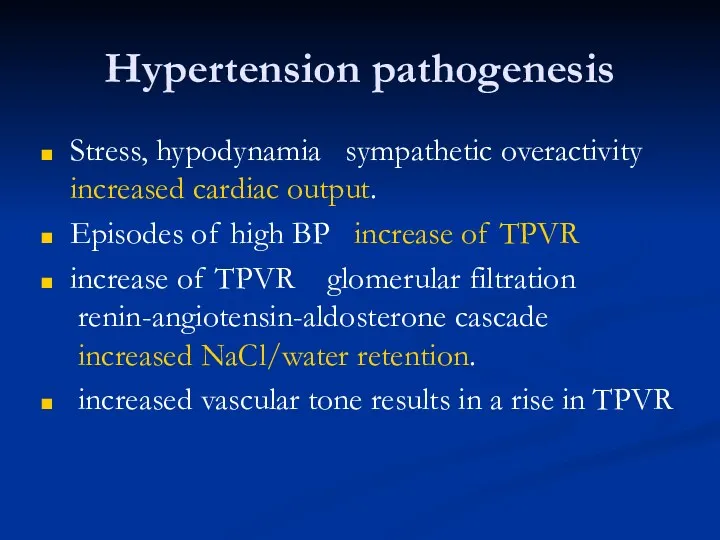
- 18. Hypertension pathogenesis Stress, hypodynamia ? sympathetic overactivity ? increased cardiac output. Episodes of high BP ?
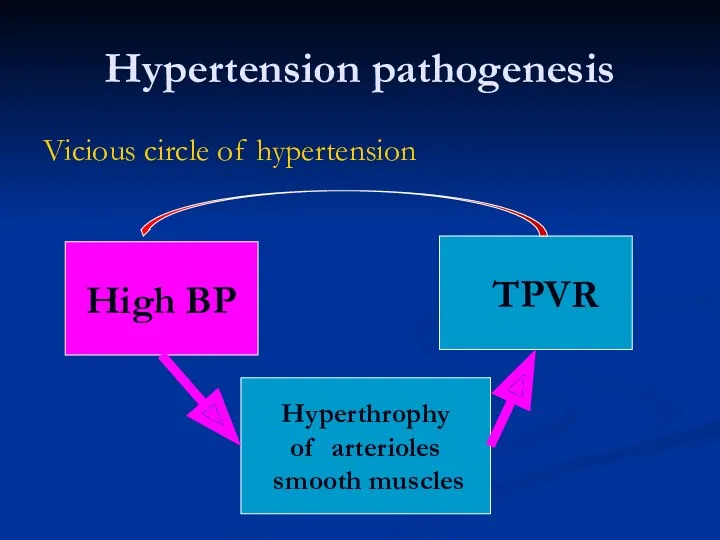
- 19. Hypertension pathogenesis Vicious circle of hypertension High BP Hyperthrophy of arterioles smooth muscles ? TPVR
- 20. Hypertension pathogenesis Deficiency of vasodilator substances bradykinin from kinin-kallikrein system neutral lipid and prostaglandin from renal
- 21. Hypertension signs and symptoms Primary hypertension is asymptomatic until complications develop in target organs. Heart left
- 22. Hypertension signs and symptoms Hypertensive retinopathy - retinal hemorrhages, exudates, vascular accidents. Hypertensive encephalopathy - dizziness,
- 23. Hypertension treatment Primary hypertension cannot be cured, but it can be controlled to prevent complications. Losing
- 24. Arterial hypotension Neurogenic causes - autonomic dysfunction or failure: central nervous system abnormalities (Parkinson’s disease) secondary
- 25. Orthostatic or postural hypotension is an abnormal drop in BP on assumption of the standing position.
- 26. Hypotension treatment Avoidance of factors that can precipitate hypotension sudden changes in posture, hot environments, alcohol,
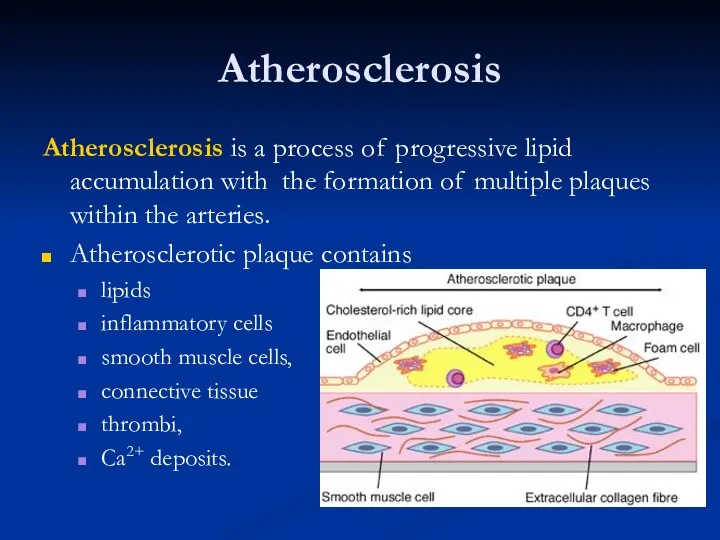
- 27. Atherosclerosis Atherosclerosis is a process of progressive lipid accumulation with the formation of multiple plaques within
- 28. Atherosclerosis Arteriosclerosis - any hardening (and loss of elasticity) of medium or large arteries Arteriolosclerosis -
- 29. Lipoproteins classification Chylomicrons - carry triacylglycerol (fat) from the intestines to the liver and to adipose
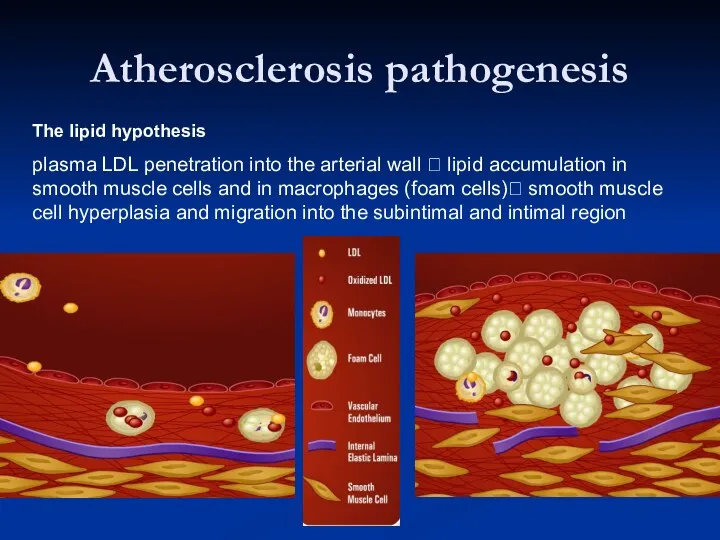
- 30. Atherosclerosis pathogenesis The lipid hypothesis plasma LDL penetration into the arterial wall ? lipid accumulation in
- 31. Atherosclerosis pathogenesis The chronic endothelial injury hypothesis Endothelial injury loss of endothelium, adhesion of platelets to
- 32. Atherosclerosis pathogenesis The atherosclerotic plaque may produce a severe stenosis or may progress to total arterial
- 33. Atherosclerosis: positive risk factors Non modifiable Age – middle to late. Sex – Males, complications Genetic
- 34. Atherosclerosis risk factors Negative risk factors high levels of circulating high density lipoproteins moderate alcohol consumption
- 35. Atherosclerosis symptoms If the narrowing of an artery is less than 70% - asymptomatic Symptoms occur
- 36. Atherosclerosis symptoms Symptoms occur due to deprivation of tissues blood supply The first symptom may be
- 38. Скачать презентацию

























 Философия сестринского дела. Модели сестринского дела
Философия сестринского дела. Модели сестринского дела Экономический анализ деятельности лечебно-профилактических учреждений
Экономический анализ деятельности лечебно-профилактических учреждений Наследственные гипо- и апластические анемии
Наследственные гипо- и апластические анемии Хроническая сердечная недостаточность у пожилых пациентов
Хроническая сердечная недостаточность у пожилых пациентов Сердечно-сосудистые заболевания
Сердечно-сосудистые заболевания Товароведческий анализ резиновых и полимерных изделий
Товароведческий анализ резиновых и полимерных изделий Повреждения голени
Повреждения голени Основы клинической физиологии сердца
Основы клинической физиологии сердца Перкуссия легких
Перкуссия легких Наркотические и ненаркотические анальгетики
Наркотические и ненаркотические анальгетики Балалардағы дермо-респираторлық синдром
Балалардағы дермо-респираторлық синдром Эндокринология. Несахарный диабет. (Лекция 10)
Эндокринология. Несахарный диабет. (Лекция 10) История российского красного креста
История российского красного креста Аускультация сердца
Аускультация сердца Жедел холецистит. Жіктемесі, диагностикасы, саралау диагностикасы. Аурудың асқынулары,асқынуларды диагностикалау
Жедел холецистит. Жіктемесі, диагностикасы, саралау диагностикасы. Аурудың асқынулары,асқынуларды диагностикалау Заболевания почек. Пиелонефрит и гломерулонефрит
Заболевания почек. Пиелонефрит и гломерулонефрит Наиболее распространенные онкозаболевания. Рак толстой кишки
Наиболее распространенные онкозаболевания. Рак толстой кишки Гельминтозы
Гельминтозы Программа государственных гарантий оказания гражданам РФ бесплатной медицинской помощи. (Лекция 2)
Программа государственных гарантий оказания гражданам РФ бесплатной медицинской помощи. (Лекция 2) Характеристика адреностимуляторов, механизм действия, бронхосиндром
Характеристика адреностимуляторов, механизм действия, бронхосиндром Краснуха. Этиология
Краснуха. Этиология Хронический гломерулонефрит. Гематурический гломерулонефрит
Хронический гломерулонефрит. Гематурический гломерулонефрит Спирометрия. Кіріспе бөлім. Спирография туралы түсінік
Спирометрия. Кіріспе бөлім. Спирография туралы түсінік Туберкулез және АИВ
Туберкулез және АИВ Мигрень: патогенез, диагностика, лечение
Мигрень: патогенез, диагностика, лечение Нарушение осанки и плоскостопие
Нарушение осанки и плоскостопие Бұлшықет ұлпасы
Бұлшықет ұлпасы Этико-правовые проблемы трансплантации органов и тканей. (Лекция 9)
Этико-правовые проблемы трансплантации органов и тканей. (Лекция 9)